An unusual heating technology, fundamentally different from the usual systems with radiators under the windows, came to us from European countries recently, although it has been used there for more than twenty years. The name of the innovation speaks for itself - warm baseboard, the demand for it is growing due to its technical advantages and modern design.
You will learn everything about the types of baseboard heating and the features of its operation by reading the article we have proposed. We will talk about the design specifics and rules for constructing all types of baseboard heating systems. Here you will find out where heating baseboards are used and which models are popular among consumers.
Baseboard heating device
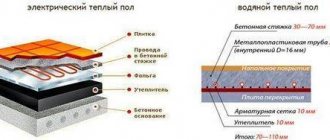
From a design point of view, a plinth radiator looks like a regular heating battery, but smaller and stretched. Skirting heaters usually have a height of 140 mm and a thickness of 30 mm. For the manufacture of such devices, expensive materials with good thermal conductivity are used - aluminum, copper and brass.
The outer part of the heater is an aluminum box. Inside this structure there is a heating element, represented by two copper tubes, on which brass, copper or aluminum plates (so-called lamellas) are strung.
There are two types of warm skirting boards:
- Liquid . Water baseboard heating radiators are filled with water or antifreeze. Each linear meter of the system requires 0.34 liters of coolant. The heater temperature can vary from 50 to 85 degrees - the exact value is set manually on the collector or in automatic mode.
- Electrical . Baseboard electric heating operates using heating elements, the operation of which is regulated by a thermostat. It is equipped with a temperature sensor that monitors the need to heat the house.
Heating elements are placed on the back aluminum plate. The plate itself is fixed to the wall directly above the floor covering. The outer part of the heater is represented by an aluminum plate that covers the body of the device.
The coolant enters the radiator from the collector. A lot of required elements are installed on the distribution manifold - flow meters, various taps, air vents, thermometers and pressure gauges. Each of these elements affects the operation of the heating system and allows you to configure it as necessary.
The safe temperature of the outer part of the baseboard is 40 degrees, and the maximum reaches 80 degrees. When properly configured, the system provides complete heating of living spaces to a temperature of about 20-24 degrees. The lower and upper surfaces of the plinth radiator have holes, which ensure convection - cold air is taken from the lower level, heated in the device and exited through the upper panel.
The heat output of baseboard radiators is 200 W per 1 meter - but to achieve this value, a coolant temperature of at least 65 degrees is required. This indicator of the external heating temperature is considered unsafe, so the heat transfer must be calculated more accurately so that it is sufficient to heat the building.
Voting by our readers
What warm baseboard would you buy or recommend?
Warm baseboard Mr.Tektum
30.00 % ( 9 )
Warm baseboard Orion
30.00 % ( 9 )
Warm skirting board TERMIA
6.67 % ( 2 )
Warm baseboard SoftTerm
3.33 % ( 1 )
Warm baseboard STN
0.00 % ( 0 )
Warm plinth Turbo-Tech
16.67 % ( 5 )
Warm plinth Megador
6.67 % ( 2 )
Warm baseboard Techno Board
0.00 % ( 0 )
Warm baseboard TherModul
0.00 % ( 0 )
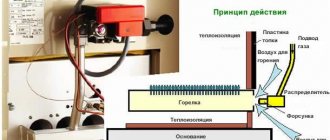
Operating principle of baseboard heating
There are two fundamental principles of heating:
- Convection heating . This heating principle assumes that the thermal energy generated by the heating system will first be transferred to the air. The heated air, in turn, moves around the room and warms it up.
- Panel radiant heating . In this case, the objects in the room are first heated, and only then the heat is transferred from them to the air. The key difference between such a system is the preservation of oxygen in the air, since it is not burned out.
It is quite difficult to determine at first glance what type of baseboard heating radiators they are. Manufacturers of such equipment claim that the thermal energy generated by the radiator is directed upward along the walls and warms them up, thereby creating reliable protection from the cold that tends to enter the living quarters. In addition, heated walls become heat accumulators, from which heat subsequently flows into the rooms.
