string(10) “error stat”
The radiator is a key element in the cooling system of the internal combustion engine. Its task is to transfer excess heat generated during fuel combustion to atmospheric air. Even the earliest cars with internal combustion engines had devices resembling a modern radiator, because in the absence of a special element that ensures cooling of the power units, the operation of the latter, as it was established, was simply impossible. A car radiator ensures that the temperature of a running engine is maintained within certain strictly defined limits, preventing it from overheating and the inevitable jamming in this case.
Purpose of the radiator
Contrary to popular belief, a car cooling radiator performs several functions at once. His tasks include:
- Heat removal from product elements and its transfer to the atmosphere.
- Providing the possibility of adding and removing coolant (antifreeze, water, antifreeze) using special holes at the bottom and top.
- Creation of optimal pressure inside the system, thanks to the presence of a relief valve.
The main function of the radiator is to exchange heat and reduce the coolant temperature to a safe level.
Depending on the situation, cooling occurs by blowing with counter air or a fan, which starts when a certain temperature is reached. Depending on the make/model of the vehicle, the fan may be mechanical, electric, or hydraulic. The second option is considered the most popular.
A little history
The history of the creation of radiators goes far back, several thousand years ago, when people began to think about how to make their home warm and comfortable for living in the cold season. Then they heated themselves using an open fire, the smoke from which escaped through a special hole. The first heating battery appeared already in Ancient Rome in the form of a stove with a pipe. Interestingly, some modern houses still use this type of heating system to this day.
In 1855, German entrepreneur Franz San-Gali created the first cast iron radiator and called this device a “hot box”. The cast iron radiator has become widespread throughout the world and was used in steam heating systems. This was a serious start for new inventions in the field of heating. The first tubular steel radiator, invented by Rubert Zehnder, appeared in 1930. This discovery was a triumph. The battery was named Zehnder and demonstrated excellent technical characteristics: lighter weight than cast iron units and high heat transfer.
A little later, bimetallic radiators appear that combine both steel and aluminum, embodying all the advantages of steel and aluminum batteries. Subsequently, many companies mastered this technology, and it is still successfully used in the modern world for the production of radiators. Cast iron batteries came to Russia in the 20s, and already in the 40s all Soviet apartments had cast iron heaters. Aluminum and bimetallic radiators in Russia became popular much later than in Europe.
How does the engine cooling system work?
When considering a radiator, it is important to know the features of the car's cooling system, which is designed to reduce engine temperature to a safe level. In addition, its functions include heating the air, cooling the exhaust gases, the flow in the turbocharged system, as well as the oil in the automatic transmission. Structurally, the cooling system can be liquid, air or mixed. The most popular is the first option. Structurally, it consists of the following elements:
- Radiator. The main unit through which coolant passes to reduce the temperature.
- Water pump. Guarantees the circulation of working coolant throughout the system. It can be belt, gear or other types.
- Thermostat. Necessary to regulate the process of antifreeze passing through the radiator. It can have three positions - closed, partially / fully open.
- Fan. Triggered to increase airflow efficiency. Most often necessary when the car is moving at low speed and the air flow is not enough for cooling.
- Temperature sensor. Controls the temperature regime and gives a command when it is necessary to start additional cooling.
- ECU. The main unit that receives signals and regulates the operation of the car’s engine cooling system.
Depending on the car, other components may also take part in the operation, for example, an engine cooling relay, a heater, a thermostat, a fan control unit, etc.
Important
All elements interact closely with each other. So, after starting the engine, the coolant circulates using a pump in a minimal circle - through the block and cylinder head without passing through the radiator.
This is done for faster heating. As soon as the temperature reaches 80-90 degrees Celsius, the sensor is triggered and sends a command to open the thermostat.
In this case, antifreeze is directed through the radiator to maintain normal temperatures. If the engine continues to heat up, a signal is sent to turn on the fan, providing additional airflow.
Operating principle: convection vs. radiation
The operating principle of a heating radiator is extremely simple. Water, which has already been heated to the required temperature, flows from the boiler into the room through pipes. Then it enters the heating devices, which heat the air in the rooms of your home.
Convective heating radiator
It is worth noting that if heat is transferred by convection - this is accelerated heating of air that flows through the heating surface, then such a heating device will be called a convector. If heat is transferred by radiation, that is, heating of the surrounding air is produced by a surface that has an increased temperature and heat capacity, then this will be a radiator.
The operating principle of a heating battery can also have a combined form - panel radiators-convectors.
Considering how a heating battery works, it is worth noting that in order to quickly warm up a room, a convector is more suitable. However, such a cross-sectional heating battery has one drawback - due to the passage of active convection, a lot of dust is released into the air, which will not have the best effect on the health of those present. That is why convector batteries are used only where there are problem areas of the heating system. For example, to create an air curtain in a room with a large glass area, where conventional devices cannot fit in size.
