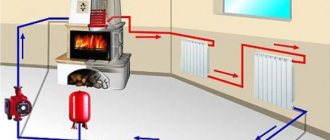
The design for heating a private house works based on the use of an expansion tank. It is in this part of the entire structure that the coolant is located. The main function of the expansion tank is to compensate for expansion from heat, depending on the specific operating mode of the equipment.
Closed heating in a private house
A closed heating system is more often used in private homes. For its correct operation, constant human control is not required - it operates automatically. In addition, any type of coolant can be used here (even antifreeze can be used). This system maintains a stable pressure level and the coolant does not interact with air.
The expansion tank can be installed anywhere - it is advisable to mount it next to the boiler. If we are talking about a wall-mounted model, then expansion tanks are immediately installed in them. Automatic air vents are also installed in closed models.
A closed heating system consists of the following main elements:
- Boiler and security group. A safety group can be immediately built into the boiler - this is typical for wall-mounted gas models, pellet variations, as well as gas generator models.
- Radiators and pipes (sometimes this also includes convectors and water heated floors).
- A circulation pump, which helps the coolant move through the system. It is placed on the return pipeline (lower temperature here).
- An expansion tank that stabilizes pressure and also compensates for the volume of coolant.
Classification of heating systems
To properly fill a water heating system.
you need to know what type it is. There is a classification of systems according to the method of pipe routing: from the top, from the bottom, horizontal, vertical or combined. According to the method of connecting devices using pipes, systems are divided into: single-pipe and double-pipe. Also, water can circulate in the system naturally or forcefully (if a pump is used). Based on the scale of operation, local and central heating systems are distinguished. As the water moves in the pipes, there are dead-end and passing pipes. All these types are used in mixed order in everyday life.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
This video material presents an example of a detailed hydraulic calculation of a 2-pipe closed-type heating system for a 2-story house in the VALTEC.PRG program:
Here is a detailed description of the design of a single-pipe heating system:
It is possible to install a closed version of the heating system yourself, but you cannot do it without consulting specialists. The key to success is a properly completed project and quality materials.
Do you have any questions about the specifics of a closed heating circuit? Is there information on the topic that would be of interest to site visitors and us? Please write comments in the block below.
Water or coolant, select the optimal filling system
Antifreeze for heating system
The optimal composition of the liquid should be determined by the parameters of the heating system. Often the heating system is filled with water, as it has a number of significant advantages. The determining factor is the affordable cost - they often use simple tap water. However, this is fundamentally wrong. A large number of metal elements and alkali will contribute to the formation of build-up on the inner walls of pipes and radiators. This leads to a decrease in the bore diameter and an increase in hydraulic losses in certain sections of the pipeline.
But how to properly fill a closed heating system with water to avoid such troubles? Experts recommend using distilled water. It is maximally purified from impurities, which has a positive effect on its physical and operational properties.
Energy intensity. Water accumulates heat well in order to subsequently transfer it to the room; Minimum viscosity index
This is important for closed heating systems with forced circulation and affects the power of the centrifugal pump; As the pressure in the pipes increases, the boiling point shifts upward. Those
in fact, the process of transition from liquid to gaseous state occurs at a temperature of 110°C. This makes it possible to use high-temperature heating modes.
But if there is a possibility of exposure to negative temperatures, then water as a liquid for filling heating systems is unacceptable. In this case, you should use antifreezes with a crystallization threshold significantly lower than 0°C. The best option is solutions of propylene glycol or glycerin with special additives. They belong to the class of harmless substances and are used in the food industry. Solutions based on ethylene glycol have the best technical qualities. Until recently, they were used to fill closed heating systems. However, they are extremely harmful to humans. Therefore, despite all their positive qualities, the use of ethylene glycol-based antifreeze is not recommended.
But what can you fill the heating system with - water or antifreeze? If there is no chance of exposure to low temperatures, water is the best choice. Otherwise, it is recommended to use special coolant solutions.
Automotive antifreeze cannot be poured into the heating system. This will not only lead to boiler breakdown and failure of radiators, but will also be hazardous to health.
Selecting the boiler type
As a rule, a closed heating system operates in automatic mode. It follows from this that it is better to give preference to boilers with built-in automation. Such a system, after installing all the necessary operating modes, operates without human intervention.
The best option is to use gas boilers. By connecting a room temperature regulator, it is possible to maintain the temperature with an accuracy of one degree. It is convenient, and it is comfortable for a person.
Some models are characterized by the fact that they have the ability to connect external sensors to adjust the operation of gas burners depending on weather conditions. Gas boilers are the best option for closed heating systems. With their help, it is possible to provide the necessary level of comfort in a person’s home, although gas is not available everywhere.
