Heating pipes with fins have been used for many decades and have not lost their popularity to this day. This equipment has its own design features that determine its use, so they are rarely found in heating systems for private housing, but they are used quite widely for heating industrial premises. A photo of finned heating pipes will tell you what kind of equipment we are talking about, after which we will consider the characteristics of this product in more detail.
The algorithm used to create
- First, pipes of the required volume are prepared and cut into pieces of the required length.
- Afterwards, the internal cleaning of the pipe products is carried out. This allows you to reduce the resistance to movement of the coolant.
- Plugs are welded on the end parts. Some of them are equipped with holes.
- After this, the pipes, which will be located horizontally, are fastened with vertical pipes, which have a smaller diameter.
- Now it's time to install the cranes. They will be needed to release air accumulated in the pipeline.
- At the final stage, all seams are cleaned and the surfaces are painted.
Calculation of registers from smooth pipes
Steel heating registers are easy to make with your own hands.
The cost of such a heating system will depend on who will cook them. If you own the welding technique yourself, the option is the most low-budget; if the welder needs to be paid, there will not be much difference in cost with inexpensive aluminum ones. In this case, the registers will occupy larger areas than standard heating devices: due to the small surface of contact with air, their efficiency is low. They increase heat transfer by installing a more powerful pump, but there are speed restrictions due to possible noise in the system. Read about how to select the pump power here.
Diameters, as mentioned, range from 32 mm to 100-150 mm. Large pipe sizes lead to an increase in system volume. When starting and accelerating the system, this is a minus - it will take quite some time until the coolant heats up. When working, a large volume is rather a plus: milder conditions for the boiler. On the other hand, with a large amount of coolant, it is difficult to regulate the temperature.
Table of heat transfer of steel pipes of different diameters for different operating conditions of the system (click on the picture to enlarge its size)
The distance between two pipes in the register should not be small: this reduces heat transfer. Therefore, they are located at a distance of no less than 1.5 radii. The number of rows and register length depend on the required power, as well as the diameter of the selected pipes. In the general case (for central Russia, for rooms with average thermal insulation and a ceiling height of 3 m), it can be calculated by the heat transfer of a meter of steel pipe. These values are given in the table. Using it you can find the size and number of registers by area of the room.
Heat transfer of one meter of steel pipes of different diameters - to calculate the heating register by area
To calculate the heat losses of a room, there are averaged data on the thermal power of a linear meter of steel pipe. You can use them for standard conditions. If the system operates at other temperatures, adjustments may need to be made up or down.
If these tables did not help you, you can calculate the register using the formula.
Formula for calculating registers made of steel pipes
By substituting the appropriate values, you will find the heat transfer of one pipe under your conditions. The heat transfer of all subsequent ones (second or more) will be slightly less. The found value must be multiplied by 0.9. So you will calculate and be able to make a register from smooth pipes with your own hands.
Application of ribbed cast iron pipe products
Cast iron finned radiators, due to their significant weight and low level of aesthetics, are used mainly for steam or water heating of production workshops, warehouses, livestock farms and other facilities of large areas. At the same time, single use of such equipment is ineffective, and the elements are installed in sections of several radiators. Such heating registers made of finned pipes increase the heating intensity of the room several times, but at the same time require a significant area for installation.
These devices are also suitable for heating homes, but they will require additional finishing in the form of decorative casings or false walls.
The high technical characteristics of cast iron determine the widespread use of cast iron finned tubes in economizers - gases and aggressive substances passing through them do not cause corrosion of the heat exchanger material.
Installation of cast iron finned pipes
Due to their significant weight, finned heating registers place increased demands on the base. The load-bearing capacity of the walls (for wall-mounted radiators) and the strength of the brackets must be high, and the embedding of the fasteners into the base must be reliable. When the unit is a floor-mounted design, supports, standard or self-made, must be welded at the bottom. If the floor is wooden flooring, then slots are made in it so that the radiator supports are located on the supporting floor slab.
