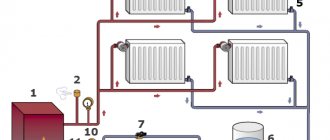
The elevator unit provides the house with hot water and heat
In this article, we will get acquainted with the design of heating and hot water systems in an apartment building and a private building, find out what basic elements are included in their composition and which pipes for water supply and heating are best used in each specific case. Let's get started.
Basic elements of heating circuits
Private houses are heated by heating systems.
They use a convenient and universal method of delivering heat using a coolant. You can heat the coolant in various ways. Often, owners use several water heating devices. Any heating scheme in a private house consists of the following components:
- heat generator (boiler);
- current diagram of the heating system of a private house, including fittings and equipment;
- control and heating devices.
If you want to create heating for a private house with your own hands, the schemes are selected based on the possibilities. There are few options, there are only two:
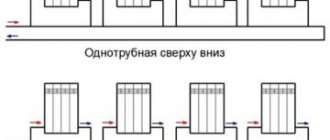
- single-pipe scheme - all batteries are connected to one pipe through which flow and return flow;
- two-pipe scheme - separate pipes for supply and return.
Determining which heating scheme for a private home is optimal is difficult, especially for a non-specialist, so you should definitely consult a professional. Most heating circuit specialists are convinced that a two-pipe heating circuit for a private house is optimal. There is a misconception that a single-pipe system costs less.
The opinion of many experts is the opposite - a single-pipe system is more expensive and more difficult to set up and adjust. The principle of its operation is the sequential movement of liquid through the radiators, which means that the temperature drops from battery to battery, so it is necessary to increase the power of the system. The main pipe is selected with a larger diameter. In addition, the mutual influence of heating devices on each other is very strong. This influence makes automatic control difficult.
Elements
What elements are included in heating and water supply systems?
Heat source
This role may include:
| Image | Description |
| Diagram of the simplest elevator unit with circulating hot water supply | Elevator unit with hot water supply. The water jet elevator provides a high speed of movement of the coolant (a mixture of supply and return water) and, accordingly, a minimum temperature difference between the beginning and end of the heating circuit. Two or four taps provide dead-end or circulation hot water. |
| Thermal point of a closed heat supply circuit. Water for domestic hot water needs is heated in heat exchangers that use the heat of water from the heating main. |
| Boiler (gas, diesel, electric or solid fuel). The first three varieties may have an additional heat exchanger or a built-in boiler for domestic hot water needs. Gas is the cheapest source of heat; followed by solid fuel boilers; Diesel and electric appliances are the most expensive to operate. |
| Heat pump. It uses electricity to pump heat into a heated building from an environment with a lower temperature compared to the internal premises - soil, water or air. In terms of cost per kilowatt-hour of heat, a heat pump is slightly behind a gas boiler, and successfully competes with a solid fuel boiler. |
| Indirect heating boiler. It can connect to any heat source (in particular, a single-circuit boiler or central heating) and use the coolant energy to heat water. |
| Independent water heaters for domestic hot water needs - electric boilers, electric and gas instantaneous water heaters. They can be located outside the boiler room, near water collection points. |
Bottlings
Spills are horizontal pipes for heating and hot water supply, to which plumbing and heating appliances are connected (in multi-storey buildings - risers with appliances).
The diameter of heating and hot water filling in apartment buildings is in the range of 32-100 mm, depending on the heat load or the number of water consumers. In a private house, the minimum filling diameter is calculated based on the heat load and peak water consumption.
Calculation of the diameter of the heating filler according to the thermal load
The above table requires a few comments:
- It is relevant for a delta temperature between the supply and return heating lines of 20°C (for example, 80/60°C);
- The upper value in the table cells is the thermal power in watts, the lower is the coolant flow rate in kilograms per minute;
- It is possible to increase the thermal load on the circuit without increasing the filling diameter, by increasing the flow rate (read: the performance of the circulation pump). However, it is better that the flow speed falls within the range of 0.4-0.6 m/s: then we will avoid erosion of plastic pipes by suspensions and the appearance of hydraulic noise on fittings and chokes.
Rough calculation of the diameter of cold water/hot water pipes
The diameter of the DHW filling is selected according to the maximum water consumption and the required flow rate.
Reference: for hot water supply and hot water supply it is recommended to limit it to a value of 1.5 m/s; for irrigation systems the permissible maximum is 2 m/s.
Risers
A riser is a vertical pipe that connects appliances (heating or plumbing) on different floors. Diameter - 20-40 mm.
Cold water and hot water risers
DHW risers with circulation are connected by jumpers on the top floor or in the attic; 2-7 risers can be looped. The jumpers must be equipped with air vents (Maevsky valves or automatic ones). The same jumpers with vents connect heating risers in houses with bottom filling.
If the jumper is flush with the radiator, the air vent is installed in its upper plug
Eyeliners
Connectors are pipes for water supply and heating systems used to connect heating and plumbing fixtures to the bottling system. Here you can do without complex calculations: when using steel pipes, their size DN15 is sufficient, plastic pipes - with a nominal diameter of 16 mm (20 mm for connecting 2-3 devices).
Polypropylene liner with a diameter of 20 mm provides water to the sink, bathtub faucet and toilet cistern
Hint: the internal cross-section of a DN16 polymer pipe is smaller than a DN15 steel pipe, due to the difference in the designation of pipes (DN is a nominal diameter approximately equal to the internal diameter, and plastic pipes are designated by the external diameter). However, corrosion of pipelines of heating and hot water supply systems reduces the internal cross-section of a steel pipe over time, but polymer pipelines have a constant hydraulic resistance throughout their service life.
Rust in steel water pipe
Pumps
Pipelines of heating and hot water supply systems with circulation, powered by an autonomous heat source or connected to a heat point of a closed heating system, are supplied with circulation pumps.
This is how the circulation pump works
The pump is selected according to two parameters:
- Napor;
- Productivity.
The purpose of the pressure created by the pump is to overcome the hydraulic resistance of the pipeline.
It is roughly calculated using the formula H = N x K, in which:
- N—pressure in meters;
- N - Number of floors in the house (including the basement or ground floor in which horizontal wiring is made);
- K - pressure loss per floor (on average 0.7-1.1 meters for hot water supply and sequential heating distribution, 1.16-1.85 for manifold heating distribution).