Two-pipe closed heating system in a house on two floors (diagram)
Electric boilers can provide no less automation. If earlier the main models were models based on heating elements, then recently induction and electrode boilers have been developed. They are characterized by more compact sizes, as well as minimal inertia. In addition, they are considered to be more economical, although the installation of electric boilers is associated with a number of difficulties. The first and main difficulty is interruptions in the supply of electrical energy. The second difficulty is related to the insufficient power of power lines, since the operation of an electric boiler requires power from 8 to 12 kW. Powering such a boiler from a generator is not so easy, nor is it profitable.
Example of a closed heating system with an induction boiler
Independent heating sources run on liquid or solid fuel, but there are many problems here too. A liquid fuel boiler will require a separate room, but a solid fuel boiler is a source of waste, which causes a lot of inconvenience.
It should be noted separately that modern solid fuel boilers have their own level of automation, although it is not comparable to the level of automation of gas boilers. The combustion of a solid fuel boiler will still have to be controlled, since its operation is periodic. In other words, it either heats up or cools down as the fuel burns.
There are also pellet boilers that run on pellets, although they can safely be called solid fuel boilers. Pellets are a kind of granules made from wood waste. They are automatically fed into the boiler from the hopper, so the boiler runs until the supply of pellets in the hopper is used up. If high-quality pellets are used, they burn almost completely, and the boiler must be cleaned once every few weeks. All operation of the boiler is ensured by automation. Unfortunately, such boilers are not popular due to the high cost of boilers, as well as the high cost of pellets.
Pellet boiler
The most important thing is to correctly calculate the boiler power for a closed heating system. As a rule, it is determined as follows: 1 kW of boiler power is required for 10 square meters of room area. Naturally, it is better to take the boiler power with a margin of at least 30 percent. Operating at extreme parameters negatively affects the longevity of the equipment. In addition, there are winters with abnormally cold periods when the boiler cannot cope with providing the required temperature in the room.
Main types of coolants
Heating system.
The operating principle of the heating system is that the coolant moves from the heat source to the end point through pipes, heating them. The type and design of the heating equipment determines the type of coolant used, which can be liquids and gases.
The most popular liquid coolants are:
- Water is the most accessible and cheapest resource. According to statistics, about 70% of heating systems use water, which has a high density and heat capacity. In addition, this type of coolant has gained such popularity due to its properties, such as low viscosity, high heat transfer coefficient, and easy temperature control. The main disadvantage is the ability to freeze at zero temperatures. If water freezes in the heating system, this will lead to rupture of pipes and failure of all equipment.
- Antifreeze - this type of coolant is not as widespread as water, and its use is 5%. It is used for heating administrative buildings and residential buildings where the heating system does not allow the use of water due to the increased risk of corrosion. The main advantage of antifreeze is freezing in frosts of 60 - 70 degrees.
The following gases are used as coolant:
- Water vapor is mainly used in industrial buildings, since its use is prohibited in residential and public buildings. Water vapor maintains the temperature of heating devices at 100 degrees; according to sanitary standards, this figure should not exceed 80 degrees.
- Flue gases are toxic, so recently they have been used only for heating water and in order to save electricity to produce a heat source.
- Air is characterized by low heat capacity, so moving it through the heating system requires large energy costs. It is most cost-effective to use air as a coolant, provided that it simultaneously performs two functions: heating and ventilation.
Currently, organic liquids are being introduced as a coolant, which have excellent freezing properties and low viscosity. However, they have not yet become widespread due to their high cost and scarcity.
Features of assembling a forced circuit
In order for the forced system to justify itself and function properly, it is necessary to correctly select the circulation pump and correctly “embed” it into the heat supply line.
Selecting a circulation pump
The main parameters for choosing pumping equipment: device power and pressure. These characteristics are determined based on the area of the heated room.
Indicative indicators:
- for houses of 250 sq.m., a pump with a power of 3.5 cubic meters per hour and a pressure of 0.4 atm is suitable;
- in rooms measuring 250-350 sq.m, install the device at 4.5 cubic meters per hour with a pressure of 0.6 atm;
- if the area of the house is 350-800 sq.m, then it is advisable to purchase a pump with a capacity of 11 cubic meters per hour, the pressure of which is at least 0.8 atm.
In a more scrupulous selection, specialists take into account the length of the heating system, the type and number of radiators, the material of manufacture and the diameter of the pipes, as well as the type of boiler.
Installing the pump in the main
The pump is placed on the return line so that the coolant that is not too hot passes through the device. It is possible to install modern models made of high-temperature resistant materials on the supply line.
When inserting the pump, the water circulation should not be disrupted. It is important that at any point in the pipeline when the pumping unit is operating, the hydrostatic pressure remains excessive.
