Roll insulation is a material with a low thermal conductivity, which is additionally characterized by sufficiently low rigidity, but at the same time holds its shape well. Coatings of this type are flexible, which allows finishing areas of complex configurations. Laying such material is not difficult. However, it is important to choose the right dimensions. Insulation in rolls is attached end-to-end; it is unacceptable to leave significant gaps between adjacent sections of thermal insulation. This will lead to the formation of cold bridges.
Scope of application of roll insulation
This type of material is universal, due to its properties (low rigidity and density, flexibility). This means that it can be used at facilities for various purposes (private, commercial, public, etc.). However, it should be remembered that each type of such material may have restrictions on its use, for example, if it does not meet operating conditions. Roll insulation is suitable for installation on horizontal and vertical surfaces. It is dense enough to maintain its shape.
A coating with a metallized layer is installed on objects and surfaces where it is important to provide the highest level of protection against heat loss: in baths, saunas, when installing water/electric heated floors, etc. The desired effect is achieved due to the presence of a heat-reflecting layer.
Roll insulation is the only affordable materials that are suitable for protecting surfaces with complex configurations: with differences in levels (stepped), bends, joints, and hard-to-reach places. This opportunity is due to flexibility and low rigidity.
Directions for using this type of thermal insulation:
- covering walls outside and inside for decorative finishing of any kind (hard boards, soft materials and even wallpaper);
- floor protection, in this case the roll insulation is protected from deformation by the lathing;
- insulation of flat/pitched roofs;
- reduction of heat loss through the ceiling;
- protection of pipes for various purposes.
Ceiling thermal insulation methods
There are several methods for thermal insulation of the ceiling of a house:
• external method (with or without replacement of the roof covering)
• insulation from the inside.
An option for external insulation is created from the attic, under-roof space and attic of the house.
Naturally, this is a labor-intensive and expensive insulation method.
If you want to insulate the ceiling from the inside, then it is better to give preference to mineral insulation, made in the form of slabs or rolls.
A strong alliance with a plasterboard suspended ceiling will create a reliable barrier to heat leaking out. Let us tell you a secret, if there is a possibility of external insulation, then this option is more preferable.
Types of materials in rolls
There are two groups of insulation materials, characterized by flexibility, low density and rigidity:
- Based on expanded polystyrene, polyethylene. Such materials are characterized by a closed-porous structure, which is achieved by foaming the raw materials. As a result, most of the volume is a gaseous medium. By foaming polyethylene, a flexible coating of small thickness is obtained. Roll insulation of this type is characterized by low thermal conductivity, wear resistance, and lasts a long time.
- Mineral wool is presented in varieties: glass and slag wool, basalt or stone wool. These are natural insulating coatings characterized by low thermal conductivity. Disadvantages include low strength, tendency to sag during operation, and hygroscopicity. The last of the properties is the reason for the short service life of the coating. This insulation is suitable for walls, floors, ceilings, attics, basements, and roofs. If you provide protection from moisture in areas with high loads, you can avoid deformation of the coating.
Inter-crown heat insulator and its features
Inter-crown thin heat insulator for buildings made of timber.
A separate type of flexible insulation is designed to fill voids in the inter-crown space of log and timber houses. A distinctive feature of the material is its small width, which facilitates the installation process. The material is made from natural raw materials - batting, jute, flax.
You can use such thermal insulation in convenient narrow rolls not only during the construction of a new house, but also several months/years later.
Roll Size Chart
For comparison, we take insulation whose thickness does not exceed 50 mm. This is due to the fact that more massive rolled thermal insulation materials roll up much worse. The review involves fiber coatings. Manufacturers of insulation in rolls:
| Material grade | Width, mm | Length, mm |
| Ursa M-11 | 1200 | The manufacturer offers two options: 7000 and 9000 |
| Heat Knauf Dacha | 1220 | 7380 |
| Isover Classic | 1220 | 8200 |
| Isover Sauna | 1220 | 12500 |
To compare coatings by cost and determine the most suitable option, take into account the number of strips in the package.
Tips for choosing
When choosing roll materials for insulating rooms, you should listen to the advice of experts:
- To insulate surfaces indoors and outdoors, it is better to use different insulation options.
