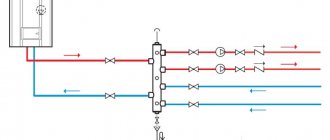
Single-pipe heating of multi-apartment residential buildings The structure of the system is a central element (boiler), a pipe to which the radiators installed in the premises are connected in series, as well as a straight pipe through which the water passed through the radiators is returned. The reverse scheme is also possible, when the water first rises through a straight pipe and descends through the batteries. The general principle of operation of a single-pipe system: water flows through a ring of pipes, gradually releasing heat and returning to the boiler cooled. Each radiator has a bypass pipe, and if the radiator is closed, then water flows only through the bypass. Typically the bypass is made narrower than the main pipes to prevent water from flowing exclusively through the bypass.
To modernize a single-pipe heating system of a multi-story building, the diagram can be supplemented:
- radiator regulators and thermostatic valves; balancing valves and ball valves.
Additions make it possible to make the system more balanced and control the temperature in the radiators.
Advantages and disadvantages of a single-pipe system
Compared to the two-pipe version, single-pipe systems require less materials and the design of such a system is simpler. and, accordingly, less financial investments are required. Minuses:
- if you reduce the heating in one radiator, the heat supply will also decrease in others connected to it; the coolant must always be under high pressure; When blocking one battery, the throughput of the entire riser is often reduced, since the outline is usually narrower. the system must be vertical.
When installing a single-pipe system in multi-story buildings, additional elements must be used to distribute heat evenly and maintain temperature. Two-pipe system The two-pipe system has several varieties, but the principle of operation is always the same. The coolant (hot water) is supplied upward through the riser, and from the main riser to the radiators in the rooms. From the radiators, water flows through return lines and lines into the pipeline, and from there again into the heating device. The design of a two-pipe system: a heating tank and two pipes, a riser for supplying coolant and a second pipe for draining excess liquid. Compared to a single-pipe system, a two-pipe system has the ability to regulate the supply and degree of heat in different rooms independently of others. Disadvantages include greater consumption of materials compared to a single-pipe system. Which one to choose? The choice of system will depend on many factors, including cost. A single-pipe system will cost almost half as much, since it requires less building materials. But at the same time, installation of single-pipe heating requires only top wiring, while two-pipe heating can be top or bottom. Two-pipe systems are universal because they are suitable for installation and operation in both single-story and multi-story buildings. Single-pipe systems will require more serious and complex calculations and planning when installed in a multi-story building.
We have already covered in sufficient detail various types of heating equipment and their applications in articles on our website.
In particular, we dwelled in detail on the features of the operation of traditional gas boilers and condensing-type boilers, universal solid fuel boilers and pyrolysis-type boilers, solar thermal heating systems based on solar collectors, and various types of heat pumps. We carried out a detailed comparison of equipment from different brands, economic aspects of using equipment for apartments and private houses. In this material, we would like to talk in more detail about two heat distribution schemes, regardless of the heat source, and also find out which system is better suited for the consumer.
Single pipe heating system
The single-pipe heating system was developed in the Soviet Union, when mass housing construction gained such momentum that engineers needed to come up with a more affordable heating system that was quick and cheap to install. The single-pipe heating system became just such a solution - minimal consumption of materials and simple installation.
How does coolant circulate in a one-pipe system?
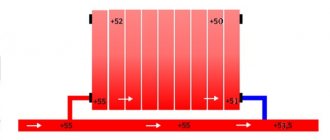
The coolant is heated in a heating boiler (or other heat source) and then supplied to heating elements (a radiator or convector can be used) installed in series. That is, the coolant, having passed through one heating element, enters the next. Thus, with each radiator passed through, the water becomes colder and in the last element of this chain the water will be the coldest.
All the disadvantages of a single-pipe system follow from this.
By adjusting the water flow in one of the radiators in a single-pipe heating system, the flow in the following heating elements of this system is also reduced.
This means, if the coolant moves from the kitchen to the plumbing unit (for example), and we want to reduce the temperature of the internal air in the kitchen by changing the water flow in the radiator with a thermostatic valve, we automatically reduce the air temperature in the bathroom unit, since the water flow there is also the radiator has decreased.
So, in a single-pipe heating system, it is impossible to regulate the heating intensity of the radiators.
The second important disadvantage is that the calculated pressure loss in a one-pipe system is greater than in a two-pipe system. This means that for such a system it is necessary to install a more powerful pump in order to “push” the coolant through the heating system.