Four acceptable schemes for heating systems with pump circulation and an open expansion tank. Hydrostatic pressure is maintained at the desired level
Option 1. Raising the expansion tank. A simple way to convert a natural circulation system to a forced one. To implement the project you will need a high attic space.
Option 2. Moving the tank to a distant riser. The labor-intensive process of reconstructing the old system and installing a new one is not justified. Simpler and more successful methods are possible.
Option 3. Expansion tank pipe near the pump nozzle. To change the type of circulation, it is necessary to cut off the tank from the supply line, and then connect it to the return line - behind the circulation pump.
Option 4. The pump is included in the supply line. The simplest way to reconstruct the system. The disadvantage of the method is unfavorable operating conditions for the pump. Not every device can withstand high temperatures.
Pressing the heating system
Pressing the heating system
Before filling the heating system with coolant, it is necessary to check the tightness of all joints and connections. To do this, pressing is performed - creating excess pressure in the pipes, i.e. a situation of destabilization of the system is artificially created.
This can be done in two ways - using air injection or coolant. This must be done before the heating system of the double-circuit boiler is filled. This procedure can be carried out using a mechanical (electric) pump or by connecting the water supply. The last option is not recommended, since it will be very difficult to control the process. The order of execution is as follows:
- Preliminary visual inspection of joints and connecting nodes;
- Connecting the mechanism to the inlet pipe of the system;
- Creation of excess pressure, the value of which should exceed the norm by 1.5 times.
The condition of the heating elements must be checked. If a leak occurs, the process stops immediately and can only begin when the defect is repaired.
Installation and configuration of equipment
Installation, connection and adjustment of automatic control is carried out by gas service specialists.
Important! Self-installation of the heating device is prohibited!
Installation and connection to the gas pipeline is carried out after the development and approval of the project in accordance with established standards and requirements of SNiPs.
Installation steps:
- Development of a project for installation and connection of heating equipment
- Remove plugs and pressure wash pipes.
- Installation of a boiler with a closed combustion chamber is carried out near a wall made of non-combustible materials. Wooden walls are covered with fireproof materials.
- Installation is carried out at a distance of at least 20 cm from electrical appliances and other heating elements.
- Cleaning filters are installed on the cold water supply pipes.
- The gas service specialist connects the gas supply.
- Plug in.
- Configuring automatic control of device operating parameters.
The price of a boiler with a closed combustion chamber depends on the model, product power, number of circuits and additional protective functions.
The best foreign manufacturers of heating boilers: Vaillant, Viessmann, Buderus, Bosch and Ferroli. Among Russian manufacturers they are distinguished by price/quality ratio
Zhukovsky Machine-Building Plant product line is represented by the “Economy”, “Universal” and “Comfort” series; JSC "Borinskoe" and LLC "Plant CONORD".
The process of starting an open gravity heating system
In modern houses, open heating systems are quite rare; such technologies have long been considered a relic of the past. But they still exist, so you should consider how they need to be filled with water. In any such heating system there is an expansion tank at its highest point; it is designed to accumulate water after increasing its volume in the system with increased pressure during rising temperatures. The tank is an open container with or without a lid. The system is filled with water through the tank. Large volumes of liquid, of course, will be quite problematic to fill in small containers, especially at the highest point.
It would be most rational to use a regular household vibration pump. To do this, prepare a capacious container and fill it with water. Pre-prepared hoses are attached to the pump with clamps. This pump has a submersible type of structure. The hose through which water will be drawn must be lowered into a prepared tank of water. The hose from which the water will be released is immersed in the expansion tank. Turn on the pump, the pressure in the system should be from one and a half to two atmospheres. When lowering, add water to the prepared tank and lower the hose into it. When the heating complex is filled, water will be visible at the bottom of the expansion tank, the system can be considered full.
Installation diagram of a water heating system.
Excess air will come out of the pipes during the first fire through the expander. It should be noted that during the heating season, when the system maintains a constantly high temperature, water will gradually evaporate from the expander. It is necessary to recharge by adding water to the expander to the required level. You should also monitor the temperature on a thermometer attached to the heating boiler. When its level reaches above 80°C, the water will soon begin to boil and splash out. In this case, it is necessary to block the access of oxygen to the firebox to reduce the intensity of combustion.
Tank selection criteria
Expansion tanks are made of steel. Inside there is a membrane dividing the container into 2 compartments. The first is filled with gas, and the second with coolant. When the temperature rises and water rushes from the system into the tank, the gas is compressed under its pressure. The coolant cannot occupy the entire volume due to the presence of gas in the tank.
The capacity of expansion tanks varies. This parameter is selected so that when the pressure in the system reaches its peak, the water does not rise above the set level. To protect the tank from overflow, a safety valve is included in the design. Normal tank filling is from 60 to 30%.
The optimal solution is to install the expansion tank in a place where there are the fewest bends in the system. The best place for it is a straight section in front of the pump.
