Types and features of a heating point
The heating station regulates the supply of coolant, its temperature, and is connected to the heating system.
The heating station includes equipment that allows connecting power plants to heating networks, liquid supply systems, measurement and control devices. Usually the heating unit is located in a separate room or building.
The purpose of any type of TP is to regulate the coolant supply. All elements of the system - mains, pipelines serving apartments, radiators - are designed to work with a coolant of a certain temperature, purity, and gas content. Violation of these indicators leads to clogging and system failure.
TP controls the indicators of incoming and outgoing water. The consumer receives liquid at the optimal temperature under the pressure for which the heating, ventilation, and plumbing systems are designed. If any indicators change to an unacceptable value, the control system turns off the water supply.
Here, the coolant is transformed, for example, steam condensation and transformation into superheated water.
TP can serve a different number of consumers and include different heat consumption systems. The methods of installation and installation of equipment also differ.
Central heating point
In order for houses to warm up well, the installation must be in every building.
The peculiarity of the heating unit is a large number of connected consumers. The central heating station serves several houses, an enterprise or even an entire neighborhood. Usually it is placed in a separate building, but installation in the basement is allowed if its size allows it.
This option is not very convenient for the average consumer - an apartment dweller. The central heating station sets the same coolant temperature, not taking into account that the length of the pipelines is not the same. Nearby buildings, as a rule, overheat, distant ones receive very cool water. During preventative and repair work, an entire neighborhood is left without heat.
Individual heating point
ITP has smaller dimensions and can be located in a basement or a separate building.
ITP is an individual heating point. It performs the same functions as the central heating station, but to a lesser extent. It supplies coolant to 1 building or even one part of it. Since its dimensions are much smaller, the heating unit is placed in the basement or in another technical room.
The advantage of an individual heating point is the supply of water to consumers at the same temperature. The length of the pipeline, even in a high-rise building, is not so long as to affect the temperature. This option is more economical, since less heating is required to maintain optimal conditions in apartments.
Modular heating substation
A block or modular heating unit is a finished factory product. The blocks are compact, assembled and work according to the same scheme. They can be placed in the smallest area. The units are installed very quickly: you only need to connect the external wires. Depending on the number of consumers, a modular point can be either individual or central.
Types of heat meters depending on the measurement method
Currently, the following types of heat meters are widely used:
- Mechanical operating principle or tachometer. The most common modification of heat metering devices. There are vane or rotor (turbine) ones. Quite easy to use and does not require electrical costs. They work thanks to an impeller or rotor and reciprocating fluid movement;
Important! Mechanical heat meters are demanding of the coolant; the water must be clean. The device is equipped with an additional filter element, since its contamination directly affects the accuracy of the readings.
- Electromagnetic. The operating principle is based on interaction with electric waves of the coolant. Of all the presented categories, these metering devices are the most accurate. The disadvantage of the device is its use in horizontal thermal systems;
- Ultrasonic. Thermal energy is measured by measuring the length of the ultrasound signal passing through the coolant. The meters are installed in pairs, opposite each other. They also differ from each other according to: frequency, time, correlation and Doppler principles of operation. Used in open and closed thermal systems;
- Vortex type. They create a vortex flow in the liquid, due to their location on the path of coolant movement, with subsequent recording of the formation and disappearance of magnetic field vortices. It is used in vertical and horizontal heating systems.
Important! Vortex heat meters require straight pipelines, since the quality of measurements directly depends on the composition of the moving hot liquid, its speed and the presence of air masses in it.
Advantages and disadvantages
Each type of TP has its own advantages and disadvantages. Advantages of TsTP:
- coolant parameters - temperature, pressure, are maintained and controlled automatically;
- The point serves a large number of consumers.
This solution has many more disadvantages:
- Each consumer receives a strictly dosed amount of heat. However, these shares are equal only at the central heating point level. Due to different pipeline lengths, building occupants receive water at different temperatures.
