General fire safety requirements for boiler houses are contained in regulations:
- main ones:
- SP 89.13330 (SNiP II-35-76), 62.13330 (SNiP 42-01-2002);
RF PP dated December 26, 2014 N 1521 “On approval of the list...” (list of applicable items);
Boiler room category for explosion and fire hazard
The boiler room is a room with a functional fire hazard class F5.1, respectively, categorized according to SP 12.13130. In SP 89.13330 it is assigned cat. D, but this provision is not categorical - calculations are carried out individually.
The boiler room almost always has a cat. D. In exceptional cases, if the calculation of the category shows this, one of the positions B is possible. Different parts of the building may have different values (see SP 89.13330).
Built-in, attached, roof-type structures are made with fireproof parameters no lower than those of the structures they serve. Detached buildings must fully comply with the rules for production facilities.
Other parameters for the PB classification are:
| Type | Fire resistance degree | Structural fire hazard class |
| Separate attached, built-in | I and II | C0 |
| III | C0, C1 | |
| Separate with reliability of release 2 tbsp. | IV | C0, C1 |
| Roof | III | C0 |
Requirements for the placement and premises of the boiler room
A boiler installation is a set of equipment with wall-mounted or floor-mounted heating boilers that converts fuel energy to create steam and heat water (coolant). For boiler houses from 36 kW, a special (dedicated) room is required.
Options:
- ceiling height from 2.5 m (for an object up to 60 kW - not lower than 2 m);
- volume 15 m³ plus 0.2 m³ per 1 kW;
- A ventilation window must be provided in gas-fired facilities.
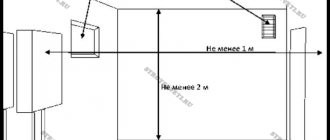
The distance from the wall of an attached structure to the nearest window of the main building is from 4 m horizontally and from 8 m vertically. You cannot place (clauses 1.6 – 1.8 SP 89.13330 and clause 7.1 SP 62.13330):
- attached:
- adjacent to and above areas with simultaneous presence of at least 50 people;
from the side of the main facade of the building;
- roof and built-in – above/under production, high-traffic premises and warehouses (except for the installations themselves), buildings cat. A and B;
- built-in boiler rooms in multi-apartment housing, under public buildings;
- roof boiler rooms in apartment buildings adjacent to housing, if their ceilings are used as a floor or base;
- gas - in basements, plinths, with the exception of single-family and semi-detached housing, if this is not regulated by building codes;
- with boilers in basements with a flash point of gas or liquid fuel below +45 °C.
For preschool educational institutions, schools, medical and inpatient buildings of medical institutions, sanatoriums, and recreational facilities, only free-standing heating structures are equipped. Exception: for residential, public, domestic and administrative buildings, all types are allowed if the boilers heat the water to 115°C and with a pressure of up to 0.07 MPa.
Boiler rooms for stone and wooden private houses are possible. Experts recommend building free-standing or attached ones so that there are no odors in the house and to reduce risks.
General standards for arrangement:
- fire-resistant materials for wall decoration are non-flammable, at least flame-retardant. Moisture-resistant paints and varnishes are used for painting;
- finishing of floors and ceilings in the boiler room with non-combustible materials must correspond to its degree of fire hazard. Fully NG facings are recommended: ceramic tiles, brick, plaster, concrete;
- types of barriers from adjacent rooms for built-in and roof-mounted ones:
- walls – 2;
partitions – 1;
- floors – 3;
- flights of stairs from common building l/c are separated by sub-barriers with a resistance of 45 minutes. and types:
- partitions – 1;
floors – 3;
- for attached ones, use type 2 subwalls, NG ceilings, adjacent walls must have a fire resistance time of 45 minutes;
- for the walls of roof boiler rooms, the fire resistance time is from 0.75 hours, the spread of flame (FP) is zero. The roof of the main building and the area of 2 m from its walls is made of NG materials or protected with concrete/plaster (from 20 mm).