So, for a three-story house with a basement, a pump for circulating hot water should create a pressure of 4 x 1.1 = 4.4 meters.
Installing a pump in a DHW system with circulation
The performance of the heating pump is calculated using the formula Q= 0.86 x P/dt.
In it:
- Q - productivity (m3/hour);
- P is the heat load on the kennel served by the pump in kilowatts;
- dt is the temperature difference between the heating lines (usually 20°C).
Let's say, for a Leningrad stove connected to a 24-kilowatt pellet boiler, you need a pump that pumps 0.86x24/20 = 1.032 m3 per hour.
Hint: don’t be afraid to make mistakes in your calculations in one direction or another. For the most part, circulation pumps have a stepped power regulator, which allows you to reduce or increase pressure and productivity.
Shut-off and control valves
What kind of fittings may be needed when installing engineering systems yourself?
| Image | Description |
| This is how a ball valve works | Ball Valves. They differ from plug valves and screw valves in their fault tolerance, complete tightness in the closed position and lack of maintenance. Among their malfunctions, the author encountered only leaks in the oil seal (to eliminate it, it is enough to tighten the oil seal nut) and rotation of the rod due to the application of great force to a valve jammed by scale. |
| Throttle for installation on the connection to the radiator | Throttles (control valves). They are installed in the heating manifold cabinet or on the supply lines of heating devices. |
| Valve with thermal head | Thermostatic valves. They differ from throttles by automatically adjusting the flow rate depending on the air temperature or working environment. |
| Thermostatic mixers stabilize the temperature in the heating circuit or DHW circulation, regardless of the temperature at the outlet of the boiler or boiler. |
| Reducers are used to reduce excess pressure in water supplies. |
| Filter for installation on eyeliner | Coarse filters are needed to protect shut-off valves, mixers and heat exchangers of water heating devices from debris carried by the network water (scale, sand, silt, etc.). |
Safety
The following are responsible for the stability of the parameters of engineering systems and the absence of the threat of their destruction:
| Image | Description |
| Expansion tanks. They compensate for the expansion of water when heated and are installed in autonomous heating systems and in the piping of large-volume boilers. |
| Safety valves. They release part of the water at excess pressure in a closed circuit. |
| Pressure gauges and thermomanometers. The devices are used for visual monitoring of parameters. |
Modern heating systems
All modern heating systems for private houses and other residential buildings can be divided into 2 groups. The first includes traditional heating methods, which use a single heat source - a boiler operating on one or more energy carriers. In this case, thermal energy is distributed throughout the premises through a coolant - water or air. Here, innovative solutions are aimed at improving heating equipment by increasing its heat output, as well as introducing modern automation equipment.
The second group should include all systems that use new heating technologies with energy-saving equipment. They do not involve the combustion of hydrocarbons; only electricity is used in heating the house. These are various solar systems, solar collectors and the latest types of electric heating. Despite all the attractiveness of these systems, most homeowners prefer heating private houses using traditional methods, and why is described in our article.
Criteria for choosing a boiler for autonomous heating of a private house
When choosing the type of boiler for heating, there are no alternatives only if gas is supplied to the house; it is the cheapest type of fuel and, in comparison with other sources (electricity is not considered), has a number of operational advantages - it does not require space for storing reserves, highlight There are fewer combustion products released into the environment and does not pollute the chimney system as intensively.
The main parameters that people pay attention to when choosing a boiler are:
- Unit power: directly related to the area of heated premises and temperature conditions, which are usually chosen based on building codes and GOSTs.
- Number of circuits: if the house does not have hot water supply, it is more practical to choose a dual-circuit model that can heat water.
- Location: usually the unit is installed downstairs in the basement on the floor; there are also hanging options for small houses.
- Material of manufacture of the unit and heat exchanger: cast iron, stainless steel, copper.
- Type of combustion chamber according to the method of supplying air to the firebox: open or closed.
- Availability of automatic control and monitoring systems, possibility of programming operating modes.
- The ability of the boiler to work with alternative fuels: relevant for liquid fuel modifications.
Rice. 14 Design of the Rinnai gas boiler
When choosing a boiler, the following tips may be useful:
- If there is no hot water supply in the house, it is rational and cheaper to choose a double-circuit boiler model than to install a separate single-circuit unit and a gas water heater, an electric boiler.
- When using electricity, the night tariff is much cheaper than the day tariff, in this case you can save on the cost of electricity. To do this, at night they warm up the entire house, with the exception of the bedrooms, and during the day they turn off the boiler for a long time or operate it in the minimum heating mode.
- For reliable operation of all boilers controlled by automation powered from the mains, you should purchase an electric generator with automatic switching on in case of power failure - this will allow the boiler equipment to continue operating in case of emergency situations on the power line.
Rice. 15 Construction of a Kolton solid fuel boiler
Requirements for modern home heating
Air heating of a private house
The purpose of any heating supply is to maintain a comfortable temperature level in the room. However, in addition to this, modern heating of a private house must meet a number of additional requirements.
First of all, this is maximum safety for those living in the house. Those. no heating element or its operation should cause harm to humans. This especially applies to relatively new polymer materials of manufacture. Also, when choosing a system, you should consider the following factors:
Economic expediency
It is important that the amount of thermal energy received tends to be similar to that consumed. Modern heating of a private house should have an efficiency close to 100%;
Minimal maintenance resources
Traditional heating schemes have several significant disadvantages - a large amount of soot (solid fuel boilers and stoves), the need for annual cleaning of pipes, constant monitoring of the volume of fuel and operating mode. Modern types of heating of a private home almost completely eliminate the influence of these factors on work;
Maximum work autonomy.
What needs to be done to fulfill these conditions as much as possible? To do this, it is recommended to study the offers on the market of heating devices and circuits, choosing the optimal assembly for a particular home.
In most cases, it makes more economic sense to upgrade an existing system than to build a completely new one.
Cast iron heat exchanger
Advantages of heating units made of cast iron:
- High thermal conductivity - cast iron elements heat up quickly and effectively transfer heat from one medium to another.
- Slow cooling – cast iron heat exchangers take a long time to cool, which makes it possible to save on the operation of the heating system.
