Correct calculation of air conditioner power is the key to efficient, uninterrupted operation and durability of climate control equipment. The choice of performance is based on the overall dimensions of the room and related factors contributing to the accumulation of thermal radiation.
Taking into account all the parameters and nuances of operation allows you to provide an optimal power reserve, but at the same time not overpay for the super-performance of the split system.
But how to correctly perform the necessary calculations? We will consider this issue in detail in our article. In addition to the two methods for calculating power, we will focus on other important criteria that influence the choice of air conditioner.
What do the power values in the documentation say?
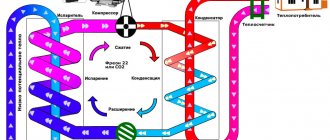
The technical documentation for air conditioners indicates two or three types of power. The indicators characterize different operating parameters: cooling and heating capacity, as well as the electrical power consumed by the split system.
The range of indicators can be misleading. In heating electrical appliances, such as a boiler or radiator, the heat output corresponds to the energy consumed. For an air conditioner, these parameters are different.
A split complex, unlike a heater, does not directly convert electricity, but uses it to operate a heat pump. The latter is capable of pumping much more heat energy than the electrical power consumed.
An example of displaying power characteristics in the passport for a Lennox GHM09 air conditioner operating in two modes: cooling and heating
Cooling capacity is the main technical characteristic that determines the ability of an air conditioner to remove heat outside the building. Power consumption is interesting from the point of view of selecting the supply cable and planning costs
Cooling power is indicated in kW, the range of values for household equipment is 2-8 kW. In addition, many manufacturers use the British marking - BTU (BTU) in technical descriptions.
The cooling capacity of the split unit must correspond to the service conditions. Otherwise, normalizing the microclimate to a given temperature will become an impossible task for the air conditioner and will damage the equipment.
There are two possible scenarios:
- low productivity - the unit operates at the limit of its capabilities;
- excess power - an increase in the number of on/off switches, which has a detrimental effect on the electric motor.
The ability to heat a room characterizes the heat output of a split. The heat transfer power is always slightly higher than the cooling capacity. The difference between the indicators is the ratio of heat loss along the freon pumping route in cooling and heating modes.
The thermal power indicator is especially relevant if the air conditioner is planned to be used as an interseasonal heating source. A split complex is many times more efficient than an electric heater. We talked about the features of a split system for heat here.
For 1 kW of electricity consumed, modern air conditioners produce about 3.6-5.5 kW of heat. This volume is enough to heat a living area of 36-55 sq.m., respectively.
Summary
When purchasing an air conditioner for a simple room without strong sunlight, you can calculate the power of the equipment based on the area of the room. The resulting indicator will be quite sufficient so that the air temperature can be adjusted with the required accuracy, high speed and low energy consumption.
In cases where the object has a large ceiling height, a lot of equipment or people, it is worth using an extended formula that takes into account all heat inflows. This ensures that the purchased “split” can cope well with the cooling task and will not fail due to wear and tear.
Based on the calculated performance, it is very easy to select the desired air conditioner model, since the manufacturers of this equipment indicate this parameter directly in the equipment labeling. When choosing a unit, you should make sure that its power fully satisfies the needs of the facility.
BTU value and labeling explanation
BTU/BTU is a British Thermal Unit for measuring heat energy. The value determines the amount of heat expended to heat one pound of water by 1° Fahrenheit.
It is this unit that expresses the refrigeration capacity of climate control equipment and is often present in product labeling.
Ratio between Watts and BTU/h:
- 1 BTU/h ≈ 0.2931 W , for ease of calculation, use 0.3 W;
- 1 kW ≈ 3412 BTU/h.
Air conditioning is an American invention that uses Western systems of measurement. For practicality and clarity of display, it was decided to standardize the cooling capacity and express it in round numbers, for example: 7000 BTU/h, 9000 BTU/h, etc.
Split models have corresponding names: “seven”, “nine”, etc. Thus, the LG GO7ANT air conditioner belongs to low-power units - “sevens”. Its performance is 2.1 kW
Understanding the digital designation in the equipment labeling, you can approximately determine for which room the air conditioner is designed.