The room is provided, in addition to individual (regular, emergency), natural lighting with glazing in the amount of 0.03 m² per 1 m³. Domestic and service rooms for personnel or repair shops are prohibited in the boiler room.
Laying under foundations and structures is prohibited. A, B (except for GRP, GRPB, GNS, GNP) through gas ducts, balconies, utilities, ventilation, elevator shafts, l/c. Fuel lines are not located below the zero mark, stuffing box compensators are not allowed, as are extraneous loads.
What to look for when choosing a boiler
Boiler units operating with two heating circuits have high efficiency, since, consuming almost the same cubic capacity of gas, they provide a residential building with both heating and domestic hot water.
Wall-mounted and floor-mounted boilers have different thermal outputs, so they can be used in buildings with different heating volumes.
For small-sized objects, wall-mounted ones are preferred, for tall country cottages - floor-mounted ones, and the most complex large-sized structures.
In order to choose which gas boiler is better, you need to consider the following parameters:
- number of people living in the house;
- number of water points;
- distance of water intake points from the boiler unit;
- cottage area;
- rating of gas boilers.
The thermal power of the boiler system is the most important thing you need to know before purchasing. It is calculated using data on the heated area.
For preliminary calculations of the power of the device for a standard room height of up to 3 m, you can use a simple ratio: multiply the heated area by 0.1 kW.
Fire safety requirements for gas boiler houses
The standard gas boiler room category is G (moderate fire hazard). It's not explosive. Chamber furnaces, main and/or liquefied gas are used.
Parameters and what the equipment should have:
- stagnant, non-ventilated (non-ventilated) zones are excluded;
- welded connections in pipelines;
- gas control units (GRU);
- easily resettable enclosing structures (reduce excess pressure during explosions);
- explosion safety valves;
- bends (each) with shut-off devices, gas burner equipment - with control devices;
- quick-acting and temperature-sensitive valves, flow measuring devices (for boilers from 1 MW);
- gas pressure up to 0.005 - 1.2 MPa (according to Table 2, 3 SP 62);
- They use steel and copper pipes with walls from 3 mm for underground pipes, and from 2 mm for external pipes. For the latter, reinforced PE is allowed (but not for LPG);
- laying depth from 0.8 m to the top of the gas pipeline;
- Pipes should be installed on blank walls or at a height of 0.5 m above the openings, but at least 0.2 m below the roof; they can be laid between windows with a gap of 0.2 m from each;
- Inside, installation is done in grooves or in floor channels with sealing.
For facilities operating on liquefied gas (LPG), the energy carrier is stored in tanks (gas holders) with control units. The recommended quantity is from two (above-ground and underground in an embankment). The distances are determined by the table. N 7 SP 62.
Service
Diesel boiler houses have many advantages, including the ability to fully automate the combustion process. At the same time, a large amount of soot remains from the work, which accumulates on the walls of the heat exchanger and the chimney.
Cleaning of diesel boilers is required regularly. The heat exchanger, chimney and nozzles are serviced by a specialist.
Heating devices need to be tuned and adjusted every year. A test start-up of the boiler is performed. The average fuel consumption per hour is determined from the fuel meter. If costs increase by more than 10%, then the boiler is stopped and the necessary work is carried out.
To maintain operability and high thermal output, proper installation, piping, and adherence to safety and maintenance rules are necessary.
When choosing any heating system, remember that the most important parameters - reliability and long service life - are provided, firstly, by the manufacturer of the equipment for the boiler room, and secondly, by the professionalism of the craftsmen who install and put the unit into operation.