However, in practice everything turns out to be not quite so. The wall temperature is usually about 26-30 degrees, which is not enough to create a heat accumulator. This statement allows us to conclude that radiation in the infrared spectrum is still not fundamental for this type of heating.
Most of the energy when using baseboard radiators is still generated by convection. Of course, thanks to the heating of the walls, it is possible to achieve uniform heating of the entire room - but this is also influenced to a much greater extent by the distribution of warm air masses.
Considering the low location of warm baseboards, we can confidently say that almost no heat is spent on heating the space directly under the ceiling. The lower and middle levels of the room experience the greatest thermal impact, thereby creating the most comfortable atmosphere for the human body.
Features of baseboard heating
From its invention to the present day, heating has been divided into two types - convection and panel radiant. In the first case, the air is first heated from the hot surface of the heating device (radiator battery, convector), after which it circulates in the room and gradually heats it up.
In the second case, objects in the room are initially heated, and the air is heated from them by useful infrared radiation, which does not dry out the air or remove oxygen from it, and this process is secondary.
Among the old examples are stoves in village houses, tiled stoves in ancient mansions, in a modern interpretation - heated floors, but what about baseboard heating and what type of heating does it belong to?
Heating a room using a warm baseboard allows you to ensure a uniform supply of heat throughout the height and area of the room being treated
Let us turn again to the opinion of the manufacturers. They unanimously claim that the heat radiated along the perimeter rises from the floor to the ceiling along the walls, warms them evenly and creates a kind of curtain from the cold penetrating from the outside. Once warmed up enough, they themselves begin to give off heat.
In fact, the temperature of walls at different heights fluctuates in the range of 26-30 ºС, and in order for heat to transfer from them, the surface must be heated much more strongly. Therefore, talk about the coveted infrared heat emanating from the walls is not so much the truth as a marketing ploy.
The planes of thermoplinths emit maximum heat at the level of the feet. It’s not just pleasant, but also optimal for well-being and health (+)
It is more correct to say that thermal baseboards are also convectors with a high surface temperature. It’s just that the room is heated more evenly by warm air currents, both emanating directly into the room and ascending along the walls. Heated walls are a guarantee that you will not find dampness or mold anywhere on them.
It is also fair to note that as you move upward, the amount of heat decreases, and this is good. It is evenly distributed in the room in the lower and middle zones, reaching the ceiling to a lesser extent. For people, such a microclimate is considered the most comfortable - they do not freeze or feel chilly, but at the same time breathe fresh and cool air.
Advantages and disadvantages of plinth radiators
Skirting-type radiators have a number of positive qualities:
- Heated air masses pass upward along the walls. The walls, in turn, warm up as a result. Thanks to this heat distribution, the wall at the lower and middle levels gives off more heat, thereby creating the most favorable atmosphere for humans in the room.
- When properly configured, baseboard radiators do not operate around the clock. Typically, baseboard-type heating works for about 6-8 hours a day - and this allows us to talk about some savings.
- The efficiency of the battery in baseboards is ensured not only due to the operating mode, but also due to the reduced temperature of the coolant. Of course, in order to have accurate data on energy consumption, it is necessary to carry out a thermal engineering calculation of a specific heating system, taking into account all the features of the building.
- From a visual point of view, plinth radiators are quite good. Such devices can be built into almost any interior, and they will look very harmonious. Problems can only arise when installing cabinet furniture - it will not allow warm air masses to spread normally throughout the room.
Among the disadvantages, the following qualities can be noted:
- The efficiency of baseboard radiators compared, for example, with heated floors, is not so great. The thing is that the heating system installed under the floor covering immediately begins to warm up the air in the room, and the baseboard radiator gives off some of the heat to the walls, and it goes to compensate for the incoming cold.