In large residential buildings with a single-pipe heating system, the coolant, having reached the last heat consumer, cools down greatly. It is worth considering this when selecting radiators. Usually, all the last radiators in the chain of a single-pipe system are selected with a larger number of sections than at the very beginning.
Advantages of a one-pipe system.
A huge advantage of a one-pipe system is its significantly lower cost compared to a two-pipe system. A single-pipe system uses fewer pipes, turns, tees, etc.
Less installation work.
Two-pipe heating system
In a two-pipe heating system, the coolant is supplied to each radiator through one pipe and removed through the other.
In operation, a two-pipe system is much more convenient than a single-pipe one. Since it is possible to regulate the water flow in each of the radiators in the heating system, without in any way affecting the following heating elements. This option is now preferred, because ultimately better controllability reduces operating costs.
Disadvantages of a two-pipe system:
One of the main disadvantages is its cost.
Installation is more difficult than in a single-pipe.
Advantages of a two-pipe system:
The temperature of the water that enters each of the radiators is the same (except for heat losses along the route, but they are insignificant)
Convenient regulation of the internal air temperature by changing the water flow rate with a thermostatic valve.
If one heating device fails, it does not affect the operation of the others.
For these reasons, Alter Air specialists primarily offer a two-pipe system to clients when they plan to start calculating the heating system.
Heat supply of a multi-storey building
Heating distribution unit for an apartment building
Heating distribution in a multi-storey building is important for the operational parameters of the system. However, in addition to this, the characteristics of the heat supply should be taken into account. An important one is the method of supplying hot water - centralized or autonomous.
In most cases, a connection is made to the central heating system. This allows you to reduce the current costs in the estimate for heating a multi-storey building. But in practice the level of quality of such services remains extremely low. Therefore, if there is a choice, preference is given to autonomous heating of a multi-storey building.
Autonomous heating of a multi-storey building
autonomous heating of a multi-storey building
In modern multi-storey residential buildings, it is possible to organize an independent heat supply system. It can be of two types - apartment-based or communal. In the first case, the autonomous heating system of a multi-storey building is carried out in each apartment separately. To do this, make independent piping and install a boiler (most often a gas one). A common house installation involves the installation of a boiler room, which has special requirements.
The principle of its organization is no different from a similar scheme for a private country house. However, there are a number of important points to consider:
- Installation of several heating boilers. One or more of them must perform a duplicate function. If one boiler fails, another must replace it;
- Installation of a two-pipe heating system of a multi-storey building, as the most efficient;
- Drawing up a schedule for scheduled repairs and maintenance work. This is especially true for heating heating equipment and safety groups.
Taking into account the peculiarities of the heating scheme of a particular multi-storey building, it is necessary to organize an apartment-by-apartment heat metering system. To do this, energy meters must be installed on each incoming pipe from the central riser. That is why the Leningrad heating system of a multi-storey building is not suitable for reducing operating costs.
Conclusions - which system is better?
A two-pipe heating system requires twice as many shut-off valves and pipelines; its cost and installation are certainly more expensive. But at the same time, it allows you to regulate the heat supply to each room with high precision, which means that when using it, you get greater comfort multiplied by economical energy consumption (gas, electricity, solid fuel).
A professionally designed single-pipe heating system can provide acceptable comfort, however, ultimately, the minor savings on materials when installing it are lost over the next couple of years of operation. This is especially noticeable for large private houses, where the issue of temperature regulation for various rooms is even more pressing.
As for the installation of such systems, there are several options for connecting radiators. You can find out more about this in the “Installation of a heating radiator” section. Also, from Alter Air you can order not only the necessary equipment, but also the entire installation of the heating system.
Congratulations, you get a 10% discount within an hour
Tags: heating
Heating systems are divided into two types:
- Open type; Closed type.
Radiator connection options
When installing a one-pipe heating system, use the following options for connecting radiator heat exchangers:
Lower. The lower connection is most often used in Leningrad. Although it is considered not the most successful in terms of the efficiency of heat exchange between batteries, due to the lowest consumption of pipe materials and the aesthetic appearance of the open line, this method has become quite widespread.
Also, with a bottom connection, all contaminants at the bottom of the batteries are better washed away, which increases their service life and reduces the likelihood of narrowing of the passage channel due to deposits.
Diagonal. Connecting batteries diagonally is considered one of the best options for heat transfer efficiency. When organizing it, the supply pipeline is connected to the upper branch pipe, and the return line to the lower terminal on the opposite side.
