Heat exchanger is equipment in the working unit of which heat exchange between elements with different temperatures is established.
What do heat exchangers look like?
Advantages of heating systems based on heat exchangers:
- ease of operation and ease of maintenance;
- durability;
- uniform heating of large areas;
- convenient thermal control system;
- no bulky radiators;
- thermal comfort in the room.
Areas of application
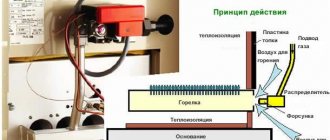
Design, diagram and principle of operation of flow-through gas columns
The following areas of use of heat exchange equipment are distinguished:
- cooling systems;
- heating systems;
- air conditioning systems;
- chemical industry;
- heating of swimming pools;
- solar collectors;
- mechanical engineering;
- ventilation systems;
- metallurgy;
- pharmacy;
- auto production;
- food industry.
In addition, it is possible to use heat exchange equipment for heating private households. You can install the device either independently or with the help of a wizard. Using this technique helps to evenly distribute heat in the room.
Booster Summary
This is very rare and expensive equipment. If you intend to buy it, then you will expect expenses in the range of 40,000 - 90,000 rubles. And for everyday tasks this is a rather unprofitable solution.
The booster itself is a container with a built-in pump that provides a change in the flow vector. Because of this, the efficiency of washing increases significantly. The devices are resistant to any reagents.
The most popular models are presented below:
| Booster | A country | Productivity (liters per hour) | Tank volume (l) | Working pressure (bar) | Price tag (RUB) |
| PIPAL PUMP ELIMINATE 20 V4V | Italy | 2600 | 18 | 1 | 38 000 |
| BWT Cillit SEK 28 | Germany | 2400 | 20 | 1,5 | 57 000 |
| TM Aquamax | Italy | 5000 | 30 | 1,2 | 53 500 |
Classification
The classification of heat exchangers involves dividing them into the following types:
- lamellar;
- tubular.
Thermostat for a heating radiator: types and principle of operation
Plate devices include a series of plates with wavy channels with stampings and surfaces designed to circulate fluids. The plates are connected using rubberized gaskets and ties. The advantages of such devices are ease of use and compactness.
Plate heat exchangers are increasingly used. The scope of their use is not limited only to industrial equipment; it is also possible to install these devices in residential buildings for the installation of heating systems.
Plate heat exchangers are classified into groups:
- non-separable (also welded and soldered);
- semi-welded;
- collapsible.
Collapsible devices are the most popular. In them, the plates are separated using rubber seals. Installation does not take much time, and operation is easy.
The classic version of plate heat exchangers has inlet and outlet pipes on the surface of the front plate. Some devices have connections on both the front and rear panels. Working media are connected to the pipes using flanged, threaded, steel connections. Some models have a smaller number of pipes, then the coolants are connected directly to the stove.
Tubular heat exchangers involve small diameter tubes welded into other tubes. The advantages of the device are considered to be used in conditions of increased pressure.
According to the criterion of the heat exchange method, equipment is divided into mixing and surface. Mixing-type devices transfer heat when the media are in close contact. Surface heat exchangers contain two circuits in which media with different temperatures move. Heat exchange between them is possible through the surface elements of plates, walls, sheets or pipes, which are made of heat-conducting materials (stainless or high-carbon steel, non-ferrous metal alloys). This type of equipment is used in housing and communal services, industrial enterprises and small businesses.
Surface heat exchangers are divided into types: recuperative and regenerative. Recuperative heat exchangers are characterized by constant heat exchange through the walls of the circuits with unidirectional movement of the carriers. In regenerative devices, alternate contact of carriers with a heat-exchange surface occurs.
Recuperative heat exchangers are also classified:
- Submersible. The principle of operation involves the movement of one coolant along a coil, which is immersed in a tank containing a second coolant liquid. The model is easy to use and has an optimal price.
- Irrigation. Field of application: as capacitors in cooling systems. Heat exchangers look like coils made of horizontal pipes that are placed in a vertical plane. Each row of pipes has a gutter through which water at a low temperature flows onto them. Water that has not evaporated is returned to the system thanks to the pump.
