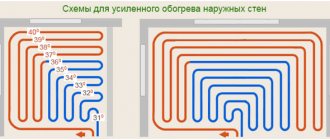
Straight radiator valve.
A manual valve for radiators is a pipeline fitting whose main task is to regulate the flow of coolant. By changing the volume of hot water supplied to the radiator, the room temperature can be adjusted using a manual valve. This device allows you to save the consumption of consumed thermal energy by reducing the operating time of the heating system at full power.
Purpose of shut-off valves
Among ordinary people, the term “faucet” is usually applied to any device for controlling the flow of liquid that is equipped with a handle. In the technical literature, taps are called shut-off valves, with the help of which you can achieve only complete blocking or opening of the coolant flow. These devices cannot be adjusted. For this purpose, there are other types of products - valves and radiator shut-off valves. Most often, the inlet pipe to the radiator is equipped with control valves.
Its functions are as follows:
- Possibility to turn off the battery. The reason could be a variety of reasons.
- Shutting off the coolant supply for flushing and testing activities.
- Manual or automatic adjustment of coolant supply. This allows you to reduce or increase the temperature of the radiator.
The range of functions performed may differ for different types of fittings. When starting to independently arrange a heating system, it is important to familiarize yourself with the design features of all types of taps that may be encountered during the installation of heating radiators.
Strapping elements
The heating device in different circuit configurations can be equipped with:
- Shut-off valves are ordinary ball valves designed to completely disconnect the device from the circuit. The ball valve has only two operating positions - “open” and “closed”.
Let us clarify: adjusting the permeability with the help of this fittings is possible in principle, but it is very difficult due to the impossibility of accurately adjusting the position of the valve shutter. In addition, intermediate positions of the valve accelerate wear of the seats (Teflon or fluoroplastic rings in the valve body) due to suspensions contained in the coolant.
It is not advisable to use ball valves to regulate heat transfer.
- Chokes . A throttle, or radiator control valve, allows for manual adjustment of the flow of the supply line and allows flexible adjustment of the heat transfer of the device.
- Thermostats . The thermal valve for the heating radiator makes it possible to automatically adjust the heat output depending on the room temperature.
- A manually controlled air valve (Maevsky valve), which serves to bleed air.
- Automatic air vent , performing the same functions without the participation of the owner.
Ball valves for heating system
The popularity of ball valves is explained by their extremely simple design, which contributes to long service life. They are very convenient to use: blocking the flow is accomplished by simply turning the handle 90 degrees. The locking mechanism of this device is based on a ball with a through hole. To block the duct, you need to turn the ball with the hole at an angle of 90 degrees to the body.
To control the ball valve, there is a handle connected to the ball via a rod. The tightness of the mechanism is ensured by the presence of a pair of elastic rings that fit tightly to the ball. The body can be made from brass, aluminum or polypropylene. Plastic taps are usually equipped with polymer pipes for the heating system.
Weaknesses of ball valves:
- They are very sensitive to impurities in water. It is advisable to equip the system with filters.
- It does not have smooth flow control. If the ball valve is frequently turned, its mechanism will quickly wear out.
A manual valve or manual shut-off valve for radiators is a device with a double change in the direction of coolant flow inside the structure. The role of the shut-off element in such valves is performed by a rod equipped with an elastic gasket. To change the position of the rod there is a worm mechanism and a handle. Shutting off the coolant supply is achieved by tightly pressing the gasket to the seat. When the handle is rotated smoothly, the passage gradually opens.
The strengths of this device include the ability not only to completely shut off the flow of water, but also to control the intensity of the pressure. On the other hand, the service life of the rubber gasket is limited, which leads to loss of tightness when overlapping. To solve this problem, you have to change the gaskets from time to time (it’s not difficult to do this yourself). The installation of a ceramic crane axle box significantly increases the intervals between scheduled repairs. It works an order of magnitude longer than the idle design with a rod.
All radiator valves are divided into two large groups:
- Straight shut-off valves for radiator. Valves of this type are most often used in lateral connections, where the pipes approach the battery opposite the inlet and outlet.
- Angle radiator shut-off valves. Used for bottom pipe connections.
We understand the types of devices
According to the method of adjustment, valves are divided into mechanical and automatic . The first require manual rotation of the mechanism for narrowing the flow in the pipes.
Both devices perform the same function - they adjust the flow of coolant to the radiator in accordance with the parameters set by the user, but using automation is less troublesome
Automatic models do not require manual adjustment. When the temperature around the thermostat decreases, they independently detect this and adjust the coolant flow.