Special design conditions
There are a number of factors that additionally influence the microclimate and, accordingly, the required cooling power. In order to subsequently avoid getting into a situation where the installed unit works without turning off around the clock, you need to take into account the following conditions:
- The room is located on the top floor of the building.
- Non-standard windows with a large glazing area or part of a translucent roof.
- There are always a large number of people in the room (office).
- Frequent ventilation or high infiltration of outside air into the building.
- A large number of household or office equipment.
In this case, it is recommended to increase the calculated cooling capacity of the air conditioner by applying a coefficient from 1.2 to 1.5.
Electricity consumption and energy efficiency assessment
As noted above, in addition to cooling and heating capacity, the power consumption is indicated in the split system passport. The value determines the energy consumption. We recommend that you familiarize yourself with the rules for calculating electricity consumption and ways to save it.
However, the coefficient and energy efficiency class are more informative.
EER and COP are indicators of the energy efficiency of the air conditioner in cooling and heating modes, respectively. The value is calculated by dividing the cooling or heating capacity by the power consumption
Essentially, the EER and COP show the amount of cold/heat produced when 1 kW of electrical power is consumed. The higher their numerical value, the higher the efficiency of the climate system and the lower the level of energy consumption.
That is, at EER=2.5 , the air conditioner at maximum cooling power consumes Q/2.5 . By multiplying the result by the operating period, you can find out the daily energy consumption.
Based on EER, splits are classified into energy efficiency classes. Category “A” includes the most economical units, group “G” represents air conditioners with the highest electricity consumption.
There are three additional premium classes that characterize energy-saving climate control equipment. A worthy representative of group A+++ - split complex MSZ-LN60VGR from Mitsubishi Electric
Energy Saving
The user asks a logical question about how to save energy: what can I do to pay less?
Everything will depend on various factors. On average, split systems with a power of two to three and a half kilowatts consume from half to one and a half kilowatts per hour.
Before installing an air conditioner, it is important to analyze the following parameters:
- what is the power consumption of the device, is the outlet designed for these indicators;
- what load will the electrical wiring withstand;
- parameters of meter safety plugs.
To avoid wasting money, you should choose the right device. There is a significant difference in the energy consumption of household, semi-industrial and industrial air conditioners. In addition to connection difficulties, industrial and semi-industrial air conditioners will consume several hundred kilowatts per month. While ordinary household air conditioners can cope with their responsibilities.
Methods for self-calculation of power
There are several ways to calculate the performance of splits. The simplest, but not reliable enough, is calculation by area. A more accurate method is the thermotechnical method, which takes into account the design features of the room and the total heat inflows.
Option #1 - choosing an air conditioner based on service area
You can determine the approximate power of the unit without mathematical calculations, using a practical assessment criterion - the area of the room.
The average cooling capacity of a split is 1 kW per 10 sq.m of service room. This standard is relevant for residential premises with a ceiling height of 2.5-3 m.
Thus, when calculating the power of the air conditioner, the service area must be divided by 10. For example, for a room of 22 sq.m., a model with a capacity of 2.2 kW is suitable. The resulting value corresponds to “seven” according to the BTU system.
The calculated power is increased by 20% in the following cases:
- location of the room on the sunny side of the house;
- the presence of panoramic windows;
- placement of a large number of office equipment and electrical appliances.
A cooling capacity reserve of 20% must be provided if many people constantly live or work in the room.
When choosing climate control equipment for spacious rooms of 60 square meters or more, industrial or commercial buildings, the direct dependence of cooling power on area no longer works
Due to the impressive dimensions, possible angularity and curvature, air flows are distributed unevenly. In this case, it is advisable to install multi-system split complexes.
Option #2 - use thermal calculation
Thermal engineering calculations taking into account the design and operational features of the building are considered more accurate. Next, consider the typical formula used for calculations.
Determining factors:
- room dimensions: area and exact height;
- number of people;
- purpose of the premises: gym, active work, recreation, etc.;
- heat sources, household/office equipment;
- the presence of insulated facades and roofs.
The main emphasis in assessing the power of an air conditioner is on the total heat gain.
The proposed thermal calculation method is applicable for office premises, separate rooms of private houses and apartments in permanent buildings. Area restrictions – 70 sq.m.
The greater the heat flow, the higher the cooling capacity of the split should be.
