Real estate
00:00, 02/11/2022 1 Scene: House in focus
Expanded polystyrene, mineral wool and EPS as the basis of the “wet facade”
Photo: m-stone.ru
We have already talked about a ventilated façade more than once in the “House in Focus” project. But his “colleague,” the so-called “wet façade,” was unfairly offended. Today we’ll talk about this facade system, or more precisely, about what main insulation materials can be used in it, what are their advantages and disadvantages. As a bonus, we’ll go over the features of installing different types of insulation in a “wet façade.”
How to choose insulation for a wet facade?
Insulation for a wet facade is the main part of the structure, on which the thermal insulation of the building, the strength and safety of the device, and the aesthetic solution depend. The choice of insulation determines what materials will be used for other parts of the structure, and the entire device as a whole is oriented towards the wall material.
The feasibility of external insulation
When insulating buildings, you should not only provide good thermal insulation performance, but also consider how you can avoid the appearance of condensation inside the walls during the cold season. Due to the change in the temperature of the building wall from minus on the outside to plus on the inside, at the conventional “dew” point, temperature changes turn into condensate, which is contained in the air of water vapor. When you move this point, along the thickness of the wall itself, the material becomes damp, and fungus and mold appear on it.
In the construction industry, the dew point is the temperature at which condensation forms. According to the rules, it should not be inside load-bearing walls.
When using wet facade technology, this point is moved beyond the building wall, thereby maintaining positive temperatures of all load-bearing structures.
What is a wet façade?
The name of this device does not at all mean that water will constantly flow down such a facade. On the contrary, it is precisely from moisture that it should protect the building. It was called wet because of the installation features - it uses several types of compounds that need time to dry.
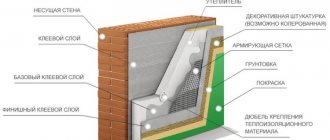
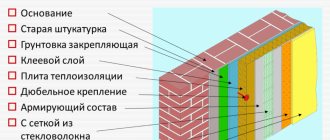
The technology for installing a wet facade involves multi-layering. Each layer is responsible for a certain quality - thermal insulation , structural strength, fastening to the wall, protection from moisture, decorative function. An important role is played by insulation and moisture protection - the design of the facade is such that it allows moisture to pass through from inside the building, but does not allow it to pass through from the outside. is carried out incorrectly , this property may be lost, and moisture will begin to condense in the insulation .
Figure 1. Installation of a wet facade
A properly made wet façade requires the following features:
In a private house, you can do the work of installing a wet facade yourself if you carefully read the instructions for the products used. But it is better to enlist the help of professionals who have the necessary knowledge for installation. Not any time of year is suitable for work; you need to wait for suitable weather and protect the walls from the adverse effects of the external environment. Materials are selected based on the characteristics of the walls.
Why choose polystyrene foam?
This material has long proven itself as a good insulation material. Today it can be easily purchased at an affordable price and is not a scarce commodity. For this reason, polystyrene foam is often used for insulation of both private houses and multi-storey houses.
Today it is profitable to insulate the facade with this decorative coating for various reasons. Insulating the facade with foam plastic is also beneficial for the reason that it does not allow moisture, noise and cold to pass through.
As a result, the thermal inertia of the walls will ensure a comfortable temperature in the building at any time of the year. Polystyrene foam will not allow the air to quickly cool inside the building in severe frosts, even without heating.
Advantages and disadvantages
The installation of a wet facade is considered the best choice that can be made, combining low price, ease of work and the desired quality. An alternative is wall-mounted structures, which create the same effects due to a sealed air cushion between the wall and the outer layer. Compared to them, wet technology has both advantages and disadvantages.
The advantages of a wet facade, in addition to simplicity and low cost:
Serious disadvantages of wet facades include the demanding conditions in which the work is carried out. They are only possible in summer, in good weather, using protection from wind, sun and rain. Violation of technology at any stage will lead not to improvement, but to deterioration of conditions in the house, the appearance of mold inside the walls and in the building, high humidity, and destruction of insulation. It is also impossible to install a wet facade in dilapidated housing, and hanging devices can extend the life of such houses.
