Russia is the coldest country in the world. The overwhelming percentage of its territory is geographically located in temperate, subpolar and polar latitudes. As a result, for the majority of the population of our vast Motherland, the heating season lasts at least six months.
It is not surprising that the range of various heating systems tested by Russians is huge - traditional wood, coal, gas, fuel oil, electric, geothermal and even solar. But, despite all this diversity, the choice of a specific type of coolant is quite limited - air, steam or liquid.
Moreover, the first two options are used mainly for heating large industrial and public premises. There is no alternative to liquid for domestic heating systems. Only this physical state of the coolant can ensure sufficient efficiency and economical heating with comparative ease of maintenance and safety.
Alas, all this does not mean that the problem of choosing a coolant is absent. Yes, almost any liquid is capable of transferring thermal energy from one point (boiler equipment) to another (heating radiator, underfloor heating system, convector). However, this is not enough. Therefore, every owner of an autonomous heating system wants to achieve the highest possible efficiency, reliability and safety from it. Thus, a number of important requirements are imposed on the coolant.
What is coolant?
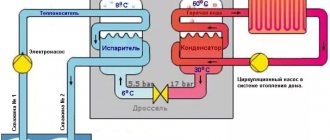
A coolant is a substance that transfers thermal energy from a source to consumers. For this purpose, steam (air heating systems) or liquid (liquid or water heating systems) is used. In private homes, the latter option is more common. The coolant is heated by the boiler and transmitted through lines to radiators or underfloor heating systems. The movement of liquid through the system is ensured by a pump or by gravity (gravity heating systems).
In liquid heating systems, ordinary water or antifreeze (“anti-freeze”) can be used as a coolant. The latter are represented by propylene glycol and ethylene glycol. There are also more exotic options: glycerin solution, salt solutions, transformer oil, etc.
Let's consider the basic requirements for coolants for heating systems.
- Inertness towards engineering equipment. The coolant must have low corrosive activity and not enter into chemical reactions with pipes, hoses, shut-off valves, rubber gaskets, boiler parts, etc.
Rust formation in radiators and pipes reduces the efficiency of the equipment. Heat transfer decreases, which leads to excessive fuel consumption. Also, rust particles can get into the pump and damage it.
- Good fluidity. The liquid should not be viscous or thick, otherwise the coolant will move slowly through the pipes and quickly lose heat. The pump will spend more energy to pump such a mass.
- Minimum thermal expansion. Various substances can expand when heated and cooled. If the building is used seasonally as a summer house, tourist center or warehouse, and during the absence of the owners the heating system is completely turned off, then substances with high expansion during freezing should be excluded as a coolant.
- High heat capacity. This characteristic reflects the ability of a substance to accumulate energy when heated and release it when cooled. The higher the heat capacity of the liquid, the more efficient the heating system is.
- Fluidity. Heating systems have many connections that can become potential leak points.
- Safety - this parameter is especially relevant for open systems, where the expansion tank is located in the attic, and the coolant from it can evaporate. It is also desirable that the substance is not flammable; if it leaks, it can cause a fire. That is why it is not recommended to use transformer oil as a coolant in private homes.
Application of coolants
There are usually no special difficulties when choosing antifreeze. But when using it, some peculiarities arise.
When preparing a solution of coolant and concentrates, the proportion requirements must be met.
Antifreeze must be replaced as needed or as part of the maintenance schedule unless replacement is required during engine repair. Do not mix coolants of different properties and types, as malfunctions of the cooling system may occur.
If the brand of antifreeze poured into the engine is unknown, then it is better to drain it all and purchase new antifreeze. It is undesirable to mix different brands of antifreeze, since different sets of additives have different properties, and as a result of chemical reactions they will become unbalanced. When mixing different reagents, malfunctions and ballast sediment may occur, water pump failure, engine overheating, clogging of the cooling system, and major repairs of the power unit. You should not save on buying antifreeze, as engine repairs will cost much more.
Antifreeze for car engines is sold in finished or concentrated form. Many car enthusiasts are accustomed to purchasing concentrate in order to make the solution themselves in the required proportion. But we must not forget that to dilute the solution, only distilled water is needed, and the proportion should be determined by the freezing temperature. Each time you need to use only the concentrate manufacturer’s instructions.
Water as a coolant for the heating system of a private house
Water is the most accessible coolant, but it cannot always be used. In terms of technical parameters, it is superior to any antifreeze, but for many homeowners its disadvantages cancel out all its advantages.