In addition to high thermal efficiency, the diagonal also ensures more uniform heating of the entire area of the radiator heat exchangers.
The diagonal connection diagram is used in single-pipe Leningrads and when connecting multi-section batteries to a vertical riser.
Rice. 3 Examples of lateral connection of steel radiators
Related article:
Bottom radiator connection unit - how to choose and install correctly . More information about the bottom connection of radiators and the special fittings used for this can be found in a separate article on our website.
Lateral. Connecting radiator heat exchangers on one side is mainly used in cases where the central pipeline is laid vertically. This option can be observed in gravity individual systems and apartments of multi-storey communal buildings. In the latter case, the coolant can enter the radiator from above or below.
To avoid emergency situations with disruption of the circulation of heating fluid along the circuit when vertically located batteries are connected sideways, a bypass jumper must be installed between the supply and return pipelines.
The main disadvantages of side connections are often insufficient heating of the sections furthest from the riser in long radiators.
Rice. 4 Features of series connection of heat exchange devices
Open heating system
An open expansion tank is used
Operating principle: the coolant heated by the boiler rises up through the pipes, since the pressure at the outlet is higher than at the inlet. Thus, water circulates under the influence of pressure differences.
Passing through the radiators, it cools down and again rushes to the boiler. An open expansion tank is required because water expands when heated. You can do without a pump. Installation requirements:
- The boiler is installed in the lowest place (which needs to be taken care of in advance), and the expansion tank is installed in the highest (most often in the attic); Heating radiators for an open system must be installed in steel or cast iron; To create a pressure difference, the diameter of the outlet pipe must be more than at the end of the supply. To ensure circulation, pipes must be installed at a slope of 0.005-0.01%.
The open heating system scheme is used in small areas (up to 150 sq.m.) and mainly in one-story houses. For large premises, this option is considered impractical and unprofitable from an economic point of view.
The main advantage: independence from electricity, even if the electricity is turned off, the coolant circulation will not stop. Also undeniable advantages are autonomy, low cost, ease of maintenance, quick start and stop.
Disadvantages: bulkiness, difficulty of installation, susceptibility of radiators to corrosion, likelihood of airing (as the liquid in the tank evaporates), slow heating, low efficiency.
Operating principle of water heating
The basis for the functioning of the heating system is the continuous circulation of the medium, which acts as a coolant. While moving through the pipes from the heating source (boiler) to the heating devices and back, thermal energy is released and the premises are heated. Not only water, but also air, steam or antifreeze (in houses of irregular residence) can be used as a coolant. However, water heating systems are most widespread.
When arranging traditional heating, physical phenomena and laws are used - thermal expansion of water, convection and gravity. After heating through the boiler, the coolant expands, causing pressure to build up in the pipeline. The medium loses its density and weight. The heavier and denser cold water below pushes the heated portions upward: this explains the exclusively vertical positioning of the supply pipe leaving the boiler.
Thanks to the created pressure and convection, the coolant circulates inside the batteries, gradually giving them its heat. This exchange of energy leads to heating of the premises. The water returning back is usually at a low temperature: after this, the cycle begins again.
Heating that operates due to natural circulation is also called gravity and gravity. Stable circulation of liquid is ensured by the inclination angle of the horizontal pipes of the system. Usually this is 2-3 mm per linear meter. As a result of heating the coolant, hydraulic pressure is created in the line. Since water can be compressed, even a slight excess of the norm is fraught with serious consequences. To prevent this, any heating circuit is equipped with a special compensating device - an expansion tank.
Closed heating system diagram
Operating principle: the boiler heats the coolant (water or antifreeze), increasing its volume; the excess liquid that appears moves into the expansion tank, which resembles a capsule - a rubber membrane divides it into two parts: the first part is a water chamber, the second is an air gas chamber filled with nitrogen under pressure. The heated liquid, entering the tank through the opening valve, equalizes the pressure in the entire system as a whole (the volume of air decreases, so the pressure increases).
The pump pushes the water back out. And its work in tandem with a thermostat will allow you to heat the room if the temperature drops below the set one. There are no restrictions on the use of this scheme in terms of the area of the heated house and the number of its floors. It can be used both in private homes and in factories.
The main difference is that the movement of the coolant is forced, i.e.
e. using a pump. Another distinctive feature is the presence of a closed expansion tank (membrane).
