Thermal conductivity and density of penoplex, comparison with polystyrene foam PSB
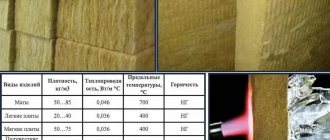
A comparative table of the values of the thermal conductivity coefficient, density of penoplex and polystyrene polystyrene PSB of various brands in a dry state at a temperature of 20...30°C is presented.
Their operating temperature range is also indicated. Penoplex thermal insulation, in contrast to non-pressed polystyrene foam PSB, is produced at elevated temperatures and pressures with the addition of a foaming agent and extruded through an extruder. This production technology provides penoplex with a closed microporous structure.
Penoplex, compared to polystyrene foam PSB, has a lower thermal conductivity coefficient λ , which is 0.03...0.036 W/(m deg) . The thermal conductivity of penoplex is approximately 30% lower than that of such traditional insulation as mineral wool. It should be noted that the thermal conductivity coefficient of polystyrene foam PSB, depending on the brand, is in the range of 0.037...0.043 W/(m deg).
The maximum temperature for using Penoplex expanded polystyrene is 75°C. For PSB foam it is slightly higher and can reach 80°C. When heated above 75°C, penoplex does not melt, but its strength characteristics deteriorate. The manufacturer does not report how much the thermal conductivity coefficient of this thermal insulation material increases under such conditions.
Thermal conductivity and density of penoplex and expanded polystyrene PSB
| Brand of expanded polystyrene | λ, W/(m K) | ρ, kg/m 3 | trab, °С |
| Penoplex | |||
| Penoplex comfort slabs | 0,03 | 25…35 | -100…+75 |
| Penoplex Foundation | 0,03 | 29…33 | -100…+75 |
| Penoplex Roofing | 0,03 | 26…34 | -100…+75 |
| Penoplex segments grade 35 | 0,03 | 33…38 | -60…+75 |
| Penoplex segments grade 45 | 0,03 | 38…45 | -60…+75 |
| Penoplex Block | 0,036 | from 25 | -100…+75 |
| Penoplex 45 | 0,03 | 40…47 | -100…+75 |
| Penoplex Slope | 0,03 | from 22 | -100…+75 |
| Penoplex Facade | 0,03 | 25…33 | -100…+75 |
| Penoplex Wall | 0,03 | 25…32 | -70…+75 |
| Penoplex Geo | 0,03 | 28…36 | -100…+75 |
| Penoplex Base | 0,03 | from 22 | -100…+75 |
| Expanded polystyrene PSB (foam plastic) | |||
| PSB-15 | 0,042…0,043 | up to 15 | up to 80 |
| PSB-25 | 0,039…0,041 | 15…25 | up to 80 |
| PSB-35 | 0,037…0,038 | 25…35 | up to 80 |
| PSB-50 | 0,04…0,041 | 35…50 | up to 80 |
It should be noted that Penoplex thermal insulation, due to its closed microporous structure, practically does not absorb moisture, is not affected by mold, fungi and other microorganisms, and is an environmentally friendly and safe insulation for humans.
In addition, extruded polystyrene foam Penoplex has fairly high chemical resistance to many materials used in construction. However, some organic substances and solvents listed in the table below can cause insulation boards to soften, shrink, and even dissolve.
Source
Comparison by main parameters
Mineral wool has a coefficient of 0.032-0.046, while penoplex has a coefficient of 0.03-0.032. The lower the indicator, the better, because there is less heat loss and the temperature inside the room is better maintained.
Duration of operation.
Penoplex is a fairly hard material that does not rot, dry out or crumble. The insulation has a long service life under the correct storage conditions, when it is reliably protected from prolonged sunlight and excessive heat. Mineral wool also does not dry out. Without exposure to high physical stress, it can last for a long time, is not afraid of high or low temperatures and long exposure to sunlight on the surface.
It is not at risk of mold and other harmful organisms, and it is also not susceptible to destruction by rodents. But mineral wool can crumble and settle on the wall. In general, both materials have an enormous service life, lasting at least 50 years.
Environmentally friendly.
Both materials are manufactured without the use of any hazardous components that could be harmful to human health, but still require absolute containment to protect the respiratory tract.
Comfortable installation.
When insulating a perfectly smooth surface, work using penoplex is carried out much faster. It is lightweight, easy to cut and sand, and with an L-shaped edge, it eliminates the formation of cold bridges. When using it, there is no need to cover it with a vapor barrier. If there is no tongue-and-groove edge, then it is tedious to seal the seams or lay them in two overlapping layers, which will lead to unnecessary costs.
Mineral wool has a little more weight, but it is much more efficient and simplifies installation in existing heavy, disproportionate areas and structures. But when working with it, you must purchase special clothing in advance, along with a respirator and safety glasses.
Which material is warmer?
If used to insulate the facade of a house, if the penoplex has a thickness of 50 mm, then the mineral wool should have a thickness of 60 mm to have a similar effect. The difference is not entirely dramatic. Depending on the situation, each of them is good in its own way, because cotton wool is capable of allowing air to pass through, unlike penoplex, which has an absolutely airtight structure.
Moisture absorption.
Mineral wool absorbs water much more strongly, subsequently losing some of its thermal insulation characteristics. In this case, penoplex is significantly better, because even with intense and frequent rains, its mass will practically not change.
Combustion.
Mineral wool has the best performance in this parameter, because it is almost inflammable. Its melting point should be more than 1000°. Cotton wool contains an adhesive base that can ignite, but it occupies a very tiny part of the total volume of the material and does not pose a significant danger.
Penoplex is completely opposite in its qualities. It can melt and burn in open fire, releasing toxins that are very harmful to the human body. To ensure a high level of protection of buildings from fire, penoplex is categorically unsuitable for use. For these purposes, the best and unconditional option is mineral wool.
Price.
The price of materials is practically no different. There may be a slight difference only depending on the choice of the manufacturer.
Penoplex 50 mm thick - properties and characteristics
Penoplex brand insulation is nothing more than extruded polystyrene foam. It belongs to a new generation of thermal insulators that are very effective in terms of heat conservation. In this article we will take a detailed look at penoplex: technical characteristics, pros and cons and areas of its application. To begin with, we note that this material is durable, almost does not absorb water at all and has a low thermal conductivity coefficient.
Description
PENOPLEX OSNOVA® is a highly efficient thermal insulation material of the latest generation, manufactured by extrusion from general-purpose polystyrene. Zero water absorption, high strength, environmental friendliness and low thermal conductivity are the main advantages of PENOPLEX insulation compared to other materials.
Application of PENOPLEX BASIS®
Intended for use in industrial and civil construction, it is a universal material for use in any structures (walls, roofs) where special requirements for loads on the structure are not imposed.
Choose what you need
Despite the fact that the production of Penoplex with technical characteristics corresponding to those declared is carried out by many manufacturers, one should take a responsible approach to the choice of the “homeland” and “parent” of the insulation. One should not discount the need to choose it to achieve maximum insulation in a particular case for certain conditions, materials, surfaces.
When selecting, you need to focus on:
- brand and series of heat insulator required for the work;
- the size of the slabs, especially if you plan to insulate a small room;
- the density of Penoplex slabs, which should not be less than 25 kg/m3 (the quality of insulation and strength depend on this indicator);
- manufacturer's brand;
- block packaging (it must be intact, which guarantees the integrity of the slabs).
If in doubt, read the characteristics on the Penoplex packaging. The description contains all the necessary data to make a selection decision.
If you are in doubt about the indicated density, weigh the slabs to determine the density yourself, subsequently dividing the weight by the volume. For example, a Comfort slab with a thickness of 50 mm and normal density should not weigh less than 1.3 kg. At the fracture of the “regular” Penoplex, you can see many polyhedra of regular shape, along the boundaries of which the fracture occurs. The fracture should be orange due to the coloring pigment included in the composition. Purchasing products from well-known European factories will guarantee the quality of the products. The domestic manufacturer, represented by the Penoplex and TechnoNIKOL enterprises, is not far behind them.
After reading about penoplex, understanding what it is, where it can be used, assessing its pros and cons, you can be confident in the targeted choice of the right brand and in its correct use. Having done insulation once using Penoplex, ensure that heat is retained in the house for many years.