- The longer the pipeline, the greater the heat loss. Because of this, it is necessary to increase the temperature at the central heating station, which leads to an increase in heating and hot water costs.
- During renovations, a large number of residents are left without heat.
- Hot water circulation is uneven. In houses located far from the central heating point, cold water has to be drained for a long time before receiving heated water. The meter takes this entire volume into account as hot water consumption.
ITP in the basement of a house saves up to 30% of hot water costs
ITP is much more profitable:
- Less heat loss during coolant transfer. Installing ITP in a building saves from 15 to 30% of costs.
- All apartments receive the same amount of heat based on area.
- The water comes out of the tap really hot and immediately.
- Since the heating unit operates without high load, the likelihood of breakdowns is lower. Installation and repair of equipment takes less time.
- When a transformer substation fails, fewer residents suffer.
The disadvantages of the individual complex are associated only with its limited capabilities. TP serves 1 house, sometimes even part of it. To modify an entire neighborhood will require a lot of money.
The advantages and disadvantages of MTP are determined by its purpose. However, such a system has its advantages:
- The finished module takes up minimal space. Even if it is a central heating station, it can be installed in the basement.
- Installation is extremely simple - you just need to connect it to the heating main and electrical network.
The higher the degree of automation of a heating unit, the lower the costs for its maintenance and service.
Permission to operate
When a heating unit is admitted for operation, the compliance of the serial number of the metering device, which is indicated in its passport, and the measurement range of the established parameters of the heat meter with the range of measured readings, as well as the presence of seals and the quality of installation, are checked.
Operation of the heating unit is prohibited in the following situations:
- The presence of tie-ins in pipelines that are not provided for in the design documentation.
- The operation of the meter is outside the accuracy standards.
- Presence of mechanical damage to the device and its elements.
- Broken seals on the device.
- Unauthorized interference with the operation of a heating unit.
What does your nose shape say about your personality? Many experts believe that you can tell a lot about a person's personality by looking at their nose.
Therefore, when you first meet, pay attention to the stranger’s nose
Why do you need a tiny pocket on jeans? Everyone knows that there is a tiny pocket on jeans, but few have thought about why it might be needed. Interestingly, it was originally a place for storage.
Contrary to all stereotypes: a girl with a rare genetic disorder conquers the fashion world. This girl's name is Melanie Gaydos, and she burst into the fashion world quickly, shocking, inspiring and destroying stupid stereotypes.
10 mysterious photographs that will shock Long before the advent of the Internet and the masters of Photoshop, the vast majority of photos taken were genuine. Sometimes the pictures captured were truly incredible.
15 Cancer Symptoms Women Most Often Ignore Many signs of cancer are similar to symptoms of other diseases or conditions, which is why they are often ignored.
Pay attention to your body. If you notice
How to look younger: the best haircuts for those over 30, 40, 50, 60 Girls in their 20s don’t worry about the shape and length of their hair. It seems that youth is created for experiments with appearance and daring curls. However, already last.
Principle of operation
Scheme of operation of IHP in a private or apartment building
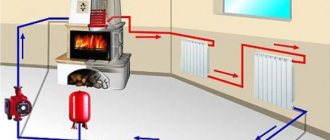
The principle of operation of a modern heating unit is simple. The liquid from the main gives off its heat through a heat exchanger to the hot water supply and heating system. The coolant is then transferred through a return pipeline to the boiler room or power plant, where it is heated again. The heated liquid from the TP is distributed among users.
The heating point supplies users with heating media and hot water. The operating schemes of the systems are different.
Tap water enters the TP. Part of the cold water is supplied to consumers, the other part is heated in the 1st stage heater. The heated liquid enters the circulation circuit. The pump ensures constant movement of hot water along the circuit from the heating unit to the users and back. The inhabitants of the house draw hot water as needed.
Since the liquid gradually cools, it is periodically reheated in the 2nd stage heater. Since the volume of water in the circuit decreases, it is necessary to constantly take in cold water, heat it up and replenish its deficiency.