Advantages of water as a coolant
- Compatible with heating equipment. Condensing boilers are designed to operate on water. All parameters are valid only when working with this coolant. Boiler heat exchangers have a small tube diameter, so when using antifreeze, over time they can become clogged with additives and other decomposition products of liquid components. For this reason, adding antifreeze will void the equipment warranty of most boiler manufacturers.
Some boiler manufacturers allow the use of antifreeze while maintaining warranty service, but in this case only recommended brands of coolants can be used.
- Power of heating devices. For radiators, this parameter depends on the heat capacity of the coolant. With water it turns out to be 15 - 20% higher compared to antifreeze.
The power of the radiator can be calculated using the formula W=c*Q*(t2-t1), where c is the heat capacity of the medium, Q is the liquid flow rate in liters per hour, t2 and t1 are the temperature difference. Also, when calculating the number of radiators per room, it is important to take into account that the power parameter of the device on the packaging is indicated for operation on water.
- Water does not require replacement. Non-freezing coolants require replacement every 5 years. Some manufacturers produce compounds that can last up to 10 years. Replacing antifreeze and flushing the system is a labor-intensive procedure that will require the involvement of specialists and significant costs. At the same time, it is almost impossible to completely remove the antifreeze carrier.
This fragility of antifreeze is due to the additives that are present in their composition. These additives reduce corrosiveness so that substances do not harm heating equipment. Over time, the additives decompose and precipitate, after which ethylene glycol and propylene glycol begin to react with the metal.
- Water cannot be faked. The likelihood of purchasing counterfeit products when using water tends to zero. There is only a possibility of purchasing ordinary water under the guise of distilled. When using antifreeze, the possibility of filling with counterfeit liquid is higher.
- Safety. Water does not belong to the group of toxic substances, does not emit harmful fumes and is disposed of without great expense. Its harmlessness to humans makes water the only possible coolant for open gravity flow systems.
Disadvantages of water
The main disadvantage of water is that it freezes at 0 degrees. When the liquid turns to ice, it increases in volume by 10% and can burst pipes. This means that in any building where the temperature drops below freezing, water cannot be used as a heating medium. Such buildings include dachas, tourist centers, campsites, etc. There are many situations when the owner is not at home and he cannot control the operation of his heating system.
Also, improperly prepared water can lead to damage to heating equipment: corrosion, salt deposits.
What kind of water can be used for heating systems?
Water for heating systems must meet the requirements for two parameters: hardness and acidity, and it must not contain sand or other large particles. The pH indicator is responsible for acidity; normally it should be 7 units. Values from 1 to 6 correspond to acid, and from 8 to 13 to alkali. An acidic or weakly acidic liquid in a closed system tends to increase its pH to normal, for this it absorbs metals from the environment. This leads to destruction of pipes and boiler elements.
Hardness reflects the amount of salts dissolved in the liquid and is expressed by the total mineralization of the solution. When the temperature rises, these substances precipitate in the form of scale. The accumulation of deposits on the internal parts of the equipment can cause equipment failure.
If the heating system is closed and no new liquid enters it, then the initial amount of water will contain too few salts to clog the heat exchanger.
- Tap water – has a normal pH, but in some regions contains high levels of salts. Over several cycles of passage through the heating system, the hardness decreases, as some of the salts precipitate and are deposited on the heat exchanger. This will not cause any harm during startup, but it is not recommended to add water from a water supply or well to such a system, as there may be more deposits.
- Boiled water differs from ordinary tap water in the lower mineralization of the solution. At the same time, boiling large volumes is problematic.
- Bottled drinking water has normal acidity and a level of mineralization acceptable for humans. Thanks to this, it does not leave scale and is safe when topping up the system.
- Distilled water does not contain mineral impurities, but has a pH level of 5.4 to 6.6, which is not normal acidity. Some boiler manufacturers do not recommend using distilled water due to the potential for corrosion.
Antifreeze for heating systems
If the owner does not have the opportunity to constantly monitor the heating in the house, there is no telemetry and remote control of the boiler operation, then non-freezing coolant is poured into the system.
Ethylene glycol solution
The substance is an alcohol and is supplied in the form of a concentrate. To fill heating systems, ethylene glycol must be diluted with water in proportions of 50/50 or 40/60. The mixture freezes at temperatures down to -65 degrees. Freezing does not lead to significant expansion (1.5% for ethylene glycol, 10% for water), so the coolant does not harm the heating system. At lower temperatures, the viscosity of the substance increases. The upper temperature threshold is 108 - 110 degrees, at such indicators ethylene glycol foams.