Typical formula:
Q=Q1+Q2+Q3,
Where: Q – final cooling power; Q1 – heat input from the structural elements of the room; Q2 – heat inflow from people; Q3 – heat generation from equipment.
Step #1 - Calculate Q1
The heat excess of a room is determined as follows:
Q1=V*g,
where: V is the volume of the serviced premises, calculated by multiplying the square footage and the height of the ceilings; g – calculated heat transfer coefficient.
The value of the g indicator depends on the orientation of the windows and the level of natural light in the room:
- 40 – sunny side, intense insolation is typical for southern, southwestern, southeastern orientation;
- 35 – moderate illumination on the eastern, northwestern, western side;
- 30 – the predominance of shading during the day is observed in rooms whose windows face north or northeast.
As you can see, the sunny side will have the highest heat transfer coefficient.
Step #2 - Define Q2
The heat production of people depends on their age and mobility.
The following heat release indicators are typical for an adult:
- rest state – 80 W;
- light work, moderate loads – 125 W;
- vigorous activity – 170 W.
When performing hard work and intense sports exercises, heat production reaches 250 W.
For a more reliable assessment, the heat inflow of children under 12 years of age is taken with a coefficient of 0.5, for children under 17 years of age - 0.75
However, this approach is justified when choosing a split system for children's institutions. The air conditioner is purchased for the future, so for a family, the heat transfer of children should be equated to “adult” indicators.
For an apartment cooling system, parameter Q2 is determined by the product of the number of residents and the average heat release value - about 110 W.
Step #3 - Calculate Q3
Excess heat from electrical equipment is calculated using the formula:
Q3=N*m*i,
Where:
- N – power of a unit of equipment;
- m is the number of household appliances;
- i – coefficient of conversion of electricity into heat.
In the calculations, it is necessary to take into account the frequency of use of equipment during the day, taking round-the-clock work as a unit.
Energy transfer coefficients for different equipment are given in the table. Additional heat gain values: TV - 0.2 kW, copy machine, computer - 0.3 kW, other lighting/household appliances - 30% of rated power consumption
By summing up the total amount of heat inflow, you can determine the power of the air conditioner. It is permissible to exceed the cooling capacity of the unit by 15% of the calculated value or reduce it by a maximum of 5%.
Operations based on room squares
This technique is especially held in high esteem by sales representatives. It has some analogies with calculations of heating equipment based on the specific heat parameter.
The essence of the technique: if the ceiling height in the room does not reach 3 m, then 100 W of cooling energy should be generated per square meter.
So for a room of 20 sq.m. You need a device with MO 2 kW.
If the ceiling height is more than 3 m, then the specific MO is calculated according to the following table:
In addition to the cooling parameter expended for the entire area of the room, it is also necessary to add the power to compensate for the heat flows from the occupants of the room and the household appliances located in it.
Here the calculation is carried out as follows: 300 W of heat comes from one resident, and 300 W from household units.
It turns out that if in a room of 20 sq.m. 1 resident stays permanently and he works with a computer, then another 600 W is added to the calculated 2 kW. Result = 2.6 kW.
In practice, with reference to regulatory documents, if a person is at rest, then 100 W of heat emanates from him. With minor movements - 130 W. For physical exercise – 200 W. It turns out that in these operations there is some overestimation of thermal parameters from people.
Step-by-step calculations of equipment power
First, let's calculate the required equipment power for a specific room with an area of 24 sq.m. And then we’ll look at the situations in which adjustments are used.
Power calculation for a specific room
Calculation data for determining split performance:
- room area – 24 sq.m, ceiling height – 2.8 cm;
- a room with a standard window facing south;
- number of residents – 2 people;
- equipment: computer, TV, refrigerator (0.3 kW), incandescent lamp (0.1 kW).
Simultaneous operation of the listed electrical appliances is possible.
Step 1 - determination of heat gains from windows, floors, walls and ceilings.
Q1=24*2.7*40=2592 W
The resulting value can be safely rounded to 2.6 kW. The calculation uses the coefficient g=40, since the room is well lit.
Step 2 - calculating heat gain from people. Let us take the heat production of an adult to be 110 W.