- Use a material suitable for specific types of work: for example, for walls, which means choosing insulation suitable for walls, etc.
- When choosing the thickness of the material, you should take into account the climatic features of the area.
- Insulation in rolls of any purpose and manufacturer must be certified.
Roll insulation materials are available to consumers in a wide range. They all have their own characteristics, their pros and cons. When choosing one or another insulation option, it is best to use the help of professionals. This will help to avoid unnecessary costs and unpleasant moments during the operation of the material.
Watch the video that explains the features of using roll insulation for pitched roofs:
conclusions
Rolled thermal insulation is in many cases preferable because it is characterized by flexibility. In addition, the material of this group has low thermal conductivity, which allows it to be used to insulate an object. However, it should be borne in mind that fiber roll coatings do not tolerate contact with liquids well, so they must be carefully protected with waterproofing.
If you plan to use foam insulation, it is important to remember that they do not allow steam to pass through, which means the microclimate in the room may worsen. To avoid negative consequences when installing this type of insulation, it is recommended to install supply and exhaust ventilation or increase the efficiency of natural air circulation in the room.
The role of the foil surface
The main feature of such insulating devices is the presence of a thin but durable foil coating. In this way, the material is protected from the negative effects of ultraviolet rays and high humidity, which is very important when equipping industrial premises, kitchens, bathrooms, baths, saunas.
Foil insulation withstands high temperatures well
Laying of foil insulation is carried out in accordance with a special technological process. A gap of 1-1.5 cm must be created between the thermal insulation and the finishing material. This is very important, since at elevated temperatures the insulation maintains a given degree by transferring it to the back wall and then returning it back to the walls, but not to the room.
In comparison with rolled materials made of slag wool, glass wool and basalt base, the foil product must be fixed to the lathing. The layers are overlapped, and their joints are carefully treated with insulation.
Flexible stone - what is it?
The starting material for its production is sedimentary rock, the smallest elements of which reach 2 mm. Essentially, this is the thinnest section of natural stone, which is applied to fiberglass using the imprint method.
Flexible stone is sold in rolls reminiscent of wallpaper.
The raw material for production is sandstone. It is cut into thin layers and then polished. It turns out that the structure of the coating replicates natural stone. The slice is placed on a textile base impregnated with acrylic. The layer is attached to special polymer compounds.
The size of the rolls varies from 2 to 2.8 meters. In addition, flexible stone can also be produced in the form of tiles. The size can be 50×600, 200×300, 600×300, 800×400 mm.
flexible stone
How to understand what exactly needs to be insulated
To reliably assess the need to insulate a house and identify problem areas, you should invite an auditor to inspect the building using a thermal imager. Based on the research results, engineers will make a “diagnosis” and make recommendations for improving problem areas. If the house was built more than 5 years ago, then with almost 100% probability it will require insulation.
If we talk about those who are just planning construction, then it is worth saying that not all wall materials allow the construction of single-layer structures. Therefore, very often developers choose the option of making load-bearing structures relatively thin, but then immediately insulating them.
That is, instead of 40 cm of aerated concrete walls, 30 cm of blocks + 10 cm of insulation, for example mineral wool, are erected. This “pie” provides much better performance in all criteria, although the overall thickness of the structure is the same. There are several types of mineral wool offered on the construction market. Let's look at the main thermal insulation options.
Plates
pros
Minuses
In principle, choosing the type of product (slabs or rolls) for insulating surfaces is not difficult, focusing on the specifics of the work and your own skills. But when applied to thermal insulation of engineering systems, it is much more complicated. Autonomous communications pipes do not have a large diameter, and working with these samples is impractical. But only if these are traditional materials.
Their main advantage is ease of installation and variety of modifications. To work with these products, professional skills are not required - the connection of mats and slabs is carried out quickly and without the use of additional devices; complete tightness of the coating is guaranteed. Fixation of pipes of the same heated floor on Uni-Fitt is ensured by the design features of the products: between special protrusions located so that the contour can be laid according to any pattern.