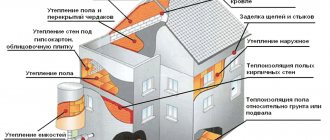
What to insulate with 50 mm penoplex
Penoplex with a sheet thickness of 50 mm is one of the most popular and popular. Due to the excellent price-quality ratio, the choice of buyers most often falls on it. It can be used to insulate:
The penoplex manufacturer has special subtypes of insulation for each of these purposes. Their technical characteristics will be discussed below.
The wall
For external insulation of wall surfaces, Penoplex “Wall” insulation was developed. The size of a sheet of such insulation is 120 by 60 cm. This means that one element of insulation can cover an area of 0.72 m2. This is a pretty good indicator, which will make it possible to finish a wall with a size of 10x4 meters in less than one day. The manufacturer has provided that special antioxidants and fire retardants be introduced into this type of penoplex. The former allow the insulation to resist the oxidizing effects of oxygen, while the latter reduce flammability. The structure of the insulation is designed in such a way that it interacts well with finishing mixtures. The ability to have sufficient adhesion prevents them from peeling off. The insulation can also withstand sufficient weight. Its resistance to compressive force is 0.2 MPa.
Note! When calculating the required amount of insulation for a specific area, it must be taken into account that with a material thickness of 50 mm, 8 units of insulation or 5.76 m2 are placed in the package.
Foundation
Due to its design and position, the foundation can experience significant temperature effects and cause up to 20% heat loss. That is why it is worth thinking about insulating it. Foam insulation “Foundation” 50 mm is perfect for these purposes. It does not contain fire retardant additives, so its cost may be slightly lower than wall insulation. The sheet size is standard, as mentioned in the previous version. The density of penoplex for these purposes has been increased, and now it is 33 kg/m3. This is necessary for greater compressive stability, because the foundation is backfilled and the soil around it is compacted. The tensile strength level also increased to 0.27 MPa. Paired with bitumen mastic, it can provide excellent waterproofing, which will reduce the likelihood of basement flooding.
Roofing
Roof insulation with penoplex can be done in two ways. One of them involves installing foam sheets 50 millimeters thick on the attic floor, and the second involves insulating the roofing itself, which is carried out from the inside. The use of penoplex in such areas of the building is very important, because heat rises by convection and will evaporate freely, increasing fuel costs. In this case, the environmental friendliness of the insulation also comes into play. The compression resistance of roofing foam is slightly lower than that of foundation foam. This is due to the fact that the roofs do not have such high loads. The thermal conductivity coefficient of such penoplex with a thickness of 50 mm is 0.03 W/(m×K).
The roof is the highest point of any building; if it is not shaded, it heats up more than other surfaces. This means that in the summer it will cause some inconvenience and will require funds for air conditioning. Penoplex allows you to solve this problem. Due to its properties, penoplex insulation prevents excess heat from entering the building. If the roofing material chosen is one based on sheet metal, then penoplex will also provide sound insulation so that the rain does not wake you up at night with the drumming of drums. The process of making insulation can be assessed in the video.
Other types of penoplex
One of the unique types of penoplex, which is most often produced with a sheet thickness of 50 mm, is insulation with index 45. It differs from all previous types in having a denser structure. The density of this penoplex is 45 kg/m3. With such a density and bending resistance of up to 0.7 MPa, it is excellent for laying under road surfaces. In areas that are characterized by significant seasonal precipitation and wet soil, it will prevent the rapid destruction of routes. Penoplex practically does not absorb water, so it will not let it through to the flooring. The thermal conductivity of penoplex 45 is at the level of 0.03 W/(m×K).
Penoplex insulation of this series is also perfect for insulating plinths and basements of buildings. In some buildings, the roof is usable; for example, it can be equipped with an observation deck or a landing spot for a helicopter. On the roofs of some multi-story buildings there may be a small truck crane for delivering goods or moving a cradle. This type of insulation is also perfect for heating mains. It allows you to minimize heat loss. In addition, due to negative moisture absorption, it protects pipes from corrosive effects. In the table below you can also see the characteristics of “Comfort” insulation - another universal line from the manufacturer.
Production of penoplex and types of material
The production of penoplex is organized using the following technology: small polystyrene granules in a sealed chamber are exposed to high temperatures (130C-140C), as a result of which they melt, and after adding foaming agents they foam. Porophores are synthetic additives that, when heated, release nitrogen and carbon dioxide, which, after the penoplex cools, turn into frozen air bubbles, evenly distributed throughout the material.
Comparison of thermal conductivity of penoplex and other building materials
Components of blowing agents for the production of extruded polystyrene foam (penoplex):
| Penoplex components | Volume by mass |
| Polystyrene | 100 |
| Fine perlite | 1 |
| Sodium bicarbonate Na2CO3 | 1 |
| Citric acid C6H8O7 | 0,8 |
| Zinc stearate (C36H70O4Zn / Zn(C18H35O2)2) or barium stearate (C36H70BaO4) | 0,2 |
| Tetrabromoparaxylene - an additive to provide self-extinguishing properties to foaming polystyrene | 1,2 |
Penoplex production
Cured foam may contain some synthetic fillers, the presence of which determines the direction of application of the insulation - for walls, foundations, etc. The most common additives are flame retardants to increase fire safety (reduce the degree of flammability), antioxidants to protect the material from oxidation in the open air, antistatic substances to relieve static and dynamic stress during insulation operation, light stabilizers (protection from the negative effects of UV radiation), modifying additives and etc.
Polystyrene foam is pressed under pressure from the extruder chamber onto a conveyor for final formation into slabs or blocks. The percentage of gases in the insulation reaches 98% of the total volume of the finished penoplex, so the products are light in weight with impressive dimensions. Dimensions for each functional line of insulation are given in the tables below.
Sizes and types of penoplex
The small size of the pores (0.1-0.3 mm) and their complete isolation from each other guarantees high thermal insulation performance of any brand of penoplex. For different construction projects, it is necessary to select the appropriate series and brands of insulation, since structures can be operated under different conditions:
- Brand “K” is designed for insulation of pitched or flat roofs and roofs. Specific gravity (density) of the “K” series – 28-33 kg/m3;
- Series “C” – insulation for internal and external walls with a substance density of 25-35 kg/m3;
- Brand “F”, basements and basements. Material with high moisture resistance, biological stability and specific gravity ≥37 kg/m3;
- Penoplex brand "Comfort" is a universal series of insulation with a density of 25-35 kg/m3. Direction of application – insulation of apartments, houses, basements, balconies and loggias;
- Brand “45” has the highest frost resistance and strength, specific gravity 35-47 kg/m3. Designed for thermal insulation of road surfaces, runways, and other heavily loaded objects and structures.
Expanded polystyrene sandwich panels
A separate category produces sandwich panels, which are an improved thermal insulator for insulating attics and attics, facades and foundations of buildings. The sandwich panel has 2-3 layers and a cement bonded particle board as the bottom layer.
Manufacturing technology
The equipment used is an extruder. Its name, arbitrary from the name of the head with dies located at the exit of the alloy from the unit, is extrusion.
The main component of the technological process is polystyrene granules. It is divided into several stages:
First
Second
Making the slab - staying in the holding chamber for 24 hours. All air is pumped out of the unit using a vacuum pump, and the material is left inside. It stabilizes, the pressure inside the granules filled with air is balanced.
Third
Blocks are formed in a closed type matrix. Steam is supplied inside the container under pressure. Residual moisture is lost. The aging stage ends for a day, with each new heating cycle increasing the density of the structure.
A moderately dried block is cut on a conveyor belt. Violation of technology leads to uneven edges. The cutting tool is a red-hot refractory steel string. The production uses equipment with an electronic program that controls the level of metal heating.
Source
Other properties of the described insulation materials
Mineral wool insulation is not flammable. The fire resistance of these materials is determined not only by the properties of the material, but also by the conditions under which they are used.
The degree of fire resistance is greatly influenced by what materials the insulation is combined with. The method of arrangement of protective and covering layers also plays a role.
As for expanded polystyrene, it is a self-extinguishing material. Therefore, walls decorated with it do not ignite so quickly. And if this does happen, the flame also spreads over their surface more slowly than in the case of other insulation materials.
Mineral wool is a non-flammable substance. Therefore, the flammability of surfaces lined with it, as well as the spread of flame along them, is minimal. Since the basis of this insulation – basalt – is a natural stone, mineral wool can withstand temperatures up to 1000 °C, and can resist the spread of fire for up to three hours.
