The construction of an autonomous gravity-type heating network is chosen if it is impractical, and sometimes impossible, to install a circulation pump or connect to a centralized power supply.
Such a system is cheaper to install and is completely independent of electricity. However, its performance largely depends on the accuracy of the design.
In order for a heating system with natural circulation to function smoothly, it is necessary to calculate its parameters, correctly install the components and reasonably select the water circuit design. We will help in resolving these issues.
We described the main principles of operation of the gravity system, provided advice on choosing a pipeline, and outlined the rules for assembling the circuit and placing working units. We paid special attention to the design and operation features of one- and two-pipe heating schemes.
Heating systems with natural circulation
The natural circulation heating system became widespread in the pre-war period due to its efficiency, simplicity and reliability. Most often, this type of heating system is used in dachas, as well as in country houses due to frequent power outages at such facilities. Such systems are conventionally divided into two types - with bottom and top water supply. To determine the choice of the type of heating system, it is necessary to consider their differences, characteristics and scope of application.
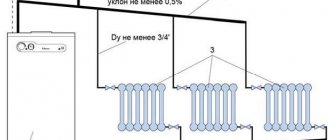
Schematic diagram of heating with natural coolant circulation
Heating systems with natural circulation
How does a properly assembled circuit work?
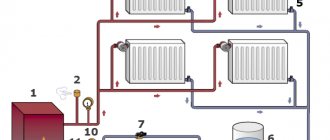
When implementing the classic one-pipe scheme (“Leningrad”), when a main pipe is laid under the radiators, the situation is different. The moving coolant, encountering the first tee on its way, is distributed into two flows in accordance with the values of the hydraulic resistance of the direct path and the side outlet of the tee. Due to the greater hydraulic resistance of the side outlet, a small part of the total coolant flow flows into the radiator (the usual “flow coefficient” is 0.2-0.3). This small part cools down inside the battery by several degrees, as shown in the figure below, mixing at the outlet with the main uncooled flow. Its resulting temperature turns out to be higher than when the entire volume of liquid is passed through the heating device.
Distribution of the coolant in the radiator piping of the “Leningrad” scheme.
When moving along the contour, the temperature of the liquid still decreases, but to a lesser extent, to a temperature of no longer 35 °C, but approximately 45 °C, i.e. The batteries in the chain are more evenly heated. Experts express the opinion that the single-pipe scheme (“Leningradka”) allows for uniform heating of up to 10-11 radiators in the circuit (ten sections in each device).
Heating systems with top water supply
The coolant - in this case water - is heated and supplied to the upper part of the heating system through a pipeline. The pipe used to supply water must have a larger diameter compared to the pipes that are responsible for supplying water to the radiator. This is necessary to achieve the greatest resistance to heat exchange. Horizontal pipes must be installed with a minimum slope of one centimeter per adjusted meter.
The expansion tank must be installed at the top of the system: it will perform the function of receiving steam and excess heat - this is necessary due to the property of water to expand when heated and turn into steam. The tank must have a drain valve and a cap or valve at the top. After the water is heated, it is distributed through the supply pipe to the vertical risers and into the radiators.
Tip: if you are going to use a heating system with natural circulation of water, remember that radiators must be connected using a diagonal method
After direct heating of the room, the water passes into the boiler through a specialized pipe - the return. Here it is heated again and the cycle of water movement is repeated. The heating boiler is located in the lowest part of the system, under the radiators. Typically, these elements are installed in boiler rooms, for which basements are allocated.
What types of heating schemes are there?
There are only two types of natural circulation systems:
- Single pipe system.
The pipe from the radiator goes directly into the boiler. - Two-pipe heating system.
The water that has cooled does not go straight through the pipe into the boiler, but first it goes into another line and then goes back into the boiler.
If the wiring diagram contains a vertical riser, then such a heating system is more convenient, since the heating device can be installed on each floor. But in a two-story house, gravitational heating, which has horizontal wiring, is considered more profitable.
Rice. 2
The most important thing you need to know when installing gravity heating in a house is that radiators have little hydraulic resistance.
The best options for installation are:
- Radiators made of cast iron.
They have the lowest hydraulic resistance. - Radiators made of aluminum.