Before installation, the finned radiator is cleaned of old paint and dirt, degreased, and then primed and painted. It is better to paint with a spray gun, since due to the configuration of the register, the painting area is large, and the fins are difficult to access with a brush.
A solution of red lead in drying oil is suitable as a primer, and the finishing layer is heat-resistant paint (enamel) of a suitable color or a solution of aluminum powder. The register to be painted should not be exposed to direct sunlight - the paint will run.
After the paint has dried, the painted radiator is installed in place, after which the device is additionally secured to the wall to avoid accidental tipping under mechanical stress.
Connection to the heating circuit is made after the final installation of the unit, so that its displacement does not violate the tightness of the connections. The insertion is made depending on the design of the register nozzles - flange connection, threaded connection or welding. For a flange connection, it is recommended to use paronite as a gasket material, cut to the size of the flange mirrors (the mirrors are cleaned of paint with fine sandpaper), or use standard gaskets, if they are included in the package.
After final installation of the unit, spot painting of areas damaged during installation is carried out.
What other types of cast iron pipes are there?
One of the broad areas of application of cast iron pipes, in addition to heating systems, is the organization of water pressure pipelines. The characteristics of cast iron pipes allow them to be used in water supply systems (usually cold) and sewers. Cast iron pipes can be laid in the ground without any problems; they can easily withstand low temperatures and soil pressure. But due to their susceptibility to corrosion, it is better to lay them in tunnels than directly into the ground.
Depending on the requirements of the pipeline, different types of products can be selected.
Non-pressure pipes ChK. This type of cast iron pipes has the least strength and pressure resistance. Gravity pipes are quite thin and fragile. In their production, simple gray cast iron with admixtures of lamellar graphite is used. Such cast iron pipes can be successfully used only in gravity sewers with a consistently low load. However, cast iron free-flow pipes also have an interesting advantage: they can be used repeatedly. Naturally, this is only possible if it is well preserved.
If it is necessary to make a connection in a free-flow sewer system with a plastic pipeline, ChK pipes are best suited. The connection is made using rubber cuffs.
VChShG pressure pipes. In most modern pipelines, it is customary to use a cast iron pressure pipe. These products are often sold under the abbreviation VChShG, which stands for “high-strength nodular cast iron.”
There are several types of cast iron pipes; their application and connection method depend on the type and size.
Cast iron pressure pipes have found their application in the construction of gravity sewers, pressure sewers (including in cases where there is a need to raise wastewater to a significant height), water pipelines and heating mains.
Ductile iron pipes are also used in industrial sectors. With their help, the construction of main oil and gas transportation systems is carried out.
Pressure socket pipes ChNR. Cast iron socket pipes are used mainly in large water supply networks. They are available in different diameters, most often from 100 mm. The peculiarity of the material makes ChNR pipes somewhat less durable than ductile iron, so their installation requires special skills. In home sewer systems, the use of cast iron pressure socket pipes is limited, mainly due to the difficulties of constructing water pipes. To extend the service life of ChNR pipes, they are sealed with varnish-bitumen compositions.
SML socketless pipes. Socketless cast iron pipes are produced by casting an alloy of cast iron and rosette graphite. A relatively new variation of cast iron pipes for water supply and sewerage, a feature of which is a special coating of their epoxy substances. Sewage systems can function for a long time using socketless structures if they were installed correctly. Unlike socket pipes, such pipes are connected with conventional clamps. The degree of tightness of the clamp being put on plays a key role in the reliability of the connection.
SML cast iron pipes can withstand both high and low temperatures. The only “contraindication” to their use is pressure sewers.
Cast iron pipes to this day remain a widely used material for the installation of heating networks, main water supply systems and sewerage systems. Economizer pipes are a mandatory element of industrial registers; they are, in fact, a ready-made radiator. Cast iron pipes can also serve well in water supply and sewerage systems.