Why is thermal insulation needed?
The relevance of thermal insulation is as follows:
Heat loss through the walls of a typical multi-storey residential building is 30-40% . To reduce heat loss, special thermal insulation materials are needed. The use of electric heaters in winter contributes to additional energy costs. It is more profitable to compensate for these costs by using high-quality thermal insulation material, which ensures heat retention in winter and coolness in the summer heat. At the same time, the cost of cooling the room with air conditioning will also be minimized.
In the case of industrial buildings using a metal frame, insulation helps protect the metal surface from corrosion, which is the most detrimental defect for this type of structure. And the service life of a brick building is determined by the number of freeze/thaw cycles. The impact of these cycles is perceived by the insulation, because the dew point is located in the thermal insulation material, and not in the wall material.
Such insulation allows you to increase the service life of the building many times.
Protection against increasing noise levels is achieved by using such noise-absorbing materials (thick mattresses, sound-reflecting wall panels).
The use of a thermal insulation system makes it possible to reduce the thickness of external walls, while increasing the internal area of the building.
Thermal conductivity characteristics of polystyrene foam
In order to consider such a characteristic as the thermal conductivity of polystyrene foam, let us first understand what the thermal conductivity of materials is, in principle. Thermal conductivity is a quantitative characteristic of a body's ability to conduct heat.
This is the amount of thermal energy (Watt) that any material is capable of conducting through itself (meter), at a certain temperature (C) for a certain time. It is denoted by λ and expressed as W/m•C.
Let us determine the optimal dimensions of this insulation based on its thermal conductivity characteristics. There are a large variety of insulation materials on the building materials market. Polystyrene foam, as we already know, has very low thermal conductivity, but this value depends on the brand of material.
The thermal conductivity of polystyrene foam is most noticeable when comparing values with other thermal insulation materials. For example, a sheet of foam plastic 30-40 mm is similar to the volume of mineral wool several times larger, and a sheet thickness of 150 mm replaces 185 mm of polystyrene foam. Of course, there are materials that have a lower coefficient. Penoplex is one of these. 30 mm of penoplex can replace 40 mm of polystyrene foam, under similar conditions.
How to choose the right insulation?
When choosing insulation, you need to pay attention to: affordability, scope of application, expert opinion and technical characteristics, which are the most important criterion.
Basic requirements for thermal insulation materials:
Thermal conductivity refers to the ability of a material to transfer heat. This property is characterized by the coefficient of thermal conductivity, on the basis of which the required thickness of the insulation is taken. Thermal insulation material with low thermal conductivity is the best choice.
Also, thermal conductivity is closely related to the concepts of density and thickness of insulation, so when choosing, you need to pay attention to these factors. The thermal conductivity of the same material can vary depending on density.
Density insulation material. Based on density, materials are divided into: extra light, light, medium, dense (hard). Lightweight materials include porous materials suitable for insulating walls, partitions, and ceilings. Thick insulation materials are better suited for insulating the outside.
The lower the density of the insulation, the lower the weight, and the higher the thermal conductivity. This is an indicator of the quality of insulation. And the low weight makes installation and installation easy. In the course of experimental studies, it was found that insulation with a density of 8 to 35 kg/m³ best retains heat and is suitable for insulating vertical structures indoors.
How does thermal conductivity depend on thickness ? There is a misconception that thick insulation will better retain heat indoors. This leads to unnecessary expenses. Too much insulation thickness can lead to disruption of natural ventilation and the room will be too stuffy.
And insufficient thickness of the insulation leads to the fact that the cold will penetrate through the thickness of the wall and condensation will form on the wall plane, the wall will inevitably become damp, and mold and mildew will appear.
If the calculation is ignored, a number of problems may arise, the solution of which will require large additional costs!
Installation technology of polystyrene insulation boards
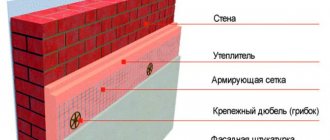
Insulation of external, internal walls and other structures using extruded polystyrene is carried out in several stages. Let's look at each of them:
- The preparatory stage consists of preparing the walls for insulation, cleaning them from dirt, dust, old finishing materials, and paint coatings. In case of large unevenness, it is recommended to level the surface using a plaster mixture (and other methods depending on the design) and treat it with an antifungal compound.
- Fixation using special adhesive facade compounds . The adhesive is applied directly to the insulating board using a comb.
- Mechanical fastening is done using dowels.
- Installation of facade mesh . For better adhesion of the glue to the insulation, you can create roughness on the surface of the slabs. The first plaster layer of façade adhesive is used to fix the reinforcing polymer mesh. Next, a second layer of plaster is applied, after which has dried, the walls are covered with decorative plaster (optional) and painted.
- Instead of plaster, it is possible to decorate the walls with siding, wood, as well as the use of ventilated facades.
EPS installation technology
Thermal insulation of roofs is carried out either at the construction stage or during the reconstruction process, for example, when converting a cold attic into a living space. In this case, the insulation is laid on the base in several layers (the joints of the top layer should not coincide with the joints of the bottom). Next, a vapor-permeable membrane is spread over the penoplex. The resulting cake is secured with longitudinal slats with a thickness of at least 40 mm to ensure ventilation between the insulation and the roofing material.
Advantages and disadvantages
Visually, both insulation materials appear identical. The materials are made from expanded polystyrene foam, but using different technologies. Changing the production method dramatically affects the characteristics of the resulting raw materials.
Styrofoam
The material is obtained by the action of steam on polystyrene granules. Due to the moderate temperature, the size of the components increases 50 times, they stick together, but do not melt. Microscopic gaps remain between the elements. The plastic balls are empty inside, so the raw material is light and airy.
Foam material Source e-pard.com
When buying polystyrene foam or penoplex, the user is looking for practical insulation. The option based on foam spheres is used in conditions of high humidity. The building material can be installed without vapor barrier. Due to the gaps in the structure, the raw materials provide good air exchange, and mold and fungi do not form on the surface.
Due to its low weight, insulation is used in frame structures. The building material has a low thermal conductivity coefficient and a long service life (20-30 years). Raw materials are produced in the form of flat blocks (sheets), which are easy to give the desired shape. When installed correctly, the parts do not change the geometry. Another advantage is the low price and soundproofing properties.
High flammability is the main disadvantage of the building material. The foam supports smoldering, causing the flame to spread to other components and start a fire. Under the influence of temperature, toxic substances that are dangerous to living organisms are released into the air.
Pros and cons of raw materials for insulation Source kaminguru.com
Production of expanded polystyrene
The French were the first to start producing it. The industrial production of expanded polystyrene was mastered in the late 30s of the twentieth century, only 10 years after the first production. In the early 60s of the last century it began to be used in construction
Possessing a whole range of qualities useful for construction, extruded polystyrene foam has attracted the attention of manufacturers of the Penoplex material
Penoplex acquires its properties during the production process. When receiving EPS, polystyrene foam is converted into a liquid state under the influence of heat and extruded using screw machines into a mold. Under the influence of temperature, the gas in the granules expands many times and the granules sinter together, filling the entire provided volume. Then the mold and material are cooled, the mold is halved and the resulting product is ready for packaging.
Table of thermal conductivity of materials
This factor is significant, especially in the case of insulating a residential building, since many materials emit formaldehyde, which affects the growth of cancerous tumors. Therefore, it is necessary to make a choice towards non-toxic and biologically neutral materials. From an environmental point of view, stone wool is considered the best thermal insulation material.
The material must be non-flammable and safe. Any material can burn, the difference is at what temperature it ignites. It is important that the insulation is self-extinguishing.
Those materials that are waterproof have an advantage, since moisture absorption leads to the fact that the effectiveness of the material becomes low and the useful characteristics of the insulation after a year of use are reduced by 50% or more.
On average, the service life of insulating materials ranges from 5 to 10-15 years. Thermal insulation materials containing cotton wool significantly reduce their effectiveness in the first years of service. But polyurethane foam has a service life of over 50 years .
Mineral wool
Mineral wool is a material based on basalt fiber.
Mineral wool cannot be used everywhere, as it has a lower temperature limit. For example, this insulation cannot be used in a refrigerator.
