In rural areas, wooden houses are in most cases built without a design. The owners independently decide how many floors there will be in the new building and their area. There is only one problem: how to heat. No one has canceled winter. Russian stoves have gone into oblivion - there is no suitable brick, the craftsmen have disappeared, and it is not prestigious. The only thing that can be installed is a fireplace. But they won’t heat the house.
What remains is a water boiler running on solid or liquid fuel, natural gas or electricity - heating is carried out by converting electrical energy into heat. At the same time, the water boiler can be used for traditional heating, using batteries, and progressive, using pipes with a liquid coolant running through the floor pie. Everyone knows about heating homes with batteries. Few owners talk about a “warm floor” in a wooden house.
The editors of the StroyGuru portal decided to fill the knowledge gap and prepared an article on how to make a heated floor in a wooden house.
Warm floor without concrete screed
Warm water floor pipes are usually placed in a concrete floor screed. In a private wooden house, and in other houses with wooden floors, it is advisable to make a warm floor with a water heating circuit without a concrete screed. This type of floor is often called a dry heated floor.
Elements of a dry heated floor are lightweight and do not create significant loads on wooden floor beams. A dry heated floor has a low height. When installing the floor, there are no wet processes for pouring the concrete screed; there is no need to wait for 28 days for the concrete screed to harden and dry.
For these reasons, it is advantageous to use dry heated floors both in new construction and in existing houses with wooden beams and wooden floors.
You can read about other advantages and features of heated floors in a private house in the article “Do I need heated floors in a private house? ”
A feature of a dry heated floor, compared to a floor with a concrete screed, is its lower thermal power.
The amount of heat transferred into the room does not exceed 60-80 W/m2 of floor area.
The heat storage capacity of a dry heated floor is also low. Due to its low weight, a dry heated floor warms up faster and reacts to changes in coolant temperature.
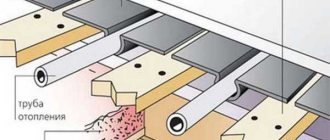
The design of a dry heated floor in a wooden house is shown in the figure:
In the picture: 1 Pipes of “warm floor”. 2 Reflector – heat distributor, galvanized corrugated sheet. 3 Beams. 4 Insulation (expanded polystyrene, density - no less than 25 kg/m3; thickness - no less than 50 mm or mineral wool boards); 5 Vapor barrier - glassine, polyethylene. 6 Subfloor compatible with “warm floors”. 7 Finishing the ceiling. 8 Damper tape with a thickness of at least 5 mm. 9 Skirting board. 10 Floor panel on cranial bars.
If a dry heated floor is installed on an interfloor floor, then attention should be paid to soundproofing the floor from impact and airborne noise. For information on protecting floors from noise, read the articles “Attic floor on wooden beams” and “Floating floor - soundproofing of interfloor floors” . To protect against impact noise, the subfloor, pos. 6, must rest on the beams, pos. 3, through elastic pads.
As a subfloor, pos. 6., it is convenient to use cement-bonded particle boards (CSP) or gypsum-bonded particleboards, moisture-resistant (GSPV). The relatively large mass and thermal conductivity of the subfloor made from such slabs will ensure more uniform heating of the surface, promote heat accumulation, and improve the protection of the floor from impact noise.
In addition, DSP and GSPV do not contain harmful substances, unlike oriented strand board (OSB) and particle board (chipboard) and plywood - read: “Formaldehyde in the house.” It should be borne in mind that when heated, the release of deadly formaldehyde from OSB, chipboard and plywood increases.
A reflector-distributor made of galvanized corrugated sheets allows you to evenly distribute heat over the entire surface of the floor.
The depth of the flooring profile should be equal to the diameter of the underfloor heating pipes.
When installing a heated floor in the basement, a vapor barrier film should be laid on top of the insulation layer.
The construction market offers dry floor heating systems with water or electric heating from different manufacturers. Such systems have better technical parameters, but they are also more expensive.
Preparatory work
A warm floor in a wooden house begins with installing a boiler, choosing a scheme for releasing excess pressure, and with it water, and mounting the pump and manifold to the wall.