- Durability - cast iron is resistant to weak acids and scale formation, so it is less susceptible to corrosion than many other metals, which ensures a long service life of the heat exchanger.
- Possibility of increasing functionality - after installing the unit, new cast iron sections can be added to it, thereby increasing the power of the heating equipment.
Disadvantages of cast iron heat exchangers:
- Bulky – cast iron units are distinguished by their impressive weight, which complicates their operation and maintenance. Moreover, the greater the mass of the heat exchanger, the higher its power.
Advice. Be sure to consider the weight of a cast iron heating appliance when choosing a place to install it - it is important that the mounting base is very strong.
- Fragility - despite their heavy weight, cast iron units are afraid of mechanical shocks: they quickly develop cracks, chips and other deformations.
- Low resistance to temperature changes - although cast iron can withstand the highest possible temperatures, sudden thermal changes can cause cracks to appear on the surface of the heat exchanger, which can lead to a significant decrease in its performance.
Connecting radiators
The choice of method for connecting them depends on their total number, installation method, length of pipelines, etc. The most common methods are:
• diagonal
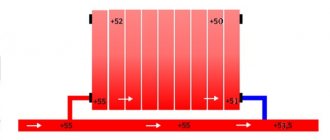
(cross) method: the straight pipe is connected to the side of the battery at the top, and the return pipe is connected to its opposite side at the bottom; this method allows the heat carrier to be distributed across all sections as evenly as possible with minimal heat loss; used with a significant number of sections;
• one-sided:
also used with a large number of sections, the hot water pipe (straight pipe) and the return are connected on one side, allowing for sufficient uniform heating of the radiator;
• saddle:
if the pipes go under the floor, it is most convenient to attach the pipes to the lower pipes of the battery; due to the minimal number of visible pipelines, it looks attractive in appearance, but the radiators heat unevenly;
• lower:
the method is similar to the previous one, the only difference is that the direct pipe and the return pipe are located almost at the same point.
Methods for connecting radiators
To protect against the penetration of cold and create a thermal curtain, the batteries are located under the windows. In this case, the distance to the floor should be 10 cm, from the wall - 3-5 cm.
Central heating of apartment buildings
Through main pipelines, coolant from the central boiler room is supplied to the heating unit of an apartment building and is further distributed among the apartments. In this case, additional adjustment of the degree of hot water supply is carried out directly at the heating point, for which circular pumps are used. This method of supplying coolant to the end consumer is called independent (more details: “Central heating is both pros and cons”).
In addition, dependent heating systems are used in apartment buildings. In this case, the coolant is transported to apartment radiators without additional distribution directly from the thermal power plant. In this case, the water temperature is determined regardless of whether it is supplied through a distribution point or directly to consumers.
Options for a two-pipe system
The main difference between a two-pipe heating scheme for a private house is the connection of each battery to both direct and reverse current mains, which doubles the pipe consumption. But the home owner has the opportunity to regulate the level of heat transfer of each individual heating device. As a result, it is possible to provide different temperature microclimates in the rooms.
When installing a vertical two-pipe heating system, the lower as well as the upper heating distribution diagram from the boiler is applicable. Now in more detail about each of them.
Vertical system with bottom wiring
Set it up as follows:
- From the heating boiler, a supply main pipeline is run along the floor of the lower floor of the house or through the basement.
- Next, risers are launched upward from the main pipe, which ensure that the coolant enters the batteries.
- A return flow pipe departs from each battery, which carries the cooled coolant back to the boiler.
When designing the lower wiring of an autonomous heating system, the need to constantly remove air from the pipeline is taken into account. This requirement is met by installing an air pipe, as well as installing an expansion tank, and using Mayevsky taps on all radiators located on the top floor of the house.
Vertical system with top wiring
In this scheme, the coolant from the boiler is supplied to the attic through the main pipeline or to the very ceiling of the upper floor. Then the water (coolant) goes down several risers, passes through all the batteries, and returns back to the heating boiler through the main pipeline.
To periodically remove air bubbles, an expansion tank is installed in this system. This version of the heating device is much more effective than the previous method with lower pipe routing, since higher pressure is created in the risers and radiators.
Horizontal heating system - three main types
The installation of a horizontal two-pipe autonomous heating system with forced circulation is the most common option for heating a private home. In this case, one of three schemes is used:
- Dead end circuit (A). The advantage is the low pipe consumption. The disadvantage lies in the large length of the circulation circuit of the radiator farthest from the boiler. This makes it very difficult to adjust the system.
- Scheme with associated movement of water (B). Due to the equal length of all circulation circuits, it is easier to adjust the system. During implementation, a large number of pipes will be required, which increase the cost of work and also spoil the interior of the house with their appearance.
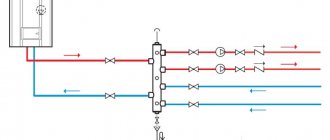
- Scheme with collector (beam) distribution (B). Since each radiator is connected separately to the central collector, it is very easy to ensure uniform distribution of all rooms. In practice, heating installation according to this scheme is the most expensive due to the high consumption of materials. The pipes are hidden in a concrete screed, which greatly increases the attractiveness of the interior. The radial (collector) floor heating distribution scheme is becoming increasingly popular among individual developers.
This is what it looks like:
When choosing a standard wiring diagram, it is necessary to take into account many factors, ranging from the area of the house to the materials used in its construction. It is better to resolve such issues with specialists to eliminate the possibility of error. After all, we are talking about heating the house, the main condition for comfortable living in private housing.
Classifications
Let's start with a brief classification of systems.
Heating
It could be:
- Central and autonomous. In the first case, the heat source is a thermal power plant or boiler house serving a settlement, its separate area or group of buildings, in the second - a boiler, stove or other heating device located directly in an apartment or in a private house;
Boiler room in an autonomous heating system
Important: in the first case, the probability of water hammer, pressure surges and exceeding the standard temperature is an order of magnitude higher. For example, an instant stop of circulation in the route when the gates of the valve fall leads to a water hammer, which triggers the start of the elevator unit with the nozzle removed and the suction muffled (practised by housing workers when there are a large number of complaints about the heat supply) - to the supply of water to the hot water system with a temperature of up to 150 degrees.