Wet facades are divided into several types depending on the insulation materials used, on which the plaster for the external coating depends. Main types of insulation:
Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Expanded polystyrene (foam)
The density of this insulation is the highest; it effectively protects the wall from moisture and heat loss. Significantly reduces heating costs in winter and air conditioning in summer, maintaining a stable temperature inside the house. Used on facades made of dense heavy materials - brick, concrete, cinder blocks. This technology is suitable for multi-storey buildings, the walls of which are made of such materials.
The wet facade uses several layers of foam with different vapor permeability to effectively remove moisture from the walls. The installation of foam plastic insulation in houses with walls made of porous types of concrete will lead to the opposite effect - water will accumulate in the pores of the concrete, gradually destroying the walls.
The main disadvantage of a foam-based device is its flammability. In addition to the actual ignition of the walls, when such a wet facade burns, extremely toxic smoke is released. To solve the problem, special impregnations are used to make the insulation resistant to fire.
For decorative purposes, two types of plaster are combined with polystyrene foam - acrylic and silicone. Acrylic resin is an organic substance with great plasticity. The plaster is produced in the form of a water-dispersion composition, the permeability to steam is average.
Silicone resin, which is part of silicone plaster, makes it extremely durable, resistant to any weather conditions, and does not allow or absorb water. It definitely requires preliminary priming with a special composition, preferably of the same brand as the plaster itself, otherwise all its useful qualities are nullified.
Mineral wool
This is a lightweight material with high vapor permeability, best suited to porous walls made of lightweight concrete. Not any mineral wool is suitable for a wet facade, but only basalt wool of increased strength. made from basalt has another important property - it does not burn at all. The bottom layer can be softer to compensate for uneven walls. The rule of reducing vapor permeability from the inside to the surface remains the same.
Plasters that are used in conjunction with mineral wool have high vapor permeability. This is a cement-based mineral plaster that easily allows steam to pass through and does not burn; a more expensive option is silicate plaster (not to be confused with silicone). It requires special primer, is expensive, but has an excellent appearance and is very durable.
Combined materials
This is a combination of foam and mineral wool in the wet facade. Two types of insulation make it possible to provide good insulation and protect the finished façade from fire. Only mineral plaster is used with them; other solutions are rarely used. It is distinguished by high reliability, but also by the same high cost of work.
Main characteristics of mineral wool
| Options | Slag wool | Glass wool | Stone wool |
| Thermal conductivity ratio in W/m2*K | From 0.46 to 0.48 | From 0.038 to 0.046 | From 0.035 to 0.042 |
| Operating temperature range degrees C | -60 to +250 | -60 to +450 | -180 to +600 |
| Fire resistance class | Not flammable | Not flammable | Not flammable |
| Sound absorption coefficient | From 0.75 to 0.82 | From 0.80 to 0.92 | From 0.75 to 0.95 |
| Moisture absorption as a percentage of mass for 1 day | Less than 1.9 | Less than 1.7 | Less than 0.095 |
| Heat capacity in J/kg*K | 1000 | 1050 | 1050 |
| Quantity as a percentage of the volume of binder components | From 2.5 to 10 | From 2.5 to 10 | From 2.5 to 10 |
| Fiber length in mm | 16 | From 15 to 50 | 15 |
| Fiber thickness in microns | From 4 to 12 | From 5 to 15 | From 4 to 12 |
Have questions? Call, Ask! +7
Or write to us Ask a question
Wet façade installation technology
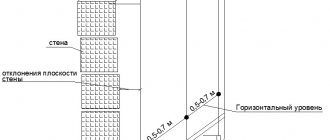
Everything is important when installing a wet façade. If the house has just been built, then external work is one of the final elements of the work; if repairs are taking place, it is important to make sure that everything necessary has been done in the remaining parts of the house, namely:
Those. When renovating and building a house, the installation of the facade occurs last. For work, you need to choose a warm time of year - the temperature outside should not fall below +5˚. The ideal period is mid or late summer, when dry and warm weather has firmly established itself. Before you begin installing a wet facade, you need to provide protection from wind, direct sunlight and sudden rain. Construction film is used for this purpose.
