An uninsulated attic floor is one of the most vulnerable building structures in terms of heat loss. Through it, 20 to 40% of the thermal energy needed by residents easily “evaporates” into the atmosphere.
The percentage of losses depends on the material used in the construction of the rafter frame, and on the type of roofing used in the construction of the roof.
Insulating the ceiling in a house with a cold roof will significantly reduce heat loss. We will talk about how thermal insulation work is carried out.
We will list in detail what materials you will need. Taking into account our recommendations, you can significantly improve the energy efficiency of your building.
The need for insulation for the ceiling
Insulating the ceiling of a house allows you to raise the room temperature in the premises, but condensation may appear in the attic. When warm air rises, it comes into contact with cold air, condensing droplets of moisture. As a result of this process, the thermal insulation material becomes saturated with water and begins to actively rot with the formation of fungus and mold. To avoid this phenomenon, it is necessary to change the physical conditions in the attic floor.
Concrete ceiling
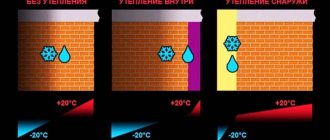
Since concrete has a high thermal conductivity, it consumes heat energy but remains cold. As a result, condensation forms, which can destroy the structure of the material when freezing. Therefore, the insulation of the attic floor on a reinforced concrete slab requires the mandatory use of vapor-permeable insulation to remove moisture to the outside.
If it is not possible to insulate the ceiling from the outside, then you will have to lay the material from the inside, but then it must be impenetrable to steam in order to protect the concrete from moisture. A layer of vapor barrier will also be required for additional protection.
Wooden ceiling
Wood is susceptible to rotting and exposure to various bacteria. If the thermal regime is not organized correctly, the ceiling will become wet and rapidly deteriorate. In this case, the insulation of a wooden ceiling can be carried out both from the inside and from the outside. With the external method, you can significantly save room space, but with the internal method, impermeable high-quality material is required. It is also recommended to install a vapor barrier between the ceiling and the insulation for greater protection.
Polystyrene foam and polystyrene foam
Polystyrene foam is more environmentally friendly and easier to use.
Waterproofing with this insulation technique is not required, and the small thickness allows this material to be used in rooms with low ceilings. Insulating the basement ceiling from the inside with foam boards will only take a few hours. The plates are easy to cut, and they can be attached with glue without building the sheathing.
Polystyrene is a direct relative of foam plastic, a denser and less friable material.
The price of such insulation is slightly higher than others, but its advantages are difficult to overestimate. Zero moisture absorption allows it to be used in any type of premises without worrying about waterproofing. The thickness of extruded polystyrene sheets is 1-10 cm.
Such a large assortment allows the use of polyplex for insulation of floors, walls, ceilings, and external communications. Manufacturers, as a rule, ensure ease of installation by cutting grooves along the edges of the plates in advance. This makes it possible to secure the material without gaps, providing maximum insulation.
When insulating from the inside, polyplex is attached to supporting structures or between them
The surface of polystyrene boards is quite smooth. Insulating the ceiling with polystyrene foam from the inside allows you to immediately begin finishing by simply filling the surface.
Types of vapor barrier
When insulating the floor of a cold attic, installing a vapor barrier layer is an important process, because without it, the entire procedure will be impractical. After installing the insulation from the inside, the condition of the ceiling will be unknown, and all possible impacts on it will be hidden. In the future, this may be the reason for partial or complete restoration of the ceiling. The most effective way to protect it is to install a vapor barrier.
Vapor barrier
It is a regular polyethylene film as a sealed barrier to wet vapor. To save money, you can use a simple polyethylene sleeve, since it has the same properties as other polyethylene materials. Laying is carried out in strips with an overlap of 15-20 cm and an overlap of up to 15 cm on the wall structures. The joints must be taped to achieve tightness.
When installed from inside the room, the film is laid only on top of the impermeable insulation; the same applies for installation on a concrete floor. If insulation is carried out in the attic, then polyethylene is located between the wooden structure and the heat insulator.
