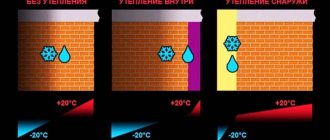
On the modern market, thermal insulation materials are presented in a huge variety of types and forms. It can be difficult for the average buyer to understand them and choose the right one, focusing not only on the price, but also on the characteristics that would best meet the operating conditions of the insulated structures and other requirements. Having obtained a general understanding of the properties of such materials, it will be easier to solve this problem.
Different building elements require different insulation materials Source greencity.com.tr
General information
Materials for thermal insulation are classified according to several criteria.
- By purpose - household, industrial.
- By origin - natural, synthetic.
- By release form - sheet, roll, bulk, sprayed, piece.
- The structure is cellular, fibrous, granular, composite.
- By type of raw material – organic, inorganic.
And all types of insulation, depending on the composition and properties, have a specific scope of application and installation technology. For example, bulk materials are more suitable for horizontal surfaces, fibrous materials need waterproofing, and structures of complex shapes are easier to insulate with sprayed insulation or special piece products.
Thermal insulation for a pipeline outlet unit Source pro-uteplenie.ru
Having understood the features of modern insulation, it will be possible to competently approach their choice.
Tips for use
Most modern insulation materials are produced in rolls, sheets and mats. The last 2 options are the most convenient to install, because they are already cut evenly, which allows for a tighter joint. The width of soft insulation mats should be 1.5 cm less than the distance between the sheathing elements. This will avoid the appearance of gaps through which the cold will penetrate into the room.
Insulation work should be planned. It is advisable to use a thermal imager to identify areas where the greatest heat loss is observed. Regardless of the type of material chosen, it is necessary to prepare the surface, eliminate small cracks, remove debris and carry out antifungal treatment.
For lathing, you can use metal profiles with an anti-corrosion coating. Most glued insulation requires additional fixation with special dowels. Liquid ceramics should not be applied with a spray gun. It is best to use a roller or brush. When using cork insulation, you need to prepare the surface in advance, because... it should be as level as possible so that condensation does not accumulate under the coating.
Basic properties of different thermal insulation materials
The most popular types of thermal insulation used in private construction are polystyrene foam, fibrous (wadding) materials, hardening foams, and expanded clay. Read more about them and some other effective insulation materials.
Expanded polystyrene
Foamed polystyrene is a synthetic material. Produced by pressing or extruding molten foamed raw materials.
- Compressed polystyrene foam, more often called polystyrene foam, has lower strength and larger granules with air sealed in them.
- Due to its denser fine-cell structure, extruded polystyrene foam has increased strength and improved characteristics.
The difference in the structure of the materials is clearly visible Source ppu-prof.ru
Expanded polystyrene thermal insulation materials are insulation that is extremely popular due to its low cost, ease of installation, versatility of use and low thermal conductivity. They are produced in the form of plates and shells for pipes and fittings of different diameters.
For installation on vertical surfaces, it is not necessary to arrange a supporting frame - rigid sheets of insulation can be glued to the surface or fastened mechanically. They can be used to insulate floors, walls, ceilings, and roofs. And loose polystyrene foam granules are used as a filler in the production of light and warm cellular concrete.
The main advantage of the material is its hydrophobicity. Closed cells do not allow water to enter, so they do not lose their thermal insulation properties. This quality allows the use of expanded polystyrene for insulation of such difficult-to-use elements as foundations, plinths, blind areas, basement walls, caissons, underground pipelines, etc.
Insulation of the foundation and blind area Source sdelai-lestnicu.ru
However, these types of thermal insulation materials also have some disadvantages, including low vapor permeability, due to which a greenhouse effect occurs in a room insulated with polystyrene foam in the absence of high-quality ventilation. They do not want to insulate wooden structures to prevent them from rotting.
This material is also considered flammable, although it does not burn, but when exposed to fire it melts, releasing toxic substances.