The operating diagram of a thermal heating unit in an apartment building is somewhat different. It is simpler: water, having given off heat to pipes and radiators, returns in almost the same volume as it was supplied. Leaks are possible, but small. The losses are compensated by a make-up system operating on the basis of the primary heating network.
Liquid fuel boilers
The cost of equipment and installation of liquid fuel boilers is approximately the same as that of gas heating appliances. The same applies to the level of efficiency, with lower performance of liquid fuel heaters. However, the amount of dirt generated as a result of their operation is the largest of all boilers. Every visit to the boiler room is fraught with dirty hands and the smell of diesel fuel. Not to mention the annual cleaning of the equipment, which is a very messy procedure. In addition, we have to take into account the high cost of liquid fuel, since prices have risen even for its cheapest option - used oil. Typically, diesel boilers are used as backup heat sources, or when all other coolants are unavailable.
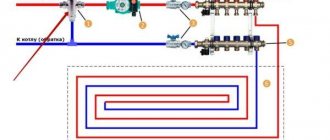
Key components of a heating substation
Components of an ITP device
The thermal complex includes several main elements:
- A heat exchanger is an analogue of a boiler room’s thermal boiler. Here, the heat from the liquid in the main heating network is transferred to the coolant TP. This is an element of a modern complex.
- Pumps – circulation, make-up, mixing, booster.
- Dirt filters – mounted at the inlet and outlet of the pipeline.
- Pressure and temperature regulators.
- Shut-off valves - act in case of leaks, emergency changes in parameters.
- Heat metering unit.
- Distribution comb – distributes coolant to consumers.
Larger TPs include other equipment.
Purpose
A thermal energy metering unit is being organized for the following purposes:
- Controlling the rational use of coolant and thermal energy.
- Control of thermal and hydraulic modes of heat consumption and heat supply systems.
- Documentation of coolant parameters: pressure, temperature and volume (mass).
- Carrying out mutual financial settlements between the consumer and the organization engaged in the supply of thermal energy.
Selection of systems
ITP with an elevator is cheaper, but more expensive to operate.
Water is prepared for transfer to users using a control unit. Based on the type of this element, there are several operating schemes for the heating unit.
Elevator – installed on an old-style transformer substation. The unit mixes liquid from the main network and cooled water from the return pipeline to obtain a coolant with a temperature suitable for secondary networks. The temperature is maintained at a certain level regardless of the air temperature outside or indoors. When overheating, the only way to remove excess heat is to open a window. If there is underheating, you have to connect electric heaters.
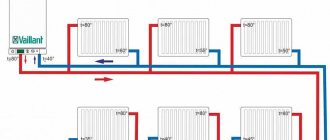
The thermal unit circuit with a controller is much more efficient. The heat exchanger and control equipment allows you to regulate the water temperature in the heating circuit based on real air readings. There are 2 systems of this kind:
- Dependent circuit - increases or decreases the temperature of the supplied liquid by mixing the cooled coolant from the return pipeline. The controller monitors temperature changes and automatically turns on pumps and valves. The installation of pressure regulators is mandatory, since this indicator is different in primary and secondary networks.
- Independent - the water used to heat the house circulates in a closed circuit, the heat from the coolant from the main is transferred only through a heat exchanger. Pressure regulators are not needed here; temperature adjustment is performed more accurately and quickly. The cost of a TP with an independent circuit is higher, but it is more economical to use: the water is not polluted, does not overheat, and does not lead to corrosion of pipes and radiators.
Hot water supply is also implemented according to 2 schemes:
- Single-stage - water from the water supply is supplied to the heater. It is heated by the network coolant that came from the source. The cooled network supply is transferred to the source, and the heated water supply is supplied to the consumer.
- Two-stage - water is heated in 2 stages. First, due to the coolant from the return pipeline - up to +5–+30 C, then it is heated up through the use of a supply heat pipe - up to +60 C. In this case, waste energy from the return pipeline is used - it is cheaper.
The more effectively a heating system reduces the cost of heat supply services, the more expensive its installation.