Membrane
It is a film where only one side is permeable. It prevents moisture from penetrating, but does not prevent it from coming out. They are used to protect heat-insulating material from getting wet and deteriorating.
If the attic floor is insulated over wooden beams with mineral wool, then the vapor barrier membrane will ensure the free release of steam, but will protect the insulation from external moisture, maintaining its performance properties.
Installation of ecowool
How to insulate a ceiling from the inside using environmentally friendly material? Professionals recommend buying ecowool, since the basis of this insulation is cellulose. Let us highlight the advantages of this material:
- resistance to atmospheric corrosion;
- fire resistance;
- elasticity;
- elasticity.
There are some subtleties of using ecowool:
- Insulation is accompanied by the formation of a large amount of dust, so it is advisable to use respiratory and eye protection during work.
- The material must not be heated, as it will smolder.
Sequencing:
- gluing ecowool to the ceiling surface (under pressure);
- decorating the surface with clapboard or sheets of plasterboard.
Advice! You need to work carefully with this heat-insulating material, wearing a respirator, protective suit, and goggles (cotton particles irritate the skin).
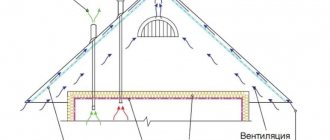
Features of cold roofs
To protect a residential building from external influences, a cold-type roof is installed. There are many heat-insulating products that help reduce heat loss. The temperature inside and outside the attic should vary within 4°C, so the air through the ventilation ducts should enter the attic, and not into the space under the roof. Then the humidity and temperature indicators will correspond to the street ones. Otherwise, an imbalance of modes will lead to the destruction of the rafter structure and roofing.
The advantages of a cold roof are:
- Easy to maintain. The roof has free space for access to any point, so repair and maintenance activities are carried out without difficulty.
- Good waterproofing. A warm attic involves the use of superstructures that violate the integrity of the waterproofing material. When installing a cold roof, no additional elements are required.
- Beneficial use. Despite the fact that the temperature in the attic is lower, it can be used as a temporary warehouse, and later converted into additional space.
- Minimum heat transfer surface area. Heat loss is only possible through the ceiling.
Inlet and outlet vents operate most efficiently when spaced far apart. When they are installed under the wind board along the entire length, complete air exchange is ensured throughout the attic space. The inlet openings are located in places of greatest pressure, thereby increasing the intensity of blowing.
Core Technology
Insulation of the ceiling under the roof allows all work to be carried out efficiently without regard to external weather conditions.
High vapor permeability and the possibility of getting wet mineral wool insulation requires the mandatory installation of a vapor barrier membrane. In residential premises there is constantly air saturated with moisture, which tends to leave the room with excess humidity.
The presence of 20% moisture in the material by volume reduces the heat-holding capacity by 2 times. When 40% is reached, the insulation efficiency is zero.
The film is secured with a construction stapler. The strips are laid perpendicular to the laid and secured joists. The tightness of the connection is ensured by securing the edges of the strips with double-sided tape.
It is more convenient to file a rough ceiling or sheathing for finishing using screws.
The insulation is installed from the attic side. The width of the insulation should be 10 - 20 mm narrower than the distance between the joists. Otherwise, gaps will form that allow heat to escape. They must be filled with insulation scraps, or the orientation of the material must be changed, which will lead to excess material consumption. The height of the joist boards should be greater than the thickness of the heat insulator.
Pressing the insulation against the enclosing structures leads to its compaction and an increase in the specific thermal conductivity coefficient.
Boards are laid on top of the low-density heat insulator to make it possible to use the attic for technical purposes. High-density slabs can be protected by installing a screed made of cement and sand.
Advantages of insulating the ceiling area
Roof insulation should be calculated at the stage of building a house. But often this question arises with a ready-made building, where thermal insulation was not previously provided. When insulating a reinforced concrete or wooden ceiling in a house with a cold roof, you can get the following benefits:
- Maintaining a microclimate by preventing the penetration of heated air from the street in the summer.