- Bimetallic radiators.
They are also good for heating, but you need to take into account before purchasing that the internal diameter must be at least ¾.
It is better to connect the batteries in the house to each other using different types of connections - this way the system will work better.
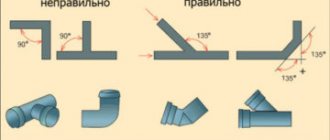
Pipes also need to be chosen wisely, since not all are suitable for a gravity system. All parameters must be complied with. You must first look at what material the pipes are made of, and then at the diameter of the pipe itself. The cheapest option is simple metal pipes. But since they are rough inside, and after some time they will become even rougher (from corrosion, etc.), they need to be purchased with the largest diameter.
The best options for a gravity heating system for a two-story house are:
- Metal-plastic pipes.
- Reinforced polypropylene pipes.
In the first option, the pipes have so-called fittings that narrow the clearance, and this is unacceptable for gravity heating. Therefore, the most ideal option is to install reinforced polypropylene pipes. But there is a “but” here too. Reinforced pipes cannot withstand temperatures exceeding 100˚C, but metal-plastic ones can. Whatever option you choose, be sure to make sure that it is a quality product.
Rice. 3
Heating systems with bottom water supply
A system in which coolant is supplied from below is usually used for heating houses where there is no attic space or access to it is closed. The main difference of the presented heating system is that the pipes are laid under the radiators. There is also an expansion tank, which is installed in the upper level of the system; Usually utility rooms are used for this purpose. If there is no water circulation in the heating system, which should occur naturally, then it is created by force.
Hot water supply options
To ensure the availability of hot water at the tap in a private home, there are several options:
It is possible to choose a flow-through or storage water heater, which will operate from a heating boiler or independently from it. You can choose a gas or electric water heater. A instantaneous water heater running on gas is usually called a geyser.
Installing a hot water supply system in a private house or cottage, first of all, involves installing a water heater.
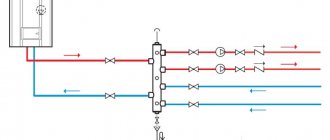
Heating systems with forced circulation
A standard forced circulation heating system operates using the same connection methods. The difference is that due to the large extent of this system or the lack of natural conditions to create an inclination of the pipes, it is necessary to include a pump in the system. The circulation pump is mounted to the main pipe - this helps to increase the service life of the heating system. Using a pump helps not only increase heating efficiency, but also reduce the number of lines. A forced circulation system has the ability to heat not just several rooms, but even a house with several floors.
Heating systems with forced circulation
In order to produce high-quality operation of this type of system, a continuous power supply is required. Installation of a circulation pump in the heating system is required in order to create forced circulation of water in a closed loop. In this type of system, the pump is the central component among the equipment. It should be noted that the circulation pump may not have significant performance: its power is only needed to direct the liquid into the supply pipe. The same pressure pushes the water in the opposite direction, since the system is closed.
The circulation pump is necessary to ensure uninterrupted operation of the heating system, therefore it must fully comply with the system into which it is installed. Due to its functionality, this type of pump can be widely used in a wide variety of pipelines.
Pipe diameter
To calculate the diameter of the pipes, you need:
- Perform a thermal calculation of the premises and add about 20% to the result.
- Calculate the cross-section of the pipeline based on the ratio of the thermal power and the internal cross-section of the pipe (the values are indicated in the SNiP tables).
- Select the pipe diameter based on the thermal calculations performed and taking into account the pipe material. For steel pipes, the minimum internal cross-sectional size is 50 mm.
To make gravity flow more intense, the following principle is used: the diameter of the supply pipe after each branch should be 1 size smaller than the previous one. The return must be assembled with an extension.
Thus, the calculation allows us to determine the minimum diameter of the supply and return pipes; relative to this value, the parameters of the pipes in different sections of the system are determined according to the prepared diagram for a one-story or two-story house.
Selecting a circulation pump for a heating system
In order to select a circulation pump for the heating system, it is necessary to make the appropriate calculations. Please note that within an hour, this element will drive three times more water than its total volume in the system. Thus, the total volume of a suitable amount of liquid is on average 10 liters per 1 kilowatt of heating boiler power. The required pump model for the heating system and its power are determined by pressure and flow parameters. The pressure must be equal to the hydraulic resistance of the heating system.