Filling the system from below
So, let's get back to pumping fluid into the system. We use a container of suitable volume (a 200-liter plastic barrel works well). We lower a pump into it, creating the pressure required for pumping liquid no higher than 1.5 atm (typical value in the range of 1-1.2 atm). Such pressure requires the pump to create a pressure of 15 m (for the submersible “Malysh” it reaches 40 m).
Having filled the barrel with water, we start the pump, monitoring the liquid level, which should be located above its inlet pipe to prevent “airing”. The level drops - add water. Antifreeze should be pumped from a smaller container (bucket) so as not to immerse the submersible pump housing in the liquid (and then wash it) - just immerse the inlet pipe. You will have to add antifreeze frequently, turning off the pump periodically.
Filling the system is carried out with Mayevsky taps open on installed heating radiators with substitute containers for collecting water. When liquid comes out of all air vents, close the taps and continue the injection process.
We control the pressure using a pressure gauge (a boiler gauge will do). When its value exceeds the hydrostatic pressure, equal to the pressure in the liquid column height from the bottom to the top point of the system (a height of 5 m gives a static pressure of 0.5 atm), we continue to fill the system, monitoring with a pressure gauge the moment the pressure reaches the required value.
Pumping antifreeze with the “Malysh” pump.
Having filled the system, turn off the pump, open the air valves (the pressure will inevitably drop), and then pump up the water. We repeat the process several times, displacing air bubbles.
We complete the filling by inspecting the system for leaks. After the pump is turned off, the liquid in the hose connected to the outlet pipe is under pressure. If antifreeze was pumped in, first disconnect the hose from the pump inlet pipe and drain the liquid into a container, being careful not to drench the mechanism body.
Closed circuit air protection
In any heating circuit, air is generated. The reasons for this phenomenon may be the following:
- heating of water, accompanied by the release of gas bubbles,
- reaction of a metal with water to release oxygen,
- filling communications too quickly,
- low pressure,
- leaks in pipelines that are not visible from the outside.
To remove air accumulations, taps are installed on the batteries. There are several models of such devices:
- The shut-off and control valve is opened to drain the liquid along with the air lock. This is inconvenient because you have to remove a large amount of media.
- Mayevsky's manual tap - fluid loss when removing an air lock is minimal, but the work will have to be done manually.
- Automatic air vent – removes air independently. However, the automation does not always work, so you need to keep an eye on the batteries. If they begin to heat poorly or cold spots appear on the body, deflate the air manually. Use a bucket, plastic bottle or other container to collect liquid.
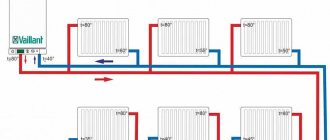
Types of closed heating system diagrams
The main advantage of natural circulation schemes is their independence from the availability of electricity, but they have a limitation: the length of the circuit must be no more than 30 meters, otherwise the system will be inoperable. There is one more nuance - with natural circulation, even in a closed system, you need to install a drain valve at the top point, with the help of which you can remove air that has entered, for example, when adding coolant.
System with natural circulation of a one-story house. Single-pipe circuit, top wiring
In a forced circulation circuit, pressure is created by a circulation pump. Some boilers have it built in, some don't. Some long circuits require the installation of two pumps. Then it is not necessary to observe slopes; the most important thing is not to make the sections slope in the other direction, which will negatively affect the performance of the heating and may even require rework.
On the one hand, the use of circulation pumps is a disadvantage, since its performance depends on the availability of electricity, but on the other hand, it is a big plus:
- allows you to use pipes of a smaller cross-section and radiators of a smaller volume, which means you spend less money on purchasing materials;
- increase the speed of movement of the coolant, and therefore reduce its inertia and increase the level of comfort;
- less coolant, less fuel is wasted on heating it - money is saved.
Reduced volumes of pipes and radiators mean a decrease in the volume of the system, which again makes it possible to reduce the heating inertia of the coolant - it heats up faster, and the heating is more efficient. A smaller volume of coolant means a smaller volume of the expansion tank, and there is no need to look for a place to install it. Modern boilers have built-in membrane tanks (for example, wall-mounted gas boilers), and the heating efficiency using them is very high due to the fact that a powerful pump is installed (it is also built-in).
It is better to connect the pump with a bypass - to be able to repair/replace it without destroying the system
When choosing a pump, remember that there is a direct relationship between its power and heating efficiency. Therefore, choose one that is low noise, powerful and reliable.