Loose and warm polystyrene foam often becomes a haven for mice, which make nests in it, destroying the integrity of the slabs. But dense extruded polystyrene foam does not attract them.
Glass wool
One of the oldest types of mineral insulation is glass wool, made from molten sand and broken glass. The hot mass is stretched into fibers, bundles of which are pressed and form a material resembling cotton wool in its structure.
Glass wool is available in rolls and mats Source huzzaz.com
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in home insulation
In addition to the fact that glass wool is a good heat insulator, it is also a material that absorbs noise well. It does not burn, does not attract rodents at all, is lightweight and affordable. But all these positive characteristics give way to the inconveniences associated with installation.
- Fragile and brittle fibers of cotton wool easily come off the mat and fly into the air, getting on the skin and mucous membranes, causing irritation.
- The low density of the material leads to its gradual settlement, which complicates installation on vertical surfaces.
Like all fibrous insulation, glass wool is afraid of getting wet and needs protection from water and wet steam getting into it.
Taking into account these features of the material, it is used mainly for thermal insulation of floors, interfloor ceilings, and roofs. And also for insulation of above-ground pipelines with a mandatory outer layer of waterproofing film.
Insulated glass wool main pipeline Source rk.gov.ru
Stone wool
Of all the types of wall insulation, the most popular is stone wool, the raw material for which is basalt rocks. This is an absolutely harmless, non-flammable material with excellent heat capacity and vapor permeability characteristics. Suitable for insulating any above-ground parts of a building, provided that a water barrier and an air gap are created between it and the finish to evaporate excess moisture.
It is produced in different densities and in a variety of forms - in rolls, mats, piece-shaped products with a protective coating. It can be laid on horizontal surfaces, mounted on walls in lathing, and the densest products can be fixed with glue or dowels and plastered.
What types of insulation and what to use?
There are many types of insulation materials on the market, differing in composition, characteristics and release form. It is necessary to choose the right insulation option, taking into account the characteristics of the surface that requires additional protection.
Floor insulation
Almost all types of materials are suitable for floor insulation. You can use bulk materials such as expanded clay and vermiculite. With additional waterproofing, the use of mineral and ecowool is allowed. Insulation with polystyrene foam boards also has a good effect. However, when treating the floor, it is not advisable to use sprayed insulation. High vibration loads can cause peeling and cracking.
Insulation of walls outside
When insulating the facade of a building, it is best to use materials with low water permeability. Insulation with fiberboard and arbolite blocks and extruded polystyrene foam slabs has a good effect. Expanded clay can be poured between the walls. If you are sure that water will not accumulate in the walls, you can use ecowool.
When insulating walls externally, you can use mineral wool, but in this case it is necessary to install waterproofing and protect the material with a layer of plaster. In addition, you can use hinged polyurethane foam panels and warm plaster. Liquid ceramic thermal insulation has a good effect when used outdoors.
Insulation of internal walls
To insulate internal walls, mineral wool slabs are most often used, which after installation are covered with plasterboard. In addition, cork boards and wallpaper can be used effectively. Warm plaster is often used for interior decoration. To decorate the interior walls of balconies, it is better to use foil insulation.
Ceiling insulation
Expanded clay and vermiculite can be used to insulate the ceiling from the attic. When arranging an internal insulation pie on the ceiling, you can use mineral wool, polystyrene foam boards, and polystyrene foam. In addition, it is permissible to use cork wallpaper and slabs. They are easy to install and are lightweight.
Roof insulation
To insulate roof slopes, mineral wool slabs are often used, which are then covered with plasterboard. However, in this case, additional waterproofing is required, because in this part of the house there is a high probability of material getting wet. Expanded polystyrene slabs are often used to construct a thermal insulation pie for the roof. The use of sprayed insulation has a good effect. Sprayed polyurethane foam is not affected by moisture and at the same time allows you to create a monolithic thermal insulation coating between the roof beams.
Video description
The types and properties of stone wool are described in the video:
Unlike glass wool, stone wool does not cause irritation when cutting and laying. But of all fiber insulation, it has the highest price.