Advantages of a closed heating system
:
- Non-corrosion of pipes and radiators; Long service life of the boiler due to the slight difference in fluid temperatures at the inlet and outlet; Possibility of using antifreeze (and it does not cause scale deposits and corrosive processes, does not freeze if turned off in the cold season); Fast heating; Great heat transfer , i.e. high efficiency.
There is increased pressure in a closed heating system even at the highest points, which reduces the likelihood of air locks to almost zero.
The only disadvantage is the dependence on electricity.
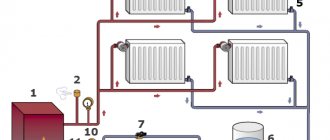
Single-pipe and two-pipe heating systems
The heating system of a private house can be two-pipe or single-pipe.
In the first case, the functions of the pipes are as follows: one supplies hot water, the second pumps it out.
It is possible to maintain a stable temperature when supplied to all batteries. Moreover, if you install a regulator on each device, then the temperature can be adjusted at your discretion in each room separately. A single-pipe closed-type heating system is a simpler method. The coolant is sequentially supplied from battery to battery, gradually cooling along the way, i.e.
That is, at distant points the temperature will be lower than at the beginning. But the cost of components and installation itself is much less.
Specialists from the studio “We’ll fix everything!” carry out installation of heating systems of any complexity. Our specialists will help you draw up a system diagram and select the necessary equipment.
Sometimes it is very difficult for an uninformed homeowner to decide on the choice of a heating system.
This problem is as old as time. The debate about which is better - a single-pipe or two-pipe heating system - has been going on for a long time and does not subside to this day. In our article we will try to objectively and impartially approach the issue by considering both schemes in relation to a private home.
Scheme of improvement of a system with one pipe in a two-story house
To equip a two-story house with good heating, you can use a wiring method, it is called a “single-pipe wiring system.” In this case, it is planned to place the supply pipe at the top, in other words, it will be located above the batteries being serviced.
Pipe distribution begins vertically with a riser, which is equipped with an expansion tank with an air vent pipe on top. On any of the 2 floors there is a horizontal section of thermal communications, to which heating radiators are connected. The pipe extending from the riser has a slope, thanks to which the hydrodynamics of natural circulation improve. The batteries are connected to the coolant supply from above, and the cooled liquid leaves from below, which is discharged into the return line.
Pros and cons of a single-pipe system
To begin with, let us recall that a single-pipe circuit represents one horizontal collector or vertical riser, common to several radiators connected to it by both connections.
The coolant, circulating through the main pipe, partially flows into the batteries, gives off heat and returns back to the same collector. The next radiator receives a mixture of chilled and hot water with a temperature reduced by several degrees. And so on until the very last radiator.
The main difference between a one-pipe heating system and a two-pipe one, which gives it some advantage, is the absence of separation into supply and return pipelines. One line instead of two means fewer pipes and work on their installation (punching walls and ceilings, fastening). In theory, the total cost should be lower, but this is not always the case.
Below we will explain why. Thanks to the advent of modern fittings, it has become possible to regulate the heat output of each radiator automatically. True, this requires special thermostats with a larger flow area. But even they will not rid the system of its main drawback - cooling of the coolant from battery to battery. As a result, the heat transfer of each subsequent device decreases and it is necessary to increase its power by increasing sections.
And this increases the cost. If the main line and the supply to the device are of the same diameter, then the flow will be divided approximately equally. This cannot be allowed, the coolant will cool down greatly in the very first radiator. In order for a third of the flow to get into it, the size of the common collector must be made twice as large, and around the entire perimeter. Imagine if this is a two-story house with an area of 100 m2 or more, where a DN25 or DN32 pipe is laid in a circle.
This is the second increase in cost. If in a one-story private house it is necessary to ensure natural circulation of water, then a single-pipe heating system differs from a two-pipe heating system by the presence of a vertical accelerating manifold with a height of at least 2 m, installed immediately after the boiler. An exception is pumping systems with a wall-mounted boiler suspended at the required height. This is the third increase in cost. Conclusion: A single pipe system is complex.
You need to very well calculate the diameters of the pipelines and the power of the radiators, and think carefully about the laying of the lines. Then it will work efficiently and reliably. The statement about the cheapness of the “Leningradka” is very controversial, especially when you decide to assemble a circuit from metal-plastic pipes, you will simply go broke on fittings. Metal and PPR will cost less.