Polymer heating and water supply pipes compared with steel pipes
The properties of different types of polymer products are largely similar: they are durable, not subject to corrosion, and do not overgrow inside. The service life of polymer pipes can reach 50 years, but largely depends on operating conditions.
Long periods of pipe operation at elevated temperatures are possible with
absence of high pressure in the system. The failure of steel pipelines due to corrosion processes and leaky connections leads to contamination of drinking water and the emergence of infectious diseases. When using polymer pipes, there is no deterioration in the organoleptic characteristics of drinking water.
If we compare pipes for heating and water supply, the advantageous characteristics of polymer pipes are the following:
- The low weight of plastic pipes facilitates their transportation, loading and unloading and installation work.
- Due to their low thermal conductivity, polymer pipes for heating and water supply do not require such thermal insulation as steel pipes; in addition, moisture does not condense on the surface of plastic pipes.
Polymer pipes are good sound insulators for flowing water, regardless of the flow speed.
An important positive characteristic of polymer pipelines is their resistance to stray currents. Unlike polymer pipes, steel pipes are often damaged by stray currents, especially near metro stations and lines and other electric transport. It is also worth considering the fact that polymer pipes in their appearance fully correspond to the modern design of residential premises and sanitary rooms.
Manufacturing of heating registers
For the production of heating registers, steel pipes of various diameters (25-200 mm) are used, which are welded together at a distance of 50 mm from each other (reducing the distance between the pipes can lead to a decrease in heat transfer). This distance allows you to achieve maximum heat transfer and minimize mutual radiation.
The register includes supply and return, as well as an air vent with a ball valve installed in the upper part of the device. The supply and return pipes can be made in two versions:
- Threaded connection;
- Welded connection.
When ordering registers individually at the manufacturer, registers can be supplied either ready-made, assembled, or disassembled, which allows you to save money on logistics.
How to install
There are two installation options: hang it on the wall or put it on a stand. The choice depends on the dimensions and weight of the resulting structure, as well as on the type of walls.
Quite often they do a combined installation: they weld racks, which are then attached to the wall. Even very massive registers can be installed in this way. This installation option also provides a high level of security.
Each such heating device must have an air vent at the top point. It is needed to bleed air from the system.
Registers made of steel with ribs
Before installing registers made of steel pipes with fins, it is recommended to pay main attention to the volume of the pipe. For a private home, craftsmen recommend installations with a volume of 3 or 4 centimeters
When performing calculations, you need to take into account the length of one register rib and its heat transfer per meter of area. To give an example, a meter-long pipe with an internal cross-section of 60 mm can heat approximately one square meter.
Having calculated the required number of registers, rounding is carried out upward. But, there are certain conditions under which the obtained indicators increase by 20 or even 50 percent. This includes:
- The presence of a large number of openings for windows and doors in the room.
- Small wall thickness.
- Low-quality insulation of the room, or its complete absence.
A simple heating register has less heat transfer than devices with fins. They not only increase heat transfer, but also turn the register into a design - a radiator, which can play an important role in the aesthetic design of the interior.
General recommendations for choosing heating radiators
Long gone are the days when people tried to hide unsightly-looking heating radiators using various tricks and third-party devices. Today you can choose a battery that will fit perfectly into any interior. Radiators differ from each other in material, size, color design and other indicators, so you can easily choose a battery that can fully satisfy all your needs and fit well into your existing or planned interior.
Today you can choose a battery that will fit perfectly into any interior.
Although radiators made in light colors are traditionally installed in residential premises, it is necessary to take into account the fact that a black device on average gives off 20-25% more heat solely due to its color. In general, when choosing the color of the battery, be guided by your own preferences and the overall design of the room. In residential premises, streamlined batteries look most organic
It is better to avoid radiators with sharp corners for safety reasons, especially if children live in the apartment or house. Any sharp corners in general are a relic that is recommended to be abandoned
In residential premises, streamlined batteries look most organic. It is better to avoid radiators with sharp corners for safety reasons, especially if children live in the apartment or house. Any sharp corners in general are a relic that is recommended to be discarded.