Further preparation depends on the status of the building. Residential: all preparatory work is discussed in this section. New construction - classified as basic installation operations. Installation of a gas boiler is possible inside a residential building, in one of the rooms. For solid fuel boilers, as well as those operating on diesel fuel, a separate technical room (annex, basement) is required.
It is more difficult for the home master to choose a pressure relief scheme. They come with open and closed circuit. Let us note that over a long period of work in construction, experts cannot cite the advantages of an open system. But here are the cons:
- moving the expansion tank to the top of the building, which is the attic, requires its insulation;
- it is necessary to constantly monitor the coolant level and add it regularly;
- boiler pressure is limited;
- metal corrosion due to contact with oxygen.
Advantages of a closed system:
- contact with air is completely limited - there are no oxidation processes (nothing rusts);
- expansion tanks compensate not only for boiler pressure, but also for expansion of the coolant under the influence of high temperatures;
- you can use antifreeze, which is important when people do not live in the house permanently;
- expanders can be placed anywhere, including next to the boiler;
- The boiling point of the coolant, due to increased pressure, shifts from +100oC to +120oC;
- high pressure makes the pumps easier to operate.
Conclusion: if you don’t want problems during operation, you need to install a closed system for compensating for water expansion.
Closed water heating system.
At the next stage, the pump and manifold are mounted on the wall. The boiler is connected to them. The connection is made with pipes of larger diameter.
Preparatory work in a residential building
Immediately before assembling the heating system in a residential building, you need to:
- remove furniture from the premises;
- remove the baseboards;
- remove old flooring;
- inspect the wood in the subfloor;
- replace rotten elements, additionally attach boards to the skull block, etc.;
- seal the gaps between the boards and holes from fallen knots;
- treat the wood with an antiseptic;
- prime the surface;
- carry out waterproofing work. Detailed instructions can be found in the work “Waterproofing a floor in a wooden house.”
More details about preparing the subfloor for further work can be found here.
Dry warm water floor on polystyrene foam boards
Another lightweight design of a dry heated floor is shown in the following figure:
1 – floor covering; 2 – prefabricated dry screed for the floor from gypsum fiber board sheets (see link to the article above); 3 – vapor barrier (polyethylene film 100-200 microns thick); 4 – heat-distributing metal plates with a heating pipe for a heated floor; 5 – polystyrene foam boards; 6 – subfloor; 7 – damper tape.
This floor can be installed on any flat surface, even over an existing floor when reconstructing a room.
The procedure for installing a “dry” heated floor is as follows:
- A hydro-vapor barrier is laid on the subfloor - a polyethylene film 200 microns thick, with an overlap at the joints of at least 10 cm and the joints are taped.
- A damper tape is installed on the walls around the perimeter of the room.
- Profiled polystyrene foam boards are laid on the floor.
- Heat-distributing metal plates are inserted into the profiles of polystyrene foam boards in straight sections.
- The heating pipe of the heated floor is placed in the prepared recesses.
- The entire laid system is again covered with a polyethylene film with a thickness of 100-200 microns.
- A dry prefabricated screed is mounted on top. The installation of a floor with a dry prefabricated screed is described in detail in the article at the link.
To install the screed, as in previous cases, it is better to use cement-bonded particle boards (CSP) or gypsum-bonded particleboards that are moisture-resistant (GSPV).
| Heat distribution plate made of galvanized iron or aluminum. The width of the plate is selected depending on the pitch of laying the heating pipe |
A factory-made dry heated floor system includes a set of materials: profiled polystyrene foam boards and heat distribution plates made of aluminum or galvanized steel. Sets of materials for installing dry heated floors of various modifications and manufacturers can be found on the construction market.
This system is by far the easiest floor heating solution. But the floor height will be slightly higher than that of a wooden system.
You can make profiled insulation boards for dry heated floors yourself.
To do this, smooth thermal insulation boards (expanded polystyrene, penoplex, etc.) are laid on the subfloor. A route for laying heating materials is drawn on the surface of the slabs. Then, using a special thermal knife, U-shaped channels are cut along these lines, into which thermal distribution plates are laid, and then loops of heating pipes.