Fire safety requirements for solid fuel boiler houses
Rules for heating installations using solid fuels:
- supply of coal, firewood, peat, sawdust, pellets for equipment with a power of 1.16 MW and the process of slag extraction, if its volume is more than 150 kg/h, is mechanized (belt conveyors);
- Compacted soil is recommended for fuel storage areas;
- warehouse capacity: 2 – 14 daily supplies according to clause 13.12 of SP 89;
- stacks are placed 5 m to the fence, 2 m to the railway tracks, 1.5 m to the road;
- in warm objects, wet cleaning (hydrowash) is allowed;
- capacity of bunkers: for coal – reserve for 3 hours; for peat – by 1.5.
Fire safety in an electric boiler room
Block-modular boiler houses (mobile, autonomous) with a capacity of 35 - 3000 kW are common. Maximum service area up to 30,000 m². Requirements:
- distribution devices (minimum 2 sections);
- variable frequency drives;
- soft start and blocking devices;
- automatic switching on of reserve;
- laying of networks is open in boxes or in channels (wires in the lining), with the exception of wet areas and fuel supply;
- electrode boilers - three-phase, with connection to industrial frequency networks;
- pipelines with insulating inserts;
- grounding, grounding;
- the transformer station is not located in the boiler room, but nearby;
- electric boilers with protective fencing;
- all nodes are isolated from the ground and pipelines;
- automatic shutdown with alarm if there is a deviation in system performance;
- sign “Caution! Electrical voltage" at the input.
Fire safety rules for the operation of boiler installations with electric boilers take into account the PUE.
Fire safety standards in liquid fuel boiler houses
Requirements:
- fuel tanks:
- steel, reinforced concrete external with sprinkling or underground. For light types of fuel and additives, plastic ones with a safety certificate are allowed;
in climates from t° to +9 °C, make thermal insulation;
- capacity according to table 13.1 SP 89 (for 2 – 10 days);
- quantity: for main stock – at least 2; for backup – more than 1;
- consumable tanks are mounted outside the building, but they are allowed in separate boiler rooms;
- for block-modular placement, the main and receiving tanks can be combined;
- on fuel oil pipelines, bends, inlets:
- steel reinforcement 1 class. tightness;
seamless welded joints, and flanges only near the fittings;
- locking unit with manual and electric drive;
- connection to a flange for a plug with a release device;
- purge unit;
- emergency shutdown;
- for boilers from 1 MW - flow meter;
- control valve, as well as a slam-shut valve with an inertia of up to 3 seconds;
- check valve;
- on boilers with a capacity of 100 Gcal/h or more, a shut-off valve, an electrically driven shut-off unit, is installed in front of each burner.
PB requirements for boiler placement
Distances for the boiler (according to R. 6 SP 89):
- the heat generator is not adjacent to any walls;
- access is open from any side;
- from the front to the opposite wall - at least 3 m;
- for gas boilers or those operating on liquid fuel - from 1 m from the burners, for mechanized fireboxes - more than 2 m;
- for heating devices with a capacity of up to 2.5 t/h, the distance can be reduced to 2 m;
- between two boilers:
- with mechanized fireboxes – 4 m and more;
on gas or liquid fuel - from 4 m, but the gap between burners is from 2 m;
- with manual loading – from 5 m;
- passages around - up to 1.5 m and up to 2 m for devices with a rate exceeding 4 t/h, if lateral maintenance is not required, then at least 1 m (but not from the front);
- the width of passages between individual protruding parts is from 0.7 m;
- free height – from 2 m.
“Podium” (backing):
- NG (concrete, brick, metal) with a thickness of 7 cm (standard 10 – 15 cm);
- protrusion of 10 cm around, in front of the firebox - 20 cm. The walls at the back and sides are lined with heat-reflecting screens;
- for a pre-furnace sheet made of steel, copper with a thickness of 1 - 2 mm, the dimensions are taken by analogy with clause 81 of the PPR: 0.5x0.7 (along) m.
Wall-mounted heating boilers are not installed in boiler rooms in the traditional sense of the term (not domestic). Mounted heat generators are rated according to different rules.
Adjustment
Automatic control is provided by the heating regulator.