The elevator and nozzle are removed, water from the heating main supply flows directly into the heating system
- District heating can be implemented using an open or closed scheme. In the first case, water for the hot water system is taken directly from the heating network, in the second, a constant (adjusted for possible leaks during accidents) volume of coolant circulates in the circuit, and hot water is heated in heat exchangers;
Heat exchanger for hot water supply
- Heating can have series or collector wiring. With sequential heating, each heating device is connected by a pair of connections to a common outlet (or a pair of outlets) for all devices; with collector connections, each battery is connected to a common comb collector. The tee circuit is easier to implement, but the collector circuit allows you to control all heating devices from one point - the collector cabinet;
Heating distribution from the manifold cabinet
- For heating, convection heating devices (radiators, registers, convectors, fan coils) or the entire floor surface can be used. In the latter case, water-heated floor pipes are laid in an insulated screed or between joists, under a heat-conducting floor covering;
Warm floor: laying in an insulated screed
- The layout can be horizontal, vertical (standing) or combined;
Hint: all apartment buildings use combined wiring. Horizontal bottlings are connected to vertical risers. In some new buildings, internal wiring is also made horizontal.
Combined vertical-horizontal layout
- Heating can be single-pipe (one bottling with devices connected to it, the so-called Leningradka) or two-pipe (separate supply and return bottlings). The first option is simpler, cheaper to implement and has absolute fault tolerance, but the second allows you to reduce the temperature spread at the beginning and end of the circuit;
Single-pipe Leningrad
Two-pipe system
- Two-pipe heating can be dead-end (when flowing from the supply to the return pipeline, the coolant turns 180 degrees) and passing (the direction of its movement does not change). A dead-end circuit requires mandatory balancing, a passing circuit works perfectly without it: several small circuits are formed in it with the same length and, accordingly, the same hydraulic resistance;
Associated and dead-end schemes
Explanation: in a dead-end circuit, the heating devices closest to the boiler or other heat source with their connections form circuits with minimal hydraulic resistance. As you move away from the boiler, the length of the circuit along which the coolant moves increases, and the batteries cool down. Balancing, which solves this problem, is called forced limitation of the capacity of nearby devices by throttling valves.
- In a two-pipe system, the supply bottling can be located together with the return bottling in the basement, or placed in the attic. In houses with bottom filling, heating risers are connected in pairs by jumpers on the upper floor. Top filling means that each riser is independent of the others and, if necessary, is turned off at two points - in the basement and in the attic.
Bottom filling: supply and return are separated in the basement
It’s interesting: starting a system with top filling after a reset is an order of magnitude easier than with bottom filling. In it, it is enough to fill the circuit from both threads and bleed the air from the expansion tank in the attic, installed at the top point of the supply filling. In the second case, the air has to be bleed from the jumper on each pair of risers, which is often complicated by the lack of access to the apartments.
Expansion tank and air vent in a heating system with top filling
Water supply
By what criteria can DHW systems be classified?
According to the source of water for hot water supply. It can be a heating network (an open heating supply circuit) and a main water supply system (preparing hot water in heat exchangers of a closed heating supply system or local water heaters).
Heating point with hot water supply in a closed heating supply circuit
Important: in the first case, the probability of water hammer and exceeding the design temperature of the hot water supply is even higher than in the case of central heating. It is enough not to switch the water supply from supply to return when cold weather sets in, and the water temperature in the water supply circuit can reach 150°C. Hence the instructions: pipes for internal hot water supply and heating of houses with elevator units should only be metal.
The temperature schedule of the heating network provides for supply temperatures of up to 150 degrees
The second sign by which DHW systems can be classified is the absence or presence of continuous circulation.
A single-pipe hot water supply system (the water does not circulate and moves only when drawing water) has two significant disadvantages:
- After long breaks in dispensing water (for example, in the morning), it has to be drained for several minutes until an acceptable temperature is obtained. At the same time, tens of liters are uselessly dumped into the sewer;
Please note: if you have a water meter, you discharge cold water, but pay for it according to domestic hot water tariffs.
A mechanical meter takes into account water consumption regardless of its temperature
- Heated towel rails connected to the DHW connections are at room temperature most of the time and heat up only when hot water is being dispensed. Hence the low temperature, dampness and fungus in bathrooms and bathrooms.
Single-pipe hot water supply: in the elevator there is one hot water connection in the supply and return
A hot water circulation pipeline is an effective solution to both problems: driven by a circulation pump or a differential in the elevator unit, water continuously circulates through looped fillers and risers. When you open any tap, the water heats up in a few seconds (after draining the contents of the water supply), and heated towel rails connected to the risers always remain hot.
The video in this article will help you learn more about how pipelines for water supply and heating are installed.
Traditional heating systems
Most often, water or various antifreeze liquids that circulate through pipes are used for heating. The liquid is heated using gas boilers, which can operate on liquid, solid and gas fuels. Recently, electrode and induction boilers have been used as heating elements.
Water heating is popular due to the availability and efficiency of the coolant among owners of cottages and other suburban housing. The water system is easy to install yourself. The positive thing is that the volume of water in the system remains constant.
The disadvantages of water heating are the long time it takes to warm up the room, possible leaks and pipe ruptures. Do not turn off the water system in winter, as the water will freeze and burst the pipes.
Heating by energy carrier type
Typical boiler room with two boilers. An electric boiler is installed on the left, a gas boiler on the right
Any type of heating for a private home differs in the way it “produces” heat. Each device uses different energy components during the heating process. Depending on the installation location, technical parameters of the room, building, and the connection of the power source itself, it is customary to use several types of fuel. The power supply of heating devices differs in the type of fuel and the method of supply.
This includes the following options:
- Gas;
- Solid fuel;
- Electric boiler.
The use of gas heating (propane-butane) involves the use of special equipment and additional systems (boilers, AGV), which ensures the correct dosage, safe supply and distribution of the fuel mixture during heat generation (combustion). Gas heating of a home is considered an effective heating method with a relatively low cost.
In the Russian Federation, gas heating is the cheapest way to provide heat in the house. The reason for this is the affordable price of gas and the relatively high heat capacity of gas (you can get 8-9 kW of heat from one cubic meter). Gas heating of a private house can be done with your own hands.
