The need for wall insulation (if insulation is not part of the construction process) is caused by the insufficient thickness of the building material.
The main reasons for this are: design errors and the desire to save money on the purchase of building materials with the expectation of insulation.
One way or another, insulation is a fairly simple process that can be accomplished with independent efforts; the main thing is to understand the meaning of the actions and take all measures to achieve the most effective result.
The list of popular insulation materials is quite large and is constantly being updated with new materials, but the cheapest, easiest to use and preferred is polystyrene foam.
What is expanded polystyrene
Expanded polystyrene (EPS) is a material consisting of a mass of gas-filled sealed granules soldered into a single conglomerate during the manufacturing process. In this case, the granules themselves are not destroyed, but are only glued together by their walls.
Depending on the initial size of the granules and the temperature during manufacturing, EPS has different densities and hardness. The finer the grains, the denser the structure and stronger the material. The most important physical property of EPS is its extremely low thermal conductivity : a layer of EPS with a thickness of 3 cm is equal in thermal resistance to a layer of concrete with a thickness of 123 cm.
The following types of expanded polystyrene exist:
- PS. Press.
- PSB. Pressless.
- EPPS. Extruded.
- PSB S. Pressless suspension.
In addition, there are subtypes of material that have a special purpose, for example PSB-S 25F - façade expanded polystyrene with a density of 25.
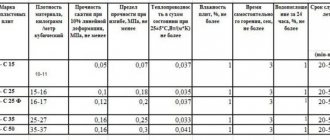
Material Specifications
The density of the material has a fairly wide range of values depending on the brand.
Samples available with densities:
- PSB-S 15.
- PSB-S 25.
- PSB-S 35.
- PSB-S50, where the last digits are the value in kg/cub.m.
Advantages:
- An excellent heat insulator.
- Effective sound insulator.
- The light weight of the material allows for widespread use.
- Self-extinguishing material (free burning time - 3 seconds).
- It is practically impenetrable to steam and moisture, depending on the density (there is a slight absorption of moisture through capillaries - micro-gaps between welded granules).
- Low price.
Flaws:
- Low plasticity; when deformed, the material crumbles or breaks.
- It does not tolerate contact with solvents such as gasoline, acetone, etc.
- When exposed to flame, it emits large amounts of toxic gases, although in itself it is not dangerous in terms of fire protection.
- It is impermeable to air, which makes it difficult to remove moisture that has seeped through the capillaries.
The capabilities of teaching staff have been tested and confirmed by many years of practice. The material is a leader among other insulation materials due to its low cost, ease of processing and other advantages.
IMPORTANT!
Currently there is a new GOST in force , in which the designations of expanded polystyrene grades look different. For example, PSB-S 25F according to the new standard is designated as PPS-16F.
The chemical basis for all types of polystyrene foam is the same, but the difference in production technology significantly changes their properties. The most different from the usual types are extruded options (EPS, penoplex, etc.).
Comparison of the thickness of materials with the same thermal conductivity
During manufacturing, this material is mixed , causing the structure to change and turn into a homogeneous frozen foam, most similar in appearance to foam rubber, but much more rigid and durable.
EPS is an excellent material for insulation and waterproofing; it is completely impervious to water or steam and is good for working in difficult and difficult conditions - for example, for insulating foundations or other buried structures.
Conditions for high-quality insulation of facades
When insulating facades with polystyrene foam, the technology for performing the work must be followed. Although the operation itself is not too complicated, shortcomings in the installation of panels can negate efforts to minimize heat loss through the walls. Slabs that are not properly fixed can cause problems such as peeling (a loose panel can be torn off by the wind), moisture getting under the insulation, the formation of fungus, etc. Within a short time, the load-bearing structures of the building will require repairs.
To insulate a building efficiently, it is necessary to follow a phased installation process.
To ensure a high-quality result, it is necessary not only to strictly follow the instructions for performing the work, but also to follow the recommendations on the use of materials and the selection of devices.
The following must be taken into account:
- Insulating a house with expanded polystyrene should be carried out only in the warm season, however, it is not advisable to choose hot days for its installation. It is optimal to work at temperatures from +15 °C to +25 °C.