Slag
Another type of fibrous mineral insulation is slag wool. In terms of its heat-saving characteristics, it is close to stone and glass wool, but its scope of application is limited to non-residential buildings. The fact is that these heat-insulating materials are highly chemically active and, in close contact with metal structures, oxidize them. They may also contain toxic substances, since slag wool is produced from waste from metallurgical production - blast furnace slag.
Stitched slag mat Source isolantisrl.it
The fibers of the material are brittle and mobile, which forces the constant use of personal protective equipment for the eyes, skin, and respiratory organs during transportation, loading and installation.
But in terms of price, it is one of the most affordable materials, so it is often used to insulate garages, warehouses and other utility buildings.
The need for thermal insulation
Thermal insulation is a design element that reduces heat transfer. The term can also mean materials for the implementation of such elements or a set of measures for their construction.
With the development of civilization, when the struggle for heat ceased to be so acute, massive hearths and Russian stoves were replaced by central heating radiators, and new heat-insulating materials replaced turf, moss, felt and tow. However, even now the problem of heat conservation remains acute.
- There are several reasons:
- To heat hundreds of millions of square meters of poorly insulated dwellings, it is necessary to spend a lot of money on fuel, and its reserves of fossil fuels are not endless.
- Secondly, the anthropogenic impact on the environment has recently increased, the progressive development of the “greenhouse effect”, not least caused by emissions from the combustion of coal, oil and other energy resources. Therefore, we have to look for new effective materials and methods of thermal insulation.
After the introduction of new building codes that tightened the requirements for thermal protection, the correct use of high-quality thermal insulation has become an urgent necessity. In construction today, modern heat-reflecting materials and technologies are used to save heat more effectively.
It is on this that the energy consumption of the floor in operating mode and the reduction of heat loss to a minimum depend.
The main function of thermal insulation is: Preventing heat loss through the subfloor. Thermal insulation under an electric heated floor ensures uniform heating of all elements, with further heat transfer to the floor covering over the entire surface. Since high-quality heat distribution occurs, this significantly reduces energy costs. It creates additional sound insulation, which is especially important in an apartment building. If there is an unheated room or ground under the floor, then thermal insulation eliminates the penetration of moisture and cold from below. If the insulation for an electric underfloor heating is selected and installed correctly, then the entire underfloor heating pie turns into a closed thermal zone in which heat spreads in the desired direction and with a uniform flow.
Reducing heat loss, saving energy, preventing the appearance of mold or mildew are important tasks that can be solved by installing floor insulation. In an ordinary house, up to twenty percent of the heat can escape through the floor, since heat goes into the ground through insufficiently insulated floors.
Thermal insulation device allows not only to reduce these heat losses, but also to more efficiently use the heat capacity of the floor. If the floor has a low temperature, then moisture may condense on its surface, at the junction of floors and walls.
And this can lead to the appearance of mold and fungi, which negatively affect building structures, as well as the health of people in the room.
By properly designing the structure and insulating the floor, you can prevent these phenomena. Maximum efficiency can be achieved if you additionally insulate both the ring beam, the plinth, and the basement wall.
In other words, good thermal insulation of floors should be organized in rooms whose floors are close to the ground or in contact with outside air. Thermal insulation is also recommended for the floors of those rooms that separate heated rooms from unheated ones.
This way you can solve three problems at once. The first is to reduce heating costs, the second is to reduce environmental pollution and the third is to create comfortable conditions for people to live in the premises.
Video description
Watch a video about the advantages and disadvantages of ecowool and the rules for its installation:
Polyurethane foam, penoizol
The most highly effective modern thermal insulation materials are substances that, after being sprayed onto the surface, form a continuous layer of hardened foam with sealed pores impenetrable to moisture. The most common example is polyurethane foam in cylinders.
To treat large areas, materials such as penoizol and polyurethane foam are applied with special installations. They adhere well to any surface, allowing you to insulate even complex curved elements, vertical and inclined structures without lathing or using fasteners.