- In winter, it will protect the room from serious heat loss through the ceiling.
- The insulation additionally has soundproofing properties. Therefore, there will be no discomfort during heavy rain, wind or extraneous noise on the street.
Effective ways to insulate the ceiling
There are several types of attic floor insulation: from the inside by nailing the insulation to the ceiling, and from the outside, using a rolled product and rolling it over the attic surface. Both methods are very practical, the main difference being the choice of appropriate products and installation method.
Working indoors
When insulating from the inside, you can use mineral wool due to its high heat-insulating and vapor-permeable properties. Often it is placed inside a suspended structure made of metal profiles and covered with plasterboard. However, it is forbidden to compress it, since it has air gaps. When compressed, they disappear, and thermal performance indicators sharply decrease.
Important! Despite their effectiveness, mineral and basalt wool are recommended to be used only for external insulation. Due to their low strength, microfibers separate and, if ingested, cause side effects and serious illness.
Other materials can also be installed on the frame or screwed directly to the ceiling, taking into account the laying of the vapor barrier layer.
Working outside
On the attic side, it is recommended to lay roll or slab material, since it does not require careful fixation or frame manufacturing. This is a practical method, since the insulation does not take away the useful height of the room. Before carrying out work, the surface should be thoroughly cleaned of foreign debris. Laying can be carried out in one or two layers 30-50 cm thick using polyurethane foam to hold them together.
If the attic space will not be used in the future, then additional coatings are not required. If it is equipped for storing things, then the insulation is covered with plank flooring or sheet moisture-resistant plywood. When using bulk materials, a coating is also not required, but this does not apply to dry leaves or sawdust.
Recommendations for carrying out thermal insulation work:
- thickness should be calculated according to the region of residence and type of material;
- based on the selected product, you should know how to properly insulate a ceiling with a cold roof to ensure maximum effect;
- when laying several materials on top of each other, the vapor barrier indicators should increase from bottom to top (the other way around is not possible);
- mineral wool cannot be coated with expanded clay or vermiculite to avoid being pressed through;
- It is forbidden to lay a vapor barrier on both sides of the heat insulator, so as not to trap moisture and spoil the material;
- All joints connecting steam and heat insulating materials must be sealed to eliminate cold bridges. For this, adhesive tapes, polyurethane foam, a special solution or glue are used.
Liquid heat insulator
Polyurethane foam is delivered to the work site in a liquid state. This insulation is obtained as a result of a chemical reaction of two components under pressure. As a result, it acquires physical and chemical properties very similar to EPS. The big advantages are:
- the possibility of insulating any building materials;
- carrying out thermal insulation in hard-to-reach places;
- creation of a single thermal insulation layer on the entire insulated surface without the formation of cold bridges.
Application of polyurethane foam requires certain preparation and equipment. Failure to comply with the technology or the dosage of starting substances can lead to the receipt of a final product with properties different from the required ones.
In the case of thermal insulation of reinforced concrete floors with subsequent transformation of the attic into a technical room, it is necessary to install floor joists. In other cases, surface preparation is not required before starting work.
There is no need to use hydro- and vapor barrier. All subsequent processing of the insulated surface consists of arranging a subfloor or screed.
Required Tools
To carry out thermal insulation work, you will need tools such as: fasteners (screws, screws, dowels, anchors, liquid nails), construction staples, tape measure, hammer drill for working with concrete, screwdriver, hammer, construction knife for cutting sheet products.
The material used is insulation, vapor barrier film or membrane, metal profiles to create a frame, wooden blocks 3x3 cm or 5x5 cm.
Which insulation is better for the ceiling in a brick house
To effectively insulate the ceiling in a house with a cold roof, the following types of material are used outside and inside:
- Monolithic - has a high density and water resistance, while the dew point goes in any direction without deteriorating the properties of the insulation. These include extruded polystyrene foam.