Q2=2*110=220 W or 0.22 kW
Step 3 - heat inflows from equipment are calculated for each type of equipment, taking into account the electricity conversion coefficient:
- computer – 0.3 kW;
- TV – 0.2 kW;
- electric lamp – 90 W (100 W*0.9);
- refrigerator – 100 W (300 W*0.3).
Q3=300+200+90+100=600 W or 0.6 kW
Step 4 - calculating the cooling capacity of the air conditioner.
Q=2.6+0.22+0.6=3.42 kW
For comparison, it is possible to make an approximate selection of an air conditioner solely by area without taking into account the number of residents and heat inflows. For an area of 24 sq.m., the estimated cooling capacity should be 2.4 kW, taking into account good lighting - 2.4 * 1.2 = 2.88 kW.
Based on the initial parameters, it is recommended to select an air conditioner with a power in the range of 3.3-3.9 kW. “Twelve” splits correspond to this value - their productivity is 3.5-3.5 kW
In this situation, the calculation results using the two methods differ. The priority is “thermal” calculation. The cooling power of the air conditioner must extinguish all possible heat gains.
Taking into account special operating conditions
The method described above in most cases does not need adjustment and gives an accurate result.
Deserves special attention:
- the need for regular ventilation;
- location of the room on the top floor;
- hot climate of the region;
- large glazing area.
Let's consider all these cases in more detail.
Fresh air supply
The documentation for split systems usually stipulates that operating the device with open windows is undesirable.
The influx of external air flow entering the room creates an unforeseen thermal load for the climate control equipment. The volume of fresh air is not standardized, and it is difficult to predict in advance the optimal power reserve
To maintain a normal microclimate without constantly moving the sash, you can leave the window on micro-ventilation or install a supply valve. Both options do not provoke drafts when the front door is closed.
When operating the split in conditions of gentle ventilation, the following should be taken into account:
- In order to compensate for the additional heat load, the Q1 indicator when calculating the power of the air conditioner must be increased by 20%.
- Electricity consumption during split operation will increase to 15%.
In hot weather, do not rely on power reserves. If there is significant heat inflow, the air conditioner will not provide the set temperature.
Top floor of living space
In attics and apartments on the top floors without an attic, the heat of the heated roof is transferred into the room. The situation is aggravated with dark-colored flat roofs.
To compensate for heat inflows from the roof, a reserve of cooling capacity is provided - when determining the power of the air conditioner, the value of Q1 is multiplied by a factor of 1.15-1.2
Hot climate of the region
One of the rules for safe use of an air conditioner is to maintain the permissible temperature difference between the outside and inside the building. The limit value is 10 °C. For example, if it is 35 °C outside the window, then the recommended room temperature is not lower than 25 °C.
The rated power of split complexes is indicated taking into account operation in conditions up to 31-33 °C. When the indicator increases to 40 °C or more, the cooling capacity of the unit is not enough to maintain the coveted 18-20 °C.
Taking into account the climate's predisposition to hot summers and one's own preferences for the level of coolness, when calculating, the Q1 indicator should be additionally increased by 20-30%.
Large windows in the room
The standard formula assumes that there is one window in the room of standard dimensions - up to 2 sq.m. Several window openings or a panoramic design increases unaccounted heat gain.
Due to the increased impact of the light flux entering through the windows, in the warm season, climate control equipment spends half the power to compensate for solar heat
The cooling power is adjusted based on each square meter of additional glazing:
- + 200-300 W – for the sunny side;
- + 100-200 W – moderate insolation of the room;
- + 50-100 W – predominance of shading.
Light-colored blinds or curtains will help reduce solar heat gain.
Rating
Listed below are popular models of split systems that have already proven themselves well among buyers.
Ballu BSVP-07HN1
Designed for 21 square meters, it has proven itself among buyers. It is distinguished by its low price, low electricity consumption (class A), and also fairly compact dimensions. A split can work not only for cooling, but also to heat an apartment in the off-season, that is, when the outside air temperature is down to -7. Useful modes include dehumidification, self-diagnosis, ventilation, night, and timer. With a low price tag, the manufacturer equipped the device with saving settings (they will not be lost when the power is turned off), the ability to direct the flow, a motion sensor, a system that prevents the formation of ice, and a deodorizing filter. Power – 2.2 kW. Price – from 13,500 rubles. (2 store).