Regardless of the temperature in the heating radiators, they will give off approximately 60 percent of the heat by radiating thermal energy, while the rest will be given off by convection. Thus, a minimum of hot air convection is achieved and those objects located in the room are well heated. In this regard, it can be noted that the way a radiator works is similar to a heated floor system.
Convectors or “in-floor” heating radiators
Types of radiators
Structurally, the devices under consideration differ in several criteria: assembly method, case material and additional elements. Taking into account the features, the price of a car radiator also differs. By design they are:
- Tubular-plate. They consist of tubes, inside of which so-called turbulators are mounted. This is done to lengthen the coolant path through the radiator and, accordingly, improve cooling. Such devices have greater rigidity and a minimal percentage of defects.
- Tubular-tape (soldered). Unlike the previous version, all elements are connected by soldering, which complicates the maintenance process. Such radiators have higher heat output and lower price.
There are two options based on the number of moves:
- One-way. Fluid flows in one direction.
- Two-way. The coolant path is more complex. First, the antifreeze passes through part of the tubes in one direction, and then in the second compartment it changes direction.
According to the material:
- Copper. More expensive. They are characterized by increased strength and better heat transfer. Easily repaired by soldering.
- Brass. They are rarely found in their pure form. Copper-brass structures are most often used.
- Aluminum car radiators. Appeared against the backdrop of rising copper prices. In production, modern welding methods are used, providing increased reliability and strength. Despite the worse heat transfer, such products cope with this task.
Today, all car engine radiators are made of aluminum. They have a lower price, but require a special approach to repair. For restoration, conventional soldering is not enough, because it usually has low efficiency. Argon welding is most often used.
Design features
When you choose radiators, there are several important points to consider. If you choose sections of radiators, you can increase the heating area if necessary. If the design of the heating radiator is panel, or it is a convector, then you will not change it structurally. When calculations are first made, it is very difficult to take into account all the nuances that will affect the amount of heat required for each individual room. And if the heating battery device is sectional, then this will make it possible to reduce and increase the number of sections, and replace those elements that have failed.
The cost of installing a heating radiator and installation rules
|
|
The heating radiator diagram is also characterized by an important aspect - the center distance, which displays the vertical distance between the centers of the inlet and outlet pipes. This point should be especially taken into account when an existing radiator or pipework is being replaced. If you buy a radiator with a different center distance, you will either have to change it or change the placement of the pipes.
The design of a heating radiator also means that it is important to consider the diameter of the pipes. If it is too small, it will cause the heating devices to clog faster.
After all, the quality of the coolant usually leaves much to be desired: the water contains sand, scale and rust. All these unpleasant moments when settling first cause the heating system to operate ineffectively, and then can even lead to its complete breakdown.
The correct choice of heating radiators is the most important nuance. A suitable sectional heating radiator is the key to good operation of the heating system.
Coolants
A coolant (liquid) moves inside the system, which, when passing through the radiator, is cooled and returned to the engine. Conventionally, all coolants are divided into several types:
- Distilled water. The most economical option that does not require the purchase of additional funds. It is used in the warm season, when there is no risk of the system freezing.
- Antifreeze is the old name for coolant used in the USSR. Previously, such compositions were poured into Zhiguli, but today they are almost never used.
- Antifreezes are modern coolants that contain special additives. They differ in terms of service life, corrosion protection features, the presence of additives and other features.
Conventionally, antifreezes are ethylene glycol, carboxyl, hybrid, lobrid and propylene glycol. They differ in characteristics, composition, set of additives and characteristics. For example, inorganic corrosion inhibitors are used in ethylene glycol compositions, and organic ones are used in carboxyl compositions. Hybrid and lobrid ones contain organic and inorganic components. As for propylene glycol coolants, they use safer propylene glycol.
The task of modern antifreezes is to remove heat, protect against corrosion and clean the car radiator from contaminants accumulated inside.
At the same time, the anti-corrosion function is considered the most important, and the effectiveness of this option directly affects the price. When choosing a coolant, you need to focus on the manufacturer’s recommendations in relation to the car brand.
Why is it needed in the car?
A car engine works due to the combustion process of fuel in the cylinders. As a result, all parts become very hot. When the temperature of metal elements increases, they expand. If they are not cooled, this will lead to various problems in the power unit, for example, cracks in the cylinder head, in the cooling jacket, cylinder head deformation, excessive thermal expansion of the pistons, and so on. Ignoring such problems will lead to expensive engine repairs.
To stabilize the temperature, all internal combustion engines are designed with a cooling jacket through which liquid circulates using a pump. The heated antifreeze flows through the line into the car radiator. In it, the liquid is cooled and then returned to the engine. This process allows you to maintain the operating temperature of the internal combustion engine.
If there were no radiator in the design of the cooling system, the liquid in it would quickly boil. In a car, this part is installed in the front part of the engine compartment. This is necessary so that more cold air enters its plane.