Source
2 Rolled thermal insulation based on mineral wool
The quality of this category of insulation is regulated in accordance with the requirements of GOST RF “52953-2008”. This quality standard allows the following thermal insulation material to be classified as mineral wool insulation:
- Basalt wool is a material produced by melting rocks and then forming microscopic fibers from them, connecting them into a solid carpet;
- Slag wool is a material made from waste from the metallurgical industry. As a rule, it costs much less than basalt wool;
- Glass wool is a morally obsolete material, but still quite often used due to its low price. Produced by melting cullet.
Rolled basalt wool has a characteristic yellow tint
Rolled insulation based on mineral wool, due to its elasticity and flexibility, is an extremely versatile material that can be successfully used for thermal insulation of walls, floors, attics, and other flat surfaces, as well as for thermal insulation of pipes.
To insulate pipes, special cylinders are made from mineral wool, which are simply placed on the surface of the pipes without any additional processing. This is an excellent analogue to polystyrene foam and extruded polystyrene foam.
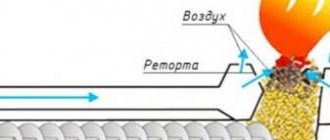
2.1 Mineral wool production
Let's look at the technology for making mineral wool using basalt insulation as an example. Basalt rocks, the chemical composition of which meets GOST requirements, can be melted in two ways - hot and cold.
The hot method involves heating basalt rocks in blast furnaces, the cold method involves exposure to electromagnetic radiation (like a conventional microwave).
The molten rock is fed into a centrifuge, which is equipped with constantly cooling carbide disks. Under pressure, molten basalt is fed into a centrifuge and falls onto rotating disks, where individual basalt fibers are formed from the melt through the process of cutting cooling and pressure drop.
The resulting fibers are immediately removed from the drum by a special functional element and supplied via a conveyor to a laying machine, which forms a carpet of basalt wool of the required thickness.
After laying the carpet, the fibers are impregnated with various impurities, which are necessary to give the final product the required characteristics - hydrophobicity, fire resistance, density and elasticity.
Slag material, as a rule, has a darkish tint
2.2 Advantages and disadvantages
Among all the thermal insulation materials on the market in the middle price category, it is mineral wool that has the lowest thermal conductivity. Although the leaders in general are polystyrene foam and mineral wool.
An important factor is that the thermal insulation properties of mineral wool do not depend in any way on any external conditions - this material does not expand under the influence of moisture, is not subject to thermal expansion, and microorganisms and rodents do not grow in mineral wool.
Rolled mineral wool insulation is produced with a wide variety of performance characteristics - you can choose either low-density mineral wool for insulating pipes and other uneven products, or dense material for thermal insulation of surfaces that experience external loads - the floor or attic floor.
An important advantage of mineral wool is its fire resistance. This material can withstand temperatures up to 700 degrees; it does not ignite even under direct exposure to fire. It is also worth noting good noise-reducing properties - by insulating walls and floors with rolled mineral wool, you will solve not only the issue of insulation, but also sound insulation of the house.
The only drawback of mineral wool is its high vapor conductivity, due to which the installation of a special vapor barrier film is required when installing this insulation.
Thermal insulation of the pipeline using rolled glass wool
Rolled mineral wool insulation can be used for the following purposes:
- Insulation of roofs, floors, walls, and any flat surfaces;
- Thermal insulation of pipes and pipelines;
- Thermal insulation of industrial equipment;
- Insulation element inside sandwich panels (here the best thermal insulation is Hitrock);
- Internal insulation in false walls and when laying hollow walls;
- External insulation of house walls followed by plastering.
Extruded polystyrene foam
Its counterpart differs from the polystyrene foam described above in its manufacturing method. The foaming consistency here is much higher. In addition, the material is subjected to additional processing through a die. Thanks to this, the result is a waterproof, durable insulation that can withstand higher loads than its direct competitors.
The operating temperature range from –500°С to +750°С allows its use in industrial, high-tech and scientific buildings. It is also used in road construction, thermal insulation of wells and roofs. Extruded polystyrene foam is indispensable in low-heating and hyper-humid rooms. When restoring such objects, an optimal combination of heat and waterproofing is required, which extrupenol can do.
However, it is banned in the European Union and the USA. The reason for this step was the main disadvantage of this material - high flammability. This factor has led to the death of newly renovated buildings in several EU countries. To protect their product, manufacturers began to add substances that prevent fire to the composition. This turned into even greater criticism - the smoldering began to release life-threatening toxins. Therefore, it is hardly appropriate to consider him the best.