Manufacturers also offer different thermostat designs:
- Common for two-pipe systems - the simplest device. If you need hydraulic linking of radiators along one branch, it is recommended to add a shut-off and control valve to the supply (return) circuit.
- With hidden and open hydraulic superstructure - such devices have a coupling with an internal rod, so hydraulic adjustment is possible.
- For single-pipe, gravity systems - due to the increased passage, the throughput of these devices is increased to 5.1 m3/hour, so they can be installed in non-pressure systems.
- 3-way for circuits with bypass - they can regulate and distribute the coolant in conjunction with the bypass. When the set temperature reaches the valve, the coolant is sent to the bypass; when it drops, the bypass is partially closed.
The percentage of thermal valves for two pipes is much greater than for single pipes, and the latter in our country are about 80%.
This is due to the fact that the device was originally invented for the former, where the coolant is distributed among the devices forcibly under high pressure. Pre-setting by valves is designed to distribute pressure evenly throughout the system.
Only some manufacturers have valves for single pipes - Heiz, Danfoss, Heimeier, Oventrop.
In single-pipe schemes, you cannot use conventional “two-pipe” thermostats : they have a lower capacity, they can only operate with a large difference in pressure between the supply and return, so there will be a risk of redirecting the coolant to the bypass.
Externally, “one-pipe” valves are larger in size.
Three-way valves are appropriate in circuits with a solid fuel boiler, as well as for flow separation and bypass piping of radiators. The device can also be used in single-pipe installations
Thermostatic valves also differ in shape. They can be straight, angular or included in sets with jumpers for pipes. Direct ones are suitable for regular batteries. Angular ones are needed in schemes with lower pipe connections, when the CO is partially disguised under the floor.
A separate type of thermal valves is electronic. They have wider functionality than regular ones. With their help, you can set different room temperatures for each day of the week and even hourly.
Electronic thermal heads are more expensive and larger than usual: inside the case there is a compartment for two batteries. There are models with removable and built-in control units
Electronic thermostats provide significant savings in coolant consumption. If there is no one in the apartment or house from 8 am to 6 pm, the device will properly maintain the minimum temperature. And when the owners arrive, it will heat the premises to a comfortable level.
Valves with anti-vandal casing are also available for sale. They are reliably protected from unqualified intervention and are suitable for installation both in a home with small children, and in kindergartens and schools.
Radiator valve equipped with thermostat
Thanks to the radiator shut-off valve with a thermostat, it is possible to switch the adjustment of the coolant flow rate to automatic mode. Another name for this device is a thermal valve or thermal valve. The shut-off valve for a heating radiator is quite simple to install.
The locking mechanism includes the following parts:
- Metal body. It has a passage hole and a seat.
- Elastic cone.
The degree of permeability of the coolant is regulated by lowering and raising the cone. How it is located depends on the thermal head (thermoelement), which consists of the following elements:
- Cylinder (bellows).
- Thermal agent. Liquid or gaseous bellows medium. The volume of the thermal agent largely depends on fluctuations in ambient temperature.
- Piston. On one side it is connected to a cylinder, on the other - to a cone.
A change in temperature provokes compression or expansion of the thermal agent. This activates the piston, which changes the position of the cone through the rod. Thanks to the thermal head, the temperature is adjusted, resulting in complete blocking of the liquid flow.
- Mechanical.
- Electronic. They have a display and a sensor that displays the air temperature. This makes it possible to plan the operating modes of the shut-off valve for different times of the day or days of the week.
For example, during the daytime work or study of family members, it is logical to set a lower temperature value. Upon the return of household members, the batteries will heat up to higher values, effectively heating the home. The cost of electronic thermostats is noticeably higher than mechanical ones. To save a little money, not all radiators in one room are usually equipped with a thermostat. It is enough to have a control device on one or more heaters, which together provide at least half of the total heat.
Modern heating systems are equipped with the following battery connection diagram:
- The supply pipe and the battery are separated by a control valve. We are talking about a manual valve or a valve with a thermostat.
- The return pipe and radiator are separated by a ball valve.
- The inlet and outlet shut-off pipes are additionally equipped with a bypass (jumper). Thanks to it, the coolant in the right situations has the ability to bypass the battery. Jumpers are used in serial radiator connection diagrams.
There is usually a ball valve in the center of the bypass. It is recommended to equip the outlet with shut-off valves with a drain fitting. This makes draining the battery much easier.
