A wet façade is a more complex technology for exterior wall finishing when compared to ordinary siding. This technology for processing construction projects implies the need to install insulating materials, which are most often used polystyrene foam or mineral wool. This finishing method got its name because in the process of cladding a building one has to deal with a variety of mixtures and solutions. The facing surface is ordinary plaster, which can have a different relief and be painted in any color.
What is a wet façade insulation system?
This is one of the lightweight insulation methods that allows you to:
- Give wall panels additional thermal protection.
- Increase heat saving of premises.
- Give the building a finished, attractive look.
Basic system for installing wall insulation using “wet facade” technology
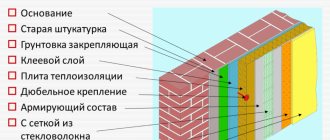
The outer decorative layer is plaster, thanks to which the facades become attractive. Insulation of facades using the wet method involves the use of thermal insulation. The list of layers of the system from internal to external looks like this:
- the wall itself;
- adhesive composition;
- insulation;
- reinforced starting plaster layer;
- decorative finishing plaster for exterior use.
The main advantage of the technology is that the wet façade can be installed in any climate zone. Minus - work must be carried out at an ambient temperature of at least +50 C and no more than +300.
During the cold period, the work site should be heated and hidden from the environment by a tent. This technology is called a wet facade because the binders are diluted with water and are wet at the time of application.
What is the importance of vapor permeability of the finishing coating?
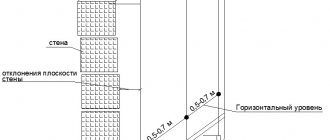
In facade insulation systems, materials with high vapor permeability should be used. At a room temperature of 20°C and a relative humidity of 55%, its air contains 8 g of water vapor per 1 kg of dry air, which creates a partial pressure of 1238 Pa. Outdoors at a temperature of –10 °C and a relative humidity of 83%, per 1 kg of dry air there is about 1 g of steam, creating a partial pressure of 216 Pa. The difference in partial pressures outside and inside leads to a constant movement of moist air through the wall to the outside. But if there is a layer of material near the outer surface of the wall that does not allow water vapor to pass through, then moisture from the passing air begins to accumulate at the border of the vapor-impermeable layer, causing dampness in the structure. As a result, its thermal protection deteriorates sharply.
What insulation materials are used in wet facade systems?
Glass wool and mineral wool are strictly prohibited. This is due to the insufficient strength of these insulation materials. They are not able to withstand the weight of plaster. Because of this, they are prone to delamination. Polystyrene foam is also not included in the thermal insulation used.
Typical insulation materials for wet facades are polystyrene foam and basalt wool
The wet façade insulation system involves the use of basalt wool or expanded polystyrene as insulation. Comparing them with each other, the choice is not in favor of the latter. This is due to the fact that polystyrene foam does not allow air to pass through at all. With such insulation, a wet facade for a wooden house will be destructive. The walls of a building insulated with this material will be damp and susceptible to the harmful effects of moisture, parasites and rot.
How thick should the insulation of a wet façade be?
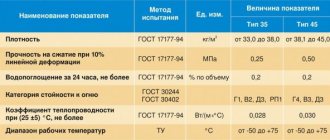
When installing a wet facade with your own hands, you involuntarily ask the question “How thick should the insulation be?” The construction market is represented by a wide range of basalt wool of various thicknesses (from 2.5 to 20 cm). Among those offered, you need to choose the one that fully satisfies the requirements. If there is a project available, then this parameter must be indicated in it.
If work is carried out without design documentation, then the climatic conditions of the region must be taken into account. The indicator of the total heat transfer parameter can be found in reference books. The climate map of the Russian Federation, which is easy to find on the Internet, can serve as a help.
It is necessary to compare the resistance to heat transfer of the wall panel material with the indicated numbers on the map. The difference must be compensated with insulation. When calculating, you need to take into account the characteristics of the external plaster. You should not overestimate the performance of an insulated building. The balance of humidity and temperature must be maintained.
What else is needed besides insulation?
The complete list of required materials is as follows:
- glue for attaching insulation to the wall;
- aluminum profile;
- dowels for fastening the profile;
- plastic dowels for fixing the insulation;
- insulation;
- primer;
- plaster reinforced mesh;
- dowels for fastening insulation and reinforced mesh (plastic);
- starting plaster (basic);
- finishing decorative plaster.
Tool kit for installing a wet façade
In addition, you will need the following equipment:
- hammer drill (for concrete, brick, reinforced concrete panels);
- drill (for wooden walls);
- screwdriver (for screwing in dowels);
- special spatula for applying glue;
- a set of spatulas for applying and smoothing plaster;
- containers for mixing construction mixtures;
- drill attachment for kneading;
- brushes for cleaning the wall surface before applying glue.
It is possible to carry out the work yourself, but this requires basic construction skills and a technological map for installing an insulated facade using the “wet method”. This is especially true for plastering work.
You can view the detailed technical map for installing a wet façade using the link (will open in a separate window).
Wet façade insulation work in stages
Step-by-step instructions for wet facade technology are as follows:
- Preparing the wall surface.
Priming insulated walls is an important stage in surface preparation.
This procedure involves cleaning the surface from any existing contaminants. In addition, it is necessary that it be level. The maximum difference per 1 m2 of area should not exceed 1 cm. Irregularities and sinks should be leveled with plaster. If the wall has areas with crumbling fragments, it is necessary to use a bonding primer. It is advisable to prime the entire surface. This will serve as additional protection for the wall. - Installation of the base profile.
