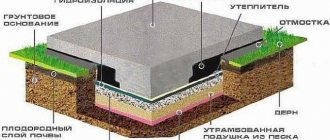
Under most old houses and under every new one, as well as under cottages built with the latest construction technologies, there is an underground floor - a basement, which the owners usually use to store vegetables, preparations, and seasonal items.
In modern buildings (brick or wooden house), the basement can be equipped as a functional living room, for example, an office, workshop, gym, home theater, billiard room, etc.
Regardless of its purpose, the basement can only be used if the temperature in it is comfortable. Even if the height of the basement does not allow you to arrange a full-fledged room in it, it still needs insulation, since thermal insulation of the basement is one of the effective ways to reduce heat loss in the house.
Is it necessary to insulate the basement?
From the description above, it becomes obvious that yes, it is better to insulate the basement. Let's give a few more arguments for those who doubt:
- effective use of usable area;
- the appearance of fungi and mold in the basement, which are a source of unpleasant odors and deterioration of the microclimate on the lower floor of the house, is excluded;
- the temperature in the insulated basement does not drop to below zero;
- insulating the basement in a house makes it possible to protect the foundation from dampness and deformation due to soil heaving;
- the rate of destruction of the building foundation is reduced;
- the consumption of electricity or gas for heating the house is reduced.
Note. If the basement is not insulated, according to GOST 9561-91 “Reinforced concrete floor slabs” it is necessary to insulate the floor that separates the floor of the first floor from the non-insulated area. The same requirement is specified in SNiP 2.08.01-85
For your information, the technology for insulating a cellar is similar, but has some differences.
Ventilation
The subfloor structure must have reliable ventilation in order to remove all water vapor that can penetrate into this space, both from the side of the house and from the ground.
A damp environment in the basement will lead to mold and mildew, which will sooner or later lead to the destruction of all the structures of the house.
In addition, in an unventilated underground room, carbon dioxide can accumulate, which is very dangerous for people living in the house.
The underground room must be equipped with natural ventilation created using two pipes: zinc or PVC. The first supply at a height of 0.5 m from the floor level is discharged into the basement, at a level of 40 cm from the blind area. The exhaust pipe is installed under the basement ceiling with a length of 0.5 m above the roof ridge.
If such ventilation was not carried out during the construction of the house, you will have to install supply and exhaust ventilation in the underground with an electric fan and an air duct system.
Types of basement insulation
Basement insulation can be done in several ways:
- internal insulation . Simpler, but requires work to eliminate moisture, otherwise the appearance of condensation will negate all insulation;
- external insulation . Allows you to prevent freezing of the wall from the outside. This method of thermal insulation is more rational, because provides better protection and does not reduce the usable space of the room, but it is more labor-intensive. As a rule, it is performed during the construction stage of a house;
- combined insulation . It is the most effective because it includes the installation of thermal insulation material and waterproofing of the basement on both sides.
The choice of method is determined by factors such as:
- humidity conditions;
- presence of heating in the basement;
- the presence of a drainage system around the basement;
- purpose of the basement.
Preparatory work
Preparation for cellar insulation consists of the following steps:
- Drawing up a project, calculating the need for building materials and tools.
- Removing communications, cleaning surfaces from fragile fragments, clearing and sealing cracks.
- Leveling walls and ceilings with cement mortar with the addition of plasticizers.
- Treatment of structures with antiseptic and primer.
To make work more comfortable and safer, a layer of sawdust and sand should be poured onto the ground around the cellar. To protect your hands, you should use fabric gloves.
Materials for basement insulation
First, the home owner must decide how to insulate the basement. There are many types of thermal insulation materials with very different characteristics on the construction market.
Let's consider the most popular insulation materials from the point of view of the feasibility of using them for thermal insulation of a basement:
- Styrofoam .
The cheapest and most accessible insulating material. For insulation, foam plastic with a density of 25 kg/m3 is used. Foam plastic is popular due to its properties: lightness, resistance to rotting, excellent thermal insulation characteristics, inability to absorb moisture, long service life. That is why insulating the basement with polystyrene foam is one of the most common ways to increase the thermal insulation characteristics of the basement. But we should not forget that polystyrene foam cannot be used in rooms with a high risk of fire in order to eliminate the possibility of a fire. This material is flammable and, most importantly, releases harmful toxic substances when burned;
- expanded polystyrene .
