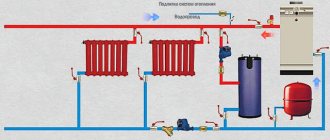
Without a high-quality heating system, no home will be as comfortable and cozy as possible. Especially if it is located in Russia - after all, our country does not have a mild climate. When planning the heating system in our own home and what the heating radiator connection system will be, we try to make sure that it heats the house or apartment well, is of high quality and works without failures.
Radiator
But many owners add one more requirement, which, it should be noted, is quite logical. The heating system must also be economical. That is, its acquisition, installation, further operation, and which connection of heating radiators is better should not cost the owner a pretty penny, as they say.
One of the most common ways to save on a heating system is to purchase and install it without the involvement of specialists.
And it should be noted that even those who have never dealt with heating systems before cope with this task perfectly. Of course, in order to do everything correctly, you need to familiarize yourself with some information, including heating radiator connection diagrams. Let's look at ways to connect heating radiators and how best to connect a heating radiator for you.
Factors affecting radiator efficiency
The main requirements for a heating system are, of course, its efficiency and economy. Therefore, its design must be approached thoughtfully so as not to miss all sorts of subtleties and features of a particular living space. If you do not have sufficient skills to create a competent project, it is better to entrust this work to specialists who have already proven themselves and have positive feedback from clients. You should not rely on the advice of friends who recommend certain methods of connecting radiators, since in each specific case the initial conditions will be different. Simply put, what suits one person may not necessarily suit another.
However, if you still want to install pipes to heating radiators yourself, pay attention to the following factors:
- the size of radiators and their thermal power;
- placement of heating appliances inside the house;
- connection diagram.
The modern consumer has a variety of heating appliance models to choose from - these include wall-mounted radiators made of various materials, and baseboard or floor convectors. The difference between them is not only in size and appearance, but also in the methods of liner, as well as the degree of heat transfer. All these factors will influence the choice of options for connecting heating radiators.
Depending on the size of the heated room, the presence or absence of an insulating layer on the external walls of the building, power, as well as the type of connection recommended by the radiator manufacturer, the number and dimensions of such devices will vary.
As a rule, radiators are placed under windows or in the walls between them if the windows are located at a great distance from each other, as well as in corners or along a blank wall of a room, in a bathroom, hallway, storage room, and often in the stairwells of apartment buildings.
To direct the thermal energy from the radiator into the room, it is advisable to attach a special reflective screen between the device and the wall. Such a screen can be made from any heat-reflecting foil material - for example, penofol, isospan or any other.
Before connecting the radiator to the heating system, pay attention to some features of its installation:
- within the same residential premises, the level of placement of all batteries must be the same;
- the fins on convectors must be directed vertically;
- the middle of the radiator must coincide with the center point of the window or can be shifted 2 cm to the right or left;
- the total length of the battery should be 75% of the width of the window opening;
- the distance from the window sill to the radiator must be at least 5 cm, and there must be at least a 6 cm gap between the device and the floor. It is best to leave 10-12 cm.
Please note that the correct choice of methods for connecting heating radiators in an apartment building will depend not only on the heat transfer of the battery, but also on the level of heat loss.
There are often cases when apartment owners assemble and connect a heating system, following the recommendations of friends. In this case, the result turns out to be much worse than expected. This means that errors were made during the installation process, the power of the devices is not enough to heat a particular room, or the scheme for connecting the heating pipes to the radiators is inappropriate for a given house.
Method for calculating and selecting a radiator model
When installing the battery, the following parameters must be observed:
- the battery must occupy at least three quarters of the window opening;
- its width should be 20...30 cm less than the width of the window sill;
- The dimensions of the battery must ensure good air circulation in the heated room (during installation, distances should be maintained - 30...50 mm from the wall, 100...150 mm from the window sill, 70...100 mm from the floor).
Before purchasing a steel radiator, you should first determine its power, which depends on the heat loss of a given room.
