If we try to characterize the bypass in the heating system from the point of view of the average person, then it will be a kind of jumper in the form of a piece of pipe that is installed between the direct and return wiring of the heating radiator.
Bypass in the heating system
The heating system of a residential building contains a list of components, and disruption of at least one of them can cause not only interruptions in operation, but also destruction. In addition, it is imperative to ensure comfortable repair and replacement of various system components. This is precisely the purpose of a bypass in a heating system. This is a section of parallel pipeline. For example, when installing a section of pipeline in parallel with the radiator, you can maintain the functionality of the entire heating system when cleaning, repairing or replacing the unit.
Bypasses with manual adjustment
Bypasses that are adjusted manually (manual bypasses) are equipped with ball valves. The use of ball valves is determined by the fact that they do not change the pipeline capacity at all when switching, since the hydraulic resistance in the system does not change. This quality makes the ball valve an optimal option for bypass.
Shut-off valves of this type allow you to regulate the volume of liquid that passes through the bypass section. When the tap is closed, the coolant moves in full along the main line. The operation of ball valves has one important nuance - they need to be turned regularly, even if there is no need to adjust the system. This is due to the fact that if left stagnant for a long time, the taps may become tightly stuck and will have to be replaced. Sometimes a heating system feed valve is also installed, which plays a significant role.
What it is
It is not difficult to understand that even initially insignificant defects in the operation of engineering systems and communications can turn into serious problems. The discomfort and even danger to health caused by heating malfunctions can hardly be overestimated. That’s why attentive, thoughtful homeowners should be busy preventing such problems. The bypass, which is widely used in heating circuits and plumbing systems, plays a significant role in it. Its design is not particularly complicated - it is just a jumper in the form of a pipe, supplemented with control devices.
The bypass valve ensures the passage of liquid (drinking water or coolant in the heating system) away from one or another technical unit. Quite simply, this is a workaround for water in case of unforeseen situations. If everything works normally, the flow moves calmly and measuredly along the jumper. But under certain conditions, the locking element closes and the liquid rushes away from the previous trajectory. This effect is achieved because the diameter of the bypass is invariably smaller than that of the pipe that supplies water to it.
The use of such a device allows:
- make service work on pipelines much easier;
- increase the efficiency of equipment;
- reduce unproductive energy costs;
- radically solve the problem of filling pipes and other water infrastructure with air;
- guarantee relatively stable performance even in unusual situations.
Sometimes you may come across arguments that installing a bypass is unprofitable. In fact, this is not so - when installing such a device, you can significantly save energy. The reduction in water supply to the batteries is up to 35%, and therefore it is possible to reduce thermal energy consumption by approximately 15%. Since many real systems consume a lot of heat, there will be no negative consequences. A more detailed picture can be understood in consultation with specialists.
Bypass design
The bypass device is simple. Structurally, the bypass device consists of the following elements: • circulation pump • coarse filter • shut-off valves.
The bypass in the heating system can operate continuously or when the radiators are started. The following elements can be used as shut-off valves in the system: • ball valve • check valve. Therefore, it is considered necessary to have a check valve in the heating system. In a heating system, a check valve can be installed instead of a tap.
In this case, when the circulation pump is turned on, the check valve is in the closed state. When there is a power outage, the valve opens automatically, allowing the system to switch to natural circulation mode. Therefore, the issue of choosing shut-off valves in the bypass design is fundamental. In the absence of a valve, the circulation pump is turned on through a small heating circuit, which is formed by a main line and a bypass.
The design of the check valve must include a spring-loaded plate and a ball that closes the gap. The advantages of having a check valve in the system are that it operates without human presence or intervention. Turning on the circulation pump under the pressure of the coolant mixture “closes” the valve. But in terms of reliability of operation, the valve is inferior to the valve, because the presence of abrasive impurities in the coolant mixture occurs.
According to experts involved in the installation of shut-off valves, the best option is to purchase a valve from the best manufacturers, because a leaking ball valve cannot be repaired.
