Mineral wool is a high-quality insulating material that can provide an optimal indoor microclimate. This is achieved due to the fact that its fibers allow air to pass through. The density of mineral wool is an important indicator of its warmth and must be selected taking into account the structural features and expected loads.
When choosing mineral wool, you need to consider its density
What is meant by the term “mineral wool density”?
You can determine which insulation has a higher density before purchasing it - material with a higher density is more expensive.
At the same time, you need to understand that, despite the fact that “you can’t spoil porridge with oil,” using cotton wool of maximum density is not always economically feasible. One of the characteristics of this parameter is specific gravity, which follows from the units of measurement of density - kg/m3. In this case, we are not dealing with “net” weight, but with the number of fibers in a volume equal to 1 m3. The number of fibers varies depending on the type of mineral wool and its manufacturing technology.
In accordance with this, the density of various types of mineral wool (glass wool, basalt wool and slag wool) has a fairly wide range - from 30 kg/m2 to 220 kg/m3. This implies a significant difference in its physical and technical qualities. However, there is a general pattern - the higher the density, the greater the mechanical load that mineral wool mats or slabs can withstand.
Therefore, in order to correctly select the optimal insulation option, it is generally necessary to understand what technological characteristics are affected by the density of mineral wool for walls
, ceilings, roofs and facades. So, the following characteristics are directly dependent on density:
- Ability to withstand static and dynamic loads.
- Ability to maintain original shape.
- Compressive resistance force.
At the same time, density does not affect:
- Noise absorption.
- Vapor permeability.
- Thermal insulation qualities.
- Thickness of slabs, mats or rolls.
How to properly use mineral wool depending on its density?
When choosing this insulation, you should strive to choose the optimal density based on your specific climatic conditions and the type of insulation object.
In other words, it is necessary to make a preliminary thermal calculation, however, due to the complexity of the calculation, you can use the empirical method - ask your neighbors, but it is best to consult the seller of a local building materials store.
- Material with a density of up to 35 kg/m3 is recommended for use only on unloaded horizontal surfaces. As a rule, such insulation is produced and sold in the form of rolls.
- If it is necessary to insulate the internal floor, ceiling and interior partitions, use mineral wool with a density of about 75 kg/m3.
- For thermal insulation of ventilated facades, the wool density must be at least 100 kg/m3. For non-ventilated facades – 125 kg/m3. In both cases, it is implied that finishing will be carried out - in the first option with siding or similar material, in the second - reinforcement and plastering.
- To insulate interfloor ceilings, the density of mineral wool should be 150 kg/m3, and for load-bearing structures it increases to 175 kg/m3.
- Floors under concrete screed, in the event that wool acts as the top layer, are insulated with cotton wool with a density of 200 kg/m3. The material with which the roof or attic is thermally insulated should have the same indicators.
As already mentioned, you must always remember that slabs (mats) with higher density have greater mass
This is important to consider when building the frame in which they will be mounted.
The market offers a wide range of thermal insulation materials, which differ from each other in raw materials for production, production method and purpose. The method of work is determined by such an indicator as the density of the insulation.
The density of insulation is the value that determines the mass of one cubic meter of material. This indicator differs for different thermal insulation materials.
| Name | kg/m³ |
| Cellulose wool | 30-70 |
| Fiberboard | 150-230 |
| Linen mats | 30 |
| Foam glass | 100-150 |
| Cotton wadding | 25-30 |
| Mineral wool | 50-200 |
| Styrofoam | 25-35 |
| Extruded polystyrene foam | 35-40 |
| Polyurethane foam | 30-80 |
| Expanded clay | 450-1200 |
This insulation parameter is determined by the purpose of the thermal insulation.
Choosing foam concrete correctly - selection criteria
2. Price matters too. On average, for the D800 brand it is about $80 per cubic meter. If the material is much cheaper, you should think about it - this may affect the quality.
3. Carefully inspect the blocks - they should not be pure and bright white. Technology will not allow this. Normally, foam concrete should be greyish, slightly lighter or darker, and uneven coloring of the surface is not allowed.
An example of improperly organized storage of foam blocks; they are not covered with anything on top and it is already clear that they have absorbed moisture from the damp earth.
Types of mineral wool
3. Vertically layered.
4. Horizontally layered.
The main component of the material is basalt. It acts as a binder, which can be urea resins, bitumen, phenolic alcohols, clay and starch.