Installation and installation of a wet facade with insulation in rainy weather is contraindicated. This way you can achieve a result that is exactly the opposite of what you expected.
Stages of work
Main stages of work:
Artificial stone or decorative panels can be used as external finishing - this will give the wet facade additional strength. A prerequisite is that the finishing must be light, otherwise the structure will not last long.
Cost of work on façade insulation with polystyrene foam
Insulation thickness 100 mm. The price is for 1 square meter.
In calculations of the cost of materials, a wet-type façade insulation system is presented. Mineral decorative plaster, grain fraction 2 mm, is indicated as the finishing layer, followed by painting the facade with light-colored façade paint.
| Name of materials | Unit change | Materials | ||
| consumption per 1 sq. m. | Price of materials, rub. | Total materials, rub. | ||
| Tiefgrund LF - base primer | l | 0,30 | 53,83 | 16,15 |
| Insulation PSB-S 25F (facade polystyrene foam), 100 mm | m3 | 0,11 | 3 100,00 | 340,84 |
| Adhesive composition for gluing thermal insulation material | kg | 6,00 | 15,27 | 91,62 |
| Facade dowel “TERMOCLIP” TKS - (8*50*180) | PC | 6,00 | 9,80 | 58,80 |
| Reinforcing composition for reinforcing heat-insulating material | kg | 6,00 | 15,27 | 91,62 |
| Reinforcing fiberglass mesh (alkali-resistant) 4×4 mm | m2 | 1,10 | 40,30 | 44,33 |
| Quarzgrund weiss - primer for plaster | kg | 0,30 | 81,94 | 24,58 |
| Mineral plaster, uniformly rough 2.0 mm | kg | 3,00 | 19,94 | 59,82 |
| Tiefgrund LF - base primer | l | 0,30 | 53,83 | 16,15 |
| Facade paint “Egalisationsfarbe” A – light tone | l | 0,40 | 202,73 | 81,09 |
| _ | ||||
| Additional components, fittings: profiles, reinforcing corners, sealing tape, connecting elements, compensation profiles, etc. | m2 | 95,00 | ||
| In total, the cost of materials per 1 sq.m. | 920,00 | |||
*prices are as of July 2022.
Plastering insulation
Plaster on a wet facade performs two functions - an additional moisture-protective layer and decorative design. Its choice depends on the type of insulation, expected weather conditions and the desired effect. The most durable plasters are silicone (used with foam plastic) and silicate, also known as liquid glass (used with mineral wool).
With the help of plaster, you can create a smooth surface that is convenient to paint, and when used, it can be kept in order; dust and dirt will not settle on it.
Various types of decorative plaster can create a surface that imitates wood, stone or any other uneven texture. This will make the appearance of the house beautiful and unusual. Requires special tools for application and subsequent painting. Dirt may become clogged in uneven walls; such a façade will need to be cleaned occasionally.
Colored plaster gives an additional shade of color and allows you to use transparent materials instead of paint. Can create both smooth and decorative surfaces. It has the same advantages and disadvantages as colorless plaster for a wet facade.
Installing a wet facade is a great way to make your home warm in winter and cool in summer, and show your design talent in decorating walls. Having assessed the advantages and disadvantages of the design, you can choose the most suitable insulation and plaster and begin installation.
Source
Installation of a base reinforcing layer on the main planes of the facade.
The base reinforcing layer is made using polymer cement adhesive Ceresit CT 85, Ceresit CT 190 and facade fiberglass mesh 165 g/m2, cell size 5 x 5 mm.
Breaking load of the mesh, not less than 2000 N/5 cm
Which manufacturers and brands of mesh are suitable can be read here:
After installing the gussets, a base reinforcing layer is installed on the main planes. CeresitCT 85 glue is applied to the surface of polystyrene foam with a metal float, a facade fiberglass mesh is applied, then it is embedded in the glue, the excess is removed into a bucket. The minimum overlap of roll on roll is 100 mm, rolls are installed vertically.
- Creation of a base reinforcing layer. Photo 1.