- Fibrous or porous - produced in the form of rolled material or mats. They are highly susceptible to moisture saturation and lose their characteristics, so they are used only in conjunction with a vapor barrier. The following types are distinguished: mineral wool, slab and sheet polyurethane foam.
- Bulk or sprayed - the first option is laid manually, and the second only with the help of special equipment.
From the outside, insulation along the wooden beams of the attic floor is carried out using lightweight rolled or bulk materials (sawdust, leaves). For concrete slabs, you can lay a dense monolith, slabs or heavy bulk material (expanded clay).
Features of insulation for outdoor use
Work from the attic side can be carried out with the following materials:
| Material | Description |
| Slab and roll | |
| Reed | It consists of mats that are laid in two layers. It is environmentally friendly with high thermal properties. Disadvantages: increased fire hazard, susceptibility to attack by rodents and insects, rotting in high humidity. |
| Seaweed | Popular material in coastal regions. Refers to environmentally friendly and effective heat insulators. They are laid in one layer outside the attic and covered with plank flooring. Not exposed to moisture, insects and rodents. |
| Penoplex | It is one of the types of extruded polystyrene foam (EPS) with high strength. Not used for wooden floors due to complete vapor tightness. Before laying the insulation, the concrete base is leveled and covered with a vapor barrier film. After insulation, the material is filled with cement-sand mortar up to 50 mm thick. During operation, you can move along the surface. |
| Mineral wool | The most common material, which is produced in slab and roll versions. It is recommended to lay mineral wool in the form of mats between wooden joists, and for concrete floors - in a roll type. To use the base as a floor, a flooring made of boards is required. |
| Sprayable | |
| Polyurethane foam | It has a number of advantages, however, due to its absolute vapor tightness, it can disrupt the indoor microclimate. It is applied using special equipment under high pressure, so independent insulation is impossible. The foam layer with optimal thermal performance is up to 12 cm thick. |
| Ecowool | A modern thermal insulation material that is laid on a wooden and concrete base without the use of vapor barrier products. However, experts still recommend laying it to avoid insulation getting into the room through joints and cracks. It is also installed using an installation that provides a monolithic coating that fills all defects in the ceiling. The layer thickness is 25-40 cm depending on the region. Can be used independently or applied to a surface. |
| Bulk | |
| Sawdust | They are most popular in conditions where they can be obtained for free or at an extremely low cost. For a ceiling with a cold roof, the layer thickness is 15-30 cm. The disadvantage is the increased flammability, so they are additionally covered with a slag layer. Before laying, a layer of carbide and slaked lime is laid as protection against rodents and insects. Sawdust is often used in conjunction with cement or clay. |
| Expanded clay | Relatively lightweight, used for insulation of different fractions: 0-5 mm, 5-20 mm, 20-40 mm. In cold regions, the thickness of the embankment layer is 40-50 cm, for temperate climates - no more than 20 cm. If the attic is not used, the material does not require additional covering; otherwise, you can make a plank floor or fill it with a layer of cement-sand screed up to 5 cm . |
Calculate the weight
To determine the mass of a heat insulator, it is necessary to multiply its volume by its density. The volume is found by multiplying the layer thickness by the area determined by the product of the length and width of the thermal insulation.
We take the density of the main insulation materials from the table:
| Material | Density, kg/m 3 |
| Fibrous materials | 100 — 120 |
| Expanded polystyrene | 25 — 35 |
| Polyurethane foam | 54 — 55 |
| Expanded clay | 200-400 |
| Ecowool | 42-75 |
| Natural materials | |
| Felt (various types) | 100-150 |
| Foliage (dry) | 50 |
| Tow | 180 |
| Moss | 135 |
| Needles | 43 |
| Straw mats | 85 |
| cotton wool | 80 |
| Thin shavings (packing) | 140-300 |
| Campfire (various types) | 150-350 |
| Sphagnum (peat) | 150 |
| Wood sawdust | 190-250 |
| Straw (stuffed, cut) | 120 |
Insulation for indoor use
Insulating the ceiling in rooms is not recommended, but if there are no other options, it is possible. Since the house is quite warm and humid, the material may be susceptible to mold and mildew. To avoid this, it is necessary to create a ventilation gap between it and the finishing trim up to 3 cm thick, which will take up even more of the room’s height.