Under the influence of low temperatures, mineral wool becomes brittle and deformed, which is unacceptable for insulation. Here, as a comparison of thermal conductivity insulation shows, the advantage is on the side of polystyrene foam, which has no lower temperature limit.
As for the upper temperature limit, it all depends on the mechanical loads during exposure to high temperatures and the duration of this exposure. If you are interested in the thermal conductivity of insulation, the table that is on our website will help in obtaining information about this. In particular, the thermal conductivity coefficient of mineral wool is given there.
Mineral wool insulation is also hygroscopic, which is why it is necessary to build ventilated walls and roofing. This in some cases leads to a large expenditure of money.
Mineral wool insulation is 1.5-3 times heavier than its polystyrene foam counterpart. Hence the higher cost of its transportation. Another disadvantage is that such insulation can only be used when the foundation of the structure that is insulated with its help is strong enough. Of course, it is more difficult to carry out loading and unloading and construction and installation work using a large mass of insulation.
Advantages and disadvantages of insulation
Types of polyurethane foam Advantages: seamless foam installation, durability, better heat and water insulation.
Disadvantages: high cost of material, instability to UV radiation.
Advantages: low thermal conductivity, low cost, ease of installation, water resistance.
Disadvantages: fragility, easy flammability, condensation.
Disadvantages: much more expensive than polystyrene foam, susceptibility to organic solvents, condensation formation.
Advantages: resistance to the formation of fungi, sound insulation, mechanical strength, fire resistance, non-flammability.
Disadvantages: higher cost compared to analogues.
Advantages: sound insulation, environmental friendliness, moisture resistance, affordable cost.
Disadvantages: thermal conductivity increases during operation, the need for special equipment for installation, and the possibility of shrinkage.
Advantages: low thermal conductivity, low vapor permeability, high noise insulation, ease of cutting and installation, environmental friendliness, flexibility, light weight.
Disadvantages: low strength, need for a ventilation gap.
Advantages: environmental friendliness, high ability to reflect heat, high noise insulation, moisture resistance, non-flammability, ease of transportation and installation, reflection of radiation exposure.
Disadvantages: low rigidity, difficulty in fastening the material; penofol alone is not enough as thermal insulation.
Physics of heat transfer
The phenomenon of heat exchange as a method of energy transfer can only occur in the presence of a temperature difference. There are three types of heat exchange in nature:
- convection;
- radiation;
- thermal conductivity.
Convection occurs due to the movement of warm and cold currents in liquid and gaseous media. For example, room air, heated by contact with a hot radiator, due to expansion, becomes lighter and rises, giving way to cold air. This process will continue continuously as long as there is a temperature difference in the room. The observed column of smoke from a chimney is a good illustration of convective heat transfer.
Radiation is a method of propagating thermal energy in the form of electromagnetic waves. All bodies around us are sources of radiation, the degree and intensity of which depends on their temperature. Some of the radiation from bodies with high temperatures can be seen with the naked eye; some bodies emit heat so weakly that it can only be detected using a thermal imager.
Thermal conduction occurs due to the transfer of energy between adjacent solid particles. Heating or cooling one area of a solid body will cause heat distribution within the body until the temperature in it equalizes. A wooden tea spoon and a metal spoon immersed in boiling water will not heat up equally. This happens because different materials conduct heat differently. Some are intense, and some are so bad that they can serve as thermal barriers.
Special properties of extruded polystyrene foam "Penoplex"
Penoplex acquires unique performance qualities as a result of the peculiarities of its manufacture. At the beginning of the production process, a homogeneous liquid melt of polystyrene granules is obtained by heating. Then a foaming agent, which is carbon dioxide, is introduced into it under high pressure. It is evenly distributed throughout the entire volume of the melt.
At the final stage, foamed polystyrene undergoes a process of extrusion or extrusion through calibrated holes. This achieves special performance properties of extruded polystyrene foam that are not available to other insulation materials.
When the finished substance cools, carbon dioxide is replaced by air from the environment, and completely closed cells with a diameter of about eight hundredths of a millimeter are formed. As a result of the described transformations of the material, the technical characteristics of penoplex become unique. The most important characteristic of thermal insulation materials is thermal conductivity, and penoplex has one of the best parameters.
Penoplex production line
Quite low thermal conductivity coefficient
The low thermal conductivity coefficient of penoplex, amounting to 0.03 W*m*0C, is explained by its cellular structure. The parameter practically does not change over time, its fluctuations are extremely insignificant and range from one to three hundredths of the original value. In terms of this performance parameter, penoplex is superior to polystyrene foam and other heat insulators, for example, mineral wool. The thermal conductivity of penoplex in comparison with them is one of the lowest.
Almost does not absorb water
The hygroscopicity of the product is amazing: it practically does not absorb water. A slab completely placed in water absorbs moisture to only six-tenths of a percent of its volume over the course of a month. All of it is absorbed in the first ten days, then the process stops completely. Moisture penetrates only into the top layer of the extruded foam board.
"Penoplex" does not favor water
Almost no steam escapes
A sheet with a thickness of 20 mm practically does not allow water vapor to pass through, especially penoplex with a thickness of 50 mm or 100 mm. When finishing surfaces with penoplex, no additional vapor barrier is required. Vapor permeability practically does not differ in its characteristics from roofing felt. In some cases, for example, when finishing walls from the inside, this performance property is rather a disadvantage, since it does not allow the walls to breathe.
Has high compressive strength
The high compressive strength, ranging from two hundred to seven hundred pascals, depending on the application, is due to the homogeneity of the structure. Evenly distributed tiny cells improve the strength properties of the material. It does not change its size when squeezed. This allows the material to be used for thermal insulation of floors and other surfaces that experience heavy loads.
The Penoplex bulldozer will not crush
Processing and installing insulation is easy and simple
Installing and processing extruded foam is easy and simple. You can cut it using an ordinary sharpened knife. The slabs are lightweight, so working with them does not require significant physical effort. Installation can be carried out in adverse weather conditions: snow or rain.
Chemically - practically passive
Expanded polystyrene, from which penoplex is made, does not react chemically with most substances used in construction work. The following chemically aggressive substances do not have a negative effect on it:
Some organic solvents can soften and disrupt the shape of the insulation. These include: diesel fuel and gasoline, aromatic hydrocarbons (such as benzene and toluene), oil paints and tar, acetone, ethers. It is worth noting the high biological stability of the material: it does not rot or decompose.
Environmentalists have no questions about the material
If you follow technological standards during production, penoplex is an environmentally friendly material, environmentalists have no questions about it. You can work with the insulator without personal protective equipment. However, one must take into account its artificial origin and understand that chemical components can evaporate under the influence of certain factors, for example, during prolonged heating by direct sunlight.
Fire resistance is not ideal at all
Exposure to an open flame causes the polystyrene foam to ignite. The flammability class varies depending on the purpose of use. Impregnation of this material with compositions that prevent fire does not lead to its complete fire safety. When exposed to high temperatures, the material will melt, turning into a fluid mass that emits extremely toxic and caustic smoke.
Visual characteristics of the flammability of insulation materials
The overall result is that it lasts long and reliably
The service life of insulation is determined by the number of cycles of negative and positive temperatures that the material can withstand without destruction. This parameter shows the ability of the insulator to withstand seasonal changes in external temperatures.
Insulation comparison table
To show clearly and schematically which insulation, figuratively speaking, what it costs, compare, it is easier to depict this in a table. Here are the most popular insulation materials. They are evaluated according to such categories as the above thermal conductivity, hygroscopicity and density.
| Material | Thermal conductivity | Hygroscopicity | Density (kg/m3) |
| Mineral wool | Low | High | 30-125 |
| Penofol | Low | Average | 60-70 |
| Expanded polystyrene | Very low | Average | 30-40 |
| Expanded clay | High | Low | 500 |
| Plastiform | Low | Very low | 50-60 |
| Styrofoam | Very low | Average | 35-50 |
| Penoplex | Low | Low | 25-32 |
| Cellular concrete | High | High | 400-800 |
| Basalt fiber | Low | High | 130 |
Foam plastic can be considered a kind of leader in the ranking of insulation materials. Availability and quite inexpensive price will also be competitive here. But it would be incorrect to advise one thing without knowing the situation, the area of insulation, financial capabilities, amount of work, etc.
How many bricks does Penoplex replace?