It is worth noting that it is easy to make a closed one from an open system - you just need to change the expansion tank - install a membrane type and the system will be operational. To make it more efficient, you will need to install a pump. Moreover, modern pumps can be installed in both supply and return. Previously, they were installed on the return line because the coolant temperatures there are lower. But modern pumps use heat-resistant materials; the temperatures of heating systems are not so critical for them
Just when buying, pay attention to the operating temperature range, or put it in the return line - only so that it “presses” into the boiler. In this case, the pump power may be small, since open systems use larger pipe diameters than closed ones, and the hydraulic resistance of the system is small
There are many nuances and features in heating a private home, and it’s not easy to figure it out. But once you set a goal, you can do everything yourself - create a workable good project, select the right equipment and install everything yourself. And closed systems in this sense are no exception.
Which closed system to choose for a private home
When choosing a design, you need to focus not only on your preferences, but also on the features of the building. Then the heating will work as efficiently as possible.
- For a small house with an area of each floor of 80–100 sq. m, a single-pipe design is suitable. It is quickly installed and requires minimal costs.
- For a large building with small rooms, a dead-end layout is optimal, the “branches” of which can be placed in any direction. It is recommended to choose it for houses that are planned to be modernized. It will be enough to throw an additional “branch” into an extension or a new room.
- The Tichelman hinge is suitable for rooms with a minimum of corners and doors. This option does not fit well into old buildings with complex layouts.
- If there are different options for installing a dead-end or associated system, choose the associated one, since it requires virtually no adjustment.
- Radiant heating systems are especially recommended for rooms with a large number of radiators. The heaters will heat up at the same time and have the same temperature.
- Closed contours can be combined with each other. For example, on the first floor, where there are many doors and partitions, install a counter loop structure, and on the second, freer floor, install a Tichelman ring.
- Vertical structures are installed in houses above one floor. For heat communications with overhead wiring, you need an attic, which will have to be insulated. Bottom supply is convenient for buildings under construction - you can heat the rebuilt lower floors until the top of the building is ready.
When choosing a scheme, you need to start from the parameters of a particular structure. Therefore, in this matter, rely on the opinion of the specialist drafting the project. Only with experience can you choose a design that will heat all rooms evenly and work without failures.
Filling technology where to supply coolant
The necessary means are a container and a pump that creates the required pressure of the coolant liquid. Submersible type “Gnome” or “Kid” are quite suitable (popular with gardeners who use them for watering areas located above the levels of reservoirs). There is evidence of successful filling of closed systems using hand pumps - from those used for spraying protective solutions on garden crops, to specialized hand pumps used for pumping motor fuels or liquid chemicals from drums. Any heating circuit can be successfully filled by monitoring the pressure using a pressure gauge.
Filling the system with antifreeze using a submersible vibration pump.
The first step is to select the fluid entry point. If the pressure created by the pump raises the liquid to the top of the system, it should be connected at the lowest point of the boiler room - the coolant make-up pipe, cut into the “return” in front of the boiler. In addition to the make-up inlet, a structurally separate drain outlet is required (two different system components). The first is equipped with a valve (ball valve) and a check valve, the second - only with a valve (ball valve). If the lowest point of the system is the water drain fitting from the boiler, then you can drain/fill the system with water through it. Since a check valve is not installed behind the boiler drain (behind the drain at all), any shutdown of the pump will cause the pumped liquid to leak out - you need to quickly turn off the tap in front of the fitting.
Design of a typical drain/recharge unit.
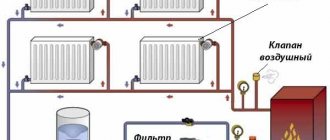
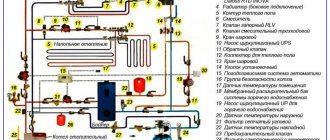
Basic elements of a closed heating system
ZSO includes the following elements:
- Boiler - gas, electric or solid fuel.
- Circulation pump.
- Closed expansion tank. Its work is described in detail in the article “Expansion tank for closed-type heating.”
- Pipes and connectors. There are two of them - the supply, through which the hot coolant enters the heating main, and the return, intended for the outflow of cooled liquid. There are single-pipe schemes without return. In buildings with water heating, an additional make-up line is installed to automatically replenish the circuit with water.
- Pressure gauge for pressure control.
- Air vent for air release.
- Emergency valve for removing excess coolant.
- Shut-off valves are taps and valves that shut off the lines of inflow and outflow of liquid.
- Filters (mud collectors) – for water purification.
- Fastening devices for mounting elements.
Additional valves, valves and thermostats are often also included in a closed circuit to balance pressure, control temperature and improve heating performance. You can connect heated floors and an indirect heating boiler for hot water supply to it.
When filling with coolant
There are only two known situations that require this technological operation:
- putting heating into operation (at the beginning of the heating season);
- restart after repair work.
Typically, coolant water is drained in late spring for two reasons:
- Water inevitably becomes contaminated with corrosion products (inside radiators, metal-plastic and polypropylene pipes are not susceptible to it). If you leave old water for the new season, you risk breaking the circulation pump with solid contaminants.