The solid fuel heating method includes the use of coal, firewood, and pressed briquettes as energy sources. In this case, special designs of boiler devices are used, adapted for such operating conditions. In areas where the supply of gas or electricity is difficult, this is the only alternative option for heating the home.
Electric home heating works by using network electricity. This type of heating is installed in places where current networks are present. Does not require additional power sources, quite economical and environmentally friendly method. Electric heating elements are used as heating elements.
By combining electricity tariffs, it is possible to make electric heating at home less expensive. A good option would be to use day-night tariffs, when electricity is cheaper at night. It is necessary to install an additional heat storage tank and heat it at night, and consume heat from it during the day.
Features of the use of polypropylene pipes
Implementing a heating scheme in a private house made of polypropylene has many advantages.
Polypropylene pipes are cheaper and lighter than metal pipes, they do not rust. Plastic pipes do not need painting, they look good and do not deteriorate the interior of the room. The procedure for creating a heating system from polypropylene pipes is reminiscent of assembling it from a construction set. Pipes are quickly and efficiently connected using a welding unit. The following equipment, tools and materials are used for installation of polypropylene pipes:
- polyfusion welding machine;
- special pipe scissors;
- roulette;
- perforator;
- polypropylene pipes (calculated diameter);
- couplings;
- fitting;
- squares;
- valves;
- fasteners.
Note: the amount of necessary materials, tools and components is determined before installation, after drawing the heating circuit diagram. Couplings, ball valves and fittings are purchased depending on the type of boiler, the selected design and the size of the polypropylene pipe.
Water electric heating
If you use electric heating of a private house with your own hands, the circuit connection diagrams are described above.
An electric boiler can be designated as the main source of heat or as a backup if the house already has a heating source, for example a gas boiler. An electric boiler consumes significant power, so the wiring cross-section must correspond to the current consumed. It is not at all necessary to make reinforced wiring throughout the house; it is enough to lay a suitable cable from the meter to the boiler. Since an electric boiler is a device that heats water, a closed system or a gravity heating system for a private house will work with it, using a standard scheme. Pipeline diagrams are no different from the diagrams described above. To create electric heating, three types of electric boilers are used:
- electrode;
- induction;
- boiler using heating elements.
It is believed that a heating element boiler that has stood the test of time is more reliable. It is advisable to fill the system with softened water so that there is less scale on the heating elements. Electric boilers have high efficiency, but the main obstacle to their widespread use is the rising price of electricity.
- How to fill water into an open and closed heating system?
- Popular floor-standing gas boiler made in Russia
- How to properly bleed air from a heating radiator?
- Expansion tank for closed heating: device and principle of operation
- Gas double-circuit wall-mounted boiler Navien: error codes for malfunctions
Recommended reading
Do-it-yourself water heating of a private house: diagrams and necessary materials Do-it-yourself air heating of a private house is a profitable and effective solution How to correctly calculate heating in a private house? How and from what are homemade home heating products made?
2016–2017 — Leading heating portal. All rights reserved and protected by law
Copying site materials is prohibited. Any copyright infringement will result in legal liability. Contacts
Main types of heating
The difference between all existing systems depends on different criteria. Installation location, heating area, technical features of wiring and installation. In frequent cases, the type of structure is influenced by the method of energy supply and, of course, the total cost of the entire complex responsible for heating a private house. Modern energy-saving technologies offer a wide selection of different heating systems using advanced developments. This article presents popular, common types of heating systems used in almost every home.
Water heating
Among all the options, heating using liquid (water) as a coolant is considered the most popular. The advantages of the classic type of water heating have been revealed during many years of use. The technical characteristics of the system allow its operation in various conditions. Both in industrial buildings and in private sector buildings, apartments, offices. All this can be done with your own hands. Main advantages:
- Same temperature in all rooms.
- Length of service life.
- Possibility of using different materials of pipes and hardware (polypropylene, metal).
- Quiet operation.
- Fuel saving, easy maintenance.
The individual design elements of this option are an electric, multifunctional or gas boiler. Coal boilers are also used. With their help, water is heated and distributed through pipes (closed circulation) to the batteries. This is how the heat of the heated liquid is transferred to the premises. For ease of use, several subtypes are used. We'll talk about them below.
Air heating
This type of heating was known and used in ancient times. Heated air was supplied into the room using an air duct system, thereby heating it. In its modern version, this is a common method of heating large areas. Until recently, it was used only in production workshops, sports facilities, and public spaces. But the development of modern technologies makes it possible to use the air method in private homes.
Heating and supply of air mass to the premises is carried out by air heaters. In large workshops, these are special installations that provide heating and constant circulation of air at a certain temperature. The local option involves the use of low-power air heating devices. Usually these are heat guns and fan heaters. The devices are quite mobile and use various construction methods (electric heaters, fuel burners, etc.) as the main heater.
The operation of air heating requires strict adherence to fire safety rules and basic hygiene requirements. The second provides for the presence of air purification filters, flow ventilation, air ducts, air curtains and other elements. As well as constant control over the air duct system as a whole.
Heating based on electricity
This type of heating works on the principle of converting electrical energy into heat. The main source of heat is an electric boiler or various heating devices (appliances). Boilers are used in water systems and are considered an environmentally friendly heating method. Individual devices have their own designs:
- Electric convectors.
- Air curtains.
- Oil radiators with heating elements.
- Infrared emitters (UVR), heated floors.
- Fan heaters, heat guns.
The use of different modifications depends on the installation location, heating area, and operating conditions. Electric convectors and oil radiators are well suited for heating apartments or private houses. This applies to UV devices and heated floors. All of the above methods are economical (subject to an affordable price for electricity) and do not require the use of several types of energy resources; only electricity can be used.
Do-it-yourself water heating in a private house
Here you will learn:
Water heating systems are most often used to heat private houses. They are characterized by simplicity, comparative cheapness and high efficiency. If you have direct hands and experience working with tools, nothing prevents you from creating a heating system yourself. With the help of our review, you will learn how to make water heating for a private house with your own hands, the diagrams of which we will provide as illustrative examples.
We will also tell you:
- About the main types of water heating systems;
- About the radiators and materials used;
- About coolant circulation systems;
- About methods of installing pipes and radiators;
- About the choice of heating boilers.