- Creation of a base reinforcing layer. Photo 2.
- Creation of a base reinforcing layer. Photo 3.
After drying, re-stretching and puttying is done, this is done in order to level out the unevenness and hide the mesh in a layer of Ceresit ST 85 glue.
The installation of a base reinforcing layer with a mineral wool slab is carried out similarly.
Before work, we re-inspect the mineral wool surface for the presence of “corks” - inclusions of pieces of metal and droplets of binder. All “kings” must be removed. If there are large beads, sections of the mineral wool slab are cut out and replaced with new ones.
After this, we proceed to priming the mineral wool board with Ceresit CT 190 cement glue. The surface of the mineral wool board is primed with Ceresit CT 190 glue, apply the glue with a metal float, press it into the structure of the mineral wool, remove the excess by scraping off. Afterwards, we wait for the glue to dry completely and inspect the surface. In some places where the mineral wool slab turned out to be inhomogeneous, we will see the primer layer blistering; it moves away from the base, clinging to inhomogeneous mineral wool fibers. In these areas, we remove the heterogeneity and repeat the operation - again let the primer layer dry completely, and if necessary, repeat again.
WE MUST OBTAIN A HOMOGENEOUS MINERAL WOOL SURFACE COATED WITH A THIN LAYER OF GLUE WITHOUT BUBBLES AND LAMPS WITH DEVIATIONS OF 4-6 MM FOR A RULE OF THREE METERS
Next, a base reinforcing layer is made. CeresitCT 190 glue is applied to the glue-primed surface and a façade fiberglass mesh is embedded into it. The overlap of roll on roll is at least 100 mm. There are corresponding marks on the rolls of Facade fiberglass mesh that make it easy to track this.
The overlap of the fiberglass mesh can be more than 100 mm, but cannot be less!
After drying, the base is re-upholstered with liquid glue to remove minor irregularities and completely hide the texture of the fiberglass mesh.
Application of quartz primer Ceresit ST 16
When the base reinforcing layer has completely dried, at least 72 hours after the last re-upholstery, you can begin applying the Ceresit ST 16 quartz primer. The Ceresit ST 16 primer is applied with a paint brush, a wide brush, or a flute. The primer can be white, not a tinted base, or it can be painted to match the color of the future Ceresit decorative plaster.
- Applying Ceresit CT 16 primer with a brush. Photo 1.
- Applying Ceresit CT 16 primer with a brush. Photo 2.
Application of decorative plaster Ceresit
Ceresit decorative plaster is applied with a metal plaster and rubbed with a plastic float. This applies to decorative plasters with bark beetle textures CeresitCT 64, CeresitCT 63, CeresitCT 175, Ceresit CT 35 and pebble textures Ceresit CT 60, Ceresit CT 174, Ceresit CT 137.
- Application of Ceresit decorative plaster. Photo 1.
- Application of Ceresit decorative plaster. Photo 2.
- Application of Ceresit decorative plaster. Photo 3.
- Application of Ceresit decorative plaster. Photo 4.
- Application of Ceresit decorative plaster. Photo 5.
- Application of Ceresit decorative plaster. Photo 6.
- Application of Ceresit decorative plaster. Photo 7.
Stone decorative plaster of the textures Ceresit CT 60, Ceresit CT 174, Ceresit CT 137 can be applied to decorative elements by spraying using a spray gun, or manually.
- Mechanical application of Ceresit stone decorative plaster. Photo 1.
- Mechanical application of Ceresit stone decorative plaster. Photo 2.
- Mechanical application of Ceresit stone decorative plaster. Photo 3.
Wet facade on different insulation materials
A wet façade is a more complex technology for exterior wall finishing when compared to ordinary siding. This technology for processing construction projects implies the need to install insulating materials, which are most often used polystyrene foam or mineral wool. This finishing method got its name because in the process of cladding a building one has to deal with a variety of mixtures and solutions. The facing surface is ordinary plaster, which can have a different relief and be painted in any color.
What is the difference between insulation materials?