Characteristics
Thermal insulation material in rolls, produced under various brands, is characterized by general characteristics.
Environmental friendliness
The insulation meets regulatory environmental safety requirements.
As a rule, salts of heavy metals, alkalis, acids, oxides, phenols or toxic organic compounds that are inactive at room temperature are present in minimal quantities.
Due to its low chemical activity, thermal insulation practically does not interact with aggressive environments, and therefore, for example, is not afraid of exposure to solvents.
Biological resistance and fire safety
The material has a high level of biological resistance. As a result, there are no rodents, fungus, or mold in it. It is of no interest to insects and animals as food. Depending on the composition and other characteristics, the insulation can withstand high temperatures.
Air and vapor permeability
If insulation is used to insulate floors or walls, air permeability is an important indicator.
When using rolled materials, you do not have to worry about excessive dampness in the room, condensation and other negative phenomena, provided that the installation is done correctly.
Technology of wall insulation with mineral wool
- Preparing walls for laying insulation depends on the material from which they are built. Wooden walls must be impregnated with an antiseptic to avoid damage to the log house by microorganisms. Areas damaged by rot, fungus, and mold must be thoroughly cleaned and soaked in appropriate solutions - after installing the insulation, access to them will be impossible. It is enough to free brick and foam concrete walls from peeling plaster and paint. If the walls are wet, they must be thoroughly dried. Window trims and slopes must be dismantled, and fastening and decorative elements that can damage the vapor barrier and insulation layer must be removed from the walls.
- A layer of vapor-permeable membrane is placed under the mineral insulation. The film is positioned so that the vapor-permeable side faces the wall of the house, and the smooth side faces the insulation. A vapor-permeable membrane is necessary to ensure the removal of water vapor from the walls of the house through the insulation. It is allowed to lay mineral insulation on smooth walls without first laying a membrane film.
- Wooden guide rails or a profile for attaching drywall are attached on top of the vapor-permeable film. They are attached to the wall with self-tapping screws or using a dowel-nail mounting pair. The distance between the slats is chosen so that it is 1-2 centimeters less than the width of the insulation. The thickness of the slats should be equal to the thickness of the insulation. Attaching the slats starts from the corner of the house. When attaching the slats, use a level. If the wall is uneven, you can use perforated plasterboard hangers to secure the frame. If you use insulation in the form of mats, you can additionally attach a horizontal strip along the lower border of the wall, on which the lower insulation mat will be installed.
- Thermal insulating mats or rolled material are placed in the space between the guide slats, while laying the mats begins from the bottom, and the rolled materials from the top, fixing the insulation to the wall either directly between the slats, or using several dowels with a wide head. The slab material is attached to brick or block walls with a special glue that ensures a tight fit of the insulation. There should be no gaps between the insulation and the guides. First, solid pieces of insulation are fixed, then the remaining areas around window and door openings are filled.
- Another layer of film is placed on top of the mineral insulation - wind protection and waterproofing. The film must also be vapor-permeable so that moisture can be easily removed from the insulation layer to the outside. The film is fastened with staples to the slats without tension, after which the entire layer of insulation and vapor barrier is additionally secured to the wall using dowels with a wide head; the attachment points can be glued with metallized tape for better waterproofing.
- An important stage in wall insulation is the installation of a ventilated façade. The ventilation gap should be at least 5-6 cm; for this, additional counter-battens are placed on top of the guides or profiles are attached on which the ventilated facade is mounted: siding, block house or other finishing materials.
- When insulating the walls from the outside, their thickness increases, so you will have to install new window slopes, window sills, as well as trim and finishing elements. It is better to purchase them immediately when purchasing a ventilated facade.
Insulating walls outside with mineral wool is one of the most popular methods of thermal insulation of buildings. Its popularity is due to the low thermal conductivity of mineral wool, due to which most of the heat remains inside the building, as well as the environmental friendliness of the material and its ability to remove moisture from inside the house. In addition, mineral wool is an excellent sound insulator.