Daikin FTXB20C / RXB20C
An inverter model with 21 square meters from a brand that is considered one of the best in the segment. The device is not budget, but this is explained by the name and inverter motor. The system is quite compact and has a beautiful appearance. The noise level is very low - 21 dB. Functions include dehumidification, self-diagnosis, anti-ice system, timer, heating, saving settings in case of failure, flow control. Unlike many competitors, it can be turned on for heating at -15 degrees. As a rule, the lower threshold of most devices is 0. Another interesting point is that there are very few inverter sevens on the market. As a rule, they are produced starting from a capacity of 27 square meters. Thus, this model has practically no competitors. Price – from 39,200 rubles. (2nd store - Russia, Belarus, UA, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, 3rd store).
Toshiba RAS-09U2KHS-EE / RAS-09U2AHS-EE
By modern standards, an inexpensive 27 square model from a popular and high-quality brand from Japan. Electricity consumption – 2.6 kW, low noise level – 26 dB. Among the modes are self-diagnosis, prevention of ice formation, night mode, and the ability to select the air direction. Can be used for heating down to -7 degrees. The system does not have a display, but all settings and parameters are displayed on the remote control. Price – from 27,000 rubles. (2 stores - Russia, Belarus, UA, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan).
Panasonic CS/CU-BE25TKE
Inverter air conditioner for 27 square meters and consumption of 2.5 kW. Received all modern functions - timer, adjustment of air flow direction, anti-ice systems, restart with specified parameters after a failure, self-diagnosis. Optionally, you can buy a module for control via Wi-Fi. That is, using this control unit you can turn on cooling or heating remotely from your smartphone. The system operates for heating at -15 degrees. Noise – 20 dB. The purchase price is from 33.5 thousand rubles. (2 stores - Russia, Belarus, UA, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan).
LG P12SP
Despite the inverter motor, this model has a very affordable price tag, which may be a reason to buy it. Designed for an area of up to 36 square meters. Noise level - 19 dB. Electricity consumption – 3.6 kW. The system operates for heating down to -5 degrees. A plus is the double cleaning filter. It is possible to direct the air flow and set a timer. It is equipped with a motion sensor, that is, it will start working if a person enters the room. Price – from 35,900 rubles. (2 stores - Russia, Belarus, UA, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan).
Additional criteria for choosing an air conditioner
In addition to the power characteristics of the system and energy efficiency class, before purchasing, you should decide on the following parameters:
- type of air conditioner;
- operating principle of the unit;
- functionality;
- by the manufacturer.
Next, we will consider each of these criteria in more detail.
Criterion #1 - type of air conditioner
For domestic use, monoblocks and split systems are used. The first category includes window models and compact portable devices. Window-mounted air conditioners have lost their former popularity.
They are being replaced by more modern modifications that do not have the disadvantages of their predecessors: noisy operation, reduced illumination due to window clutter, limited choice of location
The undeniable advantages of window “coolers”: low cost and maintainability. This unit is more suitable for seasonal country use than for an apartment.
Mobile monoblocks are equipped with a flexible air duct that removes heat to the street. A portable air conditioner is the optimal solution for a rented space. We have given the rating of the best mobile models in this article.
Advantages of a mobile monoblock: possibility of transportation, ease of installation. Disadvantages: large dimensions, high noise level, “binding” to the output channel
Split systems confidently occupy a leading position among household air conditioning systems.
Based on the form of execution, there are two categories of splits:
- Two-block design . A pair of modules are connected by a closed freon line. The complex is easy to operate and almost silent. Various design options for the indoor unit are available; the housing does not take up useful space in the room.
- Multi-system . The external module ensures the operation of two to five internal units.
The use of a multi-complex allows you to set different air conditioning parameters in individual rooms.
The disadvantage of the climate system is the dependence of indoor units on a single outdoor unit. If it breaks down, all rooms will be left without cooling.
Criterion #2 - operating principle
There are conventional and inverter models.
The operating procedure of a traditional split system:
- When the temperature rises, the air conditioner turns on.
- After cooling to the designated limit, the unit turns off.
- The on/off duty cycle is repeated continuously.