Maintenance, selection and replacement
Bypass valves are not serviceable parts and have no scheduled inspection or replacement intervals. They operate until damaged and/or fail, and then must be replaced. Also, when carrying out tuning, it is not recommended to change the classic bypass to a blow-off, because your engine will overflow. Engine operation will be disrupted, since the air bleed into the atmosphere is already taken into account by the mass air flow sensor and the fuel supply is regulated based on this data. So you shouldn’t change the spring stiffness or install analogues instead of the original, they are not always configured effectively.
Tips and tricks
Before proceeding with the installation of a bypass in the heating system of an apartment building, first of all, you should notify representatives of the local housing and communal services in writing about your decision in order to agree on the issue of temporarily shutting off the coolant supply from the boiler room. After that, follow these recommendations:
In order for water to flow normally into the heating device, it is necessary that the diameter of the pipe in the bypass section be one size smaller than in the general circuit. When purchasing a ready-made bypass unit, it is necessary to require a quality certificate, which will serve as a guarantee of durable and normal operation of the device. When purchasing elements of the bypass section, you should check the threaded connections - they should be easy to unscrew and not twist when tightened. When deciding to install a bypass, use only ball valves, since they not only have low hydraulic resistance, but are also easy to open and close. It doesn’t matter whether the bypass is working or not, it is necessary to open and close all the valves from time to time to avoid sticking of the ball and will significantly increase the service life of all elements of the assembly. Before putting the heating into operation after a long period of inactivity, it is imperative to ventilate the area with the circulation pump. Throughout the heating season, preventive cleaning of filters installed in the bypass system should be carried out. To avoid mistakes and to ensure that the heating works efficiently, it is advisable to entrust all work to an experienced specialist.
Bypass installation examples
Battery tying
When installing the system yourself, be sure to take into account the requirements for heating elements, in particular the bypass. It is often installed in places where radiators are mounted.
Next, we will consider the issue of using a bypass in a heating system more carefully.
Radiators are tied according to a simple pattern
Why do you need a bypass?
Previously, single-pipe heating was used in the construction and improvement of houses. This greatly simplified the work and also reduced costs. In this case, two collectors were installed in the elevator unit, responsible for supplying and processing the coolant. Further heating was developed according to different schemes:
- Top feed. There was a pipe running from the collector to the top floor. The coolant was supplied upward through this riser. After that, it went down, passing through all the radiators.
- Bottom feed. In this case, the coolant begins to flow into the radiators already when raised up. Such serial connection of devices has characteristic disadvantages.
In both the first and second cases, the connection is made in series. If a problem occurs with any equipment, you will have to turn off the system completely.
The problem is solved by including special jumper pipes in the system. If necessary, the radiator is cut off from the main system by taps without disrupting its operation. This makes it possible to easily repair the battery.
The jumper is installed closer to the battery
This is not the only reason for using a jumper in heating. The room is heated by radiators. If there is a bypass with valves, apartment owners have the opportunity to independently adjust the coolant supply. Thus, controlling the temperature in the house is not difficult.
The dressing tube has different shapes
Bypass installation
To carry out heating installation, you must have certain knowledge and skills. This takes into account the method of pipeline assembly. For this purpose, threaded and fitting connections are used, as well as pipe soldering. Having these skills will make the job easier. In this case, it is worth taking into account important rules and recommendations of specialists:
- No valves are used between the riser and bypass. Otherwise, the coolant circulation is disrupted.
- On the vertical riser pipe, the jumper is mounted in close proximity to the battery. In this case, a place is provided for installing shut-off valves. The valves are mounted on both sides of the radiator.
- Do not install valves on the bypass unless necessary. If you install taps on the jumper, the circuit will become unbalanced. In an autonomous system of a private house, this allows you to redirect the flow. In a multi-storey building, this option is ineffective and is a violation of standards.