If this material is so good, then why is mineral wool used? The high elasticity index makes it possible to cover internal and external curves on surfaces. Mineral wool will always be in close contact with the wall. The high sound insulation rate makes it possible to install a wet façade with such insulation on a building located close to a noisy highway. Mineral wool allows more steam to pass through it than polystyrene foam.
When a wet facade is designed, the size of the insulating layer is selected in such a way that moisture does not collect in the walls and the house remains warm. All efforts will be in vain if water vapor penetrates the wall from inside the building. Wet structures will always freeze strongly and such finishing will not last long in the future. To make the correct calculation of the material when designing a wet facade, you need to contact specialists, and it is first recommended to obtain the necessary data yourself, using one of the online calculators.
Mineral wool in SFTK
Mineral wool boards are free from the main drawback of PPS boards for facade needs - they have excellent vapor permeability. Therefore, they are often chosen if the house is built from a material with high vapor permeability (aerated concrete, expanded clay concrete and other porous materials). For “wet facades”, specialized mineral wool slabs are produced. They differ from ordinary ones in greater rigidity and a denser structure.
The energy efficiency, strength, elasticity and adhesion of mineral wool are approximately the same as that of expanded polystyrene, so today it is a worthy competitor to it in these parameters. Another advantage, compared to PPS, is that mineral wool does not support combustion at all: there is nothing to burn in it.
However, this material also has two drawbacks.
Firstly, mineral wool slabs absorb moisture well, including from the atmosphere. Being wet, they perform their heat-saving functions worse as part of the SFTK. Therefore, some experts categorically do not recommend using vapor-proof decor (acrylic plasters, tiled cladding) on such facades.
And secondly, this material is significantly more expensive than PPS.
Description of materials
Today, not a single building renovation project is complete without external cladding.
There are a huge number of different types of insulation materials available on the market. A wide range of possible varieties allows finishing of a wide variety of construction projects. When cladding residential buildings in our country, a wet facade is often used, and foam plastic or mineral wool is used as insulation. Knowledge of the composition and technology of these materials helps every homeowner make the right choice.
Polystyrene foam is produced by heating polystyrene granules. The material is given a certain density during manufacturing. After this, the foam is cut into separate blocks of standard thicknesses of 20, 30, 50 and 100 mm. The size is determined by specialists when designing each specific construction project.
Each individual granule contains air inside, which increases the moisture resistance and vapor permeability of the substance.
The main advantage of a material such as foam is its lightness. The stove is almost 98% air. This feature has a very favorable effect on the thermal insulation properties. Extruded foam differs only in the manufacturing principle. This is a solid homogeneous plate, endowed with identical properties, but at the same time has a higher elasticity index. A wet facade cannot be installed with such insulation. Extruded foam plastic is often used in floor thermal insulation systems due to its resistance to various influences, elasticity, and moisture resistance. The high cost of such material is justified by its quality.
Mineral wool consists of fibers of basalt minerals on synthetic connecting components. According to its characteristics, the material resembles ordinary asbestos, but at the same time it is absolutely safe. Mineral wool does not support combustion processes at all and has a very impressive moisture resistance indicator. These features make it possible to use the material not only as a means of absorbing noise, insulation, but also as a heat insulator. Mineral wool is also often used in the design and installation of chimneys, sauna stoves, and fireplaces. Areas of use:
Selecting a thermal insulator
Basalt mineral wool
This heat insulator is one of the natural insulation materials. Silicate rocks and metallurgical slag are used for its production. When the raw material is melted and drawn out, a material is obtained consisting of porous fibers, which are used to form thermal insulation boards.
The advantages of insulation include:
- Possibility of use with any type of surface;
- naturalness, since it is made from environmentally friendly raw materials;
- vapor permeability;
- high sound insulation;
- resistance to chemical reactions;
- resistance to rodents and pests;
- fire safety.
Among the disadvantages are:
- gyroscopicity. This type of insulation easily absorbs water. To eliminate this factor, impregnation is carried out using various types of water-repellent compounds;
- due to its low density, it is difficult to install; appropriate qualifications are required for correct installation;
- may become deformed or shrink over time;
- to perform effective thermal insulation it is necessary to use a decent layer of insulation - more than 10 cm;
- may cause harm to health. To avoid this, protective clothing should be worn.