- Twisted. They are a system of pipes wound around a core. Compact and highly efficient.
- Spiral. The equipment is characterized by the appearance of two spiral channels, which are wrapped around the central partition. Designed for cooling and heating viscous liquids.
- Shell and tube. The tube sheets are attached to the casing by welding. Pipes are fixed in them. They are fastened tightly using flaring. The grilles are closed with covers on studs, bolts and gaskets. The casing includes fittings (pipes). The principle of operation is the circulation of a coolant in the interpipe space and through the pipes. Increased heat transfer occurs with the help of fins.
- Sectional – a sequence of sections that represent shell-and-tube devices.
- Lamellar. Includes a set of plates with wavy surfaces with stamping and channels for the movement of liquids. Operation is only possible at reduced pressure.
Shell and tube heat exchanger
Material of manufacture
The heat exchanger for the boiler is made from durable materials that conduct heat well, are not prone to corrosion and are sufficiently resistant to pressure. Since the cost of the material also has to be taken into account, the choice is limited.
Steel
A steel heat exchanger is cheaper in price, but less durable.
This is the most affordable material. Steel is very strong, but can be processed well. The price is low. The advantage of this option is resistance to high temperatures. Steel is plastic and does not crack when heated, and does not deform even in areas in contact with the burner.
A steel heat exchanger for a solid fuel or gas boiler is prone to corrosion. Water inside the tubes and combustion products in the boiler chamber have a destructive effect on the material. This affects durability. The steel model weighs a lot, which leads to additional fuel consumption for heating the element itself.
The stainless steel heat exchanger is resistant to corrosion and lasts for at least 50 years.
Cast iron
The material is much more resistant to corrosion than steel, and is not afraid of rust and the action of acid anhydrides. The service life reaches 50 years. However, cast iron is a brittle alloy and can crack under the influence of temperature. To avoid damage, the cast iron tubular heat exchanger must be washed: if ordinary water is used, then once a year; if antifreeze - then once every 2 years; if distilled liquid - once every 4 years.
The weight of a cast iron element is even greater, so more fuel and time have to be spent on heating.
Copper
Copper is a noble metal that is not susceptible to any type of corrosion. It is chemically inert and tolerates pressure well. Copper conducts heat better, so less fuel is required to heat the element itself and the flowing liquid. The weight of the copper model is small, the dimensions are compact with a very developed working surface.
The disadvantage is the high price. Also, the copper heat exchanger is too sensitive to heating to high temperatures. More often found in boilers from foreign manufacturers.
Structure and principle of operation
The mechanism of action is easy to consider using the example of a factory-assembled plate heat exchanger. The structure provides two circuits and four outputs. The plate device separates the flows by pressure and temperature. Coolants are acids and other liquids.
Mayevsky crane: principle of operation
Heat exchangers for heating involve connection to one circuit of underfloor heating, and to the other - a heating plant.
Direct connection of the central coolant is impossible, since this leads to failure of the warm floor covering.
This occurs due to increased pressure in the heating plant, temperature changes and the presence of chemically aggressive substances in the coolant.
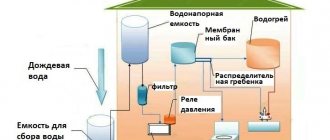
The structure of the heat exchanger is shown in the figure below.
Schematic design of a plate heat exchanger
The structure of the heat exchanger is:
- a frame, which on one side of the device is attached to a stationary pressure plate and serves as a support element;
- a package of plates that forms channels for coolant between the constituent elements;
- frame, which consists of a movable pressure plate, a fixed pressure plate and a rear pillar;
- a casing that serves to protect the device from external influences;
- studs that are placed along the edge of the holes through which coolant enters the device;
- gasket required to seal the channels;
- supporting and fastening elements (guide beams, supporting base, legs of the bed and frame, bearings, bolts, nuts, washers).
The blue and red arrows in the figure indicate the directions of movement of the cold and hot coolant inside the heat exchanger, respectively.
