The biggest danger that can threaten an individual heating system is freezing during the winter when there is a power outage. To avoid such situations, many use antifreeze for the heating system of a country house, protecting the boiler and heating pipes from deformation.
The construction market offers various brands of antifreeze for heating systems, the composition of automotive antifreeze liquids is similar, the most famous of which is Antifreeze. Therefore, many homeowners have a reasonable question: is it possible to use Antifreeze as an antifreeze for the heating circuit of an individual home and is it profitable from a financial point of view?
To get answers to this question, you should consider the physicochemical characteristics of Antifreeze and compare it with special liquids designed to protect the heating system from freezing.
Rice. 1 Antifreeze for the heating system of a country house - popular brands Teply Dom, Dixis, Thermagent
Water or antifreeze - comparison of parameters
Water is a common natural element, widely used as a heat carrier, but due to its too high freezing point, it has to be replaced in domestic heating with glycol antifreeze, which have the following indicators in comparison with water:
- Their specific thermal capacity is 15% lower than that of water, which means that with the same volume, glycol accumulates 15% less energy when heated and, accordingly, releases less. Consequently, to transport the same amount of heat as water per unit time, its speed of movement through the pipeline must be greater by the same amount.
- The density of antifreeze is slightly higher (by 5 - 10%) than water, and the viscosity is 30 - 50% higher than water indicators - this means that when the liquid moves through the pipeline, the hydraulic resistance increases. Compared with water coolant, the circulation pump will require more power and, accordingly, electricity consumption to move the same volume of antifreeze as water.
- Their thermal expansion coefficient is 30 - 40% greater than water; when heated, the glycol coolant increases in volume by 5%, the expansion is insignificant, but sometimes a slightly larger hydraulic tank may be needed.
- Due to their low surface tension, they are 50% more fluid than water - this places increased demands on sealing. Conventional rubber gaskets will have to be replaced with paronite gaskets; it often happens that the internal gaskets of heating radiators are not designed to work with glycols and measures will have to be taken to eliminate leaks between sections (modern radiators usually do not have such problems).
Rice. 2 Properties of antifreeze compared to water
- A significant drawback of relatively cheap antifreezes based on ethylene glycol is a high danger to human health; the substance is poisonous with a lethal concentration of 2 mg. per 1 kg. weight. Therefore, ethylene glycol is prohibited from being poured into systems with an open storage tank in the attic; the circuit must be closed.
- They have a short service life, designed for 10 seasons and amounting to no more than 5 years, this is due to the decomposition of anti-corrosion additives during operation. After this, you will have to drain the antifreeze from the system, dispose of it (with poisonous ethylene glycol this is a definite problem) and pour new coolant into the circuit - this will entail unjustified financial expenses.
- Unlike neutral water, low-quality or expired glycols decompose over a certain period, forming solid sediment that clogs fittings and destroys pipeline fittings.
- Another significant drawback of non-freezing coolants is the relatively high cost: a 20-liter canister of ethylene glycol with crystallization at -30º C will cost 15 USD, the price of the same volume of propylene glycol will be 30 USD.
- It should also be noted that during operation, antifreezes are very sensitive to critical temperatures - when overheated, the glycols and additives included in their composition decompose with the formation of solid insoluble precipitates and acids. This leads to the appearance of carbon deposits on the heating elements of the boiler that come into contact with the coolant; the metals are subject to destructive corrosion, and the sealing elements also suffer. The process is accompanied by increased foaming, leading to airing of the system and disruption of its functioning.
- They have restrictions in their use; their use in electrolysis boilers and pipelines made of galvanized steel is prohibited - the metal is subject to increased corrosion with the formation of an insoluble precipitate of white flakes.
Rice. 3 Features of glycol-based coolants and their cost
- A significant disadvantage of using antifreeze is the refusal of many heating boiler manufacturers to provide warranty service if glycols are poured into the system.
- The only and main advantage of antifreeze in comparison with water is the low freezing point, reaching up to -70º C. Even when a higher-temperature composition freezes (it is obtained after dilution with water in a certain concentration), the substance turns into a jelly-like mass with minimal expansion. Therefore, if you pour antifreeze into the heating system, the integrity of the pipes and boiler is guaranteed at any natural negative freezing temperatures of the circuit.