A more modern analogue of polystyrene foam. It has all the properties inherent in polystyrene foam, but is distinguished by a higher density (and therefore stronger), and the presence of a tongue-and-groove system. At the same time, expanded polystyrene is characterized by ease of mechanical processing (the sheet does not crumble when cut), resistance to stress and a higher price. Basement insulation with polystyrene foam is actively practiced because... this material is best suited for insulating the basement from the outside and inside;
- polyurethane foam . Sprayed thermal insulation material. The peculiarity of polyurethane foam is its ability to fill the smallest cracks. Polyurethane foam does not allow moisture to pass through, does not rot, does not burn, and ensures complete tightness of the room. Insulating the basement with polyurethane foam allows you to create a durable outer layer of insulation. Disadvantages include high cost and the inability to do the work yourself;
- mineral wool . Insulating the basement from the inside allows the use of soft insulation materials and only in the absence of moisture. Mineral wool is hygroscopic and, when wet, loses its thermal insulation properties;
- expanded clay Despite the fact that this is a bulk insulation, it has good thermal insulation properties. However, insulating a basement with expanded clay is only justified to insulate the floor in the basement and to protect the foundation from the outside, since expanded clay gravel (crushed stone) provides good drainage.
The insulation, its type and thickness, is selected individually for each specific case. The choice of thermal insulation material can be entrusted to a professional who will calculate the required thickness taking into account many factors. Or you can do the calculation yourself. To do this, you can use the recommendations that contain:
- SNiP II-3-79 “Construction heating engineering”
- reference book on heat and sound insulation designs. Basement walls and foundations;
- SNiP 23-02-2003 “Thermal protection of buildings”
And:
Thermal requirements for basement insulation
Studying the above documents makes it possible to highlight the main thermal technical requirements:
- heat transfer resistance (SNiP 23-02-2003). For Moscow – Ro = 4.15 m2•°C/W.
Dependence of the thermal conductivity coefficient of insulation and its thickness for internal basement insulation (table)
Dependence of the thermal conductivity coefficient of insulation and its thickness for external basement insulation (table)
- load perception (SNiP 2.01.07-85);
- heat resistance of the enclosing structure. Calculation of the amplitude of temperature fluctuations is based on the provisions of SNiP 23-02-2003;
- vapor permeability of the enclosing structure (SNiP 23-02-2003).
- fire safety requirements (SNiP 21-01-97, GOST 30247, GOST 30403).
The selected material leaves a significant impact on the choice of technology and determines what and how to properly insulate the basement in a private house.
How to insulate a cellar with foam plastic
Before insulating a basement from the inside with polystyrene foam, all its disadvantages and advantages are taken into account. Then, polystyrene foam 5 centimeters thick, grade PSB-25, is taken. For a long time, it allows you to maintain a stable temperature. No lathing is needed for its installation.
Further, the technology for carrying out the work is as follows:
- Sheets of foam plastic are glued to the brick or concrete surface of the walls using frost-resistant glue.
- Additional fixation of the joints is done with dowels with a wide head.
- A vapor barrier film is attached to protect against condensation.
- All joints are processed by gluing reinforced masking tape.
DIY basement insulation technology
Let's look at how complex basement insulation is carried out using penoplex (the technology will be similar for polystyrene foam and expanded polystyrene). Note that comprehensive thermal insulation includes external and internal insulation (in particular walls, floors, ceilings).
In addition to insulation for work you will need:
- material for interior decoration;
- polyurethane foam;
- reinforced polymer mesh;
- waterproofing material (bitumen mastic);
- adhesive solution;
- concrete or external plaster;
- tool.
Waterproofing requirements
Thermal insulation requirements
Requirements for plaster mortar
Peculiarities
A cellar refers to structures in which individual elements or even parts thereof are in different conditions, and therefore require a different approach to ensure constant temperature conditions and optimal humidity. This is explained by the fact that the walls of the cellar can be in full or partial contact with the ground, at depth or above the ground, the ceiling must provide protection from low and high temperatures from above, and the floor must be made taking into account possible flooding when groundwater rises.