In everyday life, a heat exchanger is used, whose operating principle is based on the separation of flows and maintaining the autonomous functioning of heated floors at a reduced operating pressure of 1.5 bar and the connection of clean water.
The structure of heat exchange equipment consists of three groups of plates:
- Dialed belonging to an autonomous heating system with a reduced pressure level.
- Dialed belonging to a central heating system with increased levels of temperature and pressure.
- Separating, characterized by small thickness and transferring heat from a centralized system to an autonomous one.
The number and parameters of the plates determine the power of the heat exchange equipment. Each device requires the installation of a cleaning filter. It is able to retain coarse particles: scale, chips and others. The filter needs to be periodically washed with cleaning solutions.
Operating principle of the heat exchanger
The operating principle of the heat exchanger is to transfer thermal energy from one coolant to another. The device receives a direct heating medium and a cold medium. When they pass between the plates through the channels, the cold medium is heated. At the outlet of the heat exchanger, a heated medium and a return heating medium are obtained. Inside the equipment, heat transfer fluids move towards each other, that is, in countercurrent, and cannot mix because they are separated by plates.
Model types
The devices differ in the installation method. And this directly affects the efficiency of the entire system. Very often a boiler design is used that already has a heating heat exchanger inside. Heat losses in such devices are practically reduced to zero. And for productive work all you need is proper configuration.
External structures are much less efficient. Because their position does not allow the coolant to heat up well. But they are used where there are no individual heating boilers. For example, in houses using centralized heating.
Equipment characteristics
Heat exchange equipment is marked with the following data:
- test pressure level;
- maximum operating pressure level;
- maximum operating temperature level;
- manufacturer.
In addition, the package includes a diagram and a technical passport in the language of the manufacturing country, translated, if necessary, into the language of the selling country.
Diagonal and vertical arrangement of contours is possible. When the circuits are arranged diagonally, it is necessary to install only in a vertical position. Then it is possible for hot water to flow into the heat exchanger in the direction from top to bottom. In this case, heat is transferred to the autonomous system through separating plates.
The water at the inlet is at an increased temperature, and at the outlet it is reduced. In this case, in a circuit belonging to an autonomous system, the coolant moves from bottom to top. At the lower levels, the water is slightly heated, and when approaching the upper levels, the heating intensifies. This makes the system easier to operate. Water supply to the equipment is possible thanks to forced circulation.
Malfunctions, repairs
Gas heaters have light indication. It is intended to notify of malfunctions. Each manufacturer creates its own character code contained in the passport. If you don’t have a passport, you can download it on the Internet. Malfunctions can be divided into two categories:
- those that can be eliminated on your own;
- requiring specialist intervention.
What you can fix yourself is not specified in the passport. Common heat exchanger failures:
- depressurization;
- blockage
Elimination of leaks is carried out with a soldering iron, welding, depending on the metal. The second malfunction occurs due to poor-quality coolant, scale. Eliminated by washing. To remove scale, you can use phosphoric acid or citric acid. The first one is more effective. How to do it is shown in the video:
Sometimes there is a manufacturing defect, but more often the malfunction occurs due to improper use of the devices. If you strictly follow the manufacturer's recommendations, the product will last a long time and with high quality. Boiler repair:
Installation
Installation of a plate heat exchanger, as the most common, is carried out according to three options:
- parallel;
- mixed two-stage;
- sequential two-stage.
When installing in parallel, it is necessary to install a thermostat. This method saves space, time, and also does not require large expenses. The two-stage mixed circuit provides significant savings in coolant. This is achieved by using a reverse flow of warm water to heat the flow at a lower temperature.
Using a sequential circuit splits the incoming stream into two branches. One of them passes through the regulator, the other through the heater. Next, both flows are mixed and then enter the heating unit. This saves coolant. Full automation of the equipment is impossible.