From the above, it becomes clear that water as a coolant is significantly superior to all antifreezes in its physical and chemical parameters, with the exception of its 10% expansion upon freezing, which led to the search for alternative options.
Rice. 4 Antifreeze in the heating system of a private house - instructions
What is a coolant and what should it be like?
The coolant in a liquid heating system is the substance through which heat is transferred from the boiler to the radiators. Our systems use water or special antifreeze liquids as a coolant. When choosing, you must be guided by several criteria:
- Safety. From time to time, heating systems leak or require maintenance and repair. To ensure that repair work is not dangerous, the coolant must be harmless.
- Harmless to heating system components.
- Must have high thermal capacity to transfer heat effectively.
- Have a long service life.
The coolant for heating systems is selected according to operating conditions
Taking into account these requirements, the most suitable liquid for the heating system is water. It is safe, harmless, has a high heat capacity, and its service life is unlimited. But in those heating systems where there is a high probability of downtime in winter, water can do a poor job. If it freezes, it will burst pipes and/or radiators. That’s why antifreeze is used in such systems. At subzero temperatures they lose fluidity, but the equipment does not tear. So choosing a coolant for a heating system from this point of view is easy: if the system is always under supervision and in working order, you can use water. If the house is temporary (dacha) or can be left unattended for a long time (business trips, winter vacation), if frequent and/or long-term power outages are possible in the region, it is better to pour antifreeze into the system.
Antifreeze for the heating system of a country house - properties and types
The construction market offers two main brands of antifreeze for heating systems in private homes: ethylene glycol and propylene glycol. Typically, in anti-freeze products the main component is glycol (30 - 65% depending on the concentration of the solution), deionized water occupies 30 - 50% of the total volume and there are 3 - 4% additives consisting of corrosion inhibitors, scale and sediment solvents, substances that prevent foaming.
Due to its composition, from the beginning of crystallization to the transformation of the non-freezing composition into gel-like slush, an interval of 10 - 15º C is required, the temperature inside of which changes gradually and takes a long time.
Manufacturers supply antifreeze packaged in 10-liter or 20-liter canisters to the retail chain in the following concentrations:
- Concentrate with crystallization at -65º C, which can be diluted with water to obtain the required freezing point.
- A solution that freezes at -30º C; it is used both in finished form and diluted to obtain higher temperature parameters from -20 to -15º C.
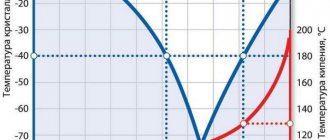
It is important for the consumer to know that when diluting the concentrate with water, there is no linear dependence on its percentage (graph in Fig. 8). For example, if we dilute 20 liters of a 65% concentrate with crystallization at -65º C with the same amount of water, then we will get 40 liters of liquid with a crystallization point of about - 20º C, and not - 32.5º C, as happens, for example, when diluting alcohol Therefore, to obtain the required temperature, tables of lower limits of the temperature dependence of glycols on their concentration are used (Fig. 9).
Antifreeze as a coolant in a heating system
Antifreeze is a development of Soviet engineers in 1971; its abbreviation comes from the name of the department of the Soviet State Research Institute of Organic Chemistry - Technology of Organic Synthesis with the addition of a prefix typical for the name of alcohols.
Antifreeze is usually produced in cans with a crystallization temperature of -40º C of various colors, the colors of antifreeze red green blue indicate the types of automobile radiators into which it is recommended to fill the composition (red - for brass or copper, blue, green - for aluminum).
Although the main component in Antifreeze is ethylene glycol and it is visually no different from glycol-based antifreezes, there are the following differences in the composition and technology of their production:
- In addition to glycol and water, Antifreeze contains nitrate, phosphate, silicate, borate and amine additive components, due to which the liquid boils at a temperature of 100º C and decomposes at 105º C. When used in automotive equipment, Antifreeze is designed for 40,000 km.