It includes the following parts:
- Computing and matching panel.
- Actuating device on the water supply section.
- An actuator that performs the function of mixing liquid from the returned liquid (return).
- Boost pump and sensor on the water supply line.
- Three sensors (on the return line, on the street, inside the building). There may be several of them in the room.
The regulator closes the liquid supply, thereby increasing the value between return and supply to the value specified by the sensors.
To increase the flow, there is a boost pump and a corresponding command from the regulator. The incoming flow is controlled by a "cold bypass". That is, the temperature decreases. Some of the liquid that has circulated along the circuit is sent to the supply.
Sensors collect information and transmit it to control units, resulting in a redistribution of flows that provide a rigid temperature scheme for the heating system.
Sometimes, a computing device is used that combines hot water and heating regulators.
The hot water regulator has a simpler control scheme. The hot water sensor regulates the flow of water with a stable value of 50°C.
Advantages of the regulator:
- The temperature scheme is strictly maintained.
- Elimination of overheating of the liquid.
- and energy efficiency
- The consumer, regardless of the distance, receives heat equally.
Safety regulations for chimney placement
Requirements for smoke exhaust take into account ordinary and industrial regulations (SP 43.1333, 7.13130). Rules:
- install one pipe, two or more - upon technical justification;
- gate with a hole of 50 mm in the upper part;
- for boilers with forced-air burners, individual chimneys or common ones with separating inserts are installed;
- if there are more than 3 boilers and with an outlet diameter of 3.6 m or more, install a multi-barrel structure;
- materials: reinforced concrete, brick, metal, fire-resistant plastic, ceramics;
- at the junction of gas ducts - temperature-sedimentation joints, compensators;
- manholes, hatches for cleaning;
- ash collection devices, condensate drainage;
- lining with brick, concrete, metal, thermal insulation;
- outlet (exhaust path from the installation to the chimney):
- vertically from the boiler at least 500 mm;
- branch – up to 1 m, number of turns – up to 3;
horizontal section with an upward slope of 2°;
- brick or concrete body – from 130 mm;
ceramic – from 250 mm.
If flammable structures are adjacent to the chimney, they are protected with offsets or cuts that reduce the rate of fire spread. The first is a gap of 260 - 500 mm. The second is a thickening of the pipe from 500 mm if the fences are flammable, and from 380 mm if with fire protection. Width – 70 cm more than adjacent structures.
Primary fire extinguishing agents
The boiler room has subclass F5.1 (industrial buildings), accordingly, they comply with the standards for fire extinguishing agents.
A fire shield is needed if there is no fire hydrant, AUPT, and the distance to water intake points is more than 100 m. A box of sand (from 0.5 m³) is required for fire class. B, E. The procedure for using primary fire extinguishing agents is prescribed in the safety instructions.
What fire extinguishers should be in the boiler room?
In boiler rooms, the fire class is usually A, B, C, and also E (electric boiler fire). According to the table NN 1 and 2 PPR (post. N 390) conditions for manual fire extinguishers are as follows:
| Fire class | Number and fire extinguishing capacity of fire extinguishers |
| A | 2 – 6A 1 – 10A |
| B | 2 – 144B 1 – 233B |
| E | 2 – 6A, 144BCE 1 – 10A, 233BCE 2 – 144BCE 1 – 233BCE |
| WITH | 2 – 6A, 144BC 1 – 10A, 233BC 2 – 144BC 1 – 233BC |
According to the table 1 NPB 166 list of fire extinguishing means in the form of fire extinguishers is as follows:
| Boiler room category | Maximum area, m² | Fire class | ORP, 10 l | , l | for 2 (3) l | , l | |||
| 2 | 5 | 10 | 2 | 5 (8) | |||||
| G | 800 | B | 2 | – | 2 | 1 | – | – | – |
| C | – | 4 | – | – | – | ||||
| G, D | 1800 | A | 2 | 4 | – | – | – | ||
| D | – | – | – | – | – | ||||
| E | – | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 | ||||
According to SP 41-104-2000 clause 14.2, mobile OPs are prescribed for areas up to 150 m³; additional standards are in Table. N2 NPB 166. It is recommended to follow the rule: the boiler room must have at least 2 fire extinguishers.