Sectional batteries must have 1 section per 1.5 square meters. m. area. Standard heating radiators have a power of 100…120 W per square meter. meter.
Differences between the main types of battery connections
All possible types of connection for heating radiators differ in the type of pipe routing. It may consist of one or two pipes. In turn, each of the options involves division into systems with vertical risers or horizontal mains. Quite often, horizontal wiring of the heating system in an apartment building is used, and it has proven itself well.
Based on which option for connecting the pipes to the radiators was chosen, the diagram of their connection will directly depend. In heating systems with one-pipe and two-pipe circuits, the bottom, side and diagonal method of connecting radiators is used. Whatever option you choose, the main thing is that enough heat gets into the room for high-quality heating.
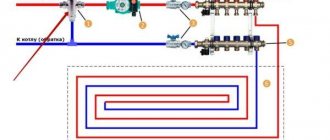
The described types of pipe routing are classified as a tee connection system. However, there is another type - this is a collector circuit, or radial wiring. When using it, the heating circuit is laid to each radiator separately. In this regard, collector types of connecting batteries have a higher cost, since such connections will require quite a lot of pipes. In addition, they will pass through the entire room. However, usually in such cases the heating circuit is laid in the floor and does not spoil the interior of the room.
Despite the fact that the described manifold connection diagram assumes the presence of a large number of pipes, it is increasingly used during the design of heating systems. In particular, this type of radiator connection is used to create a water-heated floor. It is used as an additional heat source, or as the main one - it all depends on the project.
Pipe routing methods
The effective connection of radiators in a private house and the comfortable operation of the cottage depend on the design features of the pipeline layout.
Types of pipe routing:
- Single-pipe;
- Two-pipe;
- Collector, or beam;
- Mixed schemes.
Single-pipe scheme
A single-pipe heating system is a heating system in which all radiators, without exception, are connected to one pipeline. In this case, the heated coolant at the inlet and cooled down at the return moves through the same pipe, gradually passing through all heating devices. In this case, it is very important that the internal cross-section of the pipe is sufficient to perform its main function. Otherwise, all heating will be ineffective.
A heating system with a single-pipe circuit has certain pros and cons. It would be a mistake to think that such a system can significantly reduce the cost of laying pipes and installing heating devices. The fact is that the system will function effectively only if it is properly connected, taking into account a large number of subtleties. Otherwise, it will not be able to heat the apartment properly.
Cost savings when installing a single-pipe heating system do occur, but only if a vertical supply riser is used. In particular, in five-story buildings this type of wiring is often practiced in order to save materials. In this case, the heated coolant is supplied upward through the main riser, where it is distributed to all other risers. The hot water in the circuit gradually passes through the radiators on each floor, starting from the top.
As the coolant reaches the lower floors, its temperature gradually decreases. To compensate for the temperature difference, radiators with a larger area are installed on the lower floors. Another feature of a single-pipe heating system is that it is recommended to install bypasses on all radiators. They allow you to easily remove batteries if repairs are necessary without stopping the entire system.
If heating with a single-pipe circuit is carried out according to a horizontal wiring scheme, the movement of the coolant can be parallel or dead-end. This system has proven itself in pipelines up to 30 m long. In this case, the number of connected radiators can be 4-5 pieces.
Wall marking
The installation of batteries in a wooden house (as in any other house) begins with marking the walls, according to which heating devices will be installed in the next stages of work. If a system with natural circulation of coolant is installed in the house, then the pipeline must have a constant slope of at least 6 degrees along the flow of water. Failure to comply with this rule will certainly lead to the appearance of air jams, and in the worst case, will not allow the system to function. For systems with forced circulation, this rule does not matter.
You need to mark the wall along which the brackets for the radiators will be installed. Radiators cannot be installed close to the wall - the distance between them should be about 5-10 cm. The radiator must be removed from the floor by at least 10 cm, and from the window sill by 8 cm. The markings are done level with a pencil. When marking, you need to take into account the width of the radiator sections so that the installed holders are strictly between the sections.