How to make profiled insulation boards yourself, watch this video:
Features of the flooring system
The traditional version of a water-type floor involves installing pipes in a screed. It is poured with a concrete solution with special additives that increase its thermal conductivity.
As a result, the concrete pad becomes a kind of heat accumulator, which makes it possible to use such heating as efficiently as possible. However, the traditional arrangement method has disadvantages.
The wooden base has low thermal inertia, which prevents the system from functioning normally. To correct this drawback, heat-reflecting plates are installed from metal with high thermal conductivity.
The most obvious is too much weight of the concrete screed. With a solution density of about 2000 kg/sq. m it gives a significant additional load on the base and load-bearing structures.
For reinforced concrete slabs, such a load is quite feasible. For wooden floors - prohibitive. For this reason, the traditional installation method is prohibited in such cases. The so-called flooring system is used here.
It is made in the form of a low flooring, inside of which pipes are located. Wood is most often used for its arrangement, but industrially produced polystyrene flooring has appeared relatively recently.
The pipes are placed in grooves where they are secured. It is known that wood conducts heat very poorly. For this reason, wooden systems cannot be an effective source of heat.
To correct this deficiency, metal heat-conducting elements are inserted into each groove. They also strengthen the structure. There are similar details in polystyrene flooring with metal inserts, the material of which is also a poor heat conductor. In this way, a reliable and durable heating system is assembled.
Its advantages over its traditional analogue can be considered:
- Light weight of the flooring, which even wooden floors can withstand.
- Relatively simple assembly, especially when it comes to industrial flooring models.
- There is no need to wait for the concrete screed to harden. Finishing work can be done immediately after installation.
- Full maintainability. To carry out repair work, it is enough to lift a fragment of the flooring to provide access to the area with the fault.
Another undeniable advantage of the flooring system is its versatility, which makes it possible to implement a variety of modifications. Most of which are homemade. The main disadvantage of the flooring scheme is rapid cooling. The floor heats up in a short time and gives off heat just as quickly.
A big plus of a water-based floor is the possibility of relatively simple repairs. To get to the damaged fragment, it is enough to remove a section of the floor covering and remove the flooring underneath it
Actually, the heat supply is limited to that which is in the coolant liquid in the pipes. Therefore, when the boiler is stopped, the room will soon cool down. For this reason, deck systems are more often used as an addition to the main heating system, especially in cold regions.
Dry heated floor on slats
Instead of profiled polystyrene foam boards, various molded materials can be used as the base of a dry heated floor:
edged boards, as well as slats cut from various structural boards: cement (CSP) and gypsum particleboard (GSPv), gypsum fiber (GVLv), etc.
As mentioned above, you should not use oriented strand boards (OSB) and chipboards (chipboards), as well as plywood, for flooring. When heated, these materials constantly release life-threatening formaldehyde gas .
The slats must be at least 20 mm thick and have a moisture content of no more than 10%. In the figure: 2 - floor covering (TsSP, GSPV, GVLV slabs); 5 – support rails; 8 – insulation.
The width of the slats is selected depending on the pitch of laying the heating pipe in the floor: 130 - 280 mm, the spread (gap for the pipe) between the slats should be exactly 20 mm (for pipe d=16). Where the pipe turns, the support rails must be rounded.
The slats of the support layer can be laid either directly on the joists (across the joists) or on a rough wooden floor. Laying directly on joists will reduce the height of the floor.
When laying support slats directly on the joists, the distance between the joists should be no more than 600 mm if the finishing floor covering is parquet, laminate, linoleum or carpet, and at least 300 mm apart if the floor is made of ceramic tiles.
To ensure uniform heating of the entire floor surface, the heat distribution plates must be located under 80% of the heated floor area.
Preparation for installation
When installing on the ground, a rough screed is poured at the preliminary stage.
Pour a sand and gravel cushion, put waterproofing (polyethylene or roofing felt) on it, pour in the solution, level it and wait for the concrete to set. When installing without a screed, remove the floor covering. If the floor is in order and there is a layer of insulation under it, which is also in order, you can begin installation.