Common connection options
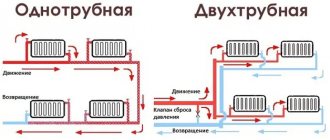
If you decide to install a single-pipe system, you will have to choose between two types:
- simple circuit without regulation;
- "Leningradka" with the ability to turn off individual radiators.
In terms of control method, the first option is clearly inferior to the second; its only advantage is its budget cost.
Installation of a simple single-pipe system of horizontal or vertical type is simple and reliable, but temperature control in the network is impossible (+)
Installing the Leningradka will cost a little more, since in addition to the pipes you need to purchase a set of shut-off valves. Using bypasses and valves, you can reduce/increase the amount of coolant supplied to the radiator.
Diagram of the Leningradka device: using shut-off valves, you can temporarily turn off individual unnecessary radiators without changing the functional qualities of the entire system as a whole (+)
"Leningradka" is recognized by professional heating engineers as the best option for a single-pipe system for a 2-story residential building.
Complete set and installation of equipment
- circulation pump;
- gas or electric boiler (power depends on the size of the house, characteristics of the coolant, etc.);
- expansion tank;
- pipes 20 mm and 25 mm;
- adapters, gaskets, plugs;
- set of radiators;
- Mayevsky cranes.
Along with steel pipes, polymer or metal-plastic pipes can be used, with the latter being preferred.
In heating circuits with closed expansion tanks, air is bled using automatic bleeders equipped with shut-off valves and floats, or Mayevsky valves supplying each radiator
First, they find a suitable place for the boiler and install it, then assemble the pipeline leading to the radiators. Tees are fixed in places of radiator branches and bypasses. The pump is installed on the return line, next to the inlet to the boiler, and connected to the power supply.
The installation location of an open expansion tank is the highest point of the system; a closed one can be mounted in any convenient place, for example, in a boiler room. Radiators are suspended from the walls using special fasteners and equipped with plugs and taps.
Balancing the system
Balancing valves are adjusted after installation of the equipment and startup of the coolant.
Calculations of any hydraulic circuit are very complex. During installation, features and deviations appear that cannot be taken into account during calculations: blockages, scale, narrowing. In practice, hydraulics are linked at the design stage, and then adjusted using balancing valves. This device is an adjustable washer. With its help, the valve capacity, that is, the hydraulic resistance, is changed. In this way, the work of all circuits is connected.
Balancing valves are installed on all components and systems of TP: heat exchanger, pumps, water supply, ventilation, heating circuits. Additional devices are required to coordinate the operation of the circuits and compensate for the operation of the pumps.
How to install correctly
Metal radiators, except cast iron, are quite lightweight. When fastening them, there are no problems with the load-bearing capacity of walls made of aerated concrete or brick. But in some cases, for example, frame houses or rooms with a large glass area, the equipment can be fixed to the floor.
To select fasteners, the battery load is taken into account. Cast iron can be hung on strong hooks or mounted with floor brackets, lightweight steel and aluminum can be hung on plate brackets or overhead corners. Installation diagram:
- for 8 sections - 2 on top and 1 on bottom;
- for every additional 5-6 sections - 1 more on top and 1 on the bottom.
Steel panel radiator diagram
With this arrangement of the fasteners, the heating device will be firmly and securely fixed to the wall. It is recommended to place the brackets closer to the outer sections.
Wall mount
Installation begins by marking the surface. First mark the points on the wall for attaching the lower brackets and screw them loose.
Then the center distance is set upward, the points are marked and the upper brackets are mounted.
The radiator is hung on the wall and checked for horizontalness. If necessary, make adjustments. After this, the brackets are finally fixed.
Installation efficiency
An individual heating unit in an apartment building reduces heating and hot water supply costs:
- The heat meter itself does not affect its consumption, but it takes it into account correctly. Heating companies often increase the cost of services without supplying sufficient heat energy. With accurate accounting, it turns out that before the installation of the TP, residents overpaid.