Tightening requirements for heat and energy conservation of building structures requires at least a twofold increase in the thickness of walls and ceilings. For brick and concrete walls this figure is 90 and 110 mm, respectively. The problem is solved by using perfect facade and foundation thermal insulation. So how much brick does Penoplex replace, and why is this material considered optimal for insulating almost any building structure?
The Penoplex price list currently in effect in our company offers several types of insulation made from extruded polystyrene foam, the thermal conductivity coefficient of which will pleasantly surprise you.
The material is difficult to counterfeit, so the risk of purchasing a low-quality counterfeit is reduced to zero.
What properties of Penoplex determine the high level of consumer demand?
When choosing a material, its unique low thermal conductivity, light weight, simple installation and long service life are taken into account.
The disadvantages of Penoplex Facade, which you can buy from our company at any time of the year - zero vapor permeability and fairly low heat resistance, are partially or fully compensated by the use of façade systems with slot ventilation and the installation of heat-resistant protective and decorative coatings.
As for the insulation of underground structures, including foundation ones, in this case moisture- and frost-resistant polystyrene foam does not have a worthy alternative.
The strength of the foundation lining is sufficient to protect the waterproofing from damage by seasonal movements of heaving soils. The range of polystyrene foam insulation includes panels of different sizes: from 30 to 100 mm thick. In most central regions, panels with a thickness of 50-60 mm are in high demand. You can buy Penoplex 50 mm in Moscow with significant discounts at promotional and seasonal sales of building materials.
How much brickwork does Penoplex replace?
For those who plan to order Penoplex, the ratio of thermal insulation material to brick plays an important role. We will tell you about the most popular thickness of thermal insulation boards and their correspondence to the thickness of the brickwork.
Now that you have found out what wall thickness Penoplex replaces, there is no reason to put off the purchase of thermal insulation material - call us and order insulation at a favorable price today!
Expanded polystyrene insulation in country and cottage-type houses
Many developers use the material for external insulation of facades and ceiling structures of country houses, which are being converted for year-round living. The main range of applications for polystyrene foam insulation is finishing foundations, blind areas, and insulating cement screeds under floor tiles.
Unlike mineral wool, expanded polystyrene does not require film or mastic waterproofing, so it can be mounted directly on a flat ground surface.
The more than moderate cost of polystyrene foam materials is complemented by the possibility of do-it-yourself installation, which allows you to reduce the cost of thermal insulation work by 35-40%.
Buy high-quality Penoplex insulation from our company right now at a competitive price!
The entry was published in the General information section. Bookmark the permalink. (0 ratings, average: 0.00 out of 5) In order to rate a post, you must be a registered user of the site.
Price
The prices in the table are valid in spring 2022:
| Model | Price in rubles |
| Foundation (50 mm thick, 8 pieces per pack) | 1400 |
| Roof (80 mm, 5 pcs.) | 1420 |
| Facade, (50 mm, 8 pcs.) | 1350 |
| Comfort, (40 mm, 10 pcs.) | 1200 |
| Wall, (50 mm, 8 pcs.) | 1350 |
| Base, (50 mm, 8 pcs.) | 1655 |
That, in fact, is all I wanted to tell you about penoplex.
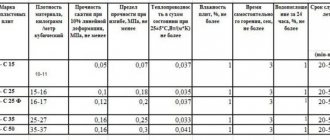
Technical characteristics of various types of material
Foam board is widely used for thermal insulation of building structure elements. As a result, depending on the purpose of use, the technical characteristics of individual types of material differ. Slabs are produced in thicknesses of 20, 30, 50 and 100 mm, of varying strength and flammability. For example, Penoplex 31 has low compressive strength, so it is used mainly for insulating pipelines and containers, and there are materials that are used for insulating airfield runways.
"Penoplex Wall" - for wall insulation
Penoplex Wall is used to insulate the walls of houses. The name appeared not so long ago; previously this material was labeled as Penoplex 31 with fire retardants. Its use for thermal insulation of plinths, building facades, internal and external walls of houses gives good results. At the same time, the walls are sheathed from the inside only if for some reason it is impossible to lay insulation on the outside. Summary of material characteristics are given in the table below.
Domestic analogues of the material
Russian manufacturers have also launched the production of extruded polystyrene foam.
There are two analogues on the market: Technoplex and Polyspen. Each brand has its own characteristics.
Technoplex
Strength and thermal conductivity indicators are the distinctive features of Technoplex slabs. The manufacturer managed to achieve outstanding technical performance through the use of nanotechnology in the manufacture of insulation. The method involves adding graphite particles to help increase the density of the material. The heat insulator is used in private construction, as well as when installing a heated floor system. Unlike penoplex, technoplex is not orange, but light silver. The insulation produced varies in thickness. The plates are equipped with a special edge that simplifies installation. After fastening, finishing should be done as quickly as possible to protect the heat insulator from atmospheric influences.
Polyspen
Extruded polystyrene foam from Polyspen LLC is manufactured in three types, which differ in technical characteristics and scope of application:
- Polyspan Standard. They are used for foundation insulation, as well as for floor insulation.
- Polyspen 35 is indispensable for insulating building envelopes.
- Polyfoam 45 with the greatest strength is used in road construction, since it can even withstand the weight of an airplane. It is recommended to use it for thermal insulation of structures subject to heavy loads.
Polyfoam slabs of different sizes and thicknesses are available on the market; therefore, the density of the material also differs.
Styrex or penoplex?
Stirex is an extrusive polystyrene foam, like penoplex. At its core, the applicability of Styrex is justified where the applicability of penoplex is, that is, there are no decisive differences. Preference may be given to one material only if it is convenient to cut slabs of a given size, to reduce waste, and in case of increased strength requirements, since Styrex has better bending strength.
Physical properties of Styrex:
At large deltas of external and internal temperatures, the slightly lower thermal conductivity of Styrex makes this material more advantageous, however, with an average difference of 0.003 W/m*K this will be barely noticeable. The production of insulation under the Stirex brand is located in Ukraine.
Density and its influence on material properties
The density indicator determines the ratio of the mass of a material to its volume. A high coefficient means a significant load on the base; this fact is taken into account when choosing insulation. There are dense materials that are inferior in insulating characteristics to looser products. For example, a wooden beam with indicators of 510 kg/m3 has a thermal conductivity of 0.15 W/m*K, and mineral wool of 50 kg/m3 has a thermal conductivity of 0.35 W/m*K.
Modern heat insulators are classified according to density level into 4 groups:
- very light - polystyrene foam with a porous structure and gas-filled cells;
- light - mineral wool products;
- medium - foam glass;
- dense - rigid slabs made of basalt fiber.
Lightweight wall insulation does not withstand mechanical loads well, so it needs to create a protective layer. The weak bond between molecules cannot withstand external influences, and the material is destroyed. When installing mineral wool, polystyrene foam, extruded polystyrene foam, waterproofing and wind protection are installed, cladding is used or a layer of plaster is applied.
Dimensions of material packages with a thickness of 20, 30, 50 and 100 mm
Manufacturers of these products produce insulation in the form of slabs measuring 600*1200 or 600*2400 mm. Sometimes the width can be 580 mm. The sheets are packaged, the number of plates in it varies and depends on the thickness of the extruded polystyrene foam. Depending on the purpose of use, the thickness of polystyrene foam may vary. One package of material with a thickness of 20 mm contains 20 slabs, 30 mm - 14 pcs., 50 mm - 8 pcs., 100 mm - 4 pcs. In practice, it is useful to know the amount of material per package by area, which is presented in the table below.
In conclusion, we note that penoplex is also produced in the form of substrates for various types of coatings, such as linoleum, laminate and parquet. Decorative interior elements, usually made of plaster, can also be made of expanded polystyrene, and they will hardly differ in appearance. The following video will complement your understanding of the properties of the material.
What is penoplex insulation, what is its thermal conductivity and what properties does it have in general? I often have to work with this material, so I am ready to answer the questions posed. In addition, I will give you the technical characteristics of this insulation, and tell you in what cases it makes sense to use it.
In the photo, penoplex is a universal and effective polymer insulation from a domestic manufacturer
Low vapor permeability - good or evil?
As you know, the same property of a material can be considered a plus in one situation and a minus in another. This is exactly the case with the low vapor conductivity that extruded polystyrene foam is characterized by. Moreover, it does not conduct steam in any direction. Moisture does not penetrate from one side or the other. This distinguishes it from vapor barrier membranes, which may have one-way conductivity.