- Due to the heating of cold walls, additional heat loss occurs. Of course, this factor is partly positive, since warm walls do not allow dampness and mold to appear in the room - but with properly equipped ventilation, excess heat loss will remain so.
- Heating when using baseboard devices is carried out due to convection, so dust rises in the room all the time. Of course, its quantity and intensity of movement are not as high as in the case of traditional heating systems, but the problem still exists, and it will not be possible to get rid of it.
- Expensive materials are used to manufacture baseboard-type heaters, which also determines the high cost of the devices themselves. In addition to the high price of radiators, a lot of money will be required to pay for the services of professional builders who will install the system. It is unlikely that you will be able to install it yourself - baseboard water distribution is considered the most complex among its analogues, and installing an electric radiator in a baseboard is not without difficulty.
Economy and the laws of physics
However, not everything here is as rosy as it seems at first glance. If your entire wall is heated, then heat loss from it increases.
This means that it must initially be made heat-intensive and strive for maximum heat resistance.
Here, for example, is the formula for calculating heat loss known from a physics course:
Where:
- S - wall area
- T = (Tinside - Toutside) - the difference in wall temperatures inside the house and outside
- R – surface heat transfer resistance
From this formula it becomes clear what heat loss primarily depends on. R - both with batteries and with the baseboard you do not change. The wall is the same.
But the parameters in the numerator will be different. The greater the temperature difference (T), the greater the heat loss. Let’s say that when heated by batteries near a window, the wall will conditionally have t=20C.
The temperature along the wall from the radiator to the farthest point (in the corners) is distributed along a gradient. The sections of walls to the right and left of the windows do not warm up at all.
If the entire wall inside the house is heated with a warm baseboard, from the same boiler with the same coolant temperature, then the wall will warm up more. Conventionally, up to +25C, which means, according to the formula, the difference in the numerator will increase, and heat transfer through the walls will increase.
It turns out that the more heat you lose, the more you will have to replace it. It doesn’t matter how this heat is pumped into the room - radiators or thermal baseboards.
As a result, there will be no significant savings and super energy efficiency here.
The same applies to the area - S. The surface heated by the baseboard is much larger than the surface located directly behind the radiator.
The situation can be improved a little if the heating baseboard is placed not only on the external walls of the house (as with radiators), but also on its internal partitions.
Most of the heat generated in this case will remain in the house, rather than trying to immediately escape outside. A little heating of the external walls is useful not only as a source of heating, but also for the building itself. Dampness as such completely disappears.
Considering all of the above, many therefore perceive such innovations with skepticism. There are long-proven and understandable methods - the same radiators under the windows, or heated floors in a screed.
All other tricks are too expensive either at the construction stage or during operation and repair.
For a room of 16 m2 you will need from 10 to 12 meters of plinth. Its price today averages 4000-5000 rubles per meter and more. And this is in addition to the cost of components. Add here the work itself (in Moscow they charge about 1,400 rubles per linear meter), all the rooms in the house and calculate your expenses.
Not everyone can afford such heating.
Is it possible to fully survive the winter with such thermoplinths? Yes, definitely. If there is sufficient linear footage and appropriate coolant temperature.
And numerous reviews on the forums confirm this. To warm up the house on the coldest winter days, the temperature of the coolant extraction in the warm baseboards collector will need to be kept around 75C. On normal days, 50-70C is enough.
Detailed review of thermal skirting boards from forumhouse
The higher the temperature, the more radiant energy you will receive. When it decreases to a level of 45C and below, the warm baseboard turns into a kind of mini-convector, which heats mainly with air flows.
Therefore, do not expect any unrealistic savings from thermal skirting boards. She won't be there. Warm floors are much more profitable in this regard.
However, the system has become widely used and some consumers actively use it both as the main and additional source of heating for their apartment or individual rooms in the house.
Preparation for installation
First of all, you need to prepare a set of tools for work:
- A hammer drill or a drill suitable for perforating;
- Hammer;
- Wire cutters;
- Pliers;
- Plastic scissors.