If the subfloor is rotten and there is no insulation between the joists, the boards are removed. If necessary, dismantle the logs.
- Lay a waterproofing film.
- The insulation boards are installed tightly spaced between the joists.
- On top is a vapor barrier film with low vapor permeability or polyethylene laminated with foil. The foil film is placed on top with the reflective surface, the vapor barrier film is placed on the rough side (discharge).
- Either chipboard sheets with ready-made grooves for pipes are installed on top, or moisture-resistant plywood is placed, which will be the basis for installing polystyrene foam mats.
Warm water floor in a prefabricated dry floor screed
A warm water floor can be placed in a prefabricated dry floor screed. The design of a floor with such a screed is described in the article “Floor with a dry prefabricated screed .
Water-heated floor without concrete screed in a wooden house.
To install a dry heated floor, a prefabricated dry screed is made from three layers of gypsum fiber (GVL) or plasterboard (GKL) sheets.
The heated floor pipe is located in the middle layer. The pipe laying route is applied to the surface of the lower layer of slabs laid in the floor. Next comes the strips of slab material. They are screwed using self-tapping screws to the first layer of gypsum plasterboard so that grooves are formed for the heated floor pipe with a depth equal to the diameter of the pipe.
Heat distribution plates and a heating circuit pipe are placed in the grooves. Then the top layer of sheets is laid, and then the finishing coating (for example, laminate). As the top layer of the screed, it is better to use cement-bonded particle boards (CSP) or gypsum-bonded particleboards that are moisture-resistant (GSPV).
Is it possible to save on materials?
Since components for underfloor heating without a screed cost a lot of money, many craftsmen have found ways to do without them:
- Place the heating branches inside the ceiling, directly on the insulation. Then Ω-shaped products are not used.
- Make the cutouts in the boards yourself, and instead of the plates, roll out aluminum foil used for baking along the length of the grooves.
- Make steel heat spreaders yourself using metalworking equipment.
- You can also make a wooden system for laying pipes in grooves yourself, for example, from chipboard sheets.
Of the listed options, only the last 2 will allow you to save money and at the same time organize efficient heating. Indeed, on a sheet bending machine you can make plates from any metal, only the profile of the groove will be rectangular and not “omega-shaped”.
Piping inside ceilings is still practiced today.
When pipes are laid inside a wooden structure, they have poor contact with the finishing coating and heat the air around them more than the room. For such heating to have an effect, the tubes must be laid at a distance of 10 cm from each other, and the coolant temperature must be raised to the maximum. Then the idea loses its meaning; it’s easier to install radiators.
Thin aluminum foil serves as a poor distributor of heat flow due to its thickness of hundredths of a millimeter. In addition, it crumbles over time due to gradual oxidation, so there is no point in using foil.
Master craftsmen independently make grooves for pipelines and roll out rolls of aluminum foil into them
There is another way to save money - to organize heating of a wooden house with electric heated floors using infrared film heaters. But such a system will lose its versatility, that is, you will be able to use only electricity for heating, and you will have to forget about gas or wood.
Floor without heat distribution plates
All design options for a dry heated floor can be made without laying heat distribution plates. The heating pipe is placed in the grooves, securing the pipe with clamps made from pieces of plastic tape and self-tapping screws.
In a prefabricated dry floor screed, the groove with the pipe is filled flush with gypsum mortar.
Due to the absence of a metal reflector - a heat distributor, the disadvantage of such a simple design of a dry heated floor will be some unevenness in the temperature of the floor surface. The floor will be underheated in the spaces between the pipes, and the thermal power will be lower - no more than 50-60 W/m2.
Household products
⇆
In floors without heat distribution plates, it is recommended to reduce the pipe pitch to 150 mm. It is highly desirable to increase the flow through the pipes to a temperature difference of dt=5 °C, instead of dt=10 °C in the usual case.
This option is quite suitable for a comfortable heated floor, which slightly warms the surface and provides a pleasant feeling when a person is on the floor. Radiators provide the bulk of the heat in winter.