It is ideal on flat roofs
Where is vapor non-conductivity needed?
If installed correctly (without gaps and cracks) with joints taped, EPPS does not require the use of vapor barrier membranes. It hardly lets through steam. Neither in liquid nor in gaseous state. So the use of membranes and waterproofing is unnecessary. When using floors in a cake, this is excellent, because moisture usually comes from the ground. When using polystyrene foam, it does not penetrate either by capillary action or in the form of steam. In this case, this is definitely a plus.
Excellent for laying under screed
These properties are also a plus when using extruded polystyrene foam in blind areas, under paths, etc. In addition to protecting against freezing, it does not get wet. This allows, with a competent approach, to get rid of frost heaving and make, for example, not a deep strip foundation, but a shallow strip or Swedish slab.
The use of EPS in the roofing pie of a flat roof is also optimal - leaks are minimized, and almost no heat is lost. When using on pitched roofs, it’s already worth thinking about. The fact that Penoplex Roofing does not allow moisture into the attic space is good. But it will be possible to remove excess moisture from the attic only with the help of very good ventilation, which includes not only dormer windows. Additional elements will be needed on the ridge, in the roof plane. In general, given the cost of Penoplex, this is not always reasonable.
How to make the necessary calculations?
The value of R established by SNiP may vary depending on the climate of the region. For Moscow and the Moscow region, the walls of residential buildings must have a heat transfer resistance of at least 3.28 m2°C/W. Let's take this indicator as a standard and calculate how many bricks and, accordingly, Penoplex slabs are needed to fit into the frame.
The calculation formula looks like this:
δ = Rx*λ , where:
δ - wall thickness, m;
λ is the thermal conductivity of the wall material, W/m2°C.
R - heat transfer resistance, m2°C/W.
For traditional brickwork in the Moscow region, according to the formula, the parameter will be:
δ= 3.28x0.7 = 2.296 m.
The same wall, but made of Penoplex with a density of 30 kg/m3, will be thick: δ=3.28x0.037=0.12136 m, or 12 cm.
Now let’s calculate the difference: 2.296/0.12136=19 . It is exactly how many times thicker the brickwork must be than the Penoplex layer in order to meet one thermal insulation indicator.
Eps insulation
- low water absorption, almost equal to zero;
- high strength;
- not subject to rotting;
- low thermal conductivity;
- high frost resistance;
- non-toxic to humans;
- easy to install;
- durability;
- light weight;
- environmental friendliness.
This is interesting: depending on the composition and manufacturer, the insulation can be white, gray, blue, orange and even black.
The disadvantages of polystyrene foam insulation include:
strong flammability and intolerance to direct sunlight
This is important to know, because storing polystyrene foam in the sun can completely ruin the material, and this will be unpleasant; Although manufacturers claim that polystyrene foam is not chewed by mice, consumer reviews show the opposite; And of course the price, and it is quite high.. But what is the difference between Technoplex and Penoplex? What's better?
But what is the difference between Technoplex and Penoplex? What's better?
What is penoplex
Characteristics
Let's compare the characteristics of penoplex and expanded polystyrene:
| Options | Penoplex | Expanded polystyrene |
| Thermal conductivity coefficient, W/mºK | 0,03 | 0,036-0,050 |
| Water absorption per day, % of volume | 0,2 | 2 |
| Density, kg/m3 | 28-45 | 15-35 |
| Compressive strength, MPa (10% deformation) | 0,25-0,5 | 0,05-0,2 |
In terms of thermal conductivity and strength, extruded polystyrene foam looks advantageous not only in comparison with polystyrene foam, but also with many other materials, such as mineral wool.
Comparison of thermal conductivity of extruded foam with other materials
As you can see, the technical characteristics of penoplex are higher.
General information
First of all, let's figure out what penoplex is. So, this material is extruded (extruded) polystyrene foam.
It must be said that in our country it is customary to call any extruded polystyrene foam foam. In fact, “Penoplex” is the name of the company that produces this type of insulation in Russia and other CIS countries. Therefore, further we will talk about extruded polystyrene foam from this company.
Let me remind you that extruded polystyrene foam is a polymer insulation that was invented in the middle of the last century. Essentially, this is the same polystyrene foam (foam), but manufactured using a special technology, as a result of which it acquires special qualities. In particular, the following differences from polystyrene foam can be distinguished:
Structure . If polystyrene foam has a granular structure, then penoplex is a more homogeneous cellular material;
Example of heat loss calculation
If we take, for example, a wall made of a material with a thermal conductivity coefficient of 1, then if the temperature difference on the two sides of this wall is 1°, the heat loss will be 1 W. If the wall thickness is not 1 meter, but 10 cm, then the losses will already be 10 W. If the temperature difference is 10°, then the heat loss will also be 10 W.
Let us now consider, using a specific example, the calculation of heat loss of an entire building. Let’s take its height to be 6 meters (8 with the ridge), width – 10 meters, and length – 15 meters. To simplify the calculations, we take 10 windows with an area of 1 m2. We will assume the indoor temperature to be 25°C, and outdoor temperature -15°C. We calculate the area of all surfaces through which heat loss occurs:
- Windows – 10 m2.
- Floor – 150 m2.
- Walls – 300 m2.
- Roof (with slopes along the long side) – 160 m2.
The formula for thermal conductivity of building materials allows you to calculate coefficients for all parts of the building. But it’s easier to use ready-made data from the directory. There is a table of thermal conductivity of building materials. Let's consider each element separately and determine its thermal resistance. It is calculated by the formula R = d/λ, where d is the thickness of the material, and λ is the coefficient of its thermal conductivity.
Floor – 10 cm of concrete (R=0.058 (m2*°C)/W) and 10 cm of mineral wool (R=2.8 (m2*°C)/W). Now we add these two indicators. Thus, the thermal resistance of the floor is 2.858 (m2*°C)/W.
Walls, windows and roofs are considered similarly. Material – cellular concrete (aerated concrete), thickness 30 cm. In this case, R=3.75 (m2*°C)/W. Thermal resistance of a plastic window is 0.4 (m2*°C)/W.
We will consider the roof to be made of mineral wool 10 cm thick and corrugated sheets. Since metal has a high coefficient of thermal conductivity, we do not take the profiled sheet into account. Then R of the roof will be 2.8 (m2*°C)/W.
The following formula allows you to find out the loss of thermal energy.
Q = S * T / R, where S is the surface area, T is the temperature difference between outside and inside (40°C). Let's calculate the heat loss for each element:
- For the roof: Q = 160*40/2.8=2.3 kW.
- For walls: Q = 300*40/3.75=3.2 kW.
- For windows: Q = 10*40/0.4=1 kW.
- For the floor: Q = 150*40/2.858=2.1 kW.
Next, all these indicators are summarized. Thus, for this cottage the heat loss will be 8.6 kW. And to maintain the optimal temperature, you will need boiler equipment with a power of at least 10 kW.
Technoplex or penoplex, which is better and what are the differences?
The presented types of insulation are made from polystyrene. The production technology for these two types of products is the same. It is based on polystyrene foaming and subsequent extrusion. The result is a material whose volume consists of isolated cells filled with air. Their size is very small and can fluctuate around 0.1mm.
Both insulation materials have approximately the same volume of static air in the cells, which indicates approximate thermal conductivity values. The extrusive method of producing technoplex and penoplex allows one to obtain higher strength characteristics than that of expanded polystyrene produced by the non-press method.
Physical indicators of the technoplex:
Physical characteristics of penoplex:
Analysis of the indicators shows approximately the same properties of the materials. The choice of technoplex can be justified if there is a risk of water ingress, since its water absorption is slightly lower. At the same time, penoplex manufacturers indicate an increased value of bending strength. When used in these insulation materials under certain conditions, their difference will be leveled out by tolerances for these parameters, due to permissible differences in the number of air cells in a given volume.
Differences in materials based on the size of the products produced can be beneficial if cutting slabs from a particular manufacturer is beneficial in terms of the minimum amount of waste, based on the geometric features of a particular building.
Warm floor - what is it?
The warm floor consists of mats and a heating system.