- Flooded systems in country houses that have not been started can “defrost” during a sudden cold snap - such cases are not uncommon. In this sense, antifreeze coolant is preferable. The high-quality composition has high anti-corrosion properties, increasing the drain interval to 5-6 years. There are known cases of uninterrupted heating operation with the same volume of antifreeze for 15-17 years. It is recommended to drain low-quality antifreeze after 2-3 years.
Pumping antifreeze into the heating system.
Features of starting a closed heating system with distilled water
Filling a closed heating system with water has the following features:
It will be much easier to provide the heating circuit with the necessary pressure if the living space has access to a central water supply. In this situation, to pressurize the heating system, it is enough to fill it with water through a jumper that removes the water supply, while carefully monitoring the increase in pressure on the pressure gauge. After completing such an event, unnecessary water can be removed using any of the valves or by means of an air vent.
Many people wonder whether special preparation of water for the heating system should be carried out or whether it is possible to limit it to water from the nearest body of water. At the same time, some argue that distilled water in the heating system will have a beneficial effect on the service life of the equipment and will not allow it to fail prematurely. But it is much more important to understand how to prepare water for heating if a special non-freezing liquid like ethylene glycol is added to it and how to subsequently fill the heating circuit with such coolant.
For these purposes, it is customary to use a special pump that serves to fill the system with water, and it can be controlled either automatically or manually. This pump is connected using a valve, and after ensuring the required pressure, the valve is closed. There are situations when such equipment is not at hand. As an option, it is possible to connect a standard garden hose to the discharge valve, the second end of which should be raised to a height of 15 meters and the circuit should be filled with water using a funnel. This method will be especially relevant if there are tall trees near the building being developed.
Another option for filling the heating system is to use an expansion tank, which performs the function of containing excess coolant caused by its expansion during the heating process.
Such a tank looks like a reservoir, which is divided in half by a special membrane made of elastic rubber. One part of the container is intended for water, and the other for air. The design of any expansion tank also includes a nipple, with which it becomes possible to establish the required pressure inside the unit by removing excess air. If the pressure is insufficient, then this parameter can be compensated by pumping air into the system using usually a bicycle pump.
The whole process is not particularly difficult:
First, air is eliminated from the expansion tank, for which you need to unscrew the nipple. Ready-made tanks go on sale with slightly excess pressure, which is equal to 1.5 atmospheres; then the heating circuit is filled with water. In this case, the expansion tank must be mounted so that it is positioned with the thread upwards
It is important to remember that it is not advisable to fill the tank completely with water. It would be more correct if the total volume of air in this device is approximately one tenth of the total volume of water, otherwise the tank will not cope with its main function and will not be able to accommodate excess heated coolant; after this, air is pumped into the system through the nipple, which, as mentioned above, can be done using a regular bicycle pump
The pressure must be monitored using a pressure gauge.
All of these actions will allow you to carefully fill the heating system with water and ensure stable and high-quality operation of the entire circuit. If necessary, you can always turn to specialists for help, who always have in stock various photos of devices necessary for such work that can help with connection.
Filling the heating system with water in the video:
Requirements for arrangement and operation
When installing heat supply to a home, it is important to take into account a number of features of an open heating system:
- To ensure normal circulation, the boiler is installed at the lowest point in the line, and the expansion tank at the highest point.
- The optimal place to place the expansion tank is the attic. During the cold season, the container and supply riser within the unheated attic must be insulated.
- The laying of the main line is carried out with a minimum number of turns, connecting and fitting parts.
- In a gravity heating system, water circulates slowly (0.1-0.3 m/s), so heating should occur gradually. Do not allow it to boil - this accelerates the wear of radiators and pipes.
- If the heating system is not used in winter, the liquid must be drained - this measure will keep the pipes, radiators and boiler intact.
- The coolant level in the expansion tank must be monitored and periodically replenished. Otherwise, air pockets will appear in the line, reducing the efficiency of the radiators.
- Water is the optimal coolant. Antifreeze is toxic and is not recommended for use in systems that have free contact with the atmosphere. Its use is advisable if it is not possible to drain the coolant during an unheated period.
Particular attention is paid to calculating the cross-section and slope of the pipeline. Design standards are regulated by SNiP number 2.04.01-85.
In circuits with gravitational movement of the coolant, the cross-sectional size of the pipe is larger than in pumping circuits, but the total length of the pipeline is almost two times less. The slope of the horizontal sections of the system, equal to 2 - 3 mm per linear meter, is suitable only when installing heat supply with natural movement of the coolant.