Creating a subfloor
Many people confuse subfloors with the subsurface that serves as the installation for the flooring. The basis is considered to be substrates made from any sheet materials: plywood, chipboard and others, or from boards installed on joists. They are intended only to level the base coating for an even, high-quality installation of the floor covering. They are also used for uniform distribution affecting weight overlap.
The subfloor is considered to be the very first layer from the bottom (a layer of a two-layer base made of boards). This layer is required for laying on beams or floor joists if there is a fairly large distance between them, while the rough boards are laid diagonally with the finishing boards. The implementation of the technique makes the strength of the floor stronger, due to the multidirectionality of the wood fibers of the layers.
Heated floor pipe laying schemes
Laying pipes according to the “Double Snake” or “Snail” schemes ensures more uniform heating of the heated floor surface.
For installation in a dry water heated floor, pipes made of cross-linked (PE-X) or heat-resistant (PE-RT) polyethylene are best suited.
If the house has a cast iron or steel boiler, a boiler with a steel heat exchanger or steel radiators, then to protect them from corrosion it is necessary to use a polyethylene pipe protected from the penetration of oxygen, with the addition of EVOH in the marking. If all metal parts of the heating system are made of copper or stainless steel alloys, then there is no need to use such pipes.
I recommend using metal-plastic pipes specifically designed for heated floors. Such pipes are cheaper.
Warm floors are most often made from pipes with an outer diameter of 16 mm. As a rule, this pipe diameter is enough to heat up to 20 m2 of floor area. The longest side of the area on which the pipe is laid should not be more than 8 m. If the dimensions of the room exceed the specified values, then the floor is divided into parts, in each of which a separate circuit, a pipe loop, is laid. It is recommended to lay the pipe in the loop in increments of no more than 200 mm.
How is the finished floor laid?
After laying the vapor barrier layer, it is necessary to lay the finishing layer, which consists of milled boards with holes for air circulation. These holes are located on the back side of the board and have a size of 40x140 mm. They need to be applied in such a way that the annual rings of the wood face in different directions.
Milled boards can be replaced with tongue-and-groove boards or trapezoidal slats. Their disadvantage is that they do not have air flow, so when applying them you need to monitor the quality of their fit on the joists.
Pump-mixing unit and underfloor heating manifold
The mixing unit with circulation pump is on the left.
On the right, a manifold of underfloor heating pipes is connected to the mixing unit. Each room with a “warm floor” is at least one circuit (one pipe loop). All these circuits must somehow be combined into one and connected to a boiler or other heat source. Both ends of the pipe of each heated floor circuit are connected to the manifold.
The underfloor heating collector must perform three tasks:
- Turn off and shut off the water supply to each individual underfloor heating loop.
- Adjust the coolant flow in the floor heating loop depending on the air temperature in the room or the temperature of the floor surface.
- Adjust the hydraulic resistance of the heated floor loop in order to balance it and make it the same in all circuits connected to the manifold.
To accomplish these tasks, there are manually operated shut-off valves on the supply side of the manifold. Control valves with a servo drive are installed on the return side. The valve is controlled through a servo drive by a thermostat, which regulates the supply of coolant to the heated floor circuit depending on the temperature of the floor surface and the air temperature in the room. With the same valve, using a special key, the hydraulic resistance of the heated floor loop is adjusted.
Heated floor pump-mixing unit
The maximum temperature of the coolant in the underfloor heating system should not be higher than 45-55 oC. For a heating system with radiators, the water temperature must be higher. Heating boilers are also designed to operate with a higher coolant temperature.
The pump-mixing unit performs the following functions:
- It lowers the temperature of the coolant that comes from the boiler through a direct pipeline by supplying it with cooler water from the return (admixture).
- Provides circulation of coolant in the loops of underfloor heating pipes. The underfloor heating system has high hydraulic resistance, which requires the installation of a separate pump to overcome.
- Protects floors from overheating - if overheated coolant enters the floors, the circulation pump will stop.
The maximum temperature of the heating water supplied to the underfloor heating pipes is set by the valve at the inlet of the mixing block.
Installation of the circuit on a wooden base
We have already written a lot about the layout of the water circuit pipes and its connection to the boiler or existing heating. In this regard, the type of base does not play any role, and these works are performed in the same way. There are only different ways to create a floor pie, and in the case of a beam floor there are also several popular methods.