- The size of the pipes is important. The diameter of the insert is two sizes smaller than the section of the stand. The pipes leading to the radiators are used one size smaller. In the horizontal scheme, the size ratio is slightly different.
Compliance with the dimensions of pipes and pipes will ensure normal operation of the system, in accordance with the laws of hydraulics. Installation features directly depend on the type of material used. If we are talking about a metal pipeline, then it is enough to simply weld a jumper and install the taps.
Installation is carried out in different ways
The use of polypropylene or metal-plastic pipes requires the use of special fittings. You can build a bypass yourself from a pipe of the required size or purchase a ready-made part.
The pump is often installed on a jumper
Bypass for a radiator in a single-pipe heating line
Installing a bypass in the heating system in parallel to the battery allows you to regulate the flow of liquid through it and, accordingly, the temperature regime, and also provides the ability to replace or repair a heating device without stopping the functioning of the heating, which is especially important in apartment buildings. How to install the bypass correctly?
Let's look at the picture, similar systems look something like this...
The bypass photo of which you see on the left is just an ordinary jumper that connects the supply (hot) and return (cold) pipes directly next to the battery.
Ball valves are installed between the jumper and the radiator. They allow you to turn off a separate device, and the coolant will calmly circulate along a parallel bypass path.
The third tap can be installed on the jumper itself and allows you to adjust the bypass mode - the balance of fluid flow through the heating battery and the bypass pipe. The closed position of this valve ensures the circulation of the entire coolant flow through this heater. Optionally, instead of a tap on the supply pipe in front of the radiator, a thermostat can be installed to maintain the temperature in the radiator set on it.
In houses with central heating, it is advisable to install a bypass for the heated towel rail, since many models of this heating device may not be designed for the parameters of our boiler rooms. In this case, the bypass diameter is chosen smaller than the diameter of the main pipes - usually a half-inch pipe.
Why is bypass needed? It allows you to reduce energy costs by limiting the amount of coolant entering the radiator. Thus, the heat transfer from the heating battery is reduced and energy is saved. The lack of adjustment options simply leads to overheating of the room, followed by opening of the vents and evaporation of heat. The heat exchanger with bypass used in boilers allows you to regulate the required coolant flow through it.
By installing a bypass yourself (if you have plumbing skills), you will leave a significant amount of money in your pocket.
Connection diagram
The standard bypass connection diagram in an apartment is as follows:
- Pipe with incoming coolant flow;
- Bypass;
- Pipe with outgoing coolant flow;
- Shut-off valves for inlet and outlet.
In this brief description we will look at the operation of a radiator with a bypass. Two valves are mounted at the inlet and outlet of the radiator. The coolant is supplied from below or from above. For most heating systems, the second option is correct. When hot water is supplied from above, the liquid reaches the bypass and is divided into two streams. The coolant is directed to sections of the heating device, heating it. The other flow through the outlet pipe - the bypass, bypassing the radiator, goes down, and then continues its movement along the riser. A valve installed at the radiator inlet allows you to control the flow, increasing or decreasing the coolant supply. A shut-off valve is installed on the bottom of the radiator to allow heat to be removed. During the heating season, the drain valve is opened all the way.
Operating principle of the bypass valve
If an unusual situation occurs, a power outage or a pump breakdown, the pressure stops and the valve automatically closes the jumper, allowing water to flow naturally. This allows the heating system to be fully automated. The disadvantage of automatic bypass is sensitivity to water contamination and small contaminants. Before installation, it is recommended to clean the water supply system of the AED to remove deposits and rust in pipes and radiators.
Before starting work, you need to decide on the material of the water supply system. For polypropylene pipes, dismountable connections are used, and first the pump block is assembled along with the bypass. The branch is connected using tees mounted in the main pipe. For the steel version, first the pipes are soldered in, then the valve on the bypass. The bypass system is installed towards the coolant and must be assembled in a certain sequence.
Assembly diagram:
- Filter;
- Check valve;
- Forced action pump.