To make the operation of heating radiators more efficient, they are equipped with different types of shut-off valves, depending on the technological requirements of the system. It is for this reason that different types of taps and valves are installed on the supply and return pipes.
Definitions
Let's start getting acquainted with the design of thermostatic equipment, moving from simple concepts to more complex ones.
Thermostat
This is a general name for all devices capable of maintaining a stable temperature of any environment under changing external conditions.
In relation to heating, a thermostat is understood as a control valve capable of ensuring a constant air temperature in the room when changing:
- weather conditions and, accordingly, heat loss through the building envelope;
- coolant temperature.
Thermostatic valve
The thermostatic radiator valve solves the problem of stabilizing the temperature in the room in the simplest and most obvious way - by limiting the flow of coolant through the heating device. The less water or antifreeze passes through the battery per unit of time, the colder it is; the more, the more its heat transfer increases.
What is the working principle of a thermostatic radiator valve? The vast majority of devices in the lower and middle price categories use the expansion of liquids and gases when heated and the reduction of their volume when cooled.
Thermostatic valve device.
When the contents of the bellows heat up, it lengthens and forces the valve against the seat, thereby limiting the coolant flow. Some time passes, and due to the decreased heat output of the heating device, the air in the room becomes colder. Compression of the working medium leads to a decrease in the length of the bellows; the opened valve allows the coolant to warm up the battery again.
Straight thermostatic valve for radiator 1:2 inches in diameter.
A more complex and expensive version of the thermostatic valve is an electric drive with digital control, which is carried out based on the analysis of data from a built-in or remote thermocouple.
Thermal head
Strictly speaking, a thermostatic head for radiators is a simple device for manually adjusting the valve position of a thermostatic valve. By rotating its handle, you can set the target temperature in the room, which will then be maintained automatically.
Head and valve.
Thermostatic kit
A typical heating device piping includes a certain gentleman's minimum, which allows you to flexibly regulate its heat output. The set includes:
| Device | Functions |
| Throttle or thermal head with thermostatic valve | Manual or automated adjustment of the supply permeability to maintain optimal room temperature |
| Shut-off valve | Complete shutdown of coolant supply to the radiator for its repair, replacement or temporary dismantling |
In some cases, the valve on one of the threads can be replaced with a check valve that stops the supply of coolant during counterflow (read: water is being discharged from the battery), or an additional throttle. In this case, the throttle provides preliminary balancing of the heating device (adjusting the permeability to equalize the temperatures of near and far heating devices).
A thermostatic kit is a set of shut-off valves from one manufacturer, including at least a thermostatic valve and a thermal head; More often, the kit additionally includes a balancing throttle.
In addition, the package can be supplemented with:
- radiator plugs;
- American ones for quick-connection of the radiator (they can be a separate element of the fittings or be part of thermostatic valves);
- Brackets for mounting the battery.
The price of a kit from a decent manufacturer starts from about 1000 rubles; the upper limit is 3 - 5 thousand, depending on the brand level and configuration.
Set of throttle, thermostatic valve and head for it.
Radiator shut-off valve. Features of ball and valve valves with thermostat
In modern heating systems, when connecting radiators, shut-off and control valves must be installed. As a rule, they perform several functions simultaneously. In this article we will look at what shut-off valves for heating radiators are usually used, and also get acquainted with its functions.
Valve for radiator
Exotic
Several other devices are used relatively rarely and are little known to the general public.
- The thermoelectric radiator valve actuator can be used with any throttling valves. It is an externally controlled servo drive powered by batteries or AC power.
The photo shows a closed thermoelectric valve.
- The internal spring valve for the radiator is a stainless steel valve with a spring that closes the manifold of the first section when the passage plug is screwed into it. The purpose of its installation is to limit circulation through the lower collector of the device, ensuring its uniform heating throughout the entire volume. (See also the article Manifold pipe routing: features.)
The damper restricts circulation through the lower manifold.
The valve for the lower connection of the radiator is equipped with a thermostatic head.
Why are cranes needed?
First of all, it should be said that people commonly call a faucet any device for controlling the flow of liquid that has a handle. Technically, it is more correct to call taps shut-off valves.
Moreover, the latter only allows you to completely shut off or open the coolant flow, but not to regulate its flow. Valves and valves are used for regulation.
As a rule, control valves are installed at the entrance to the radiator, which performs the following functions:
- Allows you to disconnect the battery, which may be necessary for various reasons.
- Allows you to shut off the coolant for washing the device or inspection.
- In manual or automatic mode, it regulates the flow of coolant and thereby the temperature of the radiator.