For the manufacture of heating units, materials such as aluminum, cast iron, steel and alloys of various metals (bimetallic radiators) are currently used.
Depending on the material of manufacture, radiators will have different heat capacity and heat transfer, operating pressure, their resistance to chemical and hydraulic influences and, of course, service life will also differ.
In terms of cost, the most expensive are steel batteries and bimetallic radiators. Cast iron units are relatively inexpensive. The only exceptions are samples using artistic casting methods and foreign-made designer models.
Special attention should be paid to the environmental safety of the material used to make heating batteries. The main components of safety for human health are high-quality polymer coating and the absence of formaldehyde in internal elements
Types of registers
The most common type is registers made of smooth pipes, and most often electric-welded steel ones. Diameters - from 32 mm to 100 mm, sometimes up to 150 mm. They are made of two types - serpentine and register. Moreover, register ones can have two types of connection: thread and column. A thread is when the jumpers through which coolant flows from one pipe to another are installed either on the right or on the left. It turns out that the coolant sequentially runs around all the pipes, that is, the connection is sequential. With a column connection, all horizontal sections are connected to each other at both ends. In this case, the movement of the coolant is parallel.
Types of registers made of smooth pipes
When used in systems with natural circulation, it is necessary to maintain a slight slope towards the movement of the coolant of the order of 0.5 cm per meter of pipe. Such a small slope is explained by the large diameter (low hydraulic resistance).
This is a serpentine heating register
These products are made not only from round, but also from square pipes. They are practically no different, only they are more difficult to work with, and the hydraulic resistance is a little higher. But the advantages of this design include more compact dimensions with the same volume of coolant.
Square tube registers
There are also registers made of pipes with fins. In this case, the area of contact between the metal and the air increases, and heat transfer increases. In fact, builders still install just such heating devices in some budget new buildings: the well-known “pipe with fins.” Although they don’t look the best, they warm rooms well.
A register with plates will have a much higher heat transfer
If you insert a heating element into any register, you can get a combined heating device. It can be separate, not connected to the system, or used as an additional heat source. If the radiator is insulated with heating only from the heating element, it is necessary to install an expansion tank at the top point (10% of the total coolant volume). When heated by a domestic boiler, the expansion tank is usually built into the structure. If it is not there (often happens in solid fuel boilers), then in this case it is necessary to install an expansion tank. If the material for the registers is steel, then the tank needs a closed type.
Electric heating can be useful in the most severe cold weather, when the boiler power is not enough. Also, this option can help out in the off-season, when there is no point in loading a long-burning solid fuel boiler and running the system to full speed. You just need to warm up the room a little. This is not possible with solid fuel boilers. And this backup option will help keep you warm in the off-season.
By adding a heating element to the register and installing an expansion tank, we get a combined heating system
Combined instruments
Any device can be supplemented with a heating element, this way a combined heating device is obtained. It may not be associated with the system, and can be used separately.
If this is an isolated register with heating only from the heating element, then an expansion tank must be installed in its upper part. Its capacity should not be less than 10% of the capacity of the heating device. For steel registers, closed tanks should be installed.
Such steel structures are a great help in very cold times, when the heating capabilities of the boiler become limited. This option is very practical during the off-season, when it is not advisable to use the network at full capacity. After all, the room at this time only needs a little warming up.
Heat dissipation of registers
The heat transfer of registers made of steel pipes is the transfer of heat energy between the battery and the environment. Heating devices made from smooth pipes are less economically profitable.
The heat output of one meter of these structures is approximately 550 W, for a diameter from 3.2 to 21.9 cm. Welding installation work is recommended to be carried out so that mutual heating of the elements does not occur.