Circulation pump
Typically, the fluid pressure velocity in systems with forced circulation is quite low, which gives the right to judge low losses of hydraulic resistance, which usually do not exceed 2 meters. It is quite difficult to calculate the exact resistance, so the performance of the circulation pump is determined by the midpoint. In order to calculate productivity, the size of the area of the heating object and the power of the electricity source are also taken into account. It should be remembered that a pump is only needed in a system with forced circulation; a system with natural circulation does not need it.
Preface
The methodological manual briefly outlines the basics of the theory of natural circulation in boilers and steam generators, provides a methodology for conducting hydraulic calculations of boilers with natural circulation and assessing the reliability indicators of natural circulation. The appendix of the manual contains graphs, tables and nomograms necessary for completing the course work. To carry out calculations, it is necessary to have a theoretical drawing of the boiler body, therefore the application includes a drawing of the body of a high-pressure boiler of type KVN-98/64 (KVG-3).
The need to publish this methodological manual is due to the fact that in the literature describing the principles and methods of calculating steam boilers, only the general principles of carrying out EC calculations are set out, without a description of the calculation methodology itself.
When writing the manual, the method of calculating natural circulation set out in the textbook by A.I. Indeikin and Yu.V. Aleksandrovsky was taken as a basis. and others. “Ship steam boilers. Fundamentals of theory and calculations", publishing house of the Leningrad Higher Naval Engineering School named after. IN AND. Lenin (now the Naval Engineering Institute) and based on the calculation method developed by the Central Boiler-Turbine Institute, St. Petersburg. In the manual, the calculation method is presented in tabular form, which is more convenient for the student audience.
Completing course work on the hydraulic calculation of a steam boiler will allow you to more fully understand the essence of the physical processes occurring during the operation of a steam boiler and their dependence on various factors.
Installing a circulation pump: what should you pay attention to?
To install the circulation pump yourself, use the following recommendations:
- To extend the service life of the entire system, install a filter to clean the liquid in front of the circulation pump. the filter must be installed on the suction pipe;
- do not choose a circulation pump for the heating system with greater power and performance than required. Otherwise, there is a risk of encountering additional unpleasant noise during its operation;
- Never turn on the pump before filling the heating line with water and removing air from it, this can lead to equipment failure;
- install the pump in an area as close as possible to the expansion tank;
- When installing the pump in a closed heating system, if possible, install the pump on the return line. This is due to the fact that this section of the highway has the lowest temperature.
Installing a circulation pump
Advice: before starting the heating system, it is necessary to rinse it with water to remove various foreign particles. Do not forget that even short-term idle operation of the circulation pump in the absence of liquid in the system can result in failure of the pump itself and other elements of the system.
Almost all circulation pumps on the market today are equipped with a connection to the automatic control of heating boilers. This function provides owners with the opportunity to regulate the air temperature in a heated facility by changing the speed of water movement in the heating system. In order to take into account the level of heat consumption in the premises, special meters are installed, thanks to which heat losses arising due to wear and tear of the lines are controlled. The heating circuit itself is not subject to any changes.
You can learn how to install the circulation pump yourself by watching the video:
Materials
Such bathtubs are usually made from two types of materials:
- acrylic;
- metal (cast iron and structural steel).
There are bathtubs made from innovative quarry, as well as from ceramics, wood and artificial stone. But this is more exotic than everyday practice.
The material most often determines the shape of the font. Acrylic is very plastic and allows you to make a product of any shape at the request of the customer. Acrylic bathtubs can be:
- regular shape (rectangular, square);
- round, bowl-shaped;
- irregular shape (asymmetrical);
- faceted (number of faces at customer's choice);
- oval;
- corner.
This is, of course, not a completely complete list. The client’s imagination and the capabilities of the technology suggest a wide variety of options.
Metal does not provide the customer and manufacturer with such freedom. Cast iron bathtubs most often have the shape of a square or rectangle. Steel ones have a little more options because steel is more ductile. But large sizes greatly limit the possibilities. In addition, cast iron bathtubs, even of standard sizes, weigh a lot.