Basement insulation from outside
Insulation of basement walls from outside
Recommendations and procedure for performing work:
- work is carried out only in dry weather and during the warm season. This guarantees minimal soil moisture near the foundation;
- Insulation work begins with excavation of soil near the foundation;
- then the foundation is inspected for the presence of cracks, peeling of waterproofing materials, significant irregularities, etc.;
- The first layer of waterproofing is applied. Experts recommend applying moisture-repellent mastic and applying it in a continuous layer;
- insulation is installed.
For external insulation of the basement, it is preferable to use polystyrene foam or polyurethane foam. Because These materials are distinguished by reliable adhesion to each other and long service life. The insulation is mounted in such a way that it is 500 mm. protruded above the foundation (above ground level). An important feature: when installing the insulation, umbrella dowels are not used, but only an adhesive solution. The solution is applied with a notched trowel, which makes it possible to evenly apply the adhesive to polystyrene foam or polyurethane foam and avoid the appearance of voids under the sheet. Also, the use of glue will prevent damage to the sheet. If there are gaps between the sheets, they are filled with foam;
- a second layer of waterproofing is applied. It is important to apply this layer to the surface of the insulation, which will be located in the soil;
- a drainage system is being installed. Drainage around the house is needed to ensure that water does not stagnate near the insulation;
- decorative design of the base (for example, plaster, siding).
How to insulate basement walls from the outside
Note. Installation of insulation from the outside is a mandatory component of the work on insulating basement walls. Because installing insulation inside the basement at high humidity will lead to the foundation being destroyed by water acting from the outside.
Reasons not to do this
Before making a decision about insulating the base from the inside, you should take into account the fact that this option is acceptable only for buried types, in which the underground part creates the basement of the household.
In construction practice , there are several good reasons why carrying out such types of work is inappropriate :
- According to calculations of the thermal insulation “pie”, it has been proven that reinforced concrete structures will still freeze, even with an insulating layer laid.
- The foundation will not be protected from temperature changes, which will lead to its destruction.
- In accordance with calculations, the “dew point” will be established at the “insulation-foundation” boundary, which will require additional means to create a vapor-tight and ventilation layer in the heat-protective “pie”.
Thermal protection of the foundation from the inside is a necessary measure, used only when an external thermal protection device is installed ineffectively or is impossible for good reasons and when calculations have proven that its use will lead to the thermal efficiency of the house.
Insulating the basement from the inside
Insulation of basement walls from the inside
Step-by-step instructions in the form of recommendations and rules.
It is advisable to install heat-insulating material indoors on all surfaces: walls, ceiling and floor. If the basement is intended to be left unheated (cold), it is necessary to insulate the heating pipes in the basement to avoid loss of coolant temperature as it passes through the basement.
Before insulating, it is important to ensure the basement is fully ventilated. The easiest way to arrange air exchange is to make two holes on opposite walls of the basement.
Ventilation hole in basement wall
Insulation of basement walls from the inside
The work procedure is largely similar to external insulation:
- a polymer mesh is attached;
- applying waterproofing. In order for the primer to dry, it is necessary to provide ventilation in the basement;
- check the walls for deformations, irregularities (which cannot be leveled with the adhesive mixture), and protruding parts;
- a heat insulator is installed;
- plaster intended for interior work is applied.
When using another finishing material, appropriate preparatory work is carried out, for example, arranging the frame when finishing with plasterboard.
Insulation of a cold basement ceiling
Thermal insulation of the ceiling is mandatory for any method of insulating the basement. Because Insulating floors on the basement side allows you to reduce the temperature difference between the floor of the room in the house and the air in it. The order of work depends on the type of ceiling that is installed between the first floor and the basement.
For wooden floors:
- polystyrene foam (foam or penoplex) is installed;
- the ceiling is inspected;
- penofol is installed - a foil film that will reflect heat into the room;
- finishing work is being carried out.
How to insulate a basement ceiling
Reinforced concrete floors require the installation of a false ceiling, the purpose of which is to reduce heat loss through the concrete. A false ceiling is a suspended ceiling - a ceiling structure with a heat-insulating layer of considerable thickness (subject to subsequent decorative finishing).