It is advisable to install foil material behind the radiators, which will act as a heat reflector. If there is a gap of at least 3 cm between this material and the radiator, it is possible to significantly increase the efficiency of the radiator and reduce heat losses.
When the marking is completed, holes of the required sizes are drilled in accordance with it. The dowels are driven in with a hammer, after which the brackets are secured using self-tapping screws. To make your work easier, you can purchase special battery holders equipped with threads that allow you to screw them directly into the dowel.
Two-pipe heating systems
Inside a two-pipe circuit, the coolant moves through two separate pipelines. One of them is used for the supply flow with hot coolant, and the other is used for the return flow with cooled water, which moves towards the heating tank. Thus, when installing heating radiators with a bottom connection or any other type of insertion, all batteries are heated evenly, since water enters them at approximately the same temperature.
It is worth noting that a two-pipe circuit when connecting batteries with bottom connections, as well as when using other circuits, is the most acceptable. The fact is that this type of connection ensures a minimal amount of heat loss. The water circulation scheme can be either associated or dead-end.
Please note that if you have a two-pipe wiring, it is possible to regulate the thermal performance of the radiators used.
Some owners of private houses believe that projects with two-pipe types of radiator connections are much more expensive, since more pipes are required for their implementation. However, if you look in more detail, it turns out that their cost is not much higher than when installing single-pipe systems.
The fact is that a single-pipe system requires pipes with a large cross-section and a large radiator. At the same time, the price of thinner pipes required for a two-pipe system is much lower. In addition, in the end, excess costs will be recouped due to better coolant circulation and minimal heat loss.
With a two-pipe system, several options are used for how to connect aluminum heating radiators. The connection can be diagonal, side or bottom. In this case, the use of vertical and horizontal joints is allowed. From an efficiency point of view, a diagonal connection is considered the best option. In this case, the heat is evenly distributed throughout all heating devices with minimal losses.
The lateral, or one-sided, connection method is used with equal success in both one-pipe and two-pipe distributions. Its main difference is that the supply and return circuits are embedded on one side of the radiator.
Lateral connection is often used in apartment buildings with a vertical supply riser. Please note that before connecting a heating radiator with a side connection, it is necessary to install a bypass and tap on it. This will allow you to freely remove the battery for washing, painting or replacement without disconnecting the entire system.
It is noteworthy that the efficiency of one-sided insertion is maximum only for batteries with 5-6 sections. If the length of the radiator is much longer, there will be significant heat loss with such a connection.
Features of panel bimetallic and steel radiators
Old cast iron batteries are gradually disappearing into oblivion, although today designer models are still produced for lovers of retro interiors.
In modern apartments, relatively new proposals are popular:
- steel panel radiators “Kermi”;
- bimetallic batteries Рurmo;
- aluminum and copper (more rare due to high cost).
The search for new types of heating equipment is primarily associated with the need to replace clogged pipes and radiators that have become “cold”. This relatively rapid wear is caused by the poor quality of water filling the system as coolant. Organic sediment, excess calcium and rust gradually narrow the duct, reducing the efficiency of heat delivery.
Bimetallic radiator with side connection
With central heating, there are often system tests, so bimetallic and steel models are preferable to aluminum ones. They are sensitive to the acidity of water and abrasive particles transported under high pressure during water hammer.
Attention! Radiators without a Mayevsky tap often air out, regardless of the metal and type of connection. These taps are recommended to be installed on upper floors, but can be installed in any room.
Bimetallic panel-type radiators cope much better with these problems due to their design features. Visually, they have a lot in common with sectional radiators with narrow clearances. Here, the outer panels hide the pipes through which the coolant passes.
The shape of the batteries with a thin metal shield absorbs a little heat for its own heating, the rest is spent on heating the air masses.