In the process of making mineral wool based on rocks of molten mineral materials, thin fibers of 1–3 microns with a thickness of 50 mm are obtained. To improve strength, molten charge or limestone can be added to the molten basalt fibers. Mineral wool substances repel moisture, thereby protecting the thermal insulation properties.
Which thermal insulators are better?
Based on the above data, the following conclusions can be drawn:
Polyurethanes have the best ratio of density and thermal insulation ability (R > 6), and the range of materials and the method of thermal insulation are not particularly important.
Advantages: ease of application; disadvantage: high cost of the material.- Good strength/thermal conductivity (R > 4.5) are characteristic of expanded polystyrene and polystyrene. They are characterized by reasonable price, low density and availability, but are not always compatible with fiberglass resins and are easily damaged.
- A good option is the use of rolled materials based on basalt and mineral wool: satisfactory thermal insulation (R > 3.5) and ease of installation. The density, however, is often greater than desired, and moisture resistance is worse than all of the above materials.
To compensate for the consequences of installing thermal insulation in various types of roofing, in addition to density, other characteristics should be taken into account:
- Resistant to chemicals that may be contained in sediment.
- Moisture resistance.
- Insensitive to vibrations.
- Fire resistance.
- Strength.
The values of most of the above parameters increase with increasing product density.
weight 1 m2, wall, roof, 150 mm, 100 mm
To quickly and inexpensively carry out construction work, sandwich panels are often used, the weight of 1 m2 of which is lower than the weight of a brick or concrete wall of the same area. Depending on the thermal insulation parameters, the optimal type of panel and its thickness are selected and the tabulated weight value required for calculating the load-bearing structures is found.
Types of Sandwich Panels
All varieties consist of outer and inner layers, between which a heat insulator is laid. The composition of the layers determines the technical characteristics and properties of the building material.
OSB sandwiches
The inside and outside of the structure are covered with oriented strand boards, and the filling is most often polystyrene foam. Ready-made “sandwiches” are 4 times stronger than wooden-frame structures, so they are suitable for capital construction. With a small thickness (from 120 to 150 mm), OSB sandwiches have a thermal conductivity that is 8 times less than a brick or concrete wall. Sandwich panels made from OSB boards have dimensions of 1.25 (2.5) m x 2.5 - 7.3 m, the weight of 1 m2 of puff material ranges from 18 to 20 kg.
Sandwich panels of element-by-element assembly
The design consists of a cassette profile into which any insulation is inserted, covered with a windproof film. Corrugated sheeting and metal siding are most often chosen as cladding. The advantage of this type of sandwich is their maintainability, the possibility of selecting insulation with a lower specific weight - if it is 40 kg/m3 (mineral wool), then the weight of a square meter of a prefabricated structure with a thickness of 200 mm does not exceed 25 kg.
Metal sandwiches
They are faced with a galvanized metal sheet (smooth or profiled) with a thickness of 0.5 mm. A decorative and protective polymer coating is applied on top, and a layer of primer is applied on the inside. Mineral wool, polystyrene foam or polyurethane foam are used as insulation. Multilayer products for walls and roofs are produced; they differ in the type of locking connection and the height of the cladding profile. The applicability of metal sandwiches is the construction of garages, hangars, and outbuildings.
Weight of wall metal sandwich panels
The information given in Table 1 shows how different the weight parameters of structures are, depending on their thickness and the insulation used. Table 1 Dimensional and weight parameters of metal sandwiches for walls
| Options | Meaning of indicators | |||||
| Thickness, mm | 60 | 100 | 120 | 150 | 200 | 250 |
| Weight of 1 m2 with mineral wool, kg | 15,8 | 20,5 | 22,8 | 26,3 | 32,1 | 37,9 |
| Weight 1 m2 with polystyrene foam, kg | 9,6 | 10,2 | 10,5 | 10,9 | 11,7 | 12,5 |
As an example, we find the weight of a 1.2 m x 10 m wall sandwich panel, 150 mm thick, filled with mineral wool. First, calculate the surface area: 1.2 * 10 = 12 m2. The result is multiplied by the weight of a square meter: 12 * 26.3 = 315.6 kg.
Weight of metal roofing sandwich panel
Roof “sandwiches” with anti-corrosion coating and unique locks serve reliably for several decades. Table 2 allows you to compare options with different insulation by weight.