Fastening a metal profile for installing insulation.
It will perform two functions: a level and a unit that takes the load of the upper insulation slabs. - Applying glue.
Applying glue to the surface of the insulation
This procedure is performed with a special notched spatula. The adhesive composition is applied to the insulation boards, not to the wall. - Gluing.
The insulation is glued from the bottom up.
It is important to pay special attention to the corners. The procedure is performed from the bottom up along the belts. The slabs located above the base profile must rest on it. When gluing door and window openings, the slabs must be glued so that the corners of the openings are located within one solid slab. For this purpose, special cutouts are made in the insulation. - Fastening insulation boards with plastic dowels with a wide head.
The insulation is attached using plastic dowels with a wide head.
The work is performed after the glue has completely dried. - Applying a base plaster layer, 3-5 mm thick.
The key stage of a wet facade is applying a plaster layer with reinforcement - Laying reinforced mesh. The work is carried out until the plaster sets. It is important that the mesh is recessed into the plaster layer.
- Leveling with finishing plaster.
- Painting.
The final finishing stage is surface painting
Armed with knowledge, materials and the necessary technical
With the equipment you can begin work on installing the wet facade.
What does it consist of?
This type of cladding includes several layers , each of which performs a specific function.
This system consists of three layers:
- thermal insulation - includes foam boards or mineral wool;
- reinforced (basic) - consists of a plaster-adhesive layer reinforced with fiberglass mesh; when using the “heavy” method, steel mesh is used;
- protective and decorative - wet facade plaster is used, which is painted with special paints; the plaster can be applied in a thick layer - 3-4 cm and a thin layer - 0.7-0.9 cm.
Heavy and light wet facades
There are two types of wet facades:
- Heavy wet facade.
A ventilated facade can be classified as heavy.
This design does not involve adhesive connection of insulation boards to the wall panel. Fastening is done using dowels with hooks. The insulation is fixed to the wall using plastic dowels. The reinforced mesh is firmly attached to the wall through the insulation. As a result, the insulation remains mobile in a small amplitude range relative to the wall surface. Next, plaster is applied and painting is done. - Light wet facade. This is the installation method described in the publication using wet facade technology.
A heavy wet facade is used in seismic-resistant zones, as well as in cases where it is necessary to absorb thermal deformations that occur during temperature changes.
Thanks to the design features, the plaster remains intact (does not crack). But there are also disadvantages. This is due to the high cost compared to a light facade. This is due to the fact that the amount of used plaster can increase significantly, since the thickness of its layer can reach 20-40 mm. The reinforced mesh will also increase the cost, because it must be metal, in contrast to a lightweight wet facade, where polymer materials are used.
Another disadvantage is the heavy weight. If the building is dilapidated and needs to be reconstructed, then the use of a heavy facade without special strength calculations can lead to collapse. For most cases, a lightweight system is suitable. Moreover, now there are companies on the market that can comprehensively provide high-quality materials.
What is the difference between insulation materials?
Polystyrene foam, which can be installed on the facade of a building, sells for approximately 2000 rubles per m, and mineral wool costs approximately 2-2.5 times more. This feature is one of the most significant arguments when choosing materials for insulation. Polystyrene foam has several distinctive features that can be considered advantages. This material can be cut any way you like and sanded very easily, which creates even corners and a perfectly smooth surface. Foam plastic is easy to process and with its help it is very easy to install various cornices and projections on the building, giving the structure an original appearance.
Wet façade using mineral woolWet facade using foam plastic
If this material is so good, then why is mineral wool used? The high elasticity index makes it possible to cover internal and external curves on surfaces. Mineral wool will always be in close contact with the wall. The high sound insulation rate makes it possible to install a wet façade with such insulation on a building located close to a noisy highway. Mineral wool allows more steam to pass through it than polystyrene foam.
When a wet facade is designed, the size of the insulating layer is selected in such a way that moisture does not collect in the walls and the house remains warm. All efforts will be in vain if water vapor penetrates the wall from inside the building. Wet structures will always freeze strongly and such finishing will not last long in the future. To make the correct calculation of the material when designing a wet facade, you need to contact specialists, and it is first recommended to obtain the necessary data yourself, using one of the online calculators.
Wet facade Ceresit - a popular system
The Ceresit brand has developed a set of products for installing facades using wet technology. The complex includes all the components of the insulation cake:
- glue;
- heat insulators based on mineral wool or expanded polystyrene;
- plaster mixtures.
Components of the Cerezit WM system
Those who decide to use the unified Ceresit wet facade system will not have to check the incompatibility components. All components were developed with this parameter in mind. Moreover, each component complements the functions of the other and compensates for its shortcomings.
Briefly about the main thing
The wet facade is a multi-layer external cladding of a house without a ventilation gap, which includes the following structures:
- Glue.
- Insulation.
- Reinforcing mesh.
- Plaster.
- Finishing.
Among its main advantages are:
- Good indicators of heat, wind, moisture, noise insulation.
- Ease.
- Durability.
- Resistance to external factors.
- High aesthetic qualities.
Disadvantages include the need to strictly adhere to installation requirements - temperature, humidity and weather conditions. During installation, it is important to consistently carry out the stages of the technology. Therefore, it is better to entrust the procedure to a professional team.