Heat exchangers are fixed to the wall using a fastening tape, a console and a corner attached to the bottom of the device. After this, you need to install filters. The minimum condition is the presence of a filter system in the heating plant system. Before installation, it is worth preparing taps and American ones - threaded detachable connecting components. Each of them includes a union nut, a gasket and two fittings. It is important to select the correct spare parts so that they match the diameter of the connection system. Then installation will not be difficult.
Appearance of plate heat exchanger
Popular manufacturers
Aster heat exchangers of domestic production
In the Russian market, collapsible and soldered heat exchangers from the RIDAN and ASTERA brands have proven themselves well, characterized by a high level of quality and availability of the necessary spare parts.
Among foreign brands, buyers more often choose diesel and standard devices from ALFA LAVAL, DANFOSS and SONDEX.
When choosing a unit, you need to take into account the features of the system as a whole, the estimate, if we are talking about a project, requirements for the number of kW, as well as other necessary parameters.
Potbelly stove with heat exchanger. Video
You can learn about the features of making a potbelly stove from gas cylinders with a heat exchanger from the video below.
Despite the wide range of applications of heat exchangers, the most popular is their use as an additional heating system. Optimal technical characteristics ensure high-quality heating of rooms of any size. Installation of floors with heat exchangers does not take much time, they are easy to use and durable. It is necessary to conduct timely preventive inspections of the system in order to promptly eliminate possible problems.
Selection rules
Types of coolants used for heating systems
The list of main criteria that you need to pay attention to when choosing includes:
- type and quality of the thermal fluid used;
- ease of disassembly and assembly;
- type of heat transfer;
- the ability to increase the amount of power during operation.
Plate exchangers are more often used for cooling and heating systems of refrigerators and swimming pools, spiral exchangers are used in various industries, horizontal ones are better suited as heating devices.
Installation methods
There are two main ways to install the device - directly on the stove or on the chimney pipe (samovar-type device or so-called water jacket).
In the first case, the efficiency of the installation will be significantly higher, because the container will receive heat not only from the chimney pipe, but also from the heat of the heater.
Note! Despite all the advantages, this method has a significant drawback: the water in the container heats up faster than the stove and begins to boil. Over time, scale forms on the surface of the tank, which is why the model needs regular cleaning.
Step-by-step instructions on how to make it yourself
You can construct a device for exchanging heat from the heating network to water with your own hands.
Tools and materials
To construct a plate heat exchanger with your own hands, you will need:
- welding machine;
- Bulgarian;
- stainless steel sheets - two corrugated, one flat. Thickness 4 mm;
- electrodes.
Manufacturing process
The entire manufacturing process of the device is divided into several stages:
- It is necessary to cut corrugated steel plates. You will need 31 plates measuring 300 by 300 mm.
- A strip 18 meters long and 10 mm wide is cut from a flat sheet. The tape must be cut into pieces 300 mm long each.
- Squares of corrugated material are welded to each other with a ten-millimeter strip from different sides, adjacent sections must be perpendicular. You will get 15 sections facing one way and 15 the other in the form of a cube.
- A flat stainless steel manifold must be welded to the parts where water will flow.
- A hole is drilled in each collector, and the connecting part of the pipe is welded to it.
- The structure is mounted with the open side facing the gas system.
Simple design: coil
Installing a heat exchanger tank on a chimney involves welding work, which not everyone can do. A simpler design is a coil wrapped in a spiral around the chimney. The coil can be made from a copper or aluminum tube - these metals are easy to bend, have high thermal conductivity and are not subject to corrosion.
The diameter of the tube is chosen so that it is convenient to connect it to the fittings of the water storage tank. For bending, pipes with a diameter of no more than 28 mm are more convenient. In any case, the length should not exceed 3 meters - this is a prerequisite for natural coolant circulation . To connect the heating coil to the tank, use a flexible hot water line.
This heat exchanger design can be used to produce hot water, or less often for heating small rooms. Maximum heating efficiency is achieved if the coil is installed on the chimney of a simple stove such as a potbelly stove with a high temperature of the flue gases.
DIY chimney coil
A pipe heat exchanger is usually installed on the chimney of a metal stove installed in a garage or workshop to produce warm water or heating. It is also possible to install a coil on a sauna stove.