After reading the review, you will be able to draw the appropriate conclusions and create an effective water heating system for a private home with your own hands.
Cheap heating
The leader in inexpensive heating can be called the scheme under the designation “Leningradka”. Of course, there is no need for extra expenses on pipes, hardware, fittings, pumps, temperature sensors and other elements. But in terms of quality of comfort, the new systems are many times better than the outdated cheap option. Typically, “Leningradka” is installed when there is a lack of funds or in a quick installation option. Experts have long recommended installing advanced heating systems. They work longer, heat better and do not require frequent maintenance.
Latest heating systems
An example of a fairly affordable and at the same time effective system, suitable for both a country house and an apartment, is an electric heated floor. By incurring relatively small expenses for the installation of such heating, you can provide your home with heat and not buy any boilers. There is only one drawback - the cost of electricity. But considering that modern underfloor heating is quite economical, and if you have a multi-tariff meter, this option may be acceptable.
For reference. When installing an electric heated floor, 2 types of heaters are used: a thin polymer film with applied carbon elements or a heating cable.
In southern regions with high solar activity, another modern heating system performs well. These are water-based solar collectors installed on the roof of buildings or other open areas. In them, with minimal losses, water is heated directly from the sun, after which it is supplied to the house. One problem is that collectors are absolutely useless at night, as well as in the northern regions.
Various solar systems that take heat from the ground, water and air and transfer it to a private home are installations that implement the most modern heating technologies. Consuming only 3-5 kW of electricity, these units are capable of “pumping” 5-10 times more heat from outside, hence the name – heat pumps. Then, using this thermal energy, you can heat the coolant or air, at your discretion.
An example of an air heat pump is a conventional air conditioner; their operating principle is the same. Only a solar system heats a country house equally well in winter and cools it in summer.
It is a well-known fact: the more efficient an innovation in a heating system is, the more expensive it is, although it requires lower operating costs. Conversely, high-tech electric heating systems that are cheap to install force us to pay subsequently for the electricity consumed. Heat pumps are so expensive that they are inaccessible to most citizens of the post-Soviet space.
The second reason why homeowners gravitate towards traditional systems is the direct dependence of modern heating equipment on the availability of electricity. For residents of remote areas, this fact plays a big role, which is why they prefer to build brick stoves and heat their houses with wood.
Features and functions of the heat exchanger
Before considering the main points of manufacturing and installation of a heat exchanger for hot water, it would be absolutely useful to find out what this unit is and what it is needed for.
A heat exchanger is a technical device that connects two coolants: cold and hot. As a rule, it takes the form of a conventional pipe structure. Heat is continuously transferred between the carriers - from cold to hot, due to which the house is provided with hot water. Moreover, the heat exchanger does not have its own heat source - it uses energy coming from the heating system.
Thus, the main function of the unit is to heat cold water and produce hot water at the outlet. The effectiveness of this function depends on three factors:
- temperature difference between two coolants;
- dimensions of the heat exchanger and, consequently, the contact area of the media;
- the material from which the heat exchanger is made.
Plate heat exchanger
The last factor is important not only in terms of the efficiency of the unit, but also in the matter of its manufacture and installation. To make a heat exchanger, plastic, steel and cast iron can be used. The first material is not always effective due to its low thermal conductivity. As for the choice between steel and cast iron, you should compare the characteristics of the two materials to decide on the most suitable one.
What is required for installation
- boiler or oven;
- pipes;
- radiators;
- expansion tank;
- standard set of installation tools.
Before purchasing all this, it is worth understanding how water heating works and developing a plan for heating your home or cottage.
The diagram looks like this: the coolant heated by the boiler (it can be water or a special mixture) enters the radiators, in which it cools, giving off heat to the room.
The cool coolant returns to the boiler, where it heats up again. Due to such continuous cycles, your room is heated.
Water heating systems are divided into natural and forced. By choosing the first option, you will be independent of electricity to operate the pump.
The movement of liquid through the system occurs due to the laws of physics - the hot coolant expands and rushes upward, and, having lowered the temperature, it decreases in volume and falls down.
With natural circulation, it is necessary to maintain a slope of all pipes of at least 2 degrees (ideally 3-5), avoid pipes of small cross-section (40 mm pipes are suitable for the riser, pipes with a cross-section of 22-24 mm can be used for supplying the heating sections).
Natural circulation has serious disadvantages: internal wiring is not allowed - when the water level in the expansion tank decreases, the movement of liquid is difficult.
It is also applicable only in cases where the distance along the pipes between the boiler and the farthest radiator does not exceed 20 meters, and the area of the heated room is less than 150 sq.m.
As you can see, natural circulation with its limitations is not always applicable. In a forced system, the flow of coolant is regulated by a circulation pump.
Of course, purchasing a pump is an additional financial expense upon purchase and an addition to monthly electricity bills, but look at the advantages - you are spared the need to clearly check the angle of inclination, there is no need to observe a wide cross-section of risers, it is possible to make internal pipe routing and connect , for example, “warm floor”.
There are two water heating systems - single-circuit and double-circuit. Installation of the first option involves heating only.
The second option, in addition to heating, provides the room with hot water and is very convenient in the country, in cases where it is not planned to install a separate source of warm water.
Pros and cons of the system
The OS has undeniable advantages. The advantages of the system are as follows:
- you can place the heater (boiler equipment) remotely, outside the heated room;
- The design is closed, there is no need to add coolant (water) during use of the system;
- the equipment does not take up much space, heat escapes through radiator elements, a “warm floor” system, etc.
There are also disadvantages:
- takes a long time to heat from zero to room temperature;
- since the OS works with water, leaks may occur that require repair;
- Plaque, mineral deposits, and scale may form on the radiator elements, as a result of which the efficiency of heat transfer is reduced.
However, in general, all the disadvantages of water heating a house with an electric boiler, for example, are offset by the advantages.
Installing heating scheme and work procedure
Do-it-yourself water heating is carried out according to a clear action plan.
So, you have drawn a diagram of a private house, future batteries are marked on it, the length of the pipes has been calculated, you have already decided on the heating system of the house, you have studied the video and are ready to begin construction work with your own hands.
If possible, the system of sections should be wider than the window unit.