Insulation of a pitched roof from the inside Source greenteamli.com
Advantages:
- very low thermal conductivity coefficient;
- absence of cold bridges;
- light weight and no load on insulated structures;
- resistance to water, high and low temperatures;
- creation of anti-corrosion protection for metal elements;
- durability.
For reference! Polyurethane foam is destroyed by ultraviolet radiation, so facades and other open-air structures cannot be left unfinished for a long time.
Thermal insulation boards and pipe shells are also made from polyurethane foam.
Manufacturers
The market now offers a large number of similar materials from different manufacturers. High-quality options that have better performance characteristics and are safe for people are produced under the following brands:
- Rockwool.
- Isover.
- Ursa.
- Knauf.
- Izovol.
- TechnoNIKOL.
- Beltep.
- Europlex.
- Penoplex.
Each manufacturer produces a line of products designed for insulating surfaces, so it is possible to choose the best option.
Video description
The types and methods of using polyethylene foam as insulation are described in this video:
Tow, construction felt
When talking about what types of insulation there are, it is worth mentioning those that are used to insulate the gaps between the crowns of a log house, cracks around window and door frames.
- Felt is a fabric felted from low-grade wool with the addition of paste, plant fibers and chemicals to protect against moths and other insects.
Felt tape Source bitrix-cdn.ru
- Tow is produced from flax and hemp waste, obtaining from them a fibrous material for caulking walls.
Liquid ceramic thermal insulation
Liquid internal thermal insulation based on ceramics, made using the most modern technologies, has the following features:
- high level of environmental friendliness, allowing the material to be used in any premises;
- resistance to steam and moisture, ensuring maintenance of performance characteristics even after getting wet;
- long service life (at least 15 years);
- resistance to rodents, insects and ultraviolet rays.
The material is applied to the protected surface at any temperature and has a relatively affordable price. The disadvantages of liquid-ceramic thermal insulation include insignificant noise protection and low resistance to mechanical stress.
Briefly about the main thing
Having studied the properties of thermal insulation materials, we can conclude that each of them is not ideal and is not without its drawbacks. There is no ideal insulation suitable for all purposes. When choosing the best option, you need to take into account the material of the insulated structure, its shape and position in space, operating conditions and other points. For example, fibrous materials that are afraid of moisture are not suitable for the underground parts of the building, and the steam room cannot be insulated with foam plastic, which releases harmful substances when heated.
Organic TIM
In the production of organic TIMs, raw materials of natural origin are used. This is usually waste from the woodworking and agricultural sectors. Sometimes, to enhance certain characteristics, certain types of plastic or cement mixtures are added to the composition. The main advantages of such TIMs:
- chemical inertness. The material practically does not react to aggressive environmental influences;
- high fire safety. Even at temperatures above 100°C, organic materials do not melt or ignite;
- good waterproofing properties.
Below we consider the types of organic insulation that the modern building materials market can offer to consumers.
Arbolit
This building material is made from wood shavings and sawdust, chopped reeds and chopped straw. The base is a cement base and some chemical additives. At the last stage of wood concrete production, the semi-finished insulator is treated with a mineralizer.
It has the following characteristics: density up to 700 kg/m3 and thermal conductivity up to 0.12 W*m/K. Since up to 90% of the composition is wood waste, wood concrete is extremely sensitive to high humidity, so it must be used in conjunction with good waterproofing agents.
Wood concrete is sold in the form of blocks, the thickness of which reaches 20 cm. This insulation is quite easy to make with your own hands.
PPVC
Foamed polyvinyl chloride TIM consists of various organic resins, which during processing acquire a foamy structure. The choice of insulation of this type is optimal: this material is a universal heat insulator and can be used at all stages of construction.
The density of PPVC does not exceed 0.1 kg/m3. PPVC is produced in elastic and hard form.