- Antifreezes are manufactured using carboxylate technology and contain additives from salts of organic acids, due to which the solution has high anti-corrosion, anti-cavitation and anti-foam characteristics. The boiling point of glycol solutions reaches 115º C; a car filled with antifreeze can travel a distance of 240,000 km. without replacing it.
It is easy to notice that obsolete Antifreeze is significantly inferior in its characteristics to modern antifreezes for automotive vehicles, produced from imported raw materials using carboxylate technology, which is inaccessible to domestic manufacturers.
Rice. 7 Antifreeze - appearance
Why it is not recommended to pour antifreeze into the heating system
Due to the low cost, some homeowners may have the idea of using Antifreeze in the home heating system as antifreeze, to make sure that this idea is futile, consider the consequences of this decision:
- In addition to the fact that Antifreeze has fully absorbed all the disadvantages of glycols, it is made using a different technology and decomposes at a lower boiling point of 105º C. When using high-temperature solid fuel boilers, the danger of its overheating increases significantly, and decomposition can lead to failure of the circular electric pump, clogging of taps and fittings. The damage will be many times greater than the penny saved on an unusable composition.
- The additives included in Antifreeze are not intended for heating systems; they will not only be useless, but are also likely to cause damage to the elements of the heating circuit, fittings and pumping equipment after some time.
- The most compelling argument is the pointlessness of using Antifreeze for the sake of saving money - in automotive technology its service life is 6 times less than modern antifreeze, a similar situation with similar temperature conditions will occur in the heating system. Antifreeze will have to be drained from the pipeline at least every year, as a result, the costs of using it will increase several times.
- Also, antifreeze produced using traditional methods is strictly forbidden to be mixed with modern antifreezes due to the difference in manufacturing technologies - a chemical reaction occurs, some additive components precipitate and clog the flow channels.
Considering the above, it will not be difficult to answer the question of whether it is possible to pour Antifreeze into the heating system; one can say more categorically - Antifreeze is the worst of all possible options.
Rice. 8 Graph of freezing temperature versus glycol concentration
What to look for when choosing antifreeze
To choose a coolant for a heating system, you should consider all the pros and cons of the solutions offered on the market. It is taken into account that in closed circuits toxic ethylene glycol compounds can be used without great risk if the expansion tank is open and harmless propylene glycol is poured into the circuit.
The construction market offers products from a wide range of manufacturers, and since they are made mainly from high-quality imported raw materials and have approximately the same price and a shelf life of no more than 5 years, it is difficult to give preference to any company.
If manufacturers offer antifreeze liquid at too low a price, you can check the authenticity of the solution using traditional methods: since counterfeits mostly contain an acid base, they use soda to check. If a pinch of soda, poured into a small amount of liquid, enters into a violent chemical reaction with it, then the purchased product is fake; with neutral interaction, the authenticity of the product should not raise doubts.
You can determine a branded product using a hydrometer - a device that measures density; the technique allows you to find out the percentage of water in the product. When taking measurements, the density of the composition should not be less than 1.075 g/cm3; if the value is lower, the liquid is most likely diluted with water.
Rice. 9 Temperature dependence of ethylene glycol on concentration
Features of filling with ethylene glycol antifreeze
Considering the toxicity of ethylene glycol, it is necessary to pour this coolant into the heating system with extreme caution, using containers that are no longer needed in the household for the purpose of their further disposal. Coolant is usually pumped into the system using an inexpensive electric pump or a special hand pump for a press operator; budget vibration models costing about $20 are suitable. After use, they are thoroughly washed with hot water and detergents and subsequently used for watering gardens in personal plots or for technical needs.
If the system uses an open circuit, and financial resources do not allow you to purchase expensive propylene glycol, you can add ethylene glycol-based antifreeze, taking simple safety precautions. To do this, the storage tank on the top floor or attic is tightly closed with a lid (to improve sealing, you can use rubber gaskets or heat-resistant sealants), and a sealed tube is inserted into it, which is led outside the house through a window or roof.
Propylene glycol products
In appearance, propylene glycol cannot be distinguished from ethylene glycol; many of their physical properties are the same. But propylene glycol has fluidity and if a leak is not noticed in time, it can leak out completely.