Under such conditions, the heat transfer rate becomes higher. If the register is assembled correctly, it becomes a reliable and durable steel heating device. Optimizing the heat transfer of a steel pipeline is decided at the design stage of its structure. To do this, use the following methods.
- Change of infrared radiation in the direction of increase. This can be done using paint.
- Ribs are installed, which also increases the required design performance.
But, there are cases when these indicators need to be reduced. Such actions are required by sections of the pipeline that pass outside residential premises. In these situations, the line is thermally insulated.
Calculations are carried out in this way: Q = K*F*dT. In this formula, Q denotes the thermal transfer coefficient, K is the thermal conductivity of steel materials, and F shows the length of the pipe taken for calculations. dT in this formula is the sum of the initial and residual temperatures, taking into account the room temperature.
The designation dT is also called temperature difference. You can find out by adding the temperature at the outlet of the boiler equipment with the numbers at its input. The resulting readings are multiplied by 0.5 or divided by two. The room temperature is subtracted from this value.
If the steel heating pipeline is in insulating material, then the resulting number should be multiplied by the efficiency of the insulating material. It shows the percentage of thermal energy of the heating system released during the flow of the coolant.
If you want to design a system competently, then you should not select steel pipe assortment by eye. Correct calculations in this case not only make it possible to reduce the cost of construction work, but also to install a heating system that will work effectively for a long time.
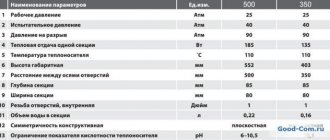
Technical characteristics of heating registers
- Working pressure: 10 atmospheres
- Working medium (coolant): water, steam.
- Connection type: threaded or welded.
- Heat dissipation: 500-600 W/meter
There are 3 main types of registers:
- sectional U-shaped;
- S-shaped coils;
- “mixed” (U-shaped coil).
The main elements of heating registers are steel pipes (or pipes made of stainless steel grade 304) with a diameter of 25 to 200 mm. Registers with a diameter of 25 to 100 mm are used for heating factory premises for administrative or utility purposes, devices with a diameter of 100 to 200 mm are used in production shops or large sports complexes (swimming pools, volleyball, basketball halls).
As for private households, the use of registers is one of the most ineffective ways to heat a private home.
2-pipe register.
The number of sections of the device can be unlimited and depends only on the area of the room and the required heat transfer.
Advice! If you use too many pipes (more than 4), it will still not be possible to significantly increase the power of the entire device, because The rising warm air heated by the lower pipes will be less able to accept thermal energy from the upper pipes.
Average service life of radiators of different types
| Battery type | Resistant to water hammer | Corrosion resistance | Duration of use, years. |
| Steel | weak | low | 15-20 |
| Aluminum | average | high (with additional protection) | 20-25 |
| Bimetallic | high | high | 25-30 |
| Cast iron | average | high | 25-35 |
In addition to the quality of the raw materials used and compliance with the technological process regulations, other factors also influence the lifespan of radiators. Among them are:
- correct installation;
- regularity of maintenance;
- working pressure value;
- maximum permissible temperature in heating networks;
- composition and quality of coolant transported through pipes.
The operating pressure depends on the heating characteristics. In autonomous networks, which are used to maintain a comfortable temperature in the premises of private houses, it varies from 3 to 5 atm. The pressure in central heating systems of multi-storey buildings is about 8-16 atm. To ensure long-term use of radiators, their operating pressure must exceed the same parameter in the network by at least 2 atm. The composition of the coolant also differs. In autonomous networks, antifreeze solutions can be used, and water for central communications is usually subjected to chemical treatment.
In addition, the duration of use of batteries installed in apartments with central heating is negatively affected by water hammer in the pipeline. They occur due to pressure changes and often occur when utilities are started at the beginning of the heating season. Since different materials are used for the production of radiators, their level of resistance to external influences, reliability and durability differ significantly. Some manufacturers achieve improved technical parameters and increased service life by introducing new technologies and methods of metal processing.