- Automation reduces maintenance costs. More precise temperature control also reduces costs.
- A closed heating system is more profitable: there is no need to constantly purify water, repair pipes and radiators. There is less heat loss in a closed system.
- The ITP works according to a schedule: it lowers the temperature at night, stops pumps, and increases it in the morning.
A heating station saves from 1.5 to 8 million rubles over 5 years.
Device
A standard UTE project requires a certain list of mandatory elements and includes the following mechanisms:
- Shut-off units. The resource supply is cut off.
- Mud trap or filters. They prevent the penetration of suspended matter and protect other devices and the overall system from damage and clogging.
- Thermal converter, which is connected to the meter. The device is most often welded into the inlet pipe.
- Thermal energy metering device (computer). Modern models solve a whole range of problems, from measurement to calculation of various parameters.
- Pressure meter. Installation is required if a multi-apartment building consumes more than 0.5 Gcal/hour of heat.
- A simple pressure gauge and a liquid thermometer are installed separately. These are auxiliary elements for service personnel.
- Flow converter, after which the valve is placed.
The system is installed on the incoming pipeline. On the return section there will be a mud trap and a temperature sensor.
In addition to the units traditional for the distribution system, the centralized heat energy metering unit is equipped with a computing unit, as well as a printer and a telemetry module for data transmission
Areas of application
IHP for heating air in the ventilation system
TP are necessary for proper distribution of heat between consumers. These include:
- Hot water supply. Part of the heat, as hot water is supplied through pipes, is used to heat the bathroom and kitchen.
- Heating systems – maintain a comfortable temperature in residential and public spaces.
- Ventilation system – the air is heated before entering the building.
- Cold water supply does not apply to consumers, but to supply elements. Cold water serves as a regulator.
They install TP for heating, water supply, air conditioning in both old and new buildings.
Schemes of metering units
Several options for creating a system of heating points are popular. Hot water connection diagrams:
- Sequential two-stage. A classic solution in which there is a division into two sections. The first is the inlet pipe of the heating system, and the second is the return pipe. The convenience of the scheme is that there is no need for network water. There are a number of significant disadvantages, among which is the need to implement an automated control system to properly distribute heat.
- Parallel single stage. Standard option, characterized by simplicity. The main problem is the significant consumption of network water, which is used to create a water supply. Connection principle: hot water supply pipes are connected in parallel to the heating system.
- Mixed two-stage. A universal solution that allows you to quickly make the necessary settings. Unlike the previous version, there is a serial connection, and the implementation principle is almost identical to the first version.
Much depends on the characteristics of the apartment building and the functioning heating system.
Methods for connecting heating devices
Nowadays, the most common are single-pipe water systems with bottom vertical wiring. In this case, the radiator is connected using hoses, because they are easy to install and well guarantee uniform heating. Such a heating system requires clear calculations of the number of sections of radiators, taking into account the level of water cooling and, in addition, carefully adjusted heating devices, since water in single-pipe systems passes through them all sequentially.
The most successful heating concept, in my opinion, is the two-pipe heating system. The principle of its operation provides for the synchronous supply of hot and draining of cold water through different pipes. In addition, this concept makes it easier to calculate individual consumption.
Three way valve
If it is necessary to divide the coolant flow between two consumers, a three-way heating valve is used, which can operate in two modes:
- constant mode;
- variable hydraulic mode.
A three-way valve is installed in those places in the heating circuit where it may be necessary to divide or completely shut off the flow of water.
The tap material is steel, cast iron or brass. Inside the faucet there is a shut-off device, which can be ball, cylindrical or conical. The tap resembles a tee and, depending on the connection, a three-way valve on a heating system can work as a mixer. Mixing proportions can be varied within wide limits. The ball valve is mainly used for:
- adjusting the temperature of heated floors;
- adjusting battery temperature;
- distribution of coolant in two directions.
There are two types of three-way valves - shut-off and control valves. In principle, they are almost equivalent, but with three-way shut-off valves it is more difficult to regulate the temperature smoothly.