The diameter of the bypass line passage must be equal to the return diameter. Experts recommend that all taps be equipped with dismountable fittings during installation. In this case, various situations will be eliminated during the repair.
Operating principle of the bypass valve
Before starting installation work on installing the pump, it is necessary to drain the coolant from the system. The entire structure is oriented so that the outlet pipelines are vertical or horizontal, depending on the stroke of the pipe.
How the bypass line works:
- They assemble a section of the bypass that will be located parallel to the highway;
- A section equal to the length of the bypass is cut off from the return;
- Tees are installed at the ends of the line;
- A section with shut-off valves or valve is mounted between them;
- The assembled section of the bypass is connected to the main line with pipes of equal length.
During installation, it is necessary to leave space for subsequent dismantling of the pump and other elements. It is necessary to carry out the installation correctly, making sure that the arrow on the housing coincides with the coolant current.
Assembly and installation of the device
The bypass is a section of the main pipeline between the heating boiler and the working circuit. In this section of direct movement, a ball valve is mounted, which, when the supercharger is turned on, blocks the movement of fluid. A solution that is less practical is a shut-off valve, the normal position of which is closed.
The pump is installed in parallel, using two outlets embedded in the main line and directed opposite each other. It is recommended to use “American” type quick-release connectors for fastening, which makes it possible to quickly remove it if necessary.
As the coolant moves, a coarse filter is mounted in front of the supercharger, and on both sides this design is limited by shut-off valves. The pipes must have a diameter that matches the inlet and outlet openings of the pump.
The most successful solution is to purchase a ready-made assembled bypass. They are produced for pumps of various diameters and are already equipped with the necessary shut-off valves and filter. All you need to do is install it on a certain section of the heating system and install the pump.
The key characteristic in this case is the distance between the fittings. For the most common type of circulation pumps it is 110 mm.
Installing a bypass in a heating system is not difficult, but simple installation rules must be followed.
First of all, you need to decide on the right place to install the circulation blower. This location must be chosen in such a way that there is a place for convenient repair and dismantling of assembly parts. In addition, it is necessary to consider the location of all valves and taps - they must be freely accessible.
In the case of a two-pipe heating system, the circulation pump must be embedded in the return coolant circuit - this will reduce the likelihood of overheating.
Bypass assembly methods vary depending on the material that was used to make the pipes:
- If the pipe material is plastic, the pump assembly is assembled immediately and is immediately connected to the pipeline using soldered tees.
- With metal pipes, you first need to weld the outlet pipes for the pump unit, and then install the bypass valve.
Overheating of shut-off valves due to welding is not allowed, as this will subsequently negatively affect its characteristics. For example, the Teflon insert in a ball valve may become deformed. Because of this, the distance from taps and valves to the welding site must be at least 20 centimeters.
The pump must be positioned so that the operating shaft is in a strictly horizontal position. This will reduce the gravitational load on the shaft and increase the service life of the pump.
Types and designs
According to the operating principles, bypass valves are distinguished with spring and membrane designs. Spring mechanisms prevail in systems where the pipeline cross-section is no more than 200 mm; in other water supply and heating networks, the lever-load principle is used.
Membrane units are increasingly used when working with liquid media that contain solid particles.
Depending on the pipeline environment, bypass devices are intended for:
- gas;
- pair;
- liquids.
According to the purpose of the system, they are used for pipelines:
- cold water supply,
- hot water supply,
- heating,
- cooling,
- conditioning.
In heating and water supply systems, bypass valves are distinguished according to their purpose:
- for radiators;
- for boiler and bypass;
- for automatic replenishment;
- for low or high pressures.
This photo shows an overflow valve with a setting scale. Made of bronze and brass, designed for installation in central heating systems.
Along with bypass regulators, the following is installed in the heating design:
- air vent to prevent air locks in pipes;
- three-way valve for mixing or separating hot and cold water flows;
- reverse, preventing backflow in the pipeline.
For industrial and utility networks, designs with a nominal diameter DN of up to 500 mm and a flange connection are used.