The following products are used as insulation for the ceiling in a private house:
- Penofol is a double material made of foil and polyethylene foam. It is used in areas with temperate climates, as it has average thermal insulation. It can be used as an independent layer or combined with other types.
- Expanded polystyrene - practical for concrete floors. It is placed in a lathing with a depth of about 3 cm and covered with finishing material (lining, plasterboard, Armstrong, suspended ceiling).
- Plaster mortars – they are characterized by high moisture resistance, fire resistance and decorative appearance. The mixture is used only for concrete bases and includes thermal insulation components.
- Cork – cork material is moisture resistant, therefore it is used without vapor barrier. It is environmentally friendly and can serve not only as insulation, but also as a finishing material in a certain room design.
When choosing a heat insulator, you should pay attention to the material of the ceiling and financial capabilities. It is recommended to insulate wooden ones with dry products, and concrete ones with slabs or coat them with special compounds.
Why can't you insulate your apartment from the outside?
All the methods described above are suitable for owners of private houses, but in multi-apartment buildings they are usually not applicable. Why, after all, it would seem possible to carry out work on the technical floor above the apartment? It's simple.
Communications are laid on the technical floor of the house, to which repair teams from housing maintenance offices must have unhindered access. There are also fire safety rules that must be followed to avoid putting yourself and your neighbors at risk.
That's all, dear reader. I hope the information was useful to you. And don't forget to tell your friends about us on social networks. Good luck with the renovation work and see you next time!
Methods for internal insulation of a cold attic floor
Before carrying out external or internal insulation, it is necessary to calculate the thickness of the material using the formula R=δ/λ, where:
- R – heat transfer resistance (according to the region of residence, for Moscow – 4.7 m² °C/W);
- δ – thickness of the insulation layer;
- λ is the thermal conductivity coefficient of the material (according to the GOST regulatory document).
Next, from the formula we find the thickness in this way: δ= λ· R.
Work begins with thoroughly cleaning the surface of debris, dust, cobwebs or moisture. When laying the product on the ceiling, be sure to leave a ventilation gap to protect against mold and moisture accumulation.
Use of penofol
Penofol consists of foamed polyethylene and a foil layer; it is used for buildings with a low level of heat loss due to low thermal insulation performance. To install insulation on the ceiling, it is necessary to create a sheathing. The product is rolled out over the surface of the frame and fixed with nails. The foil layer should face the inside of the room.
The creation of ventilation gaps on both sides requires the presence of additional sheathing, which will later be covered with sheet finishing coverings or a suspended ceiling. The most effective use of penofol is possible in conjunction with penoplex to increase thermal insulation properties.
Using penoplex from the inside
The material is practical for both external and internal use for thermal insulation of ceilings with a cold roof. Warming is carried out according to the following scheme:
- The lathing is made from wooden beams with a thickness exceeding the thickness of extruded polystyrene foam by 0.3-0.4 cm. The pitch between the slats is equal to the width of the insulation sheet minus 1-2 mm.
- The material is installed in the cells, and if the frame is assembled correctly, the slabs should fit tightly with little effort.
- The lathing is covered with plasterboard, suspended or suspended ceiling.
Attention! To increase reliability, penoplex can be fixed to the ceiling using umbrella-type dowel nails. The wide cap allows you to press it tightly without pushing through the fasteners.
Polyurethane foam and plaster mixtures
Polyurethane foam is one of the modern highly efficient products and allows you to create an ideal thermal insulation layer to reduce the heat transfer coefficient. The advantages when used on ceilings are:
- resistance to insects and bacteria;
- fire resistance;
- high sound and waterproofing;
- high adhesive properties with various types of coatings;
- resistance to temperature changes.