Regulations
You should immediately decide on the regulatory framework. Until mid-2003, SNiP standards No. 2.04.08-87 were in force. On July 1, 2003, SNiP 42-01-2002 came into force. All requirements and standards for installing boiler rooms in a private home must be taken from this document.
It is advisable to know the standards, although the design of a boiler room in a private house should be drawn up by a specialized organization. This way you can decide on the possibility and impossibility of installing this or that heating equipment, as well as what work you have to do in order to adjust the existing or under construction premises to the standards. For every difficulty or controversial issue, it is worth going to the design department of the gas supply organization and talking with them. There are a lot of nuances associated with the features of each house, which can only be solved by being tied to the house plan or its design.
What kind of door should be in the boiler room?
Door parameters:
- canvas width from 0.8 m;
- opens outwards;
- the exit must necessarily be outside from the basement/basement segments of the building if the power is above 150 kW (clause 6.18 of SP 42-101-2003);
- for an area larger than 200 m² - from 2 exits. For less – 1, but in the presence of evacuation;
- the doors of the service and household premises open in its direction;
- for roof boiler rooms, there is an exit to the roof and a second one from the main building;
- in built-in varieties, access to the street or into the house is required, but with a vestibule.
For exit to the adjacent building - only fire doors with closers, fire resistance limit as that of the enclosing structure (for power from 60 kW - EI 45 and above); to the street - any door leaves. Thresholds are not used if the ventilation gap with a cross-section of 0.2 m² is made at the bottom of the doors, and not at the top (above the doors, under the ceiling).
How is it calculated?
A control method is selected, then a calculation is made. The calculated winter and reverse order of water supply, the amount of outside air, and the order at the break point of the diagram are taken into account. There are two diagrams: one of them considers only heating, the second considers heating with hot water consumption.
For an example of calculation, we will use the methodological development of Roskommunenergo.
The input data for the heat generating station will be:
- Tnv – the value of outside air.
- TV - indoor air.
- T1 – coolant from the source.
- T2 – reverse flow of water.
- T3 – entrance to the building.
We will look at several heat supply options with values of 150, 130 and 115 degrees.
At the same time, at the exit they will have 70°C.
The results obtained are compiled into a single table for subsequent construction of the curve:
So, we have three different schemes that can be used as a basis. It would be more correct to calculate the diagram individually for each system. Here we examined the recommended values, without taking into account the climatic features of the region and the characteristics of the building.
To reduce energy consumption, it is enough to select a low temperature setting of 70 degrees and uniform heat distribution throughout the heating circuit will be ensured. The boiler should be taken with a power reserve so that the system load does not affect the quality operation of the unit.
Smoke removal from the boiler room
Solid fuel installations are equipped with flue gas purification systems (ash collectors). Gas ducts must be free of ash deposits. When using wood fuel, “wet” spark arrestors are installed. Each boiler is equipped with draft units (smoke exhausters, fans).
Supply ventilation should provide 3 air changes in 1 hour and a sufficient supply of oxygen for the burners. For each kW, 8 cm² of cross-sectional area of the ventilation duct will be required, or 30 cm² if the air is taken from the building system.
Instructions on fire safety measures in the boiler room
The fire extinguishing plan and compliance with safety regulations are specified in several versions of instructions for each type of room. The document establishes the responsibilities of personnel who must undergo emergency and fire training.