Necessary materials:
- pipe made of copper, aluminum or steel - about 3 meters;
- flexible hose for hot water supply with a diameter of ¾ inches - 2 pieces of the required length;
- a storage tank equipped with a float valve for water supply and a drain valve for its consumption;
- ball valve for draining the system.
Sequence of work:
- The most difficult thing when making such a heat exchanger is to bend the pipe into a spiral without reducing its cross-section. Copper pipes with a diameter less than 28 mm can be bent using a pipe bender without heating. Steel and aluminum, as well as larger diameter pipes, must be heated with a blowtorch before forming.
- You can also use this method: fill the pipe with dry sand and tightly plug its ends with wooden plugs. The pipe is bent according to the template - a pipe having the diameter of the chimney, after which the plugs are removed and sand is poured out, the pipe is washed under high pressure of water.
- Threads are cut at the ends of the pipe and adapters are installed for connection to the system.
- The pipe is installed on the chimney. To improve heat transfer, you can solder the coil onto the chimney with tin, having previously degreased the soldering areas and removed oxides with phosphoric acid.
- The tank is hung on the wall or placed on a support above the level of the coil. Connect the heater to the tank using flexible hoses. A drain valve is installed at the lowest point of the system.
When using a coil heat exchanger in closed heating systems, it is necessary to install a circulation pump!
The coolant may boil, and if circulation is poor, water hammer can occur, destroying the system elements! Video: receiving hot water from a coil heat exchanger installed on the chimney
Negative points
Along with the benefits of a heat exchanger on a chimney, it is worth noting a number of negative factors. Firstly, due to this design, the temperature of the exhaust gases is significantly reduced. This can provoke excessive soot accumulation, condensation formation and poor traction.
An important point in arranging such a heating system is to calculate how much water is needed for its full functioning. If there is not enough of it, the system may overheat, the water in it will boil, and the pipes may burst. In addition, it is important to ensure the tightness of the seams.
In any case, installing a heat exchanger allows you to increase the efficiency of any furnace. For safety reasons, at least twice a year, visual diagnostics of the system and its maintenance should be carried out - cleaning soot, replacing defective elements, and so on. Then it will be possible to confidently use the heat exchanger for heating the house and heating water in the bathhouse.
Air tank
You can improve an ordinary potbelly stove or sauna stove with a direct chimney by installing it on an air heat exchanger on the chimney .
It is a cylindrical body through which several hollow pipes pass. Air is sucked in from below, heated in the pipe, it leaves the heat exchanger, increasing the efficiency of the furnace by 15-20%. The air ducts can be routed to an adjacent room, thus heating several rooms or sections of the garage from one furnace. Video: how to make an air heat exchanger for a chimney
Another original design of a stove with an air heat exchanger on a chimney for heating a garage is shown in the video. With the help of such a stove you can heat not only a garage, but also any utility room, including agricultural buildings and greenhouses.
From corrugated pipe
A cheap and simple way to install an air heat exchanger is to use corrugated ventilation pipes for this purpose . They are wrapped around the uninsulated part of the chimney, as a result the air in the corrugation warms up and, due to thermal convection, enters the neighboring rooms. To make the corrugated pipe heat up more efficiently, you can wrap it together with the chimney in several layers of foil.
A system with a corrugated pipe is convenient for heating a garage in which a simple potbelly stove made of rough metal is installed. Such a stove quickly heats the air, but it rises to the ceiling, which is why the temperature at floor level remains low. If you move the air ducts closer to the floor, you can create natural circulation of heated air, and the temperature throughout the garage will become approximately the same.
Bell-type heat exchanger
Heat exchangers in the form of a bell are usually used for heating the attic or second floor . The principle of its operation is that the air heated from the chimney rises to the ceiling, where it is retained by the hood and, gradually cooling, falls down into the room.
The cap can be made of either galvanized metal or fire-resistant plasterboard and lead the air ducts to the desired location. Sometimes the cap is decorated with stones, which, when heated, serve as an additional heat accumulator.