It should be taken into account that different types of fittings may have different functions. Below we will get acquainted with the features and design of all types of taps that are used in conjunction with radiators of the heating system.
Ball valve design diagram
Types of cranes
Ball valves have recently become very popular because they have an extremely simple design, which results in their long service life. In addition, they are easy to use, since to shut off the flow you only need to turn the handle 90 degrees.
The locking mechanism of this device is made in the form of a ball with a through hole. To block the passage, the ball should be turned with its hole perpendicular to the body.
The ball valve is controlled by a handle, which is connected to the ball via a rod. To seal the mechanism, two elastic rings are used that fit tightly to the ball.
The body of the ball device can be made of brass, aluminum or polypropylene. Plastic taps are installed together with plastic pipes for the heating system.
All existing types of radiator taps are straight and angular.
A radiator direct shut-off valve is usually installed with a lateral connection, when pipes are connected to the battery at the inlet and outlet levels.
If pipes are supplied from below, for example, from the floor, it is more advisable to use corner fittings.
Pictured is an angle valve.
It should be noted that this fitting has the following disadvantages:
- Sensitivity to impurities in the coolant. Therefore, when using water, it is advisable to install filters.
- Not intended for smooth flow control. If it is used for these purposes, the mechanism will quickly fail.
Therefore, ball valves are often installed on the return line to completely shut off the coolant flow.
To facilitate the process of connecting the tap to the battery, you should purchase fittings with an “American” type connection.
A manual valve or manual radiator shut-off valve is a structure within which the direction of coolant flow changes twice. The closing element in such valves is a rod with an elastic gasket. The position of the rod is controlled by a worm gear with a handle.
When the gasket is pressed tightly against the seat, the coolant passage is closed. If you rotate the handle smoothly, the gasket will gradually open the passage. The advantage of this design is the ability not only to completely shut off the coolant flow, but also to regulate its intensity.
However, it should be borne in mind that the rubber gasket deteriorates quite quickly, as a result of which it does not seal the flow tightly. This problem can be solved by replacing the gasket, which is easy to do yourself.
In order not to periodically return to valve repair, you can install a ceramic valve axle box.
Its service life is much longer than a conventional design with a rod.
Valve with thermostat for radiator
Shut-off valve with thermostat
A shut-off valve for a heating radiator with a thermostat allows you to regulate the intensity of the coolant flow automatically. This device is also called a thermal valve or thermal valve.
The shut-off valve design for this type of radiator is relatively simple.
Its locking mechanism consists of the following elements:
- Metal body with passage hole and seat.
- Elastic cone.
Valve device with thermostat
During operation of the device, the cone lowers and rises, as a result of which the amount of coolant passed through changes.
The position of the cone in the seat is controlled by a thermal head (thermoelement), which consists of the following elements:
- Cylinder (bellows).
- Thermal agent is a liquid or gas that fills the bellows. The thermal agent greatly changes its volume as a result of changes in ambient temperature.
- The piston is connected to a cylinder on one side and to a cone on the other.
Under the influence of temperature, the thermal agent contracts or increases in volume, which sets the piston in motion, which in turn changes the position of the cone through the rod. The thermal head allows you to regulate the temperature at which the valve completely shuts off the water.
It should be noted that there are two types of thermostats:
Electronic model of thermal valve
The latter are usually equipped with a display and sensor that displays the air temperature. Such devices allow you to set the temperature conditions of the shut-off valve at different times of the day or even days of the week.
For example, from nine in the morning to five in the evening, when all household members leave, you can set the temperature to a lower value, and after five, the radiator will warm up to higher values and better warm up the room. The price of such devices, of course, is quite high.
Within the same room, it is not necessary to install thermostats on every heating radiator.
It is enough to install the device on one or more heating devices, the total heat output of which exceeds 50 percent of the total.
Heating battery wiring diagram
Design and operating features of the device
Let's look at how a thermostatic valve works and on what principle it works.
How does a thermal valve work?
The device consists of two main working elements - a valve and a thermostatic head. The first is most often made of brass, sometimes nickel-plated, its lower part blocks the pipe, and its upper part continues the pressure rod and spring.
Valves are also available in bronze (nickel-plated or chrome-plated), as well as stainless steel. The latter are rare and expensive.
What happens inside the valve? The head device contains a sensitive element. It is located in a cavity with gas or liquid (bellows).
Heating provokes expansion in this environment, the element is pushed forward, pressing on the rod, spring, and later on the valve. The force of pressure determines the degree of overlap.