Table 2 Dimensions and weight parameters of metal sandwiches for roofing
| Options | Meaning of indicators | |||||
| Thickness, mm | 60 | 100 | 120 | 150 | 200 | 250 |
| Weight 1 m2 with mineral wool, kg | 15,4 | 19,8 | 22,0 | 25,3 | 30,9 | 38,0 |
| Weight 1 m2 with polystyrene foam, kg | 10 | 10,5 | 11,0 | 11,5 | 12,0 | 12,7 |
| Weight 1 m2 with polyurethane foam, kg | 12,4 | 14,0 | 14,8 | 16,0 | 18,0 | 20,0 |
Calculation of the weight of a roofing sandwich panel 100 mm thick with dimensions 1 m x 2 m with polyurethane foam filling: area = 1 * 2 = 2 m2; weight = 14 * 2 = 28 kg.
Knowing the estimated number of sandwiches for the walls and roof, their total mass is found - the parameters of the floors, foundation and rafter system depend on this. Conclusion: the weight of 1 m2 of sandwich panel is one of its main technical characteristics.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=7IZshy4Uyrs
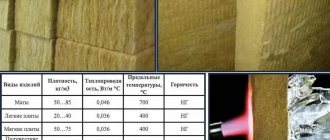
Characteristics table
The thermal conductivity value of a mineral wool board primarily depends on the selected material. The thickness of the material does not matter for the coefficient, but it is directly related to the level of protection of the enclosing structures. Therefore, for floors, partitions and interfloor ceilings, heat loss through which is lower than in other areas, mineral wool slabs up to 50 mm thick are used. The same value is acceptable for internal insulation (but due to space saving). Facades and pitched roofs are insulated with mineral wool with a thickness of 100 to 200 mm.
Types and selection
In general, all insulators can be divided into the following groups:
- dense – mineral wool under high pressure;
- medium - glass wool and polystyrene foam;
- light - mineral wool;
- very light - foam plastic boards.
To determine the type of insulation, you need to consider some factors.
For finishing in a residential building
Thus, for finishing walls and floors in a residential building, it is better to use basalt materials, which are distinguished not only by their optimal density, but also by their environmental friendliness. For basalt fiber, it can be different: for walls with siding cladding, it is better to use a material with a unit mass per unit volume of no less than 40 and no more than 90 kg/m3. This indicator should increase with the growth of the building: the more floors, the greater the rigidity.
Materials of 140-160 kg/m3 are suitable for working with plastered facades. Most often, special elements with high peel strength and vapor permeability are used. When insulation from the outside of the house is impossible, the procedure is carried out from the inside - density also affects here, insulators with a low density are needed. In both cases, mineral or glass fiber is suitable.
For roof and floor finishing
Thus, slabs for roofing insulation should have a low specific gravity. But it depends on the type of roof:
- a pitched roof requires slabs of 25-45 kg/m3;
- for the attic you need materials with a pressure of at least 35 kg/m3;
- a flat roof needs insulators that can withstand good mechanical loads - snow and wind, so basalt wool with 150 kg/m3, polystyrene foam with an indicator of more than 35 kg/m3 are suitable.
Extruded polystyrene foam is used for thermal insulation of the floor. If the insulation is carried out on joists, then mineral wool slabs can be used - rigidity is not particularly important, because the beams will take the pressure. Slabs of 50 kg/m3 are installed in the interior walls.
Penoizol and polyethylene
Penoizol has one significant difference from previous insulators - it is applied in liquid form and has a low density of 10 kg/m3, while its high porosity gives it good insulating properties. Foamed polyethylene can have different specific gravity - it depends on the availability of reinforcement and thickness:
- roll material is needed for floor insulation - 24 kg/m3;
- for frame buildings and insulation of refrigeration units, engineering structures, it is reinforced with aluminum sheets - 50-60 kg/m3.
Thus, foam glass has a thermal conductivity coefficient of 0.1 W and is much stronger than other insulation materials. The density indicator reaches 400 kg/m3 and the material is very stable - suitable for external thermal insulation without requiring a protective layer. Cellular glass has a wide range of materials:
- external insulation - 200-400 kg/m3;
- vertical structures – 200 kg/m3;
- roofs and foundations – 300-400 kg/m3;
- for light and frame structures – 100-200 kg/m3.
Insulation methods
Reducing heat loss depends on the correct selection of material, as well as its location on the building. There are several methods for insulating walls, which differ in their properties, having both advantages and disadvantages.