However, in practice this is not always followed. If the windows of a private house do not allow cold air to enter the room, then the total length of all sections may be less than the window.
Installation of radiators is carried out precisely at the level and always below the window opening. Beauty is, of course, important, but not paramount.
An accidental slope, even a small one, will create the effect of an underground river - the murmur of liquid will be heard from the side of the raised edge. Therefore, check the installation with a level.
It is important to maintain distances from the floor and from the walls. The ideal distance from the battery to the wall is 3-5 m, and to the floor - no more than 10 cm
To remove accidentally trapped air, it is worth installing a valve or Mayevsky tap.
A groove is connected to the hung radiators. Calculate so that there is a groove 4-6 mm deep from the fitting to the edge - when heated, the pipe may expand.
Use lengths less than 10 meters or weld in bends to accommodate thermal expansion.
There are options for using copper or stainless steel pipes, but reinforced polypropylene pipes have proven themselves most well in the price-quality combination.
They are relatively inexpensive and easy to install.
There are different models for connecting radiators that conduct water heat supply.
The lower scheme (inlet and outlet are connected to the lower branch pipes of the sections), it is fraught with heat loss of 12-15% and uneven heating of the batteries.
It should be taken into account when there is a risk of sand and suspended matter getting into the system - they will be carried into the mud filter. https://www.youtube.com/embed/BZ7Al3p9iO0
With a one-way connection, the inlet is mounted to the top of the section, and the return is mounted to the bottom of the same section. With this connection, all sections are heated evenly.
If the number of sections is significant, then it is optimal to use a diagonal connection. It differs from one-sided in that the outlet is mounted to the bottom of the opposite section.
When the connection diagram for the heating radiator sections is clear, we proceed to installing the pipe system.
Of course, it’s worth watching the installation video and practicing on the scraps left after the installation of the pipe in the groove is completed.
We melt the pipe and fitting with a soldering iron heated to 260 degrees. The alignment must be done by pressing the smaller section into the larger one.
Types of liquid autonomous heating systems
Heating systems for heating an individual home using water and non-freezing liquids (antifreeze) as a coolant differ in a number of ways, the main differences:
By type of fuel used. The most popular types of energy for heating coolants are electricity, gas, liquid flammable hydrocarbon mixtures (diesel fuel, fuel oil, oil, kerosene), a large amount of solid combustible materials - firewood, coal, peat briquettes and pellets of various compositions. Electricity can be obtained either from energy companies or independently using solar panels, wind or hydraulic generators.
By type of thermal generators. In modern heating systems, heating boilers are used to transfer energy to the coolant, which have design features and differences between analogues for each type of fuel. With a lack of funds, many craftsmen assemble autonomous heating with their own hands, using self-assembled structures, mainly solid fuel, instead of factory boilers, a typical example is a metal stove in a living room with an expansion tank in the attic and a steel piping system with radiators.
Rice. 7 Operating principle and main components of a gas convector
According to the pipeline material. Polymer pipes made of PP polypropylene, cross-linked polyethylene and PEX metal plastic are gradually replacing metal products; in old buildings, external steel pipelines are still used to supply water to radiators. Some homeowners, if they have significant financial resources, install coolant through copper pipelines entirely or in separate sections. Modern advanced systems are installed from special thin-walled steel pipes using crimp technology for connecting elements of plumbing fittings using fittings.
According to the method of supplying coolant to heat exchangers. There are 2 main methods of supplying heated liquid to the pipes of heating radiators - one-pipe and two-pipe, sometimes a combined connection is used. To connect the underfloor heating pipeline, manifold wiring is used, which makes it possible to connect several circuits to one distribution unit; systems with a large number of radiators are connected through hydraulic arrows or radiator manifolds. When connecting heat exchange radiators, various pipeline layouts are used - radial, dead-end, associated, special horizontal (Leningrad).
There are also various ways to connect the inlet and outlet pipes of heat exchange radiators to the heat main - vertical, horizontal, diagonal, bottom.
Rice. 8 Pipe layouts
According to the location of the storage tank. The expansion tank, which is an important element of any heating system, can be a sealed, factory-made type (red accumulator) and built into the circuit in any convenient place - such systems are called closed, since there is no direct access to the coolant. The movement of liquid through the pipeline in systems of this type is carried out using an electric circulation pump installed below, not far from the boiler, next to the hydraulic accumulator.
In another type of heating system, called gravity, the storage tank is installed at the top of the attic, the pipelines have a slight slope when approaching the radiators, and at their outlet a small angle of inclination is maintained towards the boiler. The circulation of liquid in the system occurs by gravity due to the fact that heated water or antifreeze has a lower density and is therefore pushed upward by denser cold layers.
Rice. 9 Open heating system
What are combi boilers
Since electric heating is expensive, you can use an alternative solution and choose a boiler that can operate on two types of fuel. For example, you can purchase electrical equipment that can also perform the functions of a gas water heater. Or you can choose a solid fuel boiler that can also work with electricity for some time.
As long as there are no interruptions in the gas supply, such a boiler will work properly according to the generally accepted scheme, but as soon as any problems arise, it will be possible to switch to another type of fuel and thereby provide stable heating to the house.
A combination boiler is more expensive than a regular boiler, but such expenses will be completely justified: your home is guaranteed not to be left without heat, and even if one system fails, the second will immediately be able to support it. The temperature level will remain at the same values, and it will be comfortable to be in the room.
It is quite difficult to independently design and implement an individual heating system, but it is still possible. Your home will receive reliable heating, which will not depend on the presence or absence of gas pipes.
You need to enable JavaScript or update your player!
Boiler power calculation
Regardless of the type of fuel used (solid or liquid, gas or electricity), the principle of connecting all heating systems is the same. The only difference is at the boiler installation stage. In this case, its power is calculated using a single formula:
where W is the specific power required for heating 10 square meters. m of room; S – total area of the house.
For Russian regions, the following power values are taken into account: • for houses located in central Russia up to 1.5 kW; • for Siberia and the North: for every 10 sq. m up to 2 kW; • for southern regions: up to 0.9 kW.