Features of Cast Iron Finned Economizer Tube
The heating pipe for industrial economizers can be rectangular in shape and with round fins. The dimensions of the products are standard: the internal diameter is 70 mm, and the external diameter is 175 mm. Due to the differences between the outer and inner diameters, the effect of a low pipe surface temperature with a sufficiently hot coolant is achieved.
Economizer pipes are produced in the same lengths: 2 m and 3 m. Cast iron finned pipes go on sale equipped with two plugs with holes and two blind plugs. Plugs with holes are left-handed and right-handed, with left-handed ones marked with the designation “L”.
There are certain operating conditions under which a cast iron pipe with a ribbed surface will function as efficiently as possible:
- the highest temperature allowed for cast iron economizer pipes is 95 degrees. In emergency cases, a short-term rise in temperature to 150 degrees is allowed;
- constant operating pressure – 0.6-1 MPa (10 atmospheres). However, cast iron finned tubes are compatible with steam boilers whose pressure is maximum 2.4 MPa;
- the outer surface of the economizer is coated with a special primer;
- When installing finned pipes, the mandatory distance from the floor to the middle axis of the economizer is taken into account, which is at least 200 mm. From the surface of the side wall, the distance to the pipe axis is taken into account from 130 mm;
- if economizers are arranged in two rows, the distance between the axes of the radiators is maintained at 250 mm. The rows of economizers are connected to each other by a special arc.
All economizer pipes are equipped with plugs - blind and with holes
The main disadvantages of economizer pipes include their rather heavy weight, which makes transportation difficult, and low resistance to mechanical damage.
Corrosion resistance level
The average values are presented in the table.
| Corrosion resistance (mm/year) of cast iron | |||||||||
| Cast iron | terms of Use | ||||||||
| Industrial environment | Chamber with 0.3% SO2 additive | Sheath liquid at 25 °C | Sea water* | 10% at 50 °C | 3% at 10-19 °C | 5% acid | |||
| sulfuric | salt | nitrogen | |||||||
| White | — | — | — | 0,05 | — | — | — | — | — |
| Grey | 0,14 | 0,24 | 0,27 | 0,06 | 0,02 | 0,08 | 31 | 27 | 26 |
| Lasting | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| ferrite | 0,18 | 0,29 | 0,22 | 0,06 | 0,01 | 0,08 | — | — | — |
| ferrite and pearlite | 0,18 | 0,24 | 0,26 | — | — | 0,08 | — | — | — |
| perlite | 0,14 | 0,22 | 0,29 | 0,06 | 0,01 | 0,08 | — | — | — |
| Malleable | — | — | — | 0,06 | — | — | — | — | — |
| Corrosion-resistant type 4N 15D7 | — | — | 0,05 | 0,02 | — | — | 0,15 | 0,3 | 21 |
| Silicon ChS 15 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 0,13 | 0,13 | — |
| *when tested in running water, corrosion is higher. The rate is 1 g/(m2∗h) = 1.2 mm/year. |
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages include simple design and simple calculations, availability of materials. All this together allows you to make heating registers with your own hands.
The next positive point is that most of the heat is transferred using radiant energy, and it is perceived by a person as more pleasant.
Heating registers are usually located in utility, production, and auxiliary rooms
The next plus is the smooth surface, which makes cleaning easy.
Excellent quality - compatibility with any systems - both natural and forced circulation.
There are also disadvantages: low heat transfer, susceptibility to corrosion, not the most attractive appearance, the need for regular painting (read how to choose paint here).
Pros of the system
Cast iron batteries have a number of significant advantages that make them the best option when designing a heating system. The list of the main advantages of finned tubes made of this heavy-duty material is as follows:
- high thermal conductivity;
- low susceptibility to corrosion both outside and inside the product;
- affordable price;
- service life over 100 years;
- the ability of a material to retain heat for a long period.