Propylene glycol-based antifreezes are green in color due to the presence of a food additive in it, which suggests that it is not toxic. Moreover, this additive is widely used in the production of various cosmetics and food industries. And if a leak suddenly occurs, it will not cause any terrible harm.
The temperature at which it freezes (or rather, changes consistency) is higher than ethylene glycol antifreeze and is about minus 50 degrees. Propylene glycol antifreeze does not damage the internal surface of systems, but, on the contrary, has the opposite effect. Which carries such positive qualities as less resistance and less energy loss.
Preparation of antifreeze solution for heating
If, due to various circumstances, there are no better options at hand, you can use Antifreeze in houses with a small number of heating circuits and plumbing fixtures; it is better to use radiators made of aluminum. Blue and green antifreeze is available for sale in plastic containers of various capacities; its standard freezing point is -40º C. Since ethylene glycol is the main component of the solution, the corresponding tables can be used when diluting with water.
For example, to obtain a crystallization temperature of -20º C (35% ethylene glycol), we determine from the tables that the Antifreeze solution with a freezing point of -40º C contains 54% ethylene glycol. Using a simple mathematical formula (35 x 100 / 54), we determine that 35% water should be added to antifreeze to obtain a freezing threshold of -20º C.
The percentage of added water is calculated in a similar way for other temperature limits of the coolant.
Rice. 11 Antifreeze for the heating system - how to fill it
Solid fuel boiler
The fuel used in this installation is firewood, coal, coke, and peat briquettes. Heating using a solid fuel boiler (Fig. 4) is autonomous heating for a summer house. The advantage of this equipment is the low cost and distribution of fuel. This is a way out of a situation when the village has problems with electricity and there is no gas supply.
Rice. 4 Installation of a solid fuel unit at the dacha
New models of solid fuel autonomous boilers have many advantages. They work with any coolant (antifreeze, water) and maintain the temperature in the house for a long time thanks to a special valve and sensor. This boiler has more time between fuel loads. Heating a dacha with wood is a cheap and effective option.
In this case, correct installation of the chimney is very important; its height is indicated in the instructions for the boiler model. Installation can be done independently or on a turnkey basis.
Pouring Antifreeze into the heating system
As noted above, the use of Antifreeze is justified only in emergency situations; to pour Antifreeze into the heating system, work is performed in the following sequence:
- The coolant is drained through the filling valve located at the lowest point next to the water heating boiler (this possibility should be provided for at the design stage of the system).
- The dirt filter is removed, cleaned and replaced, then using an inexpensive vibration electric pump (Malysh) water is poured into the system under a standard pressure of no more than 2 bar.
- After filling the pipeline, close the inlet valve, turn on the heating boiler for heating water and the circulation pump. Set the heating temperature to about 60 C. and pump water for an hour; at the end of the time, monitor the condition of the dirt filter.
- If too much dirt remains on the filter cartridge, turn off the circulation pump and boiler, drain the water, clean the filter and repeat the entire washing procedure again.
Rice. 12 Antifreeze viscosity chart
- Having made sure that there is practically no dirt in the system, after draining the water, they begin to fill in the Antifreeze. It is poured into a large container, a vibration pump is immersed there and they begin to pump it into the system under a pressure of about 2 bar.
- Typically, underfloor heating circuits are connected through manifolds on which automatic air vents are placed to bleed air - they cope with their task without human presence. On heating radiators, you will have to bleed air manually through Mayevsky taps. To do this, use a flat screwdriver or wrench to unscrew the slot in the upper part of the radiator and drain the coolant, thus bypassing all batteries, starting from the upper floors. If the pressure drops after draining the coolant, it is periodically pumped up.
- Bleeding water from the radiators and pumping is repeated again, then turn on the circulation pump and boiler to a temperature of about 60º C and then manually check the batteries for uniform heating on both sides. If one half of the radiator heats up less, bleed the air again and pump up antifreeze.
- If there is increased foaming during the injection of antifreeze, turn off all equipment for several hours, giving the Antifreeze a chance to settle.