The first heated floor surfaces were used by the ancient Romans to heat baths. Hot air passed through special channels installed under the floor. The principle of modern heating designs has remained the same, but during this time the heating system has been significantly improved. The design is used for installation in premises of any purpose; it is considered an excellent alternative to conventional central heating. Efficiency is achieved due to increased heat transfer. Installation of the structure does not take much time; the procedure can be carried out in any room.
How not to lose money
If designers and builders do not take into account the physical and chemical characteristics of penoplex, its strength and thermal characteristics deteriorate long before the end of its service life, which leads to a decrease in the thermal efficiency of the house. Some of the most common errors include the following solutions:
Use of material with a density lower than technologically justified. Penoplex, like any polymer, is oxidized by atmospheric oxygen. The rate of oxidation (change in chemical structure and deterioration in performance properties) depends on the density of the material. The use of slabs with a lower density (an understandable desire to save money) deteriorates the thermal protection of the structure 2-3 times faster, and this is noticeable already in the first 7-10 years of operation.
Internal insulationSource chebaki.ru
- Use of incompatible materials. Plates made of extruded polystyrene foam will deteriorate at an accelerated rate if substances that are dangerous to the structure of the penoplex (for example, oil-based paints containing volatile hydrocarbons) are used during construction.
- Ignorance of labeling features. An inexperienced person, seeing the words “Mark 25” on the packaging, makes the logical conclusion, in his opinion, that inside there are slabs with a density of 25 kg/m3. But in technical specifications this is the designation for material with a density from 15.1 to 25.0 kg/m3. Some manufacturers, caring for maximum profits, supply penoplex of the lowest density under this brand (15.1 kg/m3, the density of packaging plastic). The result of the substitution soon appears on the “insulated” façade – with damp spots and mold.
- Incorrectly carried out insulation. Improper insulation leaves an air gap between the wall and the slab material. The structure becomes inhomogeneous, the dew point shifts into the gap. Condensation is inevitably absorbed into a denser material (wall), and thermal efficiency drops, sometimes significantly.
The insulation is complete, the finishing cladding is aheadSource doma-otido.ru
Using thermal conductivity values in practice
Materials used in construction can be structural and thermal insulating.
There are a huge number of materials with thermal insulating properties
The highest thermal conductivity value is for structural materials that are used in the construction of floors, walls and ceilings. If you do not use raw materials with heat-insulating properties, then to retain heat you will need to install a thick layer of insulation for the construction of walls.
Often simpler materials are used to insulate buildings
Therefore, when constructing a building, it is worth using additional materials. In this case, the thermal conductivity of building materials is important; the table shows all the values.
In some cases, insulation from the outside is considered more effective.
Thermal conductivity concept and theory
Thermal conduction is the process of moving thermal energy from heated parts to cold parts. Metabolic processes occur until the temperature reaches complete equilibrium.
A comfortable microclimate in the house depends on high-quality thermal insulation of all surfaces
The heat transfer process is characterized by a period of time during which temperature values are equalized. The more time passes, the lower the thermal conductivity of building materials, the properties of which are shown in the table. To determine this indicator, a concept called thermal conductivity coefficient is used. It determines how much thermal energy passes through a unit area of a certain surface. The higher this indicator, the faster the building will cool. A thermal conductivity table is needed when designing the protection of a building from heat loss. This can reduce the operating budget.
Heat losses in different areas of the building will differ
Main characteristics of insulation
Let us first provide the characteristics of the most popular thermal insulation materials, which you should first pay attention to when choosing. Comparison of insulation by thermal conductivity should be made only on the basis of the purpose of the materials and room conditions (humidity, presence of open fire, etc.)
We have further arranged in order of importance the main characteristics of insulation.
Comparison of building materials
Thermal conductivity. The lower this indicator, the less thermal insulation layer is required, which means that insulation costs will also be reduced.
Moisture permeability. The lower permeability of the material to moisture vapor reduces the negative impact on the insulation during operation.
Fire safety. Thermal insulation should not burn or emit toxic gases, especially when insulating a boiler room or chimney.
Durability. The longer the service life, the cheaper it will cost you during operation, since it will not require frequent replacement.
Environmentally friendly. The material must be safe for humans and the environment.
Thermal conductivity of polystyrene foam exact numbers
The ability to conduct heat is influenced by many factors, in particular:
- Layer thickness. Sometimes, in order to achieve high-quality energy savings, it is necessary to use a large amount of insulation. For example, the thermal conductivity of 5 cm foam plastic boards will be lower than 1 cm with the same density.
- Structure. The porous structure leads to increased insulating properties, because the cells contain air that perfectly retains heat.
- Humidity. During storage, slabs must be protected from moisture. This is due to the fact that liquid does not have a very favorable effect on the characteristics of thermal insulation foams: the more it accumulates, the worse it is.
- Average layer temperature. Its increase leads to a deterioration in the efficiency of the insulator.
Types of foam plastic and their indicators
There are a huge number of insulation boards on the construction market. In general, polystyrene foam has low thermal conductivity, but this varies depending on its type. Examples: sheets marked PSB-S 15 have a density of up to 15 kg/m3 and a thickness of 2 cm, while the described indicator is up to 0.037 W/(m*K) at an ambient temperature of 20-30 °C. Its value for sheets 2-50 cm marked PSB-S 35, with a density of no more than 35 kg/m3 and 16-25 kg/m3 marked PSB-S 25 of the same size is 0.033 W/(m*K) and 0.035 W/ (m*K) respectively.
The dependence of the thermal conductivity of foam insulation on its thickness is best seen when comparing it with various materials. Thus, a sheet of 50-60 mm replaces twice the volume of mineral wool, and 100 mm is equivalent to 123 mm of expanded polystyrene foam, which has approximately similar characteristics. Basalt wool also loses greatly. But the thermal conductivity of Penoplex is slightly lower than that of polystyrene foam: in order to obtain normal temperature conditions in the room, you will need 20 and 25 mm, respectively.
How do you know which sheets to buy?
In order to most effectively apply this or that insulation method, it is necessary to select the correct dimensions of the material. Calculations are performed according to the following algorithm:
- Find out the total thermal resistance. This is a constant value that depends on the climate in a particular region. For example, for the southern regions of Russia it is 2.8, and for the central zone - 4.2 kW/m2.
- Calculate the thermal resistance of the wall itself using the formula R = p / k, which can be done knowing its thickness (p) and the coefficient of ability to conduct heat (k).
- Based on constant indicators, find out what resistance value the insulation should have.
- Calculate the required value using the formula p = R * k, where R is the value from the previous step, and k is the calculated thermal conductivity coefficient for the foam.
As an example, it is worth finding out what layer of slabs with a density of 30 kg/m3 is needed for a wall of one brick (about 0.25 m) in one of the southern regions. The total thermal resistance should not be less than 2.8 kW/m2, despite the fact that the coefficient determined using special tables is 0.047 (W/m*k). Now you need to find out other parameters.
Coefficient for sand-lime brick k = 0.7 (W/m*k). You should calculate its thermal resistance:
R = 0.25 / 0.7 = 0.36 (kW/m2).
The same indicator is calculated for insulation:
R = 2.8 – 0.36 = 2.44 (kW/m2).
It remains to find out the thickness of the insulating layer:
p = 2.44 * 0.047 = 0.11 m.
You can also calculate this value for other conditions, for example, for a wall of 0.51 m, 70 mm insulation is suitable. Thus, when selecting the required sizes of polystyrene foam, time and money for laying the wall are saved. So, 10 cm of material with a density of 15-17 kg/m3 replaces the masonry of one brick, and if you take denser sheets, this will allow you to do without two rows of stone. It is traditionally believed that 2 cm of insulation is equivalent to about 50 cm of brick.
Application of Penoplex Comfort
The use of this type of insulation is possible in almost any climate zone. It can be used not only for thermal insulation of floors, but also for insulation of swimming pools, saunas, baths and other rooms with high humidity levels. Installation work on laying sheet material does not present any difficulty; it has clear geometric shapes; for ease of joining, the edges are made in the form of the letter G. Penoplex “Comfort” is successfully used for insulation:
- balconies and floors;
- ground floor;
- building roofs;
- wall structures;
- foundation bases.
Options for using penoplex "Comfort" for roof insulation
The thickness of this type of expanded polystyrene can reach 15 centimeters, this determines the mechanical strength of the coating and significantly increases the service life of the building structure. In direct contact with moisture or soil, Comfort penoplex, due to its antifungal properties, is not subject to rotting and decomposition.