There are the following methods for wall insulation:
- Wall. It is an ordinary brick partition with a SniPov thickness of 40 cm.
- Multilayer insulation. It consists of wall cladding on both sides. This is done only at the time of construction of the structure, otherwise it will be necessary to dismantle part of the wall.
- External insulation. The most common method is to insulate the outside of the wall, after which a layer of finishing is applied. One of the disadvantages of this method is the need for additional hydro- and vapor barrier.
Mineral wool sizes
Manufacturers present 3 types of mineral wool, each of which has its own type of raw material, namely
3. Basalt mineral wool.
All types are successfully used for hydro and thermal insulation of various residential and industrial buildings. For more comfortable installation, manufacturers produce products of various sizes and shapes.
Mineral wool rolled into rolls is produced in the form of a large piece, pre-cut and completed. The dimensions of the material are indicated on the packaging, since many manufacturers have different sizes. Thickness can vary from 40 to 200 mm, width from 565 to 610 mm, length about 1170 mm. The thickness of rigid slabs for hydro and thermal insulation varies from about 50–170 mm, the width of the product is about 1190 mm, and the length is 1380 mm.
Mineral wool in this format is ideal for thermal insulation of large areas, since the rolls contain a large amount of material. As a rule, the width of the materials varies between 50–200 mm, the length of the sheet is about 7000–14000 mm, and the width is approximately 1200 mm. The material is easy to cut and adjust to the size of the room.
Mineral wool in cylinders
Designed for waterproofing hydraulic lines. The basis of this type of mineral wool includes: foil, fiberglass mesh and basalt. The structure can withstand high temperatures up to 250 C. The width of the product generally varies between 12–324 mm, length about 1200 mm, with a thickness of 20–80 mm. The exact dimensions are indicated on the packaging of the material. Mineral wool in cylinders is intended for thermal insulation of heat exchange systems and heating communications. Diameter, thickness and length are selected in accordance with the size of the pipes
The mass of mineral wool varies depending on the substances filling it
To determine what weight the builder will be dealing with, you should pay attention to the density of the material, which can also be found as the mass of mineral wool per 1 cubic meter. This figure can vary from 35 to 100 kg per 1 cubic meter.
The average weight of insulating boards is 0.6 cm. In the process of performing technical operations, weight does not play a significant role.
Manufacturers' products have different weights, on average this figure varies from 37 to 45 kg with sizes no more than 1.35 kg, and depends on the density of the thermal insulation material. Its weight changes significantly with a combined approach to insulation. In this case, the thickness of the insulation used is decisive.
Stone wool has a fibrous structure, similar in composition to basalt. It is considered a natural material, 80 percent consists of the earth's crust, and the wool itself is made from molten volcanic rocks.
Balzac fiber is produced in factories, but its composition is also similar to the chemical structure of rocks. It also contains sand, soda, limestone, borax and dolomite. When finished, the material has impressive dimensions and is permeated with air through and through. For storage and transportation, mineral wool is compressed to a sixfold state.
Many manufacturers are trying to improve the quality of the product by making changes to the composition and production process. To increase rigidity, the slabs are stitched, impregnated with bitumen and phenols with the addition of asbestos. If the composition contains additional substances, this may change the characteristics of the product. Bitumen prevents damage from insects and fungi, protects the product from moisture and provides additional strength.
The official standard applies to stone wool made from substances of rocks of the gabbro-basalt group, as well as their identical substances, sedimentary rocks, volcanic, metallurgical residues, industrial silicate slags, alloys intended for the production of heat-insulating, sound-proofing and sound-absorbing materials.
Stone wool can be used as a heat-insulating substance in the construction industry and industrial production for finishing surfaces with a temperature range from -180 C to +700 C.
Thermal insulation technology for pitched roofs
Thermal insulation of a pitched roof
So, how to properly insulate a pitched roof:
As you can see, insulating a pitched roof is not the most difficult process, so it’s possible to do it with your own hands even for a person far from the construction industry.
Construction of a pitched roof with insulation
Insulation of a gable roof
There are two possible situations here:
- The roof is already covered with roofing material.
- Not covered yet.
Let's start with the second case, because it is simpler.
Laying waterproofing on rafters
If polyurethane foam is chosen as the thermal insulation material, then all work from the inside of the attic is reduced to applying foam to the pitched plane of the roof structure. The main task is the uniformity of the applied material.