Ethylene glycol cannot be used in its pure form as a coolant due to its high corrosive activity. Heating systems should be filled with specialized compounds with corrosion inhibitors. They are usually found in antifreezes for heating systems.
Additives have a certain service life (usually 5 years), after which the corrosive properties of ethylene glycol begin to manifest themselves and destroy the metal elements of the system. Also, by the end of this period, the substance becomes thick and can clog the tubes in the boiler.
Ethylene glycol is a flammable substance and is moderately toxic (class 3). The lethal dose is 1.5-5 ml/kg body weight. The vapors are not so toxic, but if systematically ingested into the body they can cause harm to health. At the same time, it is unlikely that ethylene glycol enters the body from a closed heating system; the use of such antifreeze in open networks is not recommended.
Additives are kept in a certain amount of ethylene glycol; if its concentration decreases, then the additives begin to fall out. The coolant can only be diluted to the minimum values specified by the manufacturer.
In the event of an accident in the heating system, children and pets should be removed from rooms with coolant leaks to prevent the substance from entering the body.
According to regulations, the use of ethylene glycol is not allowed in state and municipal institutions (schools, hospitals, kindergartens, clinics, etc.).
Propylene glycol solution
Like ethylene glycol, it is a two-component alcohol. It is not sold as a concentrate, but already diluted. With a content of 54% of the substance, it freezes at -40 degrees, and begins to foam at 108 degrees.
The advantages of this coolant include less danger to humans, but in terms of toxicity it also belongs to the third class. If swallowed, propylene glycol causes symptoms of poisoning in combination with damage to internal organs. Inhalation of vapors does not pose a danger to humans; in some cases, headaches may occur. Prolonged contact with skin causes redness.
You cannot add water to propylene glycol-based antifreeze.
Disadvantages include high viscosity, which leads to a drop in pressure in the system. Also, propylene glycol is less effective at low concentrations than ethylene glycol. In addition, a canister of this coolant will cost twice as much.
Due to its viscosity, propylene glycol burns more often in systems with electric boilers with high heating intensity.
Glycerin solution
Glycerin is a transparent viscous liquid, non-toxic to humans, freezes at -30 degrees. It is cheaper than propylene glycol.
When heated intensely, it can foam and burn, and it also tends to create air pockets in the heating system. Compared to alcohol antifreezes, the heat transfer of glycerin is worse.
Why can't you use car antifreeze for heating systems?
Antifreeze is a name for a whole group of liquids and they are used not only as a coolant. The main component in almost all of them is ethylene glycol or propylene glycol, for this reason many homeowners try to pour car antifreezes and other products into their heating systems. This does not always end well, since the additives for automotive compounds are different.
In a heating system they can have unexpected effects. For example, silicate additives, which are part of the G11 automotive anti-freeze agent, contribute to the formation of films that impair heat exchange and can clog equipment. Carbon additives help with corrosion on metal, but do not prevent it.
What is the alternative?
No one is immune from unexpected power outages in winter. In this case, it is recommended to have backup power supply equipment or an alternative heating method available. After all, the financial costs of creating an uninterrupted heating system are approximately equal to the costs of antifreeze. We must not forget that antifreeze has a limited service life, so replacing it every 2-3 years will be a mandatory procedure for you.
In addition, the water in the heating system does not immediately freeze, especially in an already heated room. In this case, you will have at least four hours to make a decision.
Requirements for the heating system when using antifreeze
- Most antifreeze has a high viscosity, so the circulation pump must have the necessary power.
- The expansion tank must be a closed type to prevent evaporation of the coolant. Antifreeze cannot be used in open systems. In this case, the tank must have a larger volume compared to a similar system for water, since non-freezing liquids are characterized by increased expansion at high temperatures.
- Intense heating to high temperatures should be avoided. Such exposure may cause the substance to foam or form carbon deposits.
- When calculating batteries, it should be taken into account that heat transfer will be 15% worse than when working on water. The device data sheet usually contains data specifically for water.
- It is recommended to install paronite or Teflon gaskets in the connections to reduce the risk of leaks. Compared to water, antifreeze has increased fluidity.
- If the pressure in the system has dropped, then you cannot fill the system with water; you need to add the same coolant. To do this, leave the canister behind when filling for the first time. If you dilute the coolant with water below the permissible concentration, the additives will precipitate and the corrosive properties of the substance will increase.
- Spent antifreeze cannot be dumped into the soil; disposal must be carried out at a hazardous chemical waste recycling facility.