Determining the thickness
To find the height of the insulating layer, you need to know two values:
– standard thermal resistance of floors for the region of residence;
| Locality | Required thermal resistance of the ceiling R, m 2 °C/W |
| Anadyr | 6.0 |
| Arkhangelsk | 42829 |
| Astrakhan | 42828 |
| Barnaul | 42859 |
| Belgorod | 42889 |
| Blagoveshchensk | 42920 |
| Bryansk | 42950 |
| Vladivostok | 42981 |
| Vladimir | 42739 |
| Volgograd | 42889 |
| Vologda | 42770 |
| Voronezh | 42950 |
| Grozny | 42769 |
| Derbent | 42949 |
| Ekaterinburg | 42829 |
| Ivanovo | 42739 |
| Izhevsk | 42798 |
| Irkutsk | 42951 |
| Yoshkar-Ola | 42798 |
| Kazan | 42770 |
| Tver | 4.0 |
| Kaliningrad | 42828 |
| Kaluga | 42981 |
| Kemerovo | 42920 |
| Kirov | 42829 |
| Kislovodsk | 42797 |
| Komsomolsk-on-Amur | 42951 |
| Kostroma | 42739 |
| Krasnoyarsk | 42920 |
| Samara | 42739 |
| Mound | 42859 |
| Kursk | 42919 |
| Lipetsk | 42950 |
| Magadan | 42830 |
| Maykop | 3.0 |
| Makhachkala | 42980 |
| Moscow | 42981 |
| Murmansk | 42890 |
| Nalchik | 42797 |
| Nizhny Novgorod | 42739 |
| Novgorod region | 42981 |
| Novorossiysk | 42918 |
| Novosibirsk | 42920 |
| Oymyakon | 42832 |
| Omsk | 42890 |
| Ordzhonikidze | 42797 |
| Eagle | 42981 |
| Orenburg | 42770 |
| Permian | 42829 |
| Petrozavodsk | 42770 |
| Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky | 42770 |
| Pskov | 42950 |
| Rostov-on-Don | 42828 |
| Ryazan | 4.0 |
| Salekhard | 42891 |
| Saint Petersburg | 42981 |
| Saransk | 4.0 |
| Saratov | 42981 |
| Smolensk | 42950 |
| Sochi | 42796 |
| Stavropol | 42769 |
| Surgut | 42740 |
| Syktyvkar | 42859 |
| Tambov | 42981 |
| Tomsk | 42920 |
| Tula | 42981 |
| Tyumen | 42829 |
| Ulan-Ude | 42982 |
| Ulyanovsk | 42739 |
| Urengoy | 42983 |
| Ussuriysk | 42770 |
| Ufa | 42770 |
| Khabarovsk | 42859 |
| Khanty-Mansiysk | 42951 |
| Cheboksary | 42770 |
| Chelyabinsk | 42829 |
| Chita | 42771 |
| Elista | 42828 |
| Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk | 42770 |
| Yakutsk | 42831 |
| Yaroslavl | 42950 |
- coefficient of thermal conductivity of the material used
| Material | Specific thermal conductivity coefficient, W/m K |
| Fibrous materials | 0,038 – 0,052 |
| Expanded polystyrene | 0,032 – 0,036 |
| Polyurethane foam | 0.026 |
| Expanded clay | 0.11 |
| Ecowool | 0,038 – 0,041 |
| Natural materials | |
| Felt (various types) | 0,031-0,05 |
| Foliage (dry) | 0,05-0,06 |
| Tow | 0,037-0,041 |
| Moss | 0.04 |
| Needles | 0.08 |
| Straw mats | 0,05-0,06 |
| cotton wool | 0.037 |
| Thin shavings (packing) | 0,05-1 |
| Campfire (various types) | 0,04-0,065 |
| Sphagnum (peat) | 0,05-0,07 |
| Wood sawdust | 0,05-0,08 |
| Straw (stuffed, cut) | 0.04 |
For example: To get the result you need to divide the first indicator by the second. The resulting number shows the thickness of the layer in meters.