I would like to draw your attention to the fact that ecowool is installed using wet and dry technology. The first is when water is added to the material
In the case of insulation of pitched roofs, dry technology is used.
Filling ecowool into the space between two films
Advantages of minislabs over other insulation materials
Let's start with the most important parameter for mineral insulation - thermal insulation properties. According to verified technical data, the ministove retains heat no worse than natural sheep wool, for which it is valued. The secret of any cotton wool is that small air bubbles get stuck between its small fibers, and air, as you know, is the worst conductor of heat
Thanks to this structure, cotton wool easily stops the heat flow and prevents it from leaving the living room or attic. This property is determined by the thermal conductivity coefficient λd, and the smaller it is, the better the material retains heat. Thus, high-quality mineral wool has a thermal conductivity coefficient of no more than 0.032 W/(m•K).
Mineral boards have excellent thermal insulation and acoustic properties, as well as high fire resistance. When heated, it does not emit toxic or harmful substances, and therefore is excellent as protection or fire insulation.
Indeed, according to the European seven-point scale, mineral wool has fire resistance A1 and A2, this is the same NG parameter in domestic standards, which means “non-flammable”
During a fire, mineral fibers emit almost no smoke, which is also important, and do not crack or melt:
In terms of fire safety, mineral wool varies depending on the raw materials used:
And now – about the shortcomings. Mineral wool is a vapor-permeable material, and water vapor passes between its fibers without being absorbed into them. Therefore, the main thing that needs to be achieved during the installation process is to allow these vapors to escape so that they do not accumulate inside the slabs: wet mineral wool will not dry out and will have high thermal conductivity. This is the main disadvantage of this insulation, because the same polystyrene foam or polystyrene foam is almost 100% vapor-tight.
Thermal conductivity of basalt mats
The thermal conductivity coefficient of basalt wool is in the range of 0.032-0.048 W/mK. The same indicators characterize polystyrene foam, polystyrene, cork and foam rubber.
Important! Mineral mats have replaced asbestos, which is harmful to health, as a fire-resistant material.
Before you go shopping for insulation, consult with friends or knowledgeable people about trusted retail outlets known for the quality of the product. Only this approach guarantees the purchase of good material that meets the standards.
How much do Rockwool slabs weigh?
The weight of mineral wool from Rockwool, a popular insulation manufacturer in our country, depends on the density of the thermal insulation material that the buyer chooses to perform a certain type of work:
- Weight of Rockwool Acoustic Butts, density 45 kg/cu.m. meter, dimensions 1000 x 600 x 50 mm is no more than 1.35 kg.
- Weight of Rockwool Acoustic Butts, density 37 kg/cu.m. meter, dimensions 1000 x 600 x 50 mm is no more than 1.1 kg.
- The weight of Rockwool Light Butts Scandic mineral wool, density 37 kg/cubic meter, dimensions 1000 x 600 x 50 mm, is no more than 0.75 kg.
The mass of mineral wool can differ radically when using combined types of insulation - Rockwool Fire Butts foil plate, density 110 kg / cubic meter. meter, dimensions 1000 x 600 x 30 mm, weighs within 2 kilograms. The weight also depends on the thickness of the insulation used - Rockwool Light Butts Scandic, density 37 kg / cubic meter. meter, dimensions 1000 x 600 x 100 mm, weighs about one and a half kilograms.
The weight of the insulation does not significantly affect the application features. Of greater importance, of course, is the density of the material. In addition, knowing the density parameter and packaging volume, you can easily calculate the weight of the product.
The density of insulation can vary significantly depending on the brand, composition, and the use of various synthetic elements. For example, with a density of 28-45 kg/m 3, the weight of extruded polystyrene foam (one cubic meter of material) will be 28-45 kg.
The density of this material depends on the so-called product classes (their characteristics include not only density, but also strength, water absorption, etc.): 31, 31C, etc. For example, extruded polystyrene foam 35 has a density of approximately 30 kg/m 3 .
The weight of mineral wool (1m3), as a rule, depends on the purpose.
For example, rigid boards, which are produced by adding special synthetic additives (resins) to fibers, are used to insulate walls and ceilings - those areas where the greatest density of the material is required. The density of these plates is 175-200 gc/m3. They are marked respectively PZh-175, PZh-200. Other density indicators are provided for a ventilated facade and for insulation “under plaster” 100-125 kg/m 3.