Laying plywood on a wooden floor
Automatic temperature control in the house
In the homes of thrifty Europeans, heating systems are necessarily initially designed, and then immediately built with an automatic temperature control system in the house. A German or a Pole knows and understands that without automation it is impossible to ensure economical gas consumption and an acceptable level of thermal comfort in the house.
In Russia, owners often begin to realize the need for automatic temperature control after the house is built, the heating system is already installed and working, and gas bills begin to arrive.
It turns out that outside the house the air temperature, direction and strength of the wind are constantly changing. Day and night, the outside air temperature, even during the day, often changes by ten degrees. The house sometimes blows through, sometimes not, the wind is changeable. The sun is inconsistent, sometimes it heats the house, sometimes it doesn’t. Heat loss at home constantly fluctuates by different amounts. In order not to bother with all this leapfrog several times a day, the owner of the house manually sets the temperature on the boiler to a higher temperature, so that the temperature in the house is warmer, with a margin. And at the end of the month he looks longingly at the gas bill and scratches his turnips.
The owner learns that in order to equip the house with automatic temperature control, it is necessary to throw out some things, replace and redo the heating system, and install additional equipment. And for this you will have to drill, chisel, and lay again. That all this automation would have been much cheaper if it had been installed immediately during the construction of the house.
In a house with a dry heated floor, it is necessary to have
three automatic temperature control systems: a heated floor based on the air temperature in the room with a limitation of the floor temperature;
radiators based on room temperature; boiler based on outside air temperature. As you know, a warm floor can be either “comfortable” or “heating”.
"Comfortable" heated floor
slightly warms the surface and provides a pleasant feeling when a person is on the floor. The main heat supply to the room is provided by radiators. For a comfortable heated floor, it is necessary to maintain a constant temperature of the coolant.
"Heating" heated floor,
In addition to comfort, it provides complete heating of the room.
The relatively small thermal power of a dry heated floor makes it most often suitable only for comfortable heating.
The room temperature sensor is located in the thermostat housing.
In a house with a comfortable dry heated floor, it is necessary to have three automatic control systems to control the temperature .
One system that regulates the operation of a warm floor must be controlled by the air temperature in the room until the temperature of the floor surface reaches a comfortable level. That is, in the off-season the house will be heated with the heat of the heated floor.
the automatic radiator control system comes into effect . Radiators will heat the air in the room, adding their heat to the heat that will constantly come from the heated floor.
The heating mode of the coolant by the boiler must be regulated by another automatic system that responds to the outside air temperature .
Considering that the underfloor heating system has a high inertia (it heats up slowly and cools down slowly), it is recommended to use weather automation to control its operation. Then the temperature of the coolant supplied to the system will be adapted to the outside temperature. Due to this, along with changes in outside temperature, the temperature of the coolant circulating in the floor changes.
When adjusted using a room thermostat, the temperature of the coolant in the system will not change until it begins to rise in the room (due to warming outside). Only after this the temperature of the coolant will begin to decrease, but due to the inertia of the system, the room will already become hot (i.e., waste of energy).
Therefore, in order for home heating to be economical, a weather controller must be used in the underfloor heating system to control it.
To regulate the temperature of the heated floor, it is necessary to select and install a manifold equipped with servo drives on the control valves.
A servo drive is a device that, when electrical current is supplied to it from the thermostat, acts on the valve, opening or closing it. The servo acts as a switch, completely opening or closing the valve. The surface temperature of the heated floor will be maintained with an accuracy of +/- 0.5 - 1 °C.
Laying concrete on the ground
Initially, you need to determine the desired floor height and mark it with a cord, wrapping it around pegs. This level will indicate to what extent the concrete needs to be poured. Then the layers are laid and compacted:
- gravel is poured to the level of the pegs, which will be removed in the future;
- a layer of sand is compacted on top of the gravel;
- the next layer will be a polyethylene film, which plays the role of a waterproofing agent.