What is important to consider before buying a panel radiator
As a rule, in the living rooms of city apartments one window sill niche is allocated for batteries. However, their number and format may vary if the microclimate leaves much to be desired.
Advice! When old finned blocks are not efficient enough and the room temperature is below 20°C, it is better to purchase a panel radiator with a larger surface area.
Window niche, classic version for side connection
Before purchasing thermal equipment, it is important to determine the type of radiator, how it is connected and the need for additional equipment:
- pipes;
- a set of adapters and fittings, especially if it is necessary to adjust the width of holes and pipe diameters.
When connecting panel radiators from the side, it is assumed that they are connected to the incoming pipe from the top at the side and the outlet pipe from the bottom. Sealed and reliable installation is carried out using a threaded connection. An effective closed circuit is formed only with the correct connection, where the coolant flows by gravity from the upper collector to the lower outlet - through the entire radiator structure.
The quality of connection of panel radiators to pipes largely depends on the characteristics of the metal - rolled steel for their production and its thickness. These models are not designed for high system pressure. The internal surface is susceptible to corrosion, even if the technical description states “stainless steel”. Over time, the wall of such radiators becomes thinner (initially 1.25 - 2.5 mm) and becomes covered with plaque, making them fragile. Working pressure up to 10 Bar becomes limiting, so such models are relatively cheap, although they will last more than 10-15 years.
Features of the option with bottom pipe connection
As a rule, connecting a radiator with a bottom connection is carried out in cases where unpresentable heating pipes need to be hidden in the floor or wall so as not to disturb the interior of the room.
On sale you can find a large number of heating devices in which manufacturers provide a lower supply to the heating radiators. They are available in various sizes and configurations. At the same time, in order not to damage the battery, it is worth looking at the product passport, which describes the connection method for a particular model of equipment. Typically, the battery connection unit has ball valves that allow it to be removed if necessary. Thus, even without experience in such work, using the instructions, you can connect bimetallic heating radiators with a bottom connection.
The circulation of water inside many modern radiators with a bottom connection occurs in the same way as with a diagonal connection. This effect is achieved due to an obstacle located inside the radiator, which ensures the passage of water throughout the heating device. After this, the cooled coolant enters the return circuit.
Please note that in heating systems with natural circulation, it is not advisable to connect radiators from the bottom. However, significant heat losses from such a wiring scheme can be compensated by increasing the thermal power of the batteries.
Bottom radiator connection unit - advantages of use
Radiator fittings, which are used to connect from below, are intended for use in steel panel heat exchangers and are not suitable for aluminum radiator sections - due to this, steel types are highly competitive with them. Bottom inclusion compared to other types has the following advantages of using fittings:
- Saving pipe materials and outlets - in the floor structure or on the wall there are only two short outlets for connecting the radiator; the pipes do not go to its upper inlet.
- The connection at the bottom is aesthetically pleasing, and if the pipeline comes out of the wall, it is practically invisible under the body and does not interfere with cleaning the floor covering.
- Shut-off control valves (ball valves or valves) in the “binoculars” allow you to control the intensity of the liquid entering the heat exchanger, and when it is completely shut off, remove the batteries for maintenance or repair.
- The bottom connection unit with a vertical bypass evenly distributes water throughout the radiator with heating of its coldest upper corners, which is observed with the bottom connection. Also, with single-pipe wiring, the bypass helps to equalize the temperatures of the incoming and return flows, which in turn leads to uniform heating of the devices built into the line.
Rice. 2 Straight and elbow 3/4" bottom fittings installed
Diagonal connection
As we have already noted, the diagonal method of connecting radiators has the lowest heat loss. With this scheme, the hot coolant enters from one side of the radiator, passes through all sections, and then exits through the pipe from the opposite side. This type of connection is suitable for both single- and two-pipe heating systems.