For floor insulation, slabs of maximum strength are suitable. The size of the slabs also varies significantly and this is due to the method of their installation and the possibility of optimal adjustment of the edges.
- For example, the weight of ISOVER Standard stone wool has a density grade of 11, dimensions 1000x600x50. Having a volume of 0.03 m3 and a density of 11 kg/m3, it is easy to calculate the weight of the slabs - 0.3 kg.
- For example, for external wall insulation, it is possible to fix slabs between the slats of wooden sheathing, having previously determined the required distance.
Depending on the raw materials and production methods, mineral wool has different fiber structures. The material is easy to cut and install to the surface, and has a small percentage of additives. The composition contains basalts and large fibers that can withstand high temperatures of 1000 C.
Manufacturer Rockwool
Danish rockwool insulation for roofing occupies a leading position in the Russian sales market. Today there are three directions of the company, but we will focus only on insulation for flat roofs.
Rockwool - roofing insulation
It consists of mineral wool slabs made of basalt rock. Area of application: multilayer structures. The task is thermal insulation of flat roofs.
It is also possible to use cement-free roofing screed material. However, not all products of this brand can effectively insulate a roof. After all, the range is represented by universal and special plates.
- Rockwool Roof Butts designates the bottom layer with the letter H, the top layer with the letter B, and the universal one has no letter designation.
- Rockwool Cut-to-falls Roof Slab and Rockwool Underlao Roof Slab are used as the bottom layer in a multilayer structure.
Advice
. In places where there is no required roof slope, Cut-to-falls Roof Slab is usually used.
All products of the above-mentioned company have good characteristics and long service life. They are easy to use during installation, thanks to zero coefficients of linear expansion and shrinkage.
Types of produced mineral wool
According to the indicators of GOST 52953-2008, the technical regulations of which apply to the material - mineral wool, this class includes three types of material:
All of them differ in different thicknesses and fiber lengths, as well as other parameters - different load resistance, resistance to heat and moisture, thermal conductivity. For example, insulation is glass wool, which was very popular in the USSR, and is now cheap
However, working with it requires specialists to be careful - fiberglass mineral wool is too prickly
Let's look at each type of cotton wool separately.
This material, created from slag, has a fiber thickness of 4 – 12 microns and a length of 16 millimeters. Since mineral wool is characterized by residual acidity, when the room is damp, it has an aggressive effect on metal surfaces. In addition, the technical composition that cotton wool has makes it possible to absorb moisture well. This fact does not allow it to be used for cladding facades. Considering the previous reasons, mineral wool made from slag is not used as insulation for plastic and metal pipes.
Technical characteristics of slag wool:
- hygroscopicity – very high;
- thermal conductivity – 0.46-0.48 W/meter/Kelvin;
- maximum heating temperature – 3000C (if the limit is exceeded, the material will sinter).
This insulation consists of fibers 15–50 mm long and 5–15 microns thick, which make glass wool a durable and elastic material. Glass mineral wool suggests. You should work with it very carefully so that the glass threads do not get into your eyes or skin. Inhaling glass dust can damage your lungs, so you must use a respirator and special goggles when working with it.
- thermal conductivity – 0.03-0.052 W/meter/Kelvin;
- heating temperature – 5000C;
- cooling temperature – minus 600C.
Mineral fiber made from such fiber is characterized by fibers with dimensions close to slag wool. A significant advantage of the material is that it does not prick. By the way, professionals who talk about mineral wool most often mean stone wool.
- thermal conductivity – 0.077-0.12 W/meter/Kelvin;
- heating temperature – 6000C.
Of the many varieties, basalt mineral wool has the best parameters, since it is created from diabase or gabbro. However, the insulation - stone mineral wool - contains impurities in the form of dolomite, clay and limestone, which contribute to an increase in the fluidity of the mass. Mineral wool contains less than 10% of the resin-based binder component. When this indicator decreases, the material allows more moisture to pass through, however, the evaporation of phenol decreases, and thus the negative impact on human health is reduced.
Basalt mineral wool is characterized by the absence of additional components. That is why it can withstand heating up to 10000C and cooling down to -1900C, and this does not harm the thermal insulation material in any way. Basalt fiber is easily formed into sheets or rolls. Just like standard mineral wool, basalt mineral wool will not burn when heated above normal.