Floor insulation on joists
Insulating the floor on joists begins with inspecting and replacing damaged areas and treating the boards with a special compound that prevents them from rotting. Then all cavities are leveled with putty, the surface is dried and covered with primer. Sheets of insulation, pre-cut to the required sizes, are laid on dry boards with a minimum gap. The joints are taped with tape.
Sheets of material intended for arranging a vapor barrier layer are laid on top with an overlap. Chipboards, plywood or other similar material are attached to the most leveled surface, and parquet, laminate or linoleum is laid on top. This results in several layers:
- beam floors;
- wooden lumber;
- foam sheets;
- vapor barrier layer;
- panel covering;
- material used as flooring.
Floor insulation with laying on the ground
Penoplex "Comfort" is laid on the ground to insulate the floor in building structures, which are supported by a strip or pile type foundation. A layer of crushed stone or gravel is poured onto the leveled soil, and sifted sand is placed on top of it, which is compacted tightly.
Sheets of insulation are laid on the resulting surface with minimal gaps, the joints of which are made using tenons and grooves cut into them. A film is placed on top of the insulation to form a waterproofing layer, a reinforcing mesh is laid, and the surface is covered with cement mortar. After it dries, the floor covering is laid. The following layers are obtained:
- soil surface;
- crushed stone backfill;
- sand cushion;
- insulation;
- film waterproofing;
- mesh reinforcement;
- layer of cement mortar;
- material used as flooring.
Insulation of walls from the inside
Insulating walls from the inside begins with thoroughly cleaning them and applying a layer of soil to their surface. The insulation sheets are strengthened with glue and plastic fasteners. The gaps between the joints are filled with construction foam. If their width exceeds 100 mm, scraps of insulation boards must be inserted into the cavities.
Insulation of the walls, floor and ceiling of the loggia with penoplex
A reinforcing mesh is strengthened on the resulting surface, on top of which a layer of mounting plaster is applied. After it has dried, finishing plaster is applied to the surface and the final covering of the walls with wallpaper or painting is carried out. Thus, the following layers are formed:
- primed surface;
- adhesive layer;
- insulation sheets;
- fiberglass mesh;
- plaster layer;
- putty;
- wall finishing material.
Conclusion
We found out what penoplex is, what properties it has, and in what cases it can be used. Also watch the video in this article. If you have any questions regarding this insulation, you can contact me in the comments.
Thanks to modern technologies, high-quality and affordable home insulation has turned from a dream into a completely solvable task. There are many reviews that it is better to choose polyspen or penoplex (penoplex). We will understand this by evaluating the properties of these materials.
Peculiarities
Expanded polystyrene is a universal heat insulator endowed with unique properties.
Advantages
The positive qualities of the material include the following:
- durability and strength (with high-quality installation it will last at least 50 years, does not crumble, does not rot, does not decompose);
- low thermal conductivity;
- high thermal insulation (a 10 cm thick slab has the same thermal insulation properties as one and a half meter brickwork);
- moisture resistance (the material absorbs no more than 6% of moisture and retains more than 90% of its properties);
- resistance to temperature changes, ultraviolet radiation, chemical and biological influences (mold and mildew do not form on it);
- frost resistance (withstands up to 50 freezing/thawing cycles and does not lose its physical and chemical characteristics);
- environmental friendliness (it is even used for food storage);
- fire safety (modern types of polystyrene do not support the combustion process, as they have been treated with fire retardants);
- simple installation technology (no need to purchase expensive tools, the material is lightweight and easy to cut);
- low cost.
Due to its high moisture resistance, expanded polystyrene does not require additional hydro- and vapor barrier. Unlike its main rival in the field of mineral wool insulation, polystyrene foam does not generate dust during installation, so no protective equipment (respirator, gloves, special clothing) is required to work with it.
Flaws
Expanded polystyrene is spoiled by rodents, they make moves in it. To protect the house from them, even at the cladding stage, poison in the form of grains or special capsules can be laid around the perimeter of the building, between the insulation layer and the cladding material.
This will be enough for a while. And, of course, you definitely need to install a base profile.
Today, customers are offered several brands of expanded polystyrene. They differ in production method and technical characteristics.
Pressed polystyrene
Domestic material, produced under the brands PS-1 or PS-4.
It has a high density (60-600 kg/m3). Its area of application is radio engineering.
Pressless material
PSB, PSB-S – brands of expanded polystyrene from Russian manufacturers. The material has high physical and chemical properties. Its scope of application is facade insulation.
Pressed and non-pressed materials have one common drawback: at low temperatures, when moisture gets between the granules, they will begin to collapse.
Extrusion insulation
This type of expanded polystyrene is most often used for thermal insulation of facades. It is very durable and strong, its service life reaches 80 years.
But unlike pressless material, it has a significant drawback: it contains residual styrene, which is harmful to health.
Domestic brands of extrusion insulation are “Penoplex”, “TechnoNIKOL”.
Indicators for different brands of polystyrene foam
From the given simplified formula we can conclude that the thinner the insulation sheet, the less efficient it is. But in addition to the usual geometric parameters, the density of the foam also affects the final result, albeit slightly - only within 1-5 thousandths. For comparison, let’s take two slabs of similar brand:
- PSB-S 25 conducts 0.039 W/m°C.
- PSB-S 35 at a higher density - 0.037 W/m °C.
But with a change in thickness, the difference becomes much more noticeable. For example, the thinnest sheets of 40 mm with a density of 25 kg/m 3 can have a thermal conductivity of 0.136 W/m°C, while 100 mm of the same polystyrene foam transmits only 0.035 W/m°C.
Comparison with other materials
The average thermal conductivity of PSB lies in the range of 0.037-0.043 W/m·°C, and we will focus on it. Here, foam plastic, in comparison with mineral wool made from basalt fibers, seems to benefit slightly - it has approximately the same indicators. True, with twice the thickness (95-100 mm versus 50 mm for polystyrene). It is also customary to compare the conductivity of insulation with the various building materials necessary for the construction of walls. Although this is not very correct, it is very clear:
1. Red ceramic brick has a heat transfer coefficient of 0.7 W/m °C (16-19 times more than foam). Simply put, to replace 50 mm of insulation you will need masonry about 80-85 cm thick. Silicate insulation will need at least a meter.
2. Solid wood is better in this regard compared to brick - here it is only 0.12 W/m °C, that is, three times higher than that of expanded polystyrene. Depending on the quality of the wood and the method of constructing the walls, the equivalent of a 5 cm thick PSB can be a log house up to 23 cm wide.
It is much more logical to compare styrene not with mineral wool, brick or wood, but to consider closer materials - polystyrene foam and Penoplex. Both of them are classified as foamed polystyrene and are even made from the same granules. It’s just that the difference in the technology of “gluing” them gives unexpected results. The reason is that styrene beads for the production of Penoplex with the introduction of blowing agents are simultaneously processed under pressure and high temperature. As a result, the plastic mass acquires greater homogeneity and strength, and air bubbles are evenly distributed in the body of the slab. Polystyrene foam is simply steamed in a mold like popcorn, so the bonds between the expanded granules are weaker.
As a result, the thermal conductivity of Penoplex, an extruded “relative” of PSB, also improves noticeably. It corresponds to 0.028-0.034 W/m °C, that is, 30 mm is enough to replace 40 mm of foam. However, the complexity of production also increases the cost of XPS, so you should not count on savings. By the way, there is one curious nuance here: usually extruded polystyrene foam loses a little in efficiency as its density increases. But when graphite is added to Penoplex, this dependence practically disappears.
Prices for foam plastic sheets 1000x1000 mm (rubles):
The main types of insulation used to reduce heat loss
To carry out thermal insulation measures of any type, the following types of insulators are used:
- extruded polystyrene foam (XPS), refers to polystyrene derivatives (represented by various manufacturing enterprises, has many brands);
- polystyrene foam, its production also involves the processing of polystyrene, but using a different technology (it has a sufficient number of manufacturers, the breakdown by brand is not clear, it is positioned as “foam plastic”).
- mineral or basalt wool is fundamentally different from polystyrene products and acts as the main competitor of foamed polystyrenes (represented on the insulating goods market by a large number of manufacturers).
The number of manufacturing companies, both domestic and foreign, is measured in dozens. When choosing products, you need to rely on the physical properties of each individual product.