In the car there are access devices for:
- turbines;
- fuel supply mechanism;
- engine cooling systems.
The turbine bypass unit discharges the exhaust gases, reducing the pressure force in the manifold. Thus, it protects the engine from overheating.
Technical specifications
The technical characteristics of bypass units are indicated by letter symbols and are regulated by GOST (No. 26349-84; 28338-89). The marks are deciphered as follows:
- “DN” is the typical size of the hole in the connecting pipes. The diameter of the connecting tube may vary slightly (smaller or larger). GOST regulates the nominal volume of the pipe with the letter designation “Du” (conventional passages).
- “KVS” is the bypass capacity, expressed as a ratio. The marking corresponds to the flow rate of liquid, with a temperature of 20 °C, passing through the hydraulic device per hour and a volume equal to 1 meter per cube. The valve pressure loss cannot be more than 1 bar. This value is used to calculate the water pressure loss.
- “PN” - indicates the nominal and maximum bypass pressure, at a working fluid temperature of 20°C. The indicator indicates the relationship between temperature and pressure for safe and long-term operation of heating equipment. The guest designation “PN” (nominal pressure) is “Ru” (conditional pressure).
- “Setting range” is the pressure difference maintained by the setpoint force (spring) installed in the bypass valve - by the manufacturer.
Connecting the pump via bypass
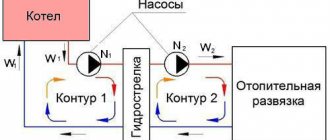
It is advisable to connect the circulation pump via bypass only in those systems that were originally designed for natural circulation, i.e. they must have an accelerating manifold, pipe slopes must be observed and their diameters must be correctly selected. The pump in such systems is not intended to ensure their operation, but to increase efficiency.
For systems that were designed for forced circulation at the design stage, a bypass is simply irrelevant. Such systems operate only due to the pump, so when it is turned off, the circulation of the coolant simply stops. Bypass in this case will not solve the problem.
When connecting the pump via a bypass line, it becomes possible for counterflow in the bypass. In addition, a closed circulation loop is formed between the pump and the bypass itself. In order for such a circuit to function normally, the bypass device must be equipped with a ball valve or check valve.
Coolant flow control
Adjusting the water flow in the system makes home heating more efficient and less energy-consuming. Excess coolant from the radiator is returned to the pipeline. Water passes through the bypass, bypassing the main pipe.
With such installation and operation, the bypass allows for repair work on radiators at the height of the heating season without disconnecting from the general system.
The device allows you to increase the speed of filling the heating system, as well as draining the coolant.
Operation with a circular pump
Installation in a system with a circulation pump
A heating bypass is indispensable when operating a circular pump. In situations where there is no electricity in the network, the pump cannot operate. A bypass with valves automatically redistributes the coolant flow from the pump to the main pipeline.
In manual mode, without a valve, the taps associated with the flow of water into the system are closed. Thus, the system switches from forced circulation to natural circulation.
Read about the difference between natural and forced circulation.
The bypass must be installed in a horizontal position, since in a vertical position air pockets may form, which negatively affects the operation of the system.
Single pipe system
A bypass for heating radiators allows you to update and improve the operation of single-pipe heating.
This work scheme is almost never used in modern construction in apartment buildings and private homes. In Soviet-era buildings, single-pipe heating is a fairly common occurrence.
The bypass in this case will regulate the flow of coolant, making the indoor climate comfortable.
The device is located close to the radiators, away from the vertical risers. The bypass must be equipped with temperature regulators. Thus, the device allows you to regulate the temperature in the room even with a single-pipe system.
When choosing, the diameter of the bypass pipe should be smaller than that of the main pipeline. This will allow, according to the laws of hydrodynamics, the coolant to bypass the battery through the bypass.