Diagonal connection of radiators can be done in 2 options:
- The hot coolant flow enters the upper hole of the radiator, and then, having passed through all sections, exits the lower side hole on the opposite side.
- The coolant enters the radiator through the lower hole on one side and flows out from the top on the opposite side.
Connecting in a diagonal manner is advisable in cases where the batteries consist of a large number of sections - 12 or more.
Strapping methods
To install a battery harness in a private house or city apartment, you will need:
- shut-off valves, which are most often used as simple ball valves;
- plugs for blocking the remaining channels;
- Mayevsky valves, which allow you to bleed air from the system during seasonal startup of equipment;
Device for removing air from the heating system
sealing material.
Additionally, you can install on any heating radiator:
- a pressure gauge that determines the pressure in the system (most often used when installing equipment in autonomous country houses);
- thermostat operating in manual or automatic mode. Using this equipment, you can set a certain temperature for any individual radiator.
Device for setting a specific battery operating mode
If tying is carried out with polypropylene, then additional welding equipment will be required.
Device for welding polypropylene pipes
So, depending on the factors presented above, the heating radiator piping can be performed according to the following schemes:
- for lateral connection;
- for diagonal connection;
- for bottom connection.
Side connection strapping
With a side connection method and a single-pipe system, installation of the piping is performed as follows:
- Ball valves are installed on the inlet and outlet pipes, making it possible to shut off the coolant supply to perform repair or maintenance work;
- taps are connected to tees;
- A section of pipe is inserted into the remaining branches of the tees, acting as a bypass.
A bypass is necessary for autonomously shutting off a separate radiator, for example, for repairs, without shutting down the entire heating system.
When connecting to a two-pipe system laterally, the work is performed in a similar manner. However, installing a bypass is not required in this situation.
Strapping diagrams when choosing a side battery connection method
Diagonal connection strapping
The connection of the radiator to the pipes with a diagonal connection is as follows:
- the incoming pipe is connected to a section of pipe no more than 10 cm - 15 cm long;
- Next, a ball valve and a tee are installed to connect the bypass;
- the outlet pipe is connected to the elbow and only after that is connected to the coolant removal pipeline;
- A tap is installed before connecting to the central line.
When connected to a two-pipe system, the work is performed in the same way, with the exception of the bypass.
Battery wiring diagram when choosing a diagonal connection method
Bottom connection strapping
Tying the bottom connection method is easier than all others:
- Shut-off valves are connected to the inlet and outlet of the radiator;
- pipe bends are introduced into the central mains. If necessary, special adapters - angles or tees - are installed at the bend points.
Radiator wiring diagram with bottom connection method
There is a separate nuance when piping the lower connection when connecting to a single-pipe system. In most cases, the connection is made as shown in the figure, that is, without a bypass, which allows autonomous shutdown of the heating device. But if you want to use the device, you can install it. To do this, an additional section of pipe is installed between the inlet and outlet pipes.
Piping the lower connection using a bypass
The following video provides a detailed description of the types of battery piping in a heating system.
Thus, with the correct choice of connection method and correct installation, the heating system will serve for a long time, evenly heating all rooms.
Natural and forced coolant circulation
It is worth noting that the method of connecting pipes to radiators will also depend on how the coolant circulates inside the heating circuit. There are two types of circulation - natural and forced.
Natural circulation of liquid inside the heating circuit is achieved through the application of physical laws, and no additional equipment needs to be installed. This is only possible when using water as a coolant. If any antifreeze is used, it will not be able to circulate freely through the pipes.
Heating with natural circulation includes a boiler for heating water, an expansion tank, 2 pipelines for supply and return, as well as radiators. In this case, a working boiler gradually heats the water, which expands and moves along the riser, passing through all the radiators in the system. Then the cooled water flows by gravity back into the boiler.
To ensure free movement of water, horizontal pipes are installed with a slight slope towards the direction of movement of the coolant. A natural circulation heating system is self-regulating because the amount of water changes depending on its temperature. When water is heated, the circulation pressure increases, which ensures uniform heating of the room.