Foam thickness
The thickness of foam insulation has already been discussed in previous articles in our series. We have shown that the minimum thickness of insulation in the first temperature zone of Ukraine, which includes Kyiv, is determined by DBN V.2.6-31:2006 “Thermal insulation budivel”, and is equal to 10 cm.
Insulation of a smaller thickness, for example, 5 centimeters, as various teams of “professionals” often suggest, is practically useless to use. In the article “What is the minimum permissible thickness of foam plastic when insulating houses,” it is mathematically proven that only with a foam plastic thickness of 100 mm does the expected insulation effect occur, and with 140 mm, heat loss through external walls is reduced to zero.
Effect on properties
Most of the characteristics of insulation are interrelated. Thus, the density indicator affects thermal conductivity.
As you know, air is the best heat insulator. A large number of air bubbles are located between the chaotically directed fibers of mineral wool insulation, for example, stone wool. However, if you increase the specific gravity of the material (in essence, compress the fibers more), the volume of air bubbles will decrease, which will lead to increased thermal conductivity.
However, the relationship between density and thermal conductivity is determined by the structure of the material. For example, when the density of polystyrene foam changes, the volume of air contained in its capsules remains unchanged. This means that thermal conductivity does not change in any way when the density of the insulation changes.
But a change in specific gravity always affects sound insulation. This is due to the fact that as the air permeability of the heat insulator decreases, its noise-absorbing properties increase.
In other words, the denser the material, the better sound insulation it is characterized by.
. However, as the density increases, the weight and thickness of the material also increases. It becomes uncomfortable to work with him.
The way out of this situation will be the use of special thermal insulation panels with improved sound insulation properties. This can be light glass wool or basalt insulation with twisted thin and long fibers. In this case, the density of the material may not exceed 50 kg/m3.
Strength indicators are also related to the ability of the material to withstand heavy loads, and the relationship here is directly proportional. In this regard, denser materials should be used in loaded areas. This is the only way to avoid deformation of the insulation.
Finally, the method of its installation depends on the specific gravity of the insulation. Thus, lightweight, low-density heat insulators can be used between the joists and sheathing elements. If this same option is mounted on walls, it will simply slide off, so the choice is made in favor of more durable mats and sheets.
In addition, dense insulation does not require additional mechanical protection; they are strong enough to withstand mechanical loads. And more friable materials - polystyrene foam, polystyrene foam, mineral wool - always need additional protection.
Effect of Density on Heat Conductivity
As a rule, consumers often pay attention to the performance characteristics of insulation rather than to physical properties such as density. And it is necessary to take it into account, since it carries important information. Any thermal insulation material contains air either in a rarefied or normal state
There is a dependence: the less vapor there is inside the insulation and the worse it is isolated from interaction with the outside air, the higher the thermal conductivity coefficient will be. And the larger the latter, the worse the material retains heat
Any thermal insulation material contains air either in a rarefied or normal state. There is a dependence: the less vapor there is inside the insulation and the worse it is isolated from interaction with the outside air, the higher the thermal conductivity coefficient will be. And the larger the latter, the worse the material retains heat.
Wool
Wool insulation is made from sheep wool fibers that are either mechanically held together or glued together using 5% to 15% recycled polyester adhesive to form insulation beads and rolls. Sheep are no longer raised primarily for their wool; however, they must be trimmed annually to protect the health of the animal. The wool used to make insulation is wool discarded as waste from other industries due to its color or quality.
Hemp
Hemp fibers are produced from the hemp straw of the hemp plant. Most hemp is imported, but home-grown crops are growing. Because the plants shade the soil, no chemical protection or toxic additives are required to cultivate hemp. The product is typically 85% hemp fiber with a balloon consisting of polyester binding and 3-5% soda added for fire resistance.
Therefore, it is necessary to select mineral wool based on the goals of insulation - for rooms where reliable insulation from the cold is required (living rooms, partitions between floors, floors), denser materials are suitable, and for areas of the house where heat preservation is not so important (non-residential attics , caisson) - lighter slabs or rolls of mineral wool
Honeycomb glass
Mainly made from recycled glass and mineral base materials such as sand, and without the use of binders. The ingredients are melted into molten glass, which is cooled and ground into a fine powder. Powdered glass is poured into molds and heated in a "sintering" process that causes the particles to stick to each other. A small amount of finely ground carbon black is then added and the material is heated in a "cellulose" process.