For insulation of a building and its subsequent plastering, the use of two-layer basalt wool slabs is considered optimal. Thus, the use of soft layers makes it possible to hide the unevenness of the walls, and hard materials with a density of more than 130 kg/m3 make it possible to easily apply glue and plaster.
Foam plastic - material for inexpensive thermal insulation
This heat insulator is a rigid plate, the structure of which is made of foamed polystyrene granules soldered to each other. Polystyrene foam has the following advantages:
- low cost. It is one of the most inexpensive insulation materials;
- has low thermal conductivity;
- lightweight, has little mass;
- environmental friendliness. The material does not pose a threat to human health;
- moisture resistant;
- not subject to deformation;
- has resistance to fungal formations and mold;
- easy to adjust and install, without the use of special tools and appropriate
- qualifications.
At the same time, polystyrene foam also has a number of significant disadvantages:
- has high vapor permeability;
- has increased fragility;
- susceptible to combustion, melts easily, releasing toxic fumes;
- when exposed to ultraviolet rays it is destroyed;
- may react with products that contain bitumen;
- susceptible to rodents and other pests;
- Installed exclusively on a flat wall surface.
Foam plastic facade insulation for plaster includes the brands PSB-S25F, PSB-S35F. They have a density from 15 to 35 kg/m3. This is a self-extinguishing material, thanks to antiprenes, in the event of combustion, all flammable processes are suppressed in 4-5 seconds.
Extruded polystyrene foam
This material is an advanced polystyrene foam. For its production, polystyrene granules are used, which are foamed in high-temperature chambers. The resulting mass is extruded through an extruder. The result is dense and durable slabs. EPPS has a finely porous, monolithic structure that is not subject to disintegration into granules.
EPS is much more practical than conventional foam plastic and has the lowest thermal conductivity coefficient among existing thermal insulators. Therefore, you can use even a thin layer of material; it will be enough to effectively insulate the walls. According to other characteristics, it is similar to polystyrene foam, but has a higher cost. For plastering facades, the material used is Penoplex 35 or Penoplex facade. They are quite durable and have increased fire safety.
Mineral wool or polystyrene foam?
Many different nuances can affect the choice of material for wall insulation. It cannot be stated unequivocally that mineral wool or polystyrene foam is best suited for installing a wet facade.
Expanded polystyrene weighs much less, performs excellently during building operation, does not allow condensation to pass through, is used almost everywhere and is more affordable. However, all positive properties will be minimized if there are mice in the building. In the external walls of houses, the insulation of which was carried out with special facade foam, the level of contained vapors will be slightly higher. This feature causes them to become moisturized. The fire resistance level of polystyrene foam is the lowest possible.
The area of use of mineral wool is also very wide. The material is used in the household, shipbuilding, manufacturing, automotive industries, as well as in agriculture. At the same time, mineral wool is less resistant to moisture, and also has relatively high thermal conductivity and fire resistance. For external insulation of wet facades, it is necessary to use high-density basalt-based material.
It is impossible to say unequivocally which material is better suited to replace insulation when designing wet facades. The choice will always be determined by the area in which certain components will be used, as well as many different nuances that should always be taken into account when designing. It is best to entrust this task to real professionals, whose highly specialized activities include determining the necessary materials. Each homeowner can always do an independent calculation if he is confident in his knowledge, but he will also have to be responsible for the result himself.
Source
Installation of abutment elements on blocks of window and door openings
During insulation, the insulation should extend onto the window frame by at least 15-20 mm to prevent a cold bridge. The abutment element with the mesh is glued to the window frame on three sides, top, right and left.
- Installation of adjoining elements on blocks of window and door openings. Photo 1.
- Installation of adjoining elements on blocks of window and door openings. Photo 2.
- Installation of adjoining elements on blocks of window and door openings. Photo 6.
- Installation of adjoining elements on blocks of window and door openings. Photo 3.
- Installation of adjoining elements on blocks of window and door openings. Photo 4.
- Installation of adjoining elements on blocks of window and door openings. Photo 5.