An example of the main aspects of instructions on fire safety measures in a boiler room:
- personnel actions must ensure the evacuation of workers and the organization of fire fighting before the arrival of firefighters;
- operator (stoker) actions:
- call the fire department;
stop and de-energize the equipment;
- when gas pipelines catch fire, the pressure is first reduced to a minimum, then the flame is extinguished, and then the gas is turned off;
- general fire safety measures:
- before lighting the boilers, check their serviceability, ventilation, control units;
the fireboxes are ventilated for 10–15 minutes by opening the dampers and/or turning on the smoke exhausters for 3–5 minutes;
- traction is checked;
- Drying any items on or near boilers is prohibited;
- the tightness of gas pipelines is checked with a soap solution;
- It is forbidden to supply fuel when the burners are extinguished, as well as ignition without pre-purge;
- checking water level and pressure is mandatory;
- When stopping the boiler, you must disconnect it from the main line and open the purge plug.
Download: Sample instructions on safety measures in a solid fuel boiler room.pdf Download: Sample instructions on safety measures in a gas boiler room.doc Download: Sample instructions for a boiler room operator.doc
Disadvantages of modern heating systems
As with any heating system, an autonomous one has its drawbacks. Although there are much fewer of them compared to the centralized one. Due to the fact that gas autonomous boiler houses are not widespread, it is quite problematic to obtain reliable equipment and all the components adjacent to it.
Therefore, boiler room elements will cost customers a tidy sum. Despite the high level of comfort that the systems in question provide, not all developers are willing to pay a lot of money for it.
In the event of an emergency, the entire heat supply system completely fails. There is up to five cubic meters of boiling water above people's heads. If the pipes burst, the water will flow down. That is why there are so many requirements for gas equipment
In addition, gas boiler rooms must be located in separate rooms or buildings. To do this, you need to allocate an area near the house, bring the roof to the required technical conditions, or install a block structure on the roof. All of these solutions require an infusion of additional resources either from the developer or from a common fund created by residents.
Gas heating systems release polluting decay products into the environment. Therefore, when installing boiler rooms, it is necessary to provide for the installation of filtration systems. Cleaning devices must perform their functions sufficiently to comply with SNiP standards. This further increases the cost of purchasing equipment.
When building a new house, the developer has a choice: to build an autonomous heating system or connect to the central highway. In order to crash into a highway, you need to obtain a number of permits. Often, resolving a problem requires a large sum of money. In addition, you will need to wait more than one month until the papers are checked by all authorities.
The high cost of connecting to existing networks, difficulties in coordinating this procedure, as well as the presence of many obstacles that impede the rapid and efficient installation of heating networks reduce the attractiveness of autonomous systems for developers.
Often the installation of gas boilers on the upper enclosing structure entails the need to strengthen the ceiling. The total load created by the heating system can reach 15 tons. Such values can be avoided by installing flow-through equipment instead of capacitive
Installing autonomous heating is also associated with a number of bureaucratic procedures. Both the initial implementation of systems and reconstruction with redevelopment have their own characteristic features. This is mainly due to the fact that you are going to use gas as a heating resource. All work with gas is strictly regulated by law.
Modern engineering developments effectively combat a number of shortcomings. If you need to heat just one house, an excellent option would be to place a block boiler room in the attic of the house. The attic becomes heated, and residents of the top floor do not experience discomfort.
Such structures are developed in detail by engineers, are lightweight and are installed on load-bearing walls. For such options, a flat roof option is required. This subtlety is usually taken into account at the design stage. Designers carry out calculations and determine in advance the location for the boiler room on the roof of the house.
The law sets a limit on the power of equipment on the roofs of 3 MW. Some regions have a 5 MW limit. If such power is not enough to fully heat the entire house, then additional permits must be requested
However, despite all the shortcomings, ultimately, the residents of the house will significantly improve their living conditions and get rid of discomfort. In addition to all the obvious advantages, autonomous systems have an increased level of security.
The new systems are equipped with threat and emergency alarms. A variety of sensors for gas boilers monitor many indicators. In the event of a breakdown, the backup boiler and additional pumps are activated.