Antifreeze has a short service life; its final phase can be determined visually - if the liquid has a rusty color, this indicates decomposition of the inhibitors and the circuit is urgently released from the coolant.
Rice. 13 Heating boilers in a private house
Diesel boiler
Diesel units are autonomous equipment that runs on diesel fuel - diesel fuel. This boiler requires electricity to operate. The diesel boiler is equipped with a fan burner, which functions so that when fuel is atomized, it mixes with air and combustion becomes more intense.
Diesel boilers from modern manufacturers have a removable burner design and the equipment can be converted to gas. To do this, install a gas burner. For a dacha, this is quite convenient, since if a gas main appears in the village, you can easily redo the system. A diesel autonomous boiler operates with a water system, during the installation of which it is better to rely on a coolant in the form of antifreeze.
But the disadvantages of this equipment include the high cost of fuel. Considering the option of heating a dacha, we can conclude that the boiler will not burn constantly, and accordingly the costs will be small. If necessary, its installation is carried out by specialists on a turnkey basis.
Do you think that such work can only be entrusted to professionals?
Of course, installing a wood-burning stove in the house or setting up a fireplace in the countryside seems much easier. However, spend a few evenings studying the theoretical part, and you will be surprised to notice that making such heating yourself is quite possible. An additional bonus for you will be that literally every centimeter will be familiar to you inside the water heating system, and if necessary, you can easily replace failed parts with your own hands. Heating using liquid circulating in the system is recognized as the most beneficial for low-rise buildings. Let's look at how to make water heating, what materials and equipment will be needed, and how to install it correctly.
What is required for installation?
- boiler or oven;
- pipes;
- radiators;
- expansion tank;
- standard set of installation tools.
Before purchasing all this, it is worth understanding how water heating works and developing a plan for heating your home or cottage. The diagram looks like this: the coolant heated by the boiler (it can be water or a special mixture) enters the radiators, in which it cools, giving off heat to the room. Schematic diagram of water heating
The cool coolant returns to the boiler, where it heats up again. Due to such continuous cycles, your room is heated. Water heating systems are divided into natural and forced. By choosing the first option, you will be independent of electricity to operate the pump. The movement of liquid through the system occurs due to the laws of physics - the hot coolant expands and rushes upward, and, having lowered the temperature, it decreases in volume and falls down. With natural circulation, it is necessary to maintain a slope of all pipes of at least 2 degrees (ideally 3-5), avoid pipes of small cross-section (40 mm pipes are suitable for the riser, pipes with a cross-section of 22-24 mm can be used for supplying the heating sections).
Natural circulation has serious disadvantages: internal wiring is not allowed - when the water level in the expansion tank decreases, the movement of liquid is difficult. It is also applicable only in cases where the distance along the pipes between the boiler and the farthest radiator does not exceed 20 meters, and the area of the heated room is less than 150 sq.m.
As you can see, natural circulation with its limitations is not always applicable. In a forced system, the flow of coolant is regulated by a circulation pump. Of course, purchasing a pump is an additional financial expense upon purchase and an addition to monthly electricity bills, but look at the advantages - you are spared the need to clearly check the angle of inclination, there is no need to observe a wide cross-section of risers, it is possible to make internal pipe routing and connect , for example, “warm floor”.
Two-pipe heating system
There are two water heating systems - single-circuit and double-circuit. Installation of the first option involves heating only. The second option, in addition to heating, provides the room with hot water and is very convenient in the country, in cases where it is not planned to install a separate source of warm water.
Selecting a heating device
Water heating can be carried out using a gas, electric or solid fuel boiler. If gas is supplied in your area, heating with a gas boiler will be convenient and least expensive. In the absence of gas, electricity and traditional fuels - wood, coal, pellets - can be considered as a heating source. The advantage of a solid fuel stove over an electric boiler is obvious - the cost of operation. The use of electric heating in a dacha is fully justified if you are not there every day in cold weather and, accordingly, do not have the opportunity to control daily fuel or gas loads.
Water heating is not practical for a small private house, since it is more practical to simply hang electric radiators.
And for a large house, using electricity to heat the coolant may be incompatible with the simultaneous operation of other electrical appliances.