Concrete is poured onto a film, the edges of which are higher than the concrete level, leveled and covered with another film for quick hardening. For maximum strength of concrete, it should not be subjected to physical stress for about a month. To create a screed, after the concrete layer has completely hardened, it is necessary to apply liquid cement.
Thermostats for heated floors
A thermostat is a device that measures the temperature of something, compares this temperature with a predetermined temperature and, depending on the result of the comparison, commands the servo drive to turn the control valve on or off. Thus, by turning on or off the heat supply, the thermostat maintains the temperature of something with minimal deviations from the set value, usually with an accuracy of +\- 0.5 oC.
To measure temperature, the thermostat may have a temperature sensor built into the body of the device. The temperature sensor can also be remote. The remote sensor is connected to the thermostat by wires.
The thermostat always has buttons or wheels with which you set the temperature, the stability of which it must ensure. All thermostats have an indication of the current state - “heating on” or “heating off”.
The thermostat, depending on the method of connection with the actuator, can be wired or wireless.
The lowest budget option is a wired thermostat. The device itself is installed in a room in which it must maintain temperature. A heated floor collector with servo drives can be installed in another place, for example, in a boiler room. These devices are connected to each other by thin wires.
The wireless thermostat transmits a control command to the collector servo drive via a radio channel. To do this, there is a radio transmitter in the thermostat housing, and a radio receiving unit is installed near the collector. Installing a wireless thermostat can be beneficial when automation work is carried out in an already built house - there is no need to lay wires and disturb the finishing of the premises.
To regulate the air temperature and the temperature of the heated floor in accordance with the algorithm - we regulate the air temperature in the room, but do not allow the floor to heat up above the set temperature, you need a thermostat that has the appropriate functions.
Thermostat for underfloor heating:
- Must work with two temperature sensors: a built-in air temperature sensor and an external heated floor temperature sensor.
- The thermostat should have the ability to set the air temperature and the heated floor temperature separately.
- There must be a control algorithm based on air temperature with a limitation on the surface temperature of the heated floor.
One thermostat can control several actuators mounted on one manifold. The thermostat and servo drives are connected through a special unit - a switching module.
More Articles on this topic:
⇒ Do you need a heated floor in a private house ⇒ Do-it-yourself floor with a dry prefabricated screed
More articles on this topic
- Setting up gas boiler power adjustment
- How to make a roof from corrugated sheets on the roof of a house
- How to reduce the high gas consumption of a boiler for heating a house
- Checking the effectiveness of ventilation in a house or apartment according to GOST
- Renovation and redevelopment will change your life for the better!
- Calculation of wall heat transfer resistance
- External three-layer stone wall with brick cladding
- Calculation of a wooden attic beam
House with strip and monolithic foundation
The heating system is provided already during the construction of the foundation. With a strip or monolithic base of the house, not only radiator heating will be effective, but also floor heating. The foundation is insulated with gravel, expanded clay, and insulating materials. Perform waterproofing.
A well-prepared base does not have high heat losses. Heating elements for “warm floors” in the house are laid on a concrete surface. Both liquid and electric heating are used.
Liquid floor line
The system is a pipeline through which coolant circulates. It is heated in a heat exchanger located in a furnace or boiler. The supply and return circuits are removed from the boiler. The pipes are connected to the communication comb. The liquid circuit is laid on a concrete base. It supplies hot water or antifreeze.
The main line is connected to the collectors. For automatic regulation, a three-way mixing valve with a thermal head is provided. The liquid line is covered with a deep concrete screed 7-8 cm thick.
“Warm floor” in a private house can be installed in all rooms, including the bathroom, toilet, sauna, garage. Installation will require high equipment costs, but maintenance will be inexpensive for the cottage owner. The floor covering can be anything, regardless of thermal conductivity and texture.
Cable sections and mats
Electric heating elements can be laid on a concrete base. If the room has a complex geometry, it is recommended to use cable sections. A section is a conductor of a certain length and power.
Mats are used to heat a room with the correct geometry. They can be rotated by removing the mesh or cutting it with mounting scissors. The mesh is made of fiberglass or heat-resistant plastic. Sections and mats can be installed in a wooden house with your own hands. Underfloor heating systems are used in Moscow and other cities.