The figure shows a device with liquid in a bellows. Gas thermostats react faster to temperature changes (5-10 minutes), but are also more expensive. There is no significant difference from this during operation
An additional part of the thermostat is a plug or handle with a scale. Some devices have electronic controls.
Operating principle of the device
Let's take a closer look at the working principle of battery thermostatic valves. The mechanics of their action looks schematically like this: when the temperature of the coolant or the environment changes, the gas or liquid in the head reacts to these fluctuations.
The sensing element acts on the pressure rod, and it goes up or down. When the rod moves down, the valve blocks the flow of coolant, which stops the flow of heat and slows down the circulation rate. No heat enters the battery, so the room temperature does not rise.
And here it is important to distinguish a thermostatic valve from a control valve. The latter can reduce the valve capacity and thus regulate the temperature of the batteries.
When turning the knob or entering a digital value on the panel, the user sets the initial pressure value in the thermal head, to which it “adjusts” during operation
The control valve does not have a thermal head. The thermostat is open or closed, it is controlled by a thermal head, it does not change the volume of coolant, but only turns its supply on and off
Let's look at the operating principle of a thermal valve using an example. So, set the device to the recommended temperature of 20 degrees. This is usually a three or the largest point on the regulator scale.
What happens inside the device? If the surrounding air heats the head to 21 degrees, i.e. increases the set temperature by 1 degree, it presses the rod, the flow of coolant into the battery is completely blocked by the valve.
The radiator does not heat up and the room temperature begins to drop. When the ambient temperature drops to 19 degrees, the thermal valve will open and the battery will begin to heat up.
Strapping scheme
As a rule, in modern heating systems, the battery connection diagram (piping) looks like this:
- A control valve is installed between the inlet pipe and the battery - this can be a manual valve or a valve with a thermostat.
- A ball valve is installed between the outlet pipe and the radiator.
- A bypass (jumper) is installed in front of the input and output shut-off valves , which allows the coolant to bypass the battery if necessary. The jumper is installed when connecting radiators in series.
As a rule, a ball valve is embedded in the middle of the jumper.
At the outlet, it is better to install shut-off valves with a drain fitting.
This will make draining the battery easier.
Here, in fact, are all the instructions for connecting a heating battery.
For heating radiators, different types of shut-off valves can be used. Moreover, each type has different functions. Therefore, different types of taps are most often installed at the input and output of the battery.
You can find additional useful information on the topic discussed in the video in this article.
Features of installation and operation
- The valve can be installed in a vertical or horizontal position.
- First of all, the half-grip pipe is connected to the system (before installing it, the integrity of the O-ring is checked). Coupled manual valves for radiators are installed with the mandatory use of fluoroplastic seals. Installation and fastening of the pipe is possible using a special wrench. (The use of lever wrenches is strictly prohibited.)
- Before disassembling the shut-off and control manual valve, the coolant is drained.
- Before installation and operation, you must familiarize yourself with the rules for using the fittings, because Each type of device has special technical limitations and features.
Why do you need shut-off and control valves when installing a battery?
In general, this category of devices includes not only faucets of various types, but also various dampers and valves. And the shut-off valves for heating radiators also include plugs that are installed on the holes in the side of the battery.
When installing the battery, it is advisable to use:
- a couple of ball valves - they will be useful to quickly stop the flow of coolant into the battery. For this purpose, a bypass is installed, and shut-off valves are installed on the supply and return pipes;
Bypass will increase the reliability of the heating system
- when connecting the radiator to the system, a special shut-off valve can be used, which provides the ability to quickly drain water.
Among the regulating devices, an automatic thermostat will be useful; it will allow you to change the heat transfer of each battery individually. Thanks to this, you can save on heating costs, and the house will be more comfortable.
Note!. The thermostat is connected to the radiator itself, followed by a shut-off valve, then a bypass tube. Only with this sequence will the system work normally.
Detailed characteristics of shut-off valves
The normal operation of the heating system largely depends on the correct choice of the type of tap for the specific task. So it makes sense to take a closer look at the types of shut-off valves and their scope of application.
Ball Valves
A ball shut-off valve for a heating radiator is so called because its shut-off part is shaped like a ball with a hole in the middle. And the principle of its operation is that with one turn of the handle the water supply through the pipe is shut off.
This is very useful, for example, if the battery breaks, you can turn off the water supply almost instantly; if a screw device were used for the same purpose, you would have to spend much more time.