Basement floor insulation
The main task of thermal insulation of the floor is to prevent heat from escaping from the basement into the ground. Even if we are talking about an unheated basement. When choosing how to insulate the floor in the basement, you should take a closer look at two options:
Option 1. Floor insulation with expanded clay or “floor on the ground”
Scheme of floor insulation in the basement on the ground
Expanded clay is poured onto the floor, leveled, and a metal mesh is laid on top of it and a layer of lean concrete is poured. To avoid the displacement of expanded clay during movement, a frame is made from treated timber, into the cells of which expanded clay gravel is poured or metal beacons are installed (if the layer is thin). The filled expanded clay is leveled using the rule. After this, the floor is waterproofed and the floor is screeded.
Option 2. Floor insulation with polystyrene foam
Insulation of the basement floor with penoplex (at the stage of building a house)
Basement floor insulation with polystyrene foam
In this case: the floor in the basement is leveled, rigid polystyrene foam slabs are laid on it, waterproofing (for example, roofing felt) is placed on the slabs so that the edges of the panel extend 150 mm onto the wall. After this, a concrete screed 30-50 mm thick is poured, which is recommended to be reinforced to prevent deformation of the heat-insulating cake.
Waterproofing the floor in the basement of a private house
Pouring screed on the floor in the basement
Insulating doors in the basement
The last stage, which will prevent the flow of cold air from the unheated basement through the doors into the rooms on the first floor of the house.
A good method of action when insulating basement walls
We will exclude from this description a detailed study of preparatory work, but we will note those that need to be done first:
Firstly, treatment of wall sections covered with thermal insulation. It should be done using modern deep impregnations with the addition of antiseptics that prevent the formation of mold and fungi.
Secondly, perfect leveling of the walls when working with extruded polystyrene foam is not required. However, cracks should be repaired, significant protrusions and depressions should be smoothed out, and other major imperfections should be removed.
Thirdly, it is necessary to prepare channels for ventilation of the basement in advance in the structure. To make it easier to regulate the flow of clean air, you can choose devices with bimetallic drives. They automatically open/close holes when the temperature changes, and perform all their functions without power supply or additional settings.
Fourthly, at this stage it is necessary to install a soil water drainage system. To create drainage, pipes made of specialized membrane fabric are used.
Choice of insulation
Many materials are used to insulate the floors of a wooden house. The simplest and most inexpensive is expanded clay or sand, which is poured between the rough and finishing coating. They are hygroscopic and protect the boards from rotting, the spread of fungus and provide ventilation. However, bulk non-metallic insulation has its own drawback - over time, their hygroscopicity decreases.
Today on the market you can find many materials for insulating a wooden house. In addition to good thermal insulation, it must meet basic requirements:
- ecologically pure;
- be safe for the residents of the house;
- long service life.
For insulation, fiberglass, mineral wool, penoplex, expanded polystyrene, etc. are used. Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages:
o Mineral wool. It can be slag, stone and glass. The form of release is also varied - plate, roll, mat. Mineral wool has a high density, does not burn, conducts heat poorly and is quite economical. The main disadvantage is considered to be low moisture resistance.
When using mineral wool, you should carefully consider the vapor barrier system and ventilation. The side of the stove that is not covered with foil should be on the bottom.
When purchasing mineral wool, carefully read the composition, since the impregnation often contains substances hazardous to the body. The more saturated the yellow color of the material, the more dangerous it is.
The following are more in demand in construction stores:
- Izovol is a mineral fiber product. A distinctive feature is its high hydrophobic efficiency in comparison with conventional mineral wool. Additionally, it has low thermal conductivity, is non-flammable, biologically and chemically resistant.
- Rockwool is a basalt tile. Its peculiarity is that it does not cake, does not lend itself to deformation and shrinkage, like mineral wool. Rockwool resists mechanical stress well. The material is additionally used for sound insulation, since the porous structure absorbs noise well at any frequency. Like Izovol, Rockwool conducts heat poorly, does not burn and is resistant to biological and chemical influences.
- Expanded polystyrene - has a high thermal insulation rate. It is resistant to moisture and does not absorb water, holds its shape well under temperature changes, is durable, environmentally friendly, durable and is not subject to the destructive effects of microorganisms. Expanded polystyrene is easy to process and use.
- Penofol is a modern heat insulator. Sold in rolls, it is insulation with a layer of foil. The thickness and weight are small. The base may vary, but in most cases it is penofol (foamed polyethylene). Thermal insulation properties are maintained under high mechanical load. Laying occurs overlapping or butt. The seams must be taped with metallized adhesive tape. Penofol does not require an additional layer of hydro- and vapor barrier, since the foil already performs these functions.