The required thermal resistance for the ceiling in Saratov is 3.9 m2 K/W. It is planned to use polyurethane foam with a thermal conductivity coefficient of 0.026 W/m K. When divided, we obtain 0.1014 m. To obtain the required heat savings, it is necessary to apply 10.2 cm of insulation.
Methods for external insulation of attic floors in a house with a cold roof
To reduce heat loss in the room and save space, insulation can be installed from the outside of the ceiling. This gives the advantage of using a larger number of different materials with high thermal insulation properties and low weight (does not create a large load on the supporting structures of the house).
Installation of slabs and mats
The construction of such options is carried out in one or two layers using the following technology:
- Laying vapor barrier material. When installing a suspended ceiling, a membrane or film is nailed to the ceiling from the inside. If roll insulation is used, the vapor barrier is laid from the attic side.
- Installation of heat insulator. Products in the form of slabs or rolls are placed tightly between the beams without forming gaps. When using mineral or basalt wool, this will not be a problem, and the gaps between the slabs will have to be sealed with polyurethane foam. It is better to choose products with a width slightly larger than the pitch between the beams, then the installation will go flawlessly.
- Laying waterproofing. To protect the insulation from moisture, a waterproofing membrane is installed, followed by gluing all joint areas.
- Assembling the counter-lattice. It is necessary to create a ventilation gap between the insulation and the boardwalk. The frame is stuffed on top of the beams to a height of up to 4 cm.
Application of sprayed materials
In this case, polyurethane foam or ecowool is used. They are applied to the surface using special installations that ensure uniformity of the layer, dense filling of the space and high-quality thermal insulation.
Important! Using polyurethane foam, additional vapor and waterproofing is not required. It is enough to clean the surface well from foreign debris and blow it with foam.
Ecowool can be laid manually in a uniform layer 10 cm thick, then compacted and poured with new material until a dense material of a given height is obtained. Such events are carried out quite rarely, since the efficiency of special machines allows us to reduce the time and labor costs for completing the work. To prevent fibers from penetrating into the room, the ceiling is protected with a vapor barrier film, and the insulation itself is protected with waterproofing.
Laying bulk materials
This type includes vermiculite, sawdust, expanded clay and wood leaves, although the latter option is used extremely rarely due to its fragility and increased hydrophilicity. Work on installing insulation to cover the attic is carried out according to the following scheme:
- Laying a vapor barrier (overlapping film or membrane).
- Heat insulator mound. If expanded clay is used, then waterproofing is not required, as it repels moisture.
- Wind protection device. Required to block the outlet of warm air and protect against cold air.
- Installation of flooring from boards 20-30 mm thick for convenient movement and storage of things.
Sawdust must undergo antiseptic and fire retardant treatment before use. When mixed with lime in a 5:1 ratio, the material can be protected from rodent attacks. It is also recommended to make a solution of sawdust and cement in a ratio of 10:1 and fill the ceiling with an even layer.
All technologies for laying thermal insulation material are practical and popular in modern construction. However, there are many other products of natural and artificial origin that have thermal protection properties. The main selection criterion is the building construction material, since it is recommended to use appropriate types of insulation for concrete and wooden houses.
Thermal insulation with expanded clay
This method of insulation is more suitable where heat loss is not very large and the insulation layer can be of small thickness. Although expanded clay is a lightweight material, too much insulation layer puts a lot of pressure on the ceiling.
After laying the plastic film, the entire space between the ceilings is covered with crushed clay, onto which expanded clay is poured. For greater thermal insulation density, it is worth using expanded clay of fine and coarse fractions. It is necessary to fill the expanded clay very carefully so that there are no voids left.
Then the surface is leveled and a cement-sand screed is applied to protect the insulation layer from damage. Again, if you plan to use the attic space frequently, you should lay the floor from boards or other materials.