But an inverter air conditioner operates more “smoothly”. After startup, the room is cooled, but the device continues to operate at reduced power, maintaining the desired temperature.
The inverter version of the split is 30-40% more economical than a conventional air conditioner. The energy efficiency EER value of some models reaches values of up to 4-5.15
Due to the absence of “sharp” cyclical operation, inverter air conditioners are low noise and durable.
You also don’t know what is better to choose - an inverter or a regular air conditioner? In this case, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with their main differences, as well as the pros and cons of each option.
Criterion #3 - features and brand
Manufacturers, in an effort to win the favor of customers, equip split systems with additional options.
It’s good if the air conditioner has the following functions:
- fan distribution of air flow;
- automatic restoration of device settings;
- remote control;
- built-in timer.
Another popular air conditioner function among users is the flow of fresh air. Many manufacturers offer such models.
Air conditioners of popular brands are represented by a wide range of models in different price categories - from budget economy class to split systems in the premium segment
The equipment manufacturer plays a significant role in the choice - the better the brand reputation, the higher the quality indicators and reliability of the equipment.
The ranking of leading manufacturers is dominated by foreign companies: Daikin, LG, Sharp, Hitachi, Panasonic and General Climat. We reviewed the best air conditioner models in the following article.
Varieties of design
Air conditioner indoor unit
According to their design, there are two types of air conditioners - monoblock and consisting of two blocks. The two-block version is also called a split system.
Monoblock devices
A monoblock air conditioner looks like a single body, inside which all the components necessary for the operation of the equipment are located. These include a compressor, a filter for cleaning the air coming from outside, a fan, an evaporator and a condenser. The device controls are located on the monoblock body.
Floor standing monoblock
Monoblocks differ:
- window (built directly into the window opening)
- floor-mounted (placed near the window on the floor, connected with corrugated pipes to channels embedded in the window, or pipes are simply led out into the street through an open sash)
Floor-standing models are also called mobile - they can be easily disconnected from the channels and installed in a new location. Condensation from such monoblocks must be removed manually.
Monoblock air conditioners are inexpensive and easy to install - you can install the equipment yourself. At the same time, the demand for such equipment is steadily falling - it has low productivity and is noticeably noisy during operation.
Two-unit devices
Air conditioner external unit
The split system consists of two units: the external one (with a condenser and compressor) is mounted outside the building on the wall, and the internal one (with the evaporator) is placed indoors. The blocks are connected by a line designed for refrigerant circulation.
Air conditioners of this type include a multi-split system, consisting of an external unit of increased power and several internal ones, which can be installed in different rooms.
- Wall-mounted. The indoor unit is mounted on the wall, on the outside of which the outer part of the two-block air conditioner is mounted
- Floor-ceiling. If the glazing occupies a significant area of the wall, an internal block is used, which can be mounted near the wall on the ceiling or installed on the floor
- Cassette. The unit is designed for hidden installation in a suspended ceiling. Such models are more suitable for large areas in public buildings
- Duct. Indoor units are also mounted in a suspended ceiling. Such systems are usually installed at industrial, commercial and sports facilities with large areas
The advantages of split systems include wide functionality and economical energy consumption. Thanks to the low noise level, acoustic comfort in the apartment will be ensured even at night, when extraneous sounds are especially audible and can interfere with sleep. It is worth noting the rich set of equipment functions and the convenience of remote control.
The disadvantage of such climate control equipment is the high price, as well as the need to contact specialists for installation and maintenance of the air conditioning system. Before purchasing a split system, you need to make sure that local authorities do not prohibit the installation of external air conditioner units on the facade of the house.
Veranda attached to the house - expanding the living space: projects, tips on how to create it yourself (200 original photo ideas)
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Practical recommendations from a specialist will help you determine the power characteristics of the air conditioner:
Understanding the principles of calculating the performance of air conditioning systems, you will be able to independently determine the range of permissible power.
It is better to entrust the final calculation of suitable parameters to professionals - an experienced specialist will take into account all operational nuances and select the optimal air conditioner model.
Do you need an air conditioner, but you don’t want to make a mistake with the power and choose insufficiently efficient equipment for your apartment/house? Maybe you still have questions about the calculations or want to clarify certain nuances? Ask for advice in the comments - our experts and competent site visitors will try to clarify all the points.