In systems with natural circulation of liquid, it is possible to install a radiator with a bottom connection, provided there is a two-pipe connection, and also use a scheme with a top connection in a one- and two-pipe circuit. As a rule, this type of circulation is carried out only in small houses.
Please note that the batteries must have air vents through which air pockets can be removed. As an option, you can equip the risers with automatic air vents. It is advisable to place the heating boiler below the level of the heated room, for example, in the basement.
If the area of the house exceeds 100 m2, then the method of circulation of the coolant must be forced. In this case, you will need to install a special circulation pump, which will ensure the movement of antifreeze or water along the circuit. The power of the pump depends on the size of the house.
The circulation pump can be mounted on both the supply and return pipes. It is very important to install automatic bleeders at the top point of the pipeline or provide Mayevsky taps on each radiator in order to remove air pockets manually.
The use of a circulation pump is justified in both one- and two-pipe systems with vertical and horizontal radiator connections.
Main installation features
When assembling and installing fittings on a heating device, it is laid lying on the floor. Instead of a radiator liner, a special valve is used, which allows you to connect the supply and return to the bottom of the battery. An O-ring seal is used to seal the connections.
On a note! It is recommended to mark the location of the through hole on the valve, which is located on the shank. This will allow you to align it in a vertical direction during installation.
The design of the injection unit often lacks a nut, which is used instead of a radiator liner. Despite this, its installation is similar to that of a valve. If a one-sided bottom connection is created, plug the outlet located on the reverse side with a plug. After this, install all the fittings on the battery using tow and paste. Then the assembled radiator is usually hung on wall brackets. Finally, it is connected to the heating system pipelines.
Installed and connected radiator to polypropylene pipelines Source santeh42.ru
Why is it important to properly connect heating radiators?
Whatever connection method and type of radiator you choose, it is very important to carry out proper calculations and correctly install the equipment. It is important to take into account the characteristics of a particular room in order to choose the best option. Then the system will be as efficient as possible and will avoid significant heat loss in the future.
If you want to assemble a heating system in a large, expensive mansion, it is better to entrust the design to specialists.
For small houses, you can handle the choice of connection diagram and installation of batteries yourself. You just need to consider the quality of a particular connection scheme and study the features of installation work.
Please note that the piping and radiators must be made of similar material. For example, plastic pipes cannot be connected to cast iron batteries, as this is fraught with trouble.
Thus, provided that the features of a particular house are taken into account, you can connect heating radiators yourself. A well-chosen scheme for connecting pipes to radiators will minimize heat loss so that heating devices can operate with maximum efficiency.
Functions
Winding and unaesthetic pipes of the heating system are not the best decoration in interiors. Design experts come up with ingenious ways to hide standard cast iron radiators. It should be noted that this does not always work out. This problem is solved more effectively if you use heating devices with a lower coolant connection. Then all the pipes will not be located in plain sight, but under the finishing floor covering.
bimetallic radiators
In aluminum as well as cast iron batteries, there is no possibility of creating a bottom connection. But steel panel or tubular radiators are quite suitable for organizing the connection in this way. Next we will look at installation methods.
Tichelman scheme: all radiators in the same conditions
As the name implies, this heating radiator connection diagram is quite simple, but at the same time tricky. The first radiator is located closest to the pump, but farthest from the return pipe, and the last is located farthest from the pump, but closest to the return pipe. It turns out that the resistance on each radiator, or the pressure on each radiator, is the same. The flow through all radiators is the same. If we take and shut off any of these radiators, the rest will work as they did, the system balances itself. It seems like there are more pipes here, but in fact, if these radiators are located in a circle around the building, then the design turns out to be much lighter, simpler, and more elegant than the previous ones. The Tichelman loop can be tied around two or even three floors. Moreover, if you close all the radiators on one floor, they will continue to heat normally on the other.