- Ecowool is a natural heat insulator made from cellulose. The fibers are bound with boric acid and lagnin (an organic antiseptic). The uniqueness of the material is that it does not absorb water and removes it outside. The composition contains no components hazardous to health. Ecowool is fire- and bio-resistant, absorbs sound well and does not conduct heat. A special sprayer is used for application, but the material consumption then increases by 40%.
- Isolon is a new material in construction. With a thickness of 2-10 mm, it insulates well heat and sound, has high moisture resistance, is not subject to rotting and is durable.
For insulation, ordinary sawdust can be used. This heat insulator has been used for many centuries. The natural material is quite cheap and completely safe for the body. Sawdust is often left behind after building a house. This is the most affordable insulation for a wooden house.
Sawdust is added to some building materials:
- sawdust concrete consists of sawdust, cement, sand and water;
- granular heat insulator - sawdust, glue and antiseptic-fire retardant;
- wood concrete – sawdust with cement and chemical additives;
- wood blocks - sawdust, cement and copper sulfate.
Microclimate of the underground room
Room thermometer
In order for the operation of a constructed building (residential building, barn, barn, etc.) to be successful for a long time, it is necessary to ensure a certain microclimate inside the basement (subfloor) located under such a building.
The microclimate inside any room depends on the combination of a number of parameters of the air environment in this room, such as temperature and humidity, as well as the frequency of air exchange carried out by the ventilation system.
Temperature
The subfloor in a wooden house can be cold or warm, which is determined by the nature of the use of the house.
If this is a country house that is used periodically, then the subfloor is made small and cold, without laying utility networks and installing equipment in it. Insulation in this case is done only on the floor covering, so that cold air from the underground does not enter the premises of the first floor.
In houses of permanent residence, the underground floor is made warm, for which the foundation, basement, underground floor and floor of the first floor are insulated.
Humidity and air exchange
Humidity in the underground and air exchange are two interrelated parameters.
In the cold version, there is no connection between the air inside residential premises and the underground air. Ventilation of the underground space is carried out through ventilation holes provided in the foundation (basement) of the building.
When the underground is warm, air circulates between the premises of the residential building and the basement. Ventilation is carried out through openings provided in the floor of the first floor.
To reduce heat losses, the foundation and other underground elements are insulated.
Insulation and sealing of the first floor ceiling above the ventilated underground
It is very important that the ceiling above the ventilated underground is provided with reliable wind protection from the outside. To do this, skull blocks or strips from scraps of OSB boards are nailed to the floor beams from the outside, which in turn hold the subfloor made of lining or OSB 9 mm thick
The subfloor serves as a support for windbreaks and thermal insulation boards. Special vapor-permeable membranes sold in rolls are used as wind protection. Windproof material is stapled to the floor beams and then pressed using slats for a more secure fit. See fig. 14 and 15.
Fig. 14. Insulation and sealing of the first floor ceiling above the ventilated underground.
1 – OSB 9 mm2 – Windproof membrane3 – Pressure strip4 – Vapor barrier To ensure that the subfloor slabs are not exposed to fungi and other microorganisms as a result of excessive dampness, the underground must be well ventilated.
Fig. 15. The connection of the first floor ceiling above the ventilated underground to the foundation strip.
1 – Windproof membrane2 – Sub-floor made of clapboard3 – Skull block4 – Insulation from bitumen or roofing felt5 – End beam6 – Mineral wool carefully cut and laid vertically7 – Windproofing of walls8 – Pressure strips9 – Vapor barrier of the wall10 – Vapor barrier of the ceiling11 – Embedded bars for installing OSB The key point in installation of thermal insulation and sealing of the first floor floor is that the installation occurs from the upper surface of the basement floor. Those. Before installing the OSB subfloor of the first floor, it is necessary to purchase and install hydro-wind insulation, insulation and vapor barrier. This is not always possible, especially due to bad weather conditions during construction. Therefore, it is recommended to provide embedded bars in the floor frame for fastening OSB, and install load-bearing walls directly on the floor beams. See fig. 15, paragraph 11. In this case, all of the above actions can be performed after the final assembly of the house.