Ball valve with hole visible
In addition to ball ones, you can find analogues on sale with a conical or cylindrical locking part (these were used in Russian samovars). But in terms of performance indicators, it is the ball ones that are beyond competition. Conical ones, for example, are characterized by increased wear.
As for the choice of a ball shut-off valve, you need to take into account its dimensions and the type of metal from which it is made (it is necessary that, together with the metal of the radiator, it does not form a galvanic couple).
You also need to pay attention to the size of the hole in the locking part:
- full bore - in them the diameter of the hole exactly matches the internal diameter of the pipe itself. Thanks to this, once installed in the open state, it does not reduce the volume of water entering the battery;
In the full bore model, the hole in the ball is equal to the diameter of the pipe
- standard - their hole diameter is approximately 20% smaller than the internal diameter of the pipe. When using this model, we will reduce the heat transfer of the radiator by 10-15%;
- partial bore - due to the small hole in the ball, the liquid consumption is reduced by approximately half.
Note! Taking this into account, only full bore shut-off devices should be used for installation in front of the battery.
As for what the radiator shut-off valve device looks like, the section will show a metal ball and a gasket that ensures tightness when closed. Relatively recently, polymer shut-off valves have appeared on the market; they are suitable for installation on any radiator, regardless of what material it is made of.
Ball valve device
Note! Models with a plastic body are slightly inferior in strength to metal ones. But the thickness is greater; this must be taken into account when choosing.
Metal taps can be considered more traditional. Usually either brass or alloys containing it are used, so there should be no problems with the combination of metals.
It has only 2 working positions, which is why it belongs to the “shut-off valve” class. You can also find 3-way taps on sale; they can also be used when connecting radiators. The only difference is that there are 3 working positions, and the water flow can be directed in one of two directions.
A three-way valve is somewhat more complex than a regular valve
The price of such devices is low, and given the flexibility of the heating system, the additional costs are justified.
Stop valve
This category of devices can be used to connect heating radiators (in a 2-pipe heating system). Thanks to their design, valves, like ball valves, allow you to quickly shut off the flow of water into the battery, without interrupting the operation of the heating system. They can also be used to conveniently drain water from a heating device or fill it with liquid.
Simple shut-off valve
Note! The radiator direct shut-off valve does not include the installation of a drain valve in the basic configuration. But a useful addition can always be purchased separately.
As for the feasibility of the purchase, from a technical point of view there is no difference between installing a ball valve on the return line or choosing a shut-off valve. If there is at least a simple thermostat on the supply pipe, then both options will work the same.
But there are still differences in the design of a ball valve and a shut-off valve. The first can only be in the open/closed position, but the hex valve can regulate the coolant flow.
Diagram of draining water from the radiator
There are significant differences in appearance. Ball valves come with a clearly visible red butterfly, but the radiator shut-off valve looks much better.
It does not have a valve to turn, so it will not stand out much against the background of the pipes and the battery itself. Its cost is higher than that of a ball valve, but considering that the heating system is not built for 1 year, you can spend money.
The drain valve, used to drain water from the radiator, is installed on the shut-off valve. When you turn it with a special handle, the water supply to the radiator is shut off.
Stopcock installation
The whole process takes only a few minutes; you can do all the work yourself, without the help of specialists. You just need to take your time; for example, a slight misalignment when installing a tap on a pipe can result in a serious leak during the heating season.
Manufacturers produce shut-off valves with several types of connections. On sale you can find valves for welded joints, flanged joints, and coupling joints. The one-piece type of joint cannot be recommended due to difficulties with repairs in the future; the flange type of joint is used only in industrial enterprises, and in everyday life preference is given to detachable joints.
The photo shows an example of a combination of external and internal threads
Most often, taps with a union nut or an American one are used, the tightness is ensured high, and the labor intensity is minimal.
In this case, more attention is needed at the preparatory stage:
- you need to decide on the type of thread. The valves can be either coupling, external thread or combined, you need to choose based on the type of thread on the pipe;
- The type of handle also matters. If the pipe goes close to the wall, then you only need to choose the option with a butterfly; the long handle will simply rest against the wall.
Choosing the right option is not difficult
The installation instructions consist of several steps:
- the installation location of the crane is selected;
- the handle stroke is checked;
- Next, a threaded connection is made. It is mandatory to use a winding for additional tightness of the connection;
FUM tape guarantees the reliability of the threaded connection
Note! It is allowed to tilt the handle from the vertical by 45° on a horizontal pipe. So you don’t have to screw the joint all the way, but turn the tap a little to the side to make it easier to use.
- The final stage is checking the joint for leaks.