Chipboard and DVIP
Particle boards are another type of thermal insulation made from waste from the wood processing industry. Chips make up more than 95% of the total chipboard volume. The remaining 5% consists of adhesive resins and water repellents. To increase resistance to the effects of the external environment, chipboards are treated with antiseptics - against various microorganisms and insects.
Wood fiber insulating board (FIP) is similar in composition and characteristics to chipboard, but differs from it in its density (WIP is much lighter) and lower strength. The thermal conductivity of wood boards is slightly lower than that of wood concrete - up to 0.07 W*m/K. Both chipboard and DVIP are widely used for insulation of residential and commercial premises.
Insulation of walls from the inside
Internal thermal insulation is less effective than external insulation and is performed if it is impossible to insulate from the outside. For work, it is better to use environmentally friendly insulation materials, for example, Isover Warm Walls Strong mineral wool. The main task when insulating from the inside is to prevent contact of moist air with the supporting structure and the thermal insulation layer through high-quality installation of the Izover Paranet vapor barrier membrane with mandatory gluing of joints and possible damage with Izover Paranet adhesive tape. To do this, it is necessary to correctly select the thickness of the thermal insulation, take into account the need to use membranes and strictly follow the installation technology.
Coconut fiber (Coir)
Coconut fiber (coconut coir) is a fiber that is hand-harvested from the coconut shell (mesocarp), washed, dried, combed and pressed into slabs or rolls. The largest producers and exporters are India, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia. It is used as insulation for external walls, roofs, ceilings, attics, interfloor ceilings, as well as for internal partitions in houses, as a substrate for laminate and parquet. Production in the form of mats, rolls, slabs, blocks, in accordance with the international certificate ISO-9001.
Coconut fiber
Pros and cons of coconut fiber
pros
- 100% environmentally friendly
- Does not rot, does not absorb foreign odors
- Hypoallergenic
- Not susceptible to bacteria and mites
- High moisture resistance due to lignin, which prevents the spread of fungus and mold
- Not electrified
Disadvantages - high cost due to the complexity of obtaining raw materials and production.
Specifications
- Density 30 kg/m³
- Thermal conductivity 0.038-0.042 W/mK
- Heat capacity 1600 J/kgK
- Flammability - class B2 (moderately flammable)
- Sound absorption 70%
If coconut insulation loses its primary characteristics, it can be used as a fertilizer in agriculture, as well as for recycling into a new product.
What does thermal conductivity depend on?
Thermal conductivity is a physical quantity and largely depends on the parameters of temperature, pressure and type of substance. Most of the coefficients are determined empirically. Many methods have been developed for this. The results are compiled into reference tables, which are then used in various scientific and engineering calculations. Bodies have different temperatures and during heat exchange it (temperature) will be distributed unevenly. In other words, you need to know how the thermal conductivity coefficient depends on temperature.
Numerous experiments show that for many materials the relationship between the coefficient and the thermal conductivity itself is linear.
The thermal conductivity of metals is determined by the shape of its crystal lattice.
In many ways, the thermal conductivity coefficient depends on the structure of the material, the size of its pores and humidity.
Which thermal conductivity measurement method is best for your material?
There are methods for measuring thermal conductivity such as LFA, GHP, HFM and TCT. They differ from each other in the sizes and geometric parameters of the samples used to test the thermal conductivity of metals.
These abbreviations can be deciphered as:
- GHP (hot guard zone method);
- HFM (heat flow method);
- TCT (hot wire method).
The above methods are used to determine the coefficients of various metals and their alloys. At the same time, using these methods, they study other materials, for example, mineral ceramics or refractory materials.
The metal samples on which the research is carried out have overall dimensions of 12.7 × 12.7 × 2.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Peat (peat slabs, peat blocks)
According to Wikipedia, peat is an undecomposed, loose sedimentary rock made from the remains of moss. Output - in slabs, blocks. Peat blocks are a fairly new and exotic type of insulation for Russia. Peat blocks are produced by grinding natural raw materials, adding water, chopped straw, sawdust, flax kernels for binding, pressing to the desired size and thoroughly drying. To avoid block fragility, many manufacturers add silica to the composition.