Failure to comply with the slope when installing systems with natural movement of coolant leads to airing of the pipes and insufficient heating of radiators distant from the boiler. As a result, thermal efficiency decreases
Closed heating system. How to fill with water correctly
Nowadays, many owners of apartments and private houses choose closed heating systems. A closed system is a circuit within which the movement of the coolant is carried out using the movement of the coolant - a pump, that is, forced. A special feature is a membrane-type expansion tank. Essential elements. boiler, tank - membrane, radiators, pump, pipes, also fittings, fasteners and filtering equipment. But very often, buyers of such “closed heating” soon wonder how to fill it and how to close the heating pipes. Below we will tell you how to properly fill a closed heating system with water.
The heating system is filled through the boiler power supply. This is done using an electric pump, as well as a manual crimping machine. The system is filled with prepared network water or antifreeze made using a special method - it is a non-freezing coolant. At this time, air is released throughout the entire internal part of the system (faucets, radiators, vents, etc.). When the required pressure has been achieved, the system can be put into operation. Sometimes there are difficulties in creating ideal pressure. Closing the heating pipes will largely depend on individual wishes, the design solution of the room and the location of the pipes themselves in the apartment, their number and size.
Difficulties often arise when filling with water. If the system is closed, then the expansion membrane tank (pressure inside the tank up to 6 bar) and the safety valve up to 3 bar must also be closed. Special valves must be installed to bleed air in accumulation areas, as well as a valve for feeding and filling pipes and heating equipment. The sequence of actions when filling a closed system is as follows:
Unscrew the screw located on the pump. Use a screwdriver to unscrew the pump system shaft. Tighten the screw tightly. Open the make-up screw. Fill the system until the pressure reaches approximately 0.5 bar. (you can start from 0.3 bar). Be sure to check if there are any leaks during this procedure! Raise the operating pressure in the system to 2 bar. Make sure that there are no leaks anywhere. Bleed the air in absolutely all internal places of the system. The next step is to increase the pressure in the system to about one and a half bar. This will be the most optimal pressure for a closed heating system. If the system undergoes cooling or heating, then the fluctuations should not be significant (from 0.1 bar to 0.5 bar). Watch the range of fluctuations! Sudden changes threaten to break all equipment, pipes and fittings!
There is no water level in such closed systems. The presence or absence of water is controlled using pressure. At normal levels, it should be between one and two bars.
A closed heating system is easy to operate, less susceptible to corrosion and destruction, and is easy to replenish and, if necessary, drain. If you have any questions or find malfunctions in the operation of the heating system (freezing, leaking, etc.), then immediately contact support!
Heating boilers are one of the main types of heating equipment and are devices for heating the coolants entering the heating system to a certain temperature. The coolant passes through a closed circle of the heating system.
Before you start looking for contractors to improve your own balcony, answer yourself one question: what do I want to get as a result of glazing? Perhaps you just want to use this room for drying.
Such cast iron radiators, which are familiar to the majority of the population and were installed many years ago, can no longer fully cope with the functions assigned to them for heating rooms and have a rather unattractive appearance.
Solid fuel heating boilers are devices that heat a room using solid fuels (for example, wood, coke, briquettes or coal). Typically, such boilers are universal, as they can work on anyone.
Security group
A safety group is placed on the supply pipeline at the outlet of the boiler. She must control its operation and system parameters. Consists of a pressure gauge, automatic air vent and safety valve.
The boiler safety group is placed on the supply pipeline before the first branch
The pressure gauge makes it possible to control the pressure in the system. According to recommendations, it should be in the range of 1.5-3 Bar (in one-story houses it is 1.5-2 Bar, in two-story houses it is up to 3 Bar). If you deviate from these parameters, appropriate measures must be taken. If the pressure drops below normal, you need to check if there are any leaks, and then add some coolant to the system. At increased pressure, everything is somewhat more complicated: it is necessary to check in what mode the boiler is operating, whether it has overheated the coolant. The operation of the circulation pump, the correct operation of the pressure gauge and the safety valve are also checked. It is he who must discharge excess coolant when the threshold pressure value is exceeded. A pipe/hose is connected to the free branch pipe of the safety valve, which is discharged into the sewer or drainage system. Here it is better to do it in such a way that it is possible to control whether the valve works - if water is discharged frequently, you need to look for the reasons and eliminate them.
Security group composition
The third element of the group is an automatic air vent. Air trapped in the system is removed through it. A very convenient device that allows you to get rid of the problem of air locks in the system.
Security groups are sold assembled (pictured above), or you can buy all the devices separately and connect them using the same pipes that were used to wire the system.
What to do if the pressure in the system drops and increases
If you notice a decrease in pressure, the first thing you need to do is turn off the pump. And then act based on the pressure gauge readings:
- If the static pressure also drops, there is a leak somewhere. It is necessary to inspect all the elements and eliminate it. Please note that even a very small hole (less than a millimeter) can be the cause, so it can be difficult to find the damage. If the pipeline is long, you can localize the leak area by disconnecting the branches one by one. As soon as the fall has stopped, the area is determined - depressurization on the one that was just turned off.