The efficiency of heat exchangers depends on the following factors:
- number of tubes - the more there are, the better the antifreeze will cool;
- tube cross-section - oval shape increases the area of contact with air, which increases heat transfer;
- forced airflow - especially useful in city driving;
- cleanliness - the more debris there is between the fins of the heat exchanger, the more difficult it will be for fresh air to get to the hot tubes.
Damage, malfunctions and repairs
The radiator cannot be called the most reliable component of a car. During operation, it is affected by many negative factors, including mechanical ones. The most common damages include:
- Contamination of pipes and central part. In this case, flushing may be required.
- Fan damage.
- The accumulation of dirt and leaves on the outside of the product, which reduces heat transfer.
- Damage to the pipes or the radiator itself with subsequent leakage of coolant from the system.
- Corrosion of internal elements.
If any of the problems discussed above occur, there is a high risk of engine overheating, so the car’s radiator needs to be repaired. A sign of a breakdown may be the appearance of an antifreeze leak or rapid overheating of the engine during moderate operation.
The most difficult case is when the engine “boils” and steam starts coming out from under the hood. In this case, you need to stop and wait for the system to cool down. Only after this can you begin to troubleshoot the problem. If the problem occurs on the road, do the following:
- Check the tightness of the connections of all tubes.
- Make sure the cooling fan operates.
- Check relay wiring and temperature sensor.
- Add the required amount of coolant. Be careful as there is a high risk of hot liquid splashing.
It is better to entrust repairs to professionals. If it is not possible to go to a service station, you can use epoxy resin or “cold welding”. You must first drain the coolant from the system and remove the device from the car for easier access. There are other repair methods:
- Welding. Used when there is minor damage. Suitable for copper or brass devices. Requires a gas torch and degreaser. When performing argon welding on an aluminum “cooler”, aluminum wire is needed.
- Replacement. In a situation where the tube is damaged along its entire length, it will not be possible to solder the car radiator or weld the hole. The only way to solve the problem is to replace the old tube with a new one.
When deciding on the need and method of repair, it is necessary to assess the damage. In the most severe cases, the entire radiator may need to be replaced.
What is better to fill in in winter: antifreeze or antifreeze?
Experts never tire of saying that almost half of all car engine breakdowns are associated with problems in the cooling system. Using good technical fluids, timely maintenance and monitoring the tightness and quality of cooling will make engine operation much more convenient.
In Russia, drivers have a certain choice among technical fluids: antifreeze or antifreeze. By the way, except for the CIS countries, such a division does not exist anywhere else. However, it is worth determining the difference between these two liquids and understanding what is best to pour into your car in winter to avoid unexpected breakdowns.
Prevention and care
To extend the life of the product, proper care and regular maintenance are required. It is important to understand that the radiator absorbs all the dirt and dust and therefore needs to be flushed periodically. If nothing is done, the device quickly becomes clogged and stops performing its functions.
The main means of prevention is periodic flushing and cleaning of the car’s cooling system. You can do this yourself or entrust the work to a specialist.
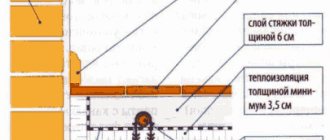
| Stages of flushing a car's cooling system |
| 1. Allow the engine to cool, secure the hood and put on special gloves that do not allow water to pass through. |
| 2. Drain the antifreeze from the cooling system and fill it with distilled water |
| 3. Start the engine and leave it for 20-25 minutes |
| 4. Drain the liquid and repeat this procedure several times to completely clean the system. It is necessary to act until clean water begins to come out of the system. |
| 5. At one stage, add cleaning agent to the water to better clean the system. You can find special formulations on sale, for example, Winns Radiator Flush |
During operation, we must not forget that the radiator can become clogged from the outside. The pollutants are leaves, dirt, dust, etc. To solve the problem, you need to dismantle the product and blow it with air pressure or rinse it with a stream of water under high pressure. The main thing is not to overuse the pressure to avoid damaging the device’s cells.
After this, it is necessary to fill the system with high-quality antifreeze with a set of necessary anti-corrosion additives. To eliminate air locks, open the cap on the radiator and start the engine. After some time, the air will come out on its own, and all that remains is to add coolant to the system.
What is better: repair or change?
Replacing the engine cooling radiator on a VAZ-2114 with your own hands: removal and replacement
All motorists can be divided into two categories. The first ones believe that the failed part needs to be replaced with a new one. The latter are confident that everything can be repaired. And repairing radiators is a frequent topic of controversy.
The Internet is replete with all kinds of advice on how to fix leaks yourself. Some use special plastic compounds. Others pour products into the system designed to plug cracks. Sometimes some methods help to temporarily extend the life of a part. But in most cases, these methods only clog the cooling system.
It makes sense to repair copper models because they are quite easy to solder. In the case of aluminum analogs, the situation is different. They can be soldered, but this will require expensive welding. Therefore, the cost of repairing a leaking radiator will be almost identical to the price of a new part. It makes sense to agree to this procedure only in the case of an expensive heat exchanger model.