Correct installation of the structure without a bypass pipe
Such a scheme will not require parallel pipe laying based on welding or fastening using adapters and fittings.
Primitivism in installation and some cost savings will subsequently bring a lot of problems to the homeowner. The most expensive item is shutting down the system due to local leaks in the pipeline or radiator.
Tools
To organize heat supply, you do not need to purchase special sets of tools - plumbing fixtures and the keys that a home handyman has available will handle the task. Add only specific tools to your home kit:
- special keys for connecting American women;
- tools for screwing on adapters;
- torque wrenches for “delicate” parts.
Reference.
Professionals advise not to purchase expensive equipment for attaching parts with a union nut. An open-end (or adjustable) wrench with pliers copes with the task. The first one holds, the other twists.
Connection diagrams and methods
With a single-pipe scheme for connecting heat supply to a home, several schemes for obtaining energy from a heat source are used.
Diagonal connection is an effective method. The pipes alternate with upper and lower connections within the border of one radiator: the heat input is at the top pipe, the output is at the bottom of the battery. This system has proven itself to be excellent when connecting radiators of more than 10 units; the batteries are heated evenly.
Photo 2. Connecting a heating radiator in a diagonal pattern. Hot coolant is indicated in red, cold coolant in blue.
- The lower piping, according to experts, is less efficient in terms of thermal conductivity, but is used in closed heating systems, when pipes run horizontally from the boiler and are hidden under the floor.
- The vertical connection is based on the installation of a riser in the boiler area; the remaining elements of the heating structure are connected to it. The advantage of this method is the absence of air pockets when water flows by gravity.
- Top wiring (incoming and outgoing pipes are installed at the top on different sides) is used in radiators of a special design, where forward flow is excluded. The carrier descends down the first section and passes through the remaining links.
Types of heating systems
Heating systems are installed in different ways. But the main component is the installation that produces heat. With its help, the temperature regime of the heat carrier is formed, which is transferred to heating devices by natural or forced circulation.
Conventionally, such a network is divided into two types, as it is assembled using a single-pipe or two-pipe interchange
The first option can be installed independently, but for the second type you will have to perform complex calculations, taking into account the mass of operating parameters of all technical components
Single-pipe
This type of installation has been used for a long time. Significant savings are generated due to the absence of return risers for the transfer of coolant.
The operating principle is simple. The coolant is transmitted through one closed system, which includes a heating installation and appliances. The binding is made with one common contour. A hydraulic pump is used to ensure the transfer of coolant.
What does a one-pipe heating system look like?
Schematically, a single-pipe heating system is divided into:
- vertical – used in multi-storey buildings;
- horizontal - recommended for private houses.
Both types do not always give the desired effect in work. Radiators connected in series cannot always be adjusted so that all rooms are equally warm.
No more than a dozen batteries are connected along the vertical riser. Failure to comply with this rule leads to the fact that the lower floors in the house will not warm up well.
A serious disadvantage is the need to install a pump. It is this that is the source of leaks and forces you to periodically replenish the heating network with water.
For normal operation of such a network, you will have to install an expansion tank in the attic.
Despite the negative aspects, there are also positive aspects to such heating, which perfectly compensate for all the shortcomings:
- new technologies have made it possible to solve the issue of uneven heating of rooms;
- the use of balancing devices and high-quality valve equipment allows repair work to be carried out without shutting down the overall system;
- installation of a single-pipe system will cost much less.
Two-pipe
In such a network, the coolant moves up the riser and is supplied to each battery. After this, it goes back to the heating boiler.
With the help of such a system it is possible to organize uniform heating of all radiators. During the circulation of water, large pressure losses do not occur; the liquid moves by gravity. It is possible to repair the heating network without stopping the supply of heat to the facility.
Two-pipe heating system
If we compare systems, the two-pipe system will be much more effective. But it has a main drawback - assembly requires twice as many pipes and components, which affects the final cost.