Pure peat and peat blocks
Advantages of peat blocks
- Light weight
- Low thermal conductivity
- Excellent sound insulator
- Service life from 70 years
- 100% eco-friendly
- Breathable material
- Easy installation, the ability to produce blocks yourself
Insulation of house walls with peat blocks
Disadvantages of peat blocks
- Fire hazard is a big disadvantage of peat. Although manufacturers are trying to combat this problem by adding fire retardants to the composition, it is still better to plaster a wall made of such blocks and cover it with non-combustible siding.
- Also a disadvantage in the case of hand-made production is that the blocks take a very long time to dry . Prepare blocks, taking this feature into account, in advance.
Thermal insulation of the roof with peat blocks
Specifications
- Thermal conductivity 0.047 - 0.08 W/mK
- Compressive strength 10.7 - 12 kg/cm²
- Sound insulation 50-53 dB
- The weight of one cubic meter is approximately 250 kg
Roof insulation
When thermally insulating a roof, the selection of insulation is carried out taking into account the geometry and angle of inclination of the roof. For a complex roof with different pitches between the rafters, Isover Warm Roof Strong mineral wool is ideal. It makes it easier to bypass all the bends of the structure, and also to install the material reliably the first time and for many years without additional fastening and unnecessary joints (cold bridges). Even if the “clear” distance is up to 800mm. Pay attention to this insulation in thicknesses of 150 and 100mm. The ideal formula for roof insulation is 150+100mm. It is imperative to waterproof the roof side using the “breathable” hydro-windproof membrane Isover Hydranet. It is important not to forget about vapor barrier from the inside using Izover Paranet.
Disadvantages of the high thermal conductivity of copper and its alloys
Copper has a much higher value than aluminum or brass. But meanwhile, this material has a number of disadvantages that are associated with its positive aspects. The high thermal conductivity of this metal forces the creation of special conditions for its processing. That is, copper billets must be heated more accurately than steel. In addition, there is often pre- or auxiliary heating before starting treatment. We must not forget that pipes made of copper imply that careful thermal insulation will be carried out. This is especially true for those cases when the heating supply system is assembled from these pipes. This significantly increases the cost of installation work. Certain difficulties arise when using gas welding. To get the job done, a more powerful tool is required. Sometimes, to process copper with a thickness of 8 - 10 mm, it may be necessary to use two or even three torches. In this case, one of them welds the copper pipe, and the rest are busy heating it. In addition, working with copper requires more consumables.
Read also: Stages of the production process
Working with copper requires the use of specialized tools. For example, when cutting parts made of bronze or brass with a thickness of 150 mm, you will need a cutter that can work with steel with a large amount of chrome. If it is used for processing copper, then the maximum thickness will not exceed 50 mm.
Floor insulation
When insulating the floor, the presence of a basement, the number of floors, technologies and building materials used in construction are taken into account. If the building has a basement, it is insulated from the outside to prevent contact of water and cold soil. If you have a foundation with a ventilated underground or a pile foundation, the floor of the first floor is insulated using Izover Profi mineral wool laid between the joists. A vapor barrier is installed from the inside of the room, and a sheathing board or hydro-windproof membrane is installed from the outside, if necessary.
Ceiling insulation
The ceiling is insulated in cases where the building does not have an attic or attic, or the roof is not insulated. When installing between floors on wooden floors, it is better to use cotton wool insulation placed between the joists, for example, Izover Profi. If the floors are slab, you can take mineral wool (for example, Izover Warm Roof Strong or Izover Pro with laying a vapor barrier and a log filled with mineral wool), this type of floor is more convenient to insulate from the attic side (do not forget to ensure ventilation of the under-roof space), since insulation work is carried out from the inside will reduce the height of the room.
Comparative analysis
With such a variety of thermal insulation materials, it is difficult to choose the one that will be needed specifically for certain purposes. We must pay tribute to the manufacturers who began to separate products by model. For example, insulation made of expanded polystyrene brand Penoplex. Models are offered only for indoor use, for facades, for roofs and so on. As indicated on the packaging.