- If the pressure is stable when the pump is turned off, the pump has failed and needs to be repaired or replaced.
An increase in pressure is observed less frequently, but it also happens. It is usually caused by an increase in temperature in the system, and it rises due to insufficient coolant circulation. But why the coolant circulates poorly needs to be understood.
- First, we check the functionality of the pump. Let's turn it off and watch. If the pressure continues to rise, the problem is not with the pump. If it stabilizes, it’s his fault.
- We clean filters and dirt traps.
- If the pressure still rises, an air lock may have formed - bleed the air in the system.
- If this does not help, we check the condition of the shut-off valves - maybe someone accidentally or intentionally closed it, blocking the flow of coolant.
- Another reason is that due to a breakdown or failure of the automation system, the system is under constant recharge.
Using this algorithm, you can independently determine the cause of the abnormal condition of the heating system and eliminate it.
Expansion tank
The expansion tank is designed to maintain pressure in the heating system depending on the temperature conditions of the system. In closed systems, the expansion tank is a sealed container, which is separated by an elastic membrane. In the upper part of the tank there is air under pressure (or inert gas, which is typical for more expensive models), and in the lower part there is a coolant.
Operating principle of a membrane expansion tank
When heated, the coolant begins to expand, increasing in volume. As a result, the membrane begins to shrink as part of the coolant enters the tank. If there were no membrane and air under pressure in the tank, there would be no place for the liquid to go, and the pressure in the system would rise, and significantly. We should not forget that this is a closed heating system. Without an expansion tank, it would be difficult to control the pressure in the system, constantly either bleeding off the coolant or adding it to the system. At low temperature operating conditions of the system, coolant would have to be added, and if the temperature increased, it would have to be bled off, since the pressure would go beyond the optimal limits.
As soon as the system begins to cool and the volume of coolant decreases, in theory the pressure in the system should decrease. To prevent this from happening, the pressure may drop so much that it goes beyond the lower limit mark. In this case, the boiler may stop, as this will indicate an emergency mode. This is where the air in the expansion tank comes to the rescue, compensating for changes in the volume of coolant. Despite the fact that the volume of coolant has decreased and the pressure in the system should drop, the air that is under pressure compensates for this difference, and the pressure in the system is at the same level, without going beyond normal limits. It should be said that the shape of the membrane that is located in the tank does not in any way affect the characteristics of the system as a whole.
Types of membranes for expansion tanks in closed systems
Calculation of expansion tank volumes
As a rule, the volume of the expansion tank should be at least 10 percent of the total coolant volume if the coolant is water. In other cases, the volume of the tank should be 10 percent plus another 50 percent of the result obtained.
Using this example, you can calculate the volume of the expansion tank:
- If the volume of the heating system is 30 liters.
- The volume of the expansion tank will be 3 liters.
- If non-freezing liquid is used, then 3+3*0.5=4.5 liters.
When purchasing a boiler, you should pay attention to this indicator, although each boiler is designed for a certain power, therefore the expansion tank (built-in) is designed for a certain amount of coolant. This is only necessary if the heating system is installed independently, and the heating boiler is designed for an unknown power.
What to pay attention to
Expansion tanks in red and blue colors are sold at retail outlets. Blue tanks are designed for cold water, so they are not suitable for a heating system.
There are also tanks with a permanent membrane, as well as tanks with the ability to replace the membrane. Tanks with a non-replaceable membrane are much cheaper, but if the membrane is damaged, you will have to buy a tank, and in the case of tanks with a replaceable membrane, you will only have to buy the membrane.
Expansion tank
Installing an expansion tank
It is better to install the expansion tank on the return pipeline in front of the circulation pump. To do this, a tee should be installed in this location, after which a piece of pipe is connected to it. Then, an expansion tank is installed using fittings. It is better to place the tank at some distance from the circulation pump so that it does not affect the operation of the expansion tank. The section of the heating system where the expansion tank is connected must have a rectilinear shape.
Installation diagram of an expansion tank for membrane-type heating
A ball valve should be installed at some distance from the tee, which will allow you to replace the expansion tank without stopping the functioning of the heating system. The connection point of the tank should be thought out so that it can be removed with minimal time. An American type (flare nut) is better suited for this purpose, which allows you to remove the tank by tightening only one nut.
It is important to know! Almost all models of gas boilers have an expansion tank, so there is no point in installing another one.
An empty expansion tank is light in weight, but when filled with coolant, it has an impressive weight. In this regard, it is necessary to consider a tank mounting system, and a reliable one.
How and where to install an expansion tank for heating in a closed system