Other materials are also used to insulate walls, for example, polystyrene foam or extruded polystyrene. These methods are used for plaster finishing, since slab insulation is an excellent basis for plaster. We also have an article that describes the advantages and disadvantages of all types of insulation for walls from the inside.
Ecotherm
Ecotherm is an eco-insulation material that consists of 70% flax and 30% two-component polyester fiber. This fiber is the one that gives it sufficient strength and elasticity. The ability to hold its shape well is an additional advantage during installation - the slabs can be installed between beams and joists without additional fastenings. The main advantages of linen insulation:
- Durability – expected service life 60 years.
- Safe insulation. This means that it is absolutely hypoallergenic, leaving a pleasant feeling when touched.
- Not subject to electrification.
- Antiseptic - it does not harbor parasites, perfectly absorbs odors and purifies the air.
- Breathable - absorbs and releases moisture well, regulating heat exchange and humidity.
A natural antiseptic, it absorbs excess moisture well and prevents the formation of fungus and mold. The properties of the fiber are close to wood, and the use of linen thermal insulation in a frame house will help you easily achieve the effect of a “log house” - the material allows the walls to breathe.
Flax is non-flammable, difficult to ignite, and even when burning does not emit hazardous substances. In terms of fire safety, it is comparable to good quality basalt wool. Has excellent sound insulation. The use of plant fiber makes linen one of the safest insulation materials. Available in the form of slabs with a thickness of 50 and 100 millimeters.
The qualities and properties of linen insulation allow you to work with it without fear, even when installing thermal insulation in children's rooms.
Video description
About mineral wool in the following video:
There are several varieties of this fibrous material, differing in the method of production and properties:
- Stone wool
. The starting materials are rocks (basalite, diarite, porphyrite), but more often basalt. In construction, a second name has taken root - basalt wool, although this particular variety is more often used for thermal insulation of industrial equipment and pipelines. Stone wool is a durable, non-flammable and environmentally friendly material with a high ability to retain heat. The small shrinkage of this slab material during operation prevents the formation of cold bridges. - Glass wool
. It is made from molten glass, produced in slabs and rolls, and has characteristics similar to mineral wool. Glass wool has increased strength, elasticity and vibration resistance. However, glass wool fibers are fragile, and debris poses a health hazard. Working with the material requires the use of a respirator and special clothing, as well as installation using special technology. Glass wool is cheaper than mineral wool, but its service life is shorter.
Glass wool requires careful handling Source pinterest.fr
Slag wool. The raw material is molten blast furnace slag. This type of filler is similar in properties to glass wool; It is recommended to use it only for dry rooms. The main advantage of slag wool is its low cost.
Walls, ceilings and roofs are insulated with cotton wool; The thickness of the layer in a country house for year-round use should be 200-250 mm. The peculiarity of cotton wool is that its hygroscopicity is neutralized by the use of vapor and waterproofing membranes. The density and thickness of the material affects not only the cost, weight and load resistance, but also the way it is used:
- Rolled fabric
(often laminated, with foil coating). Effective heat retaining material. Used for thermal insulation of horizontal surfaces, has a density of 35 kg/m3. - Plates
. Material with a density of 75 kg/m3 is used to insulate the floor, ceiling and interior partitions, and a density of 125 kg/m3 is used to insulate the facade. More rigid slabs (200 kg/m3) are used for interfloor ceilings, roofing and screed floors.
Element of the roofing pie - mineral wool with foil coating Source pinterest.cl
Ecowool
Cellulose wool (known to the general public as ecowool) is an example of an environmentally friendly product. It consists of 80% of newspaper waste paper and waste from the cardboard and paper industry, and 20% of additives that perform a flame-extinguishing function (boric acid and sodium tetraborate). In appearance it is a loose material of various shades of gray.
Ecowool has proven itself well as sound and heat insulation; it insulates all parts of the frame structure. The disadvantages of ecowool are its high cost and the use of special equipment during installation. Insulation of a frame structure with ecowool is carried out in one of four ways:
- Dry backfill
. Manual labor-intensive method, limited in application. Suitable for insulation and soundproofing of small-area interfloor ceilings, ground floor floors, and attic floors. - Dry blowing
. The most preferred (fast and high-quality) method, suitable for insulating any cavities. It is carried out using blow molding equipment.