Pros and cons of a two-pipe system
All people who have the slightest understanding know the difference between a single-pipe and a two-pipe heating system. It lies in the fact that in the latter, each battery is connected with one line to the supply line, and the second to the return line.
That is, hot and cooled coolant flows through different pipelines. What does this give? Let's present the answer in the form of a list:
- distribution of water over all radiators with the same temperature; accordingly, the number of sections does not need to be increased; regulation and automation of the entire system is much simpler; pipe diameters for forced circulation are at least 1 size smaller than with a single-pipe scheme.
As for the disadvantages, there is only one that deserves attention. This is the consumption of pipes and the cost of laying them. But these pipes are of smaller diameter with a relatively small number of fittings.
A detailed calculation of materials for one and the other system, as well as the nuances of their operation, are shown in the video: Conclusion. The advantage of a two-pipe heating system is its simplicity. The owner of a small house, who has correctly determined the power of the batteries, can randomly make the wiring with a DN20 pipe, and make the connections from DN15 , and the circuit will work normally. As for the high cost, it all depends on the material used, the ramifications of the system, and so on. Let us take the liberty of asserting that a two-pipe scheme is better than a one-pipe one.
Forced circulation
Neutralization of almost all of the listed disadvantages is achieved by introducing a circulation pump into the system. As a result, the coolant receives an additional impulse, thanks to which it effectively overcomes the hydraulic resistance of the pipeline. Single-pipe heating system wiring is currently the most popular solution in private homes.
The installation location for the pump can be any section of the highway. However, it should be borne in mind that when rubber elements (gaskets) are exposed to hot water, the service life of the pump is noticeably reduced. Therefore, they try to install the device on the return pipe, because The coolant there is not so hot. A coarse filter must be installed in front of the pump to prevent various contaminants from entering the mechanism. When connecting all instruments and devices, it is recommended to use shut-off valves and bypasses. This will significantly simplify repair and maintenance activities at individual units: in this case, there is no need to stop the entire system and completely drain the coolant.
Strengths of forced circulation heating circuits:
- Possibility of using more complex branched circuits, leading to an increase in the total length of the circuits.
- There is no need to increase the diameter of the pipes. Thanks to the pump, sufficient pressure is created inside the system for movement and uniform distribution of liquid.
- The circulation has a stable speed. This indicator is not affected by the level of heating of the coolant and the installation of the accelerating manifold.
- There is no need to organize inclination angles on horizontal sections of the pipeline, because A pump is used to stimulate the movement of the coolant.
- It becomes possible to insert control devices on all batteries, which ensures the maintenance of an optimal heating level, reducing energy consumption and heating costs.
There are also disadvantages:
- The need for electrical power.
- Noise from a running pump.
- The need for additional capital investments (when compared with the gravity scheme).
Neutralizing them usually does not cause difficulties. To maintain a stable energy supply, an autonomous electric generator is being installed. Systems that provide the possibility of switching to a natural circulation mode have proven themselves very well. To reduce the noise from a running pump, it is usually installed in a non-residential area.
How to convert a one-pipe heating system into a two-pipe one?
Since the difference between one-pipe and two-pipe systems is the separation of two flows, technically the conversion is quite simple. It is necessary to lay a second pipeline along the existing main, whose diameter can be taken 1 size smaller. The end of the old collector must be cut off near the last device and plugged, the remaining section up to the boiler must be connected to the new pipe.
The result is a scheme with a passing movement of water, only the coolant leaving the batteries needs to be directed into a new main. To do this, one supply section of each radiator will have to be reconnected from the old collector to the new one, as shown in the diagram:
You must understand that during the remodeling process you may encounter difficulties such as lack of space for the second pipe, the inability to punch a hole in the wall or ceiling, and so on. Therefore, before starting such a reconstruction, you need to think through everything carefully. It may be possible to restore normal operation of the existing single-pipe system.
New single-pipe heating systems for apartment buildings
Russian new buildings are equipped with single-pipe radiator units with thermostatic valves (thermostats). They look as shown in the photo below.
Radiator assembly with thermostat.
Such heating systems are 30–40% cheaper than their two-pipe counterparts and have high hydraulic stability. But do they provide a level of operating comfort for two-pipe circuits, determined by the following components:
- automatic mode for stabilizing the set temperature in each room;
- overall energy savings in the heating system;
- possibility of hidden pipe laying;
- apartment heat metering.
Let's evaluate the single-pipe heating option according to these criteria.