In order for baseboard heating to be installed quickly and efficiently, you need to prepare all connection points in advance. To simplify the work, it is worth creating a system design in advance, selecting suitable heating devices and how to place them in the rooms.
Installation of a water baseboard system
The technology for assembling water baseboard heating includes the following operations:
- First you need to measure the distance between the location of the baseboard and the distribution manifold. Next, you need to cut two lengths of the protective pipe, and two exactly the same, but with an allowance of 20 cm - they will act as connecting pipes. The connecting pipe is inserted into the protective pipe, after which their edges are covered with adhesive tape to prevent dirt from entering.
- The pipes are laid along the floor in such a way that, if necessary, several additional ones can be placed next to them. Each pipe is fixed with mounting tape, covered with a protective layer to prevent damage to the structure, and placed on the wall in the desired area. The distance from the floor should be 6 cm, from the edge of the wall or corner - 10-15 cm. Final fixation is carried out using cement.
- When the installation of the finished floor is completed, you can continue installing the baseboard heating. An insulating strip is glued along the entire length of the structure and an aluminum edge is stretched, which will cover the junction of the wall and the floor covering. The edge is fixed with any fastening material.
- A special profile is laid along the top line of the structure. Later, holders are put on it. The distance of the holders from the corners is 15 cm, the installation step is 40 cm.
- Heating pipes are connected to heating elements using couplings, bushings and gaskets. Rotating elements are installed in the corners, and end rotating tubes and plugs are installed at the end sections. Individual sections of devices are connected to each other using adapters.
- When the heater sections are connected, they must be carefully inserted into the holders. Next, decorative panels and corner parts are mounted using screws or latches. The assembled system is connected to the distribution manifold, filled with water and tested for leaks (both operating and maximum pressure must be used during testing).
If each stage of installation was carried out correctly, then baseboard heating will be able to work normally. If leaks are detected at the inspection stage, weak areas must be tightened with a wrench. Since the circuit is supplied with coolant through heating equipment (a boiler or a centralized system), it is imperative to ensure that it is operational.
Assembly and installation of the heating module
Connecting the heating module
- Before installation, it is necessary to measure the distance for connecting them to each other and the wiring. Using a hacksaw, we cut the module into the required parts. We remove the excess slats from the edge of the module with pliers.
- We install a heating element (tubular electric heater) in the lower tube.
- We lay a special (heat-resistant) three-core connecting cable into the upper tube. We cut the cable so that there are ends sufficient for electrical connections, approximately 15 cm.
Assembling an electrical circuit.
- We assemble a system for connecting to the electrical network. We use a single-phase electrical circuit with three conductors: phase, ground, 0. The silicone cable has 3 conductors with a cross-section of 1.5 mm². The connection of tens is carried out according to a parallel circuit. We supply the grounding and the tip of the contact group with a crimp clamp (insulating tape). To connect to the wires, we attach terminals with PVC cuffs: a flat piece is for grounding, and a round terminal is used for the phase.
- We install the heating module into the brackets. Then we insert a plastic wedge between the bracket and the module, ensuring rigid fixation of the heating module. We cut off the protruding part of the wedge with a mounting knife.
- We connect the corresponding contacts of the ten to the phase and neutral wire using a lock washer and a nut with a thread diameter of m4.
- We close the contacts with a coupling, which we heat evenly with a hairdryer. This will ensure tight connections and electrical safety.
Installation of an electrical skirting system
To install warm electric baseboards, you need to install a separate circuit breaker in the distribution panel. The power of the switch is calculated depending on the number and parameters of the skirting boards used.
The installation technology for electric baseboard heating is as follows:
- First of all, the electrical network is connected to the distribution box. The box should be located close to the system at a height of about 5 cm from the floor level.
- The wall is sealed with insulating tape.