Let's compare some insulation materials with each other, after which it will become clear which one is best to choose for thermal insulation.
Penofol
For example, let's take the famous brand Penofol - this is insulation made of foamed polyethylene. Let's start with the fact that the manufacturer supplies this heat insulator with a double-sided foil layer. Penofol 4 mm thick can replace 80 mm of rolled mineral wool, 30 mm of expanded polystyrene board. In addition, there is no need to install hydro- and vapor barriers.
But it cannot be used under plaster. In this regard, polystyrene foam boards win. You just need to apply a plaster mesh on them and you can level them.
Minvata
Mineral wool is the cheapest insulation on the market. But its cheapness is imaginary, because for installation you will have to build a wooden frame, which must be treated with an antiseptic. That is, all these expenses will negate its cheapness.
Plus, mineral wool is afraid of moisture, and this means two more layers of protective materials. And yet, together with polystyrene foam boards, it is a leader in the category of modern insulation materials.
PPU
As for polyurethane foam, it is rarely used in private housing construction. This pleasure is too expensive. It is impossible to apply it with your own hands. Special equipment and permission to carry out work are required.
Arbolit and penoizol
These materials are most often used for insulating balconies and loggias. Both insulation materials today compete with cellular concrete blocks.
Unfortunately, they are still losing due to the lack of promotion of the brand. Although the thermal insulation characteristics of foam blocks are not inferior. But for thermal insulation of facades, wood concrete is a good option.
Foam glass
Foam glass is a foamed glass mass obtained by sintering quartz sand at a very high temperature (more than 900 degrees Celsius) with the addition of broken glass.
It is used for insulating vertical and horizontal structures, metal, brick and wooden surfaces. They can be fastened either mechanically or using various mortars.
Foam glass
Pros and cons of foam glass slabs
Pros:
- Non-flammable material
- 100%eco-friendly
- Greater water resistance
- Chemically resistant
- Prevents rodents, insects, mold and mildew
- Shelf life 100 years
- Retains its characteristics under any load and exposure to any temperature.
drawback - the high price compared to other organic insulation materials.
Insulation with foam glass slabs
Specifications
- Density 115-145 kg/m³
- Compressive strength 0.7 MPa
- Thermal conductivity 0.052 W/mK
- Operating temperature from -260 to 730°C
- Flammability - class A1 (non-combustible)
Foam glass slabs are widely used for insulating floors, walls of houses, basements, garages, bathhouses, etc. Also, special foam glass cylinders of the required internal diameter (from 76 mm to 3000 mm) are used to insulate pipelines.
The role of thermal conductivity coefficient when making architectural and construction decisions
The thermal conductivity of solids, which are all building materials, is manifested due to the transfer of heat occurring as a result of vibrations of the crystal lattice.
The high thermal conductivity of building materials is unacceptable for the construction of architectural structures. The greater the thermal conductivity, the lower the thermal insulation qualities of the material necessary to maintain a room temperature different from the ambient temperature.
Building materials with low thermal conductivity help maintain the achieved temperature in the room, regardless of weather conditions, due to minimal maintenance of diffusion between particles of different temperatures.
The lower the thermal conductivity coefficient of a material, the better its thermal insulation qualities.
Good thermal insulation will eliminate drafts, cold walls, rapid cooling, freezing or heating of the room, and will allow you to significantly save on heating or cooling devices.
Or read HERE about installing plastic windows yourself.
RESULT
When choosing a natural material for thermal insulation, you first need to consider its cost-effectiveness, biodegradability, thermal conductivity and durability. The low thermal conductivity and fibrous nature of most organic materials contribute to a significant improvement in the thermal insulation performance of a building. Natural organic materials have a higher specific heat capacity and are more sensitive to moisture. It is these physical properties that prevail in comparison with conventional silicate materials.
The article was written for the site.
Tags:Wall insulation