Installing a bypass: do-it-yourself installation details
By and large, the bypass jumper has a fairly simple design, and it can be assembled even with minimal plumbing experience. I repeat once again that the operating principle of this device and its understanding are important here - knowing this, making a bypass for a circulation pump or something else yourself is not so difficult. Let's look at this process in a little more detail.
- What we have? For example, a heating line on which a circulation pump is mounted. The first thing to do to install the bypass is to remove it and slightly alter the line - in particular, you will need to slightly increase the distance between the threaded ends onto which the pump was screwed. It is best to determine this distance locally - in the sense of assembling the pump and assembly around it as expected.
- To do this, immediately behind the pump, on one side and the other, we screw on the ball valves - this can be done immediately completely. We have detachable connections on the pump, so quickly disassembling the unit and mounting it on the pipeline will not be a problem.
- Following the taps (also on both sides of the meter), tees of exactly the same diameter as the pipeline itself are installed. A caveat should be made here - the type of tee depends on the pipeline itself. In most cases, tees are used that are made of the same material as the pipes - if polypropylene or metal-plastic, then first the threaded ends are screwed into the taps and then the tees are soldered or screwed to them.
- In principle, that’s it, the size is set, and now we try on the assembled unit in place, cut the pipeline according to the marked marks and insert the assembled unit. For ease of operation, it can be disassembled using American models - simply put, remove the pump, after which you will be left with two parts of the pipelines, which will need to be connected to the main line. After this section of the bypass has been assembled, the pump is installed in place (completely) - only after this will it be possible to focus on the bypass pipe itself.
- Everything here is also simple - first, we raise the pipeline upward from the tees so that it does not interfere with the pump. Then, by turning, we bring the two pipes coming from the two tees together - at least we give them the correct direction to each other. And then there is a jumper and a tap, for installation of which, again, you will need a detachable connection and a pair of threaded ends.
In principle, this is the entire bypass for the circulation pump - exactly the same principle is used to install the bypass for other plumbing fixtures. The bypass pipeline can be positioned either vertically or horizontally - from this point on, its functionality and quality of work do not change.
That's all. Now you know what a bypass is and how it works. Moreover, now it will not be difficult for an attentive and scrupulous reader to independently manufacture this unit, without the help of qualified specialists. I’m not afraid to repeat myself - if you understand the principle of its operation and understand the structure and purpose of each element, then assembling a bypass with your own hands will not be difficult.
Author of the article Alexander Kulikov
Bypass device
The use of a bypass for the installation of an additional pressure unit is often accompanied by the inclusion of an element such as a check valve in the main part of the pipeline.
It is a small device whose body consists of two parts. There is a ball or spring-loaded baffle located inside the bypass housing. The main task of the valve is to ensure the operation of the heating system in the absence of additional pressure created by the pump. The operation of the valve in the heating system is automated and does not require human intervention. This is very convenient in case of emergency shutdown of the pump in the absence of residents of the house.
The operating principle of the check valve is as follows. When the pump is turned on and in good working order, additional pressure is created at the outlet of the valve, which closes it and prevents the movement of fluid (lower part of the figure).
In the event of an emergency shutdown of the pump (upper part of the figure), there is no additional pressure in the system, which “unlocks” the bypass check valve and opens the main pipeline for the movement of the heated coolant. In this case, the device operates regardless of the presence of an operator, using only the laws of physics. This allows you to protect the entire heating system of the house from destruction.
One of the fastening elements that has appeared and is actively used in recent years when installing elements of heating systems is the so-called American nut.
It consists of two parts equipped with threads and screwed onto each other. Available in two versions - straight and angular. When attaching one or another element of the system, one part of the nut is screwed onto the threaded part of the pipe of the device being installed, and the moving part of the connection is driven onto a threaded pipe or fitting. The use of such parts makes it relatively easy to secure certain elements not only in the bypass, but also in any other place in the heating system. The main advantage of the “American” connection is the ability to remove the installed device - pump, radiator and others without disassembling the system itself.
Dear readers, comment on the article, ask questions, subscribe to new publications - we are interested in your opinion