- Next, the lower aluminum edge and the upper profile are attached to the wall. Holders are attached to the upper profile. The installation parameters for the holders are exactly the same as in the case of the water system - 15 cm from the corners, installation step - 40 cm.
- The next step is to install a remote thermostat. This element is installed opposite the radiators. Installation height – 1.5 meters, distance from the heating system – from 2 meters.
- Heating elements are installed in the lower pipe of the heating module. The modules must be fixed in holders so that they do not have direct contact with the wall. The modules are connected in parallel using a power cable. The cable must have a silicone coating and heat resistance up to 180 degrees.
- The upper part of the structure is closed with a plastic box.
It is not recommended to install electric baseboard heating yourself. It's all about a complex wiring diagram, the arrangement of which requires high qualifications and a set of measuring instruments.
Design and scope of warm skirting boards
Baseboard heaters have quite high decorative qualities. They are quite compact and pleasant to look at, which allows them to be used to implement a wide variety of design solutions. The plinth system is also good because it requires little space for its installation, so there is no infringement of free space in the room.
Due to their characteristics and heating method, baseboard-type heating devices can be placed next to any objects located in the room - as long as they do not interfere with the movement of warm air. In addition, the type of devices in question can be installed regardless of the materials used to make the floors and walls.
On the heating market, baseboard radiators are presented in a wide range of colors, and choosing the option that best suits a specific interior is not difficult. In addition to devices with a smooth surface, you can also find those whose surface will imitate the texture of various materials - stone, marble or wood.
The greatest efficiency from the use of baseboard radiators is achieved when they are installed in corner and end rooms, which are often the coldest. Baseboard heating will compensate for the lack of temperature. The type of heating system under consideration can be used with equal success both in private houses and in apartments - for example, for heating balconies.
In addition to residential premises, baseboard-type heaters are actively used in public spaces - for example, in swimming pools, museums, concert halls, etc. The most relevant baseboard devices are in the case of panoramic windows on the entire wall - there is no room left for traditional radiators, but warm baseboards installed without problems.
A few final words...
Believe me, you should not always trust the colorful pictures drawn by manufacturers or sellers of certain products. It is clear that they are always interested people, and are often capable of either lying or embellishing this or that information for their own purposes.
Just for fun, go to the websites of manufacturers of warm baseboards, no matter which ones. With a probability close to 100%, there will be a whole array of seemingly very convincing calculations, with references to some phenomena of “sticking” of warm air flows to vertical surfaces, named after some Romanian pilot, to the theory of energy transformation, to turning cold and damp walls into sources of life-giving radiant heat, and much more. With final promises of energy savings from 30% to (I’m not lying) five times! We also encountered this - 200 W of heat with a real consumption of 40 W of electrical energy. Wow, how great!
Such reasoning can easily be broken not only by a certified heating engineer, but even by an ordinary school physics teacher. At least from the standpoint of the inviolability of the well-known law of conservation of energy. Read it - it's interesting...
Warm baseboards have a right to exist, and can be very convenient and effective. But you shouldn’t expect miracles from them.
Expert opinion: Afanasyev E.V.
Chief editor of the Stroyday.ru project. Engineer.
Understand correctly - the author does not at all advocate that warm baseboards are bad, ineffective, and should be “consigned to oblivion.” Not at all! Such heating devices have a number of important advantages. First of all, they are inconspicuous, and for some interiors this is very important. They are compact and can be placed along the entire free perimeter of the room, thereby distributing the heat entering the room as evenly as possible. They can really help dry up the ever-wet external walls and get rid of condensation on the windows, especially if the windows, as they say, are on the floor. In addition, the baseboards will create some kind of thermal curtain, and the cold from the window will not penetrate deep into the room.
You can find other arguments in favor. But you don’t need to believe in the fabulous effects of huge energy savings from the start. It’s just that the inevitable early disappointment will be all the more bitter.
And, by the way, in terms of the efficiency of distribution of generated heat, baseboard heaters are still inferior to “warm floors”. So that…