Since 10 sq.m. is sufficient for heating. m of a residential building located in central Russia requires up to 1.5 kW of power, then, for example, for heating 100 sq. m you will need a 15 kW boiler:
(100 x 1.5)/10 = 15 kW
This figure is increased by 15-20% (power reserve for possible heat loss, which is inevitably lost even with ideal insulation of the building). Thus, to heat a house of 100 sq. m will need (15 + 2.3) = 17.3 kW.
Recommended boiler power
Water heating devices
The following can serve as heating elements for rooms:
- traditional radiators installed under window openings and near cold walls, for example, on the north side of the building;
- pipe underfloor heating circuits, otherwise heated floors;
- baseboard heaters;
- in-floor convectors.
Water radiator heating is the most reliable and cheapest option among those listed. It is quite possible to install and connect batteries yourself; the main thing is to correctly select the number of sections according to power. Disadvantages are poor heating of the lower zone of the room and the placement of appliances in plain sight, which is not always consistent with the interior design.
All commercially available radiators are divided into 4 groups according to the material of manufacture:
- Aluminum - sectional and monolithic. In fact, they are cast from silumin, an alloy of aluminum and silicon, and are the most efficient in terms of heating speed.
- Bimetallic. A complete analogue of aluminum batteries, only the frame is made of steel pipes inside. Scope of application: multi-apartment high-rise buildings with central heating, where the coolant is supplied at a pressure of over 10 bar.
- Steel panel. Relatively cheap monolithic radiators made from sheets of stamped metal plus additional fins.
- Cast iron sectional. Heavy, heat-intensive and expensive devices with an original design. Due to their considerable weight, some models are equipped with legs - it is unrealistic to hang such an “accordion” on the wall.
Note. We are talking about cast iron radiators in a modern design. Soviet-style MS-140 batteries are outdated in all respects.
In terms of demand, steel appliances occupy a leading position - they are inexpensive, and from the point of view of heat transfer, thin metal is not much inferior to silumin. Next come aluminum, bimetallic and cast iron heaters. Choose which ones you like best.
Construction of heated floors
The underfloor heating system consists of the following elements:
- heating circuits made of metal-plastic or polyethylene pipes, filled with cement screed or laid between joists (in a wooden house);
- distribution manifold with flow meters and thermostatic valves to regulate water flow in each loop;
- mixing unit - a circulation pump plus a valve (two- or three-way) that maintains the coolant temperature in the range of 35...55 °C.
The mixing unit and the manifold are connected to the boiler by two lines - supply and return. Water heated to 60...80 degrees is mixed in portions by valve into the circuits as the circulating coolant cools.
Warm floors are the most comfortable and economical heating method, although installation costs are 2-3 times higher than installing a radiator network. The optimal heating option is shown in the photo - floor water circuits + batteries, controlled by thermal heads.
Warm floors at the installation stage - laying out pipes on top of the insulation, attaching a damper strip for subsequent filling with cement-sand mortar
Skirting and in-floor convectors
Both types of heaters are similar in the design of the water heat exchanger - a copper coil with thin plates mounted on it - ribs. In the floor-standing version, the heating part is covered with a decorative casing that looks like a plinth; gaps are left at the top and bottom for the passage of air.
The heat exchanger of the in-floor convector is installed in a housing located below the level of the finished floor. Some models are equipped with low-noise fans that increase the heater's performance. The coolant is supplied through pipes laid hidden under the screed.
The described devices fit well into the design of the room, and underfloor convectors are indispensable near transparent external walls made entirely of glass. But ordinary homeowners are in no hurry to purchase these devices because:
- copper-aluminum convector radiators are not a cheap pleasure;
- to fully heat a cottage located in the middle zone, you will have to install heaters around the perimeter of all rooms;
- in-floor heat exchangers without fans are ineffective;
- the same products with fans emit a quiet monotonous hum.
Baseboard heating device (pictured left) and in-floor convector (right)
Hence the conclusion: a convector is a useful thing for certain places where it is difficult to place conventional batteries. But heating an entire building with such devices is unreasonably expensive.
Methods of water circulation in heating systems
The movement of liquid along a closed circuit (circuits) can occur in a natural or forced mode. Water heated by the heating boiler rushes to the radiators. This part of the heating circuit is called forward stroke (current). Once in the batteries, the coolant cools down and is sent back to the boiler for heating. This period of the closed route is called the return stroke (current). To speed up the circulation of the coolant along the circuit, special circulation pumps are used, embedded in the pipeline at the “return”. Models of heating boilers are produced, the design of which provides for the presence of such a pump.
Natural coolant circulation
With natural circulation, the movement of water in the system occurs by gravity. This is possible due to the physical effect that appears when the density of water changes. Hot water has a lower density. The liquid flowing in the reverse direction has a high density, and therefore easily displaces the water that has already heated up in the boiler. The hot coolant rushes up the riser, and is then distributed along horizontal lines laid at a slight slope of no more than 3-5 degrees. The presence of a slope allows liquid to move through the pipes by gravity.
The heating scheme, based on the natural circulation of the coolant, is the simplest and therefore easy to implement in practice. In addition, in this case, no other communications are required. However, this option is only suitable for small private houses, since the length of the contour is limited to 30 meters. Disadvantages include the need to install larger diameter pipes, as well as low pressure in the system.
Forced coolant circulation
In autonomous heating systems with forced circulation of water (coolant) in a closed circuit, there is a mandatory circulation pump, which provides an accelerated flow of heated water to the batteries, and cooled water to the heating device. The movement of water is possible due to the pressure difference that occurs between the forward and reverse flow of the coolant.
When installing this system, it is not necessary to observe the slope of the pipeline. This is an advantage, but a significant disadvantage lies in the energy dependence of such a heating system. Therefore, in case of a power outage, a private home must have a generator (mini-power plant), which will ensure the functioning of the heating system in an extreme situation.
A circuit with forced circulation of water as a coolant can be used when installing heating in a house of any size. In this case, a pump of suitable power is selected and its uninterrupted power supply is ensured.
Natural circulation systems
Systems with natural circulation, due to their characteristics, are more suitable only for houses with a total area of up to 200 square meters. m, or rooms with few thermal circuits. In addition, they will require large diameter pipes (at least 40-50 mm). Moreover, they are laid at an angle to the horizontal plane so that the water flows under the influence of its own weight. Such systems are difficult to regulate, but they are independent of the power supply.