- Thermal insulation should not be installed in rainy weather or during periods when the air humidity level exceeds 80%.
- Polystyrene foam that is glued but not protected by a coating must be protected from sunlight and water. During long breaks, the wall can be covered with a cloth, for example, polyethylene.
How to calculate the thickness of insulation
Calculation of material thickness is carried out according to a two-step scheme:
- First, the thermal resistance of the wall is determined . This refers to the general value, together with the insulation. If there are many layers of the pie, all are taken into account. The value is standard, determined according to SNiP tables for a given climate zone.
- Then the thickness of the PPS is determined - the product of the thermal resistance of the wall and the thermal conductivity coefficient of the material.
It should be borne in mind that theory is largely corrected by practice, since it’s all about subtle effects, which are individual in each case and cannot be taken into account in calculations.
Therefore, during private construction, they do not go into complex theoretical research , being content with generally accepted standards for a given region.
If in doubt, you can always use an online calculator (preferably several) to find out the desired value. You just need to substitute your data into the required columns of the attached table and get the finished result.
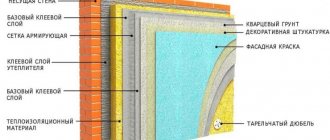
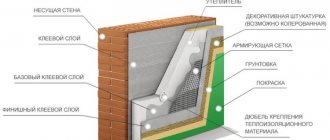
Wall pie device
Advantages and disadvantages of extruded polystyrene foam
The material obtained by extrusion has a higher density than its related foam. This quality allows the use of polystyrene foam for finishing the exterior walls of buildings. Extruded boards have slightly worse thermal insulation characteristics than foamed polystyrene panels, however, they are much better resistant to mechanical loads, atmospheric factors and aggressive environments. It should be added that the thermal conductivity coefficient of polystyrene foam is more than 10 times lower than that of brick and 3 times less than that of wood.
Subject to insulation technology, polystyrene foam has no disadvantages
- Dense polystyrene foam does not allow water to pass through. The building material is easy to process and easy to install, so insulating the facade with polystyrene foam can be done with your own hands. The purchase of plates and consumables does not require significant financial resources.
- Extruded polystyrene is significantly better than polystyrene foam in terms of fire resistance. As for the safety of the building material for the health of the inhabitants of the house, it does not pose any threat, since the slabs are located on the outer walls. To protect the insulation from damage and minimize the evaporation of styrene (which releases any type of foam to a greater or lesser extent), the treated walls are covered with a layer of finishing.
Some homeowners make the mistake of insulating the walls of the house with polystyrene foam not from the outside, but from the inside. One can understand the reasons for this decision, but it should be noted that such thermal insulation will not perform its tasks. It will not protect the facade from freezing. The consequence of this will be the formation of mold between the wall and the insulation and the destruction of the supporting structures of the building.
Internal insulation will worsen the vapor permeability of the partitions, so the humidity level in the rooms will be increased. In addition, it can pose a danger to residents by releasing harmful substances into the room. If a fire occurs, the toxic smoke from polystyrene foam will cause at least severe poisoning.
Another circumstance speaks in favor of using insulation outside: with this method, the area of the premises remains unchanged.
Is polystyrene foam suitable for insulating wooden, brick, foam concrete houses?
Expanded polystyrene is a universal insulation material suitable for performing its tasks in any conditions. However, for the insulation cake to work properly, the correct ratio of vapor permeability of all layers is required, which should be maximum inside and gradually decrease towards the outside.
This introduces some difficulties in the use of polystyrene foam, which has extremely low vapor permeability (EPS is considered completely impermeable to vapor).
According to the degree of suitability of PPS for insulation, materials can be arranged in the following sequence:
- Foam concrete. The most permeable material for steam.
- Wooden wall. Wood itself does not conduct steam, but joints, cracks and joints are replete with loopholes for steam.
- Brick wall. The closest (relatively) material in terms of vapor conductivity.
NOTE!
Some experts do not recommend PPS for outdoor use at all , considering it a “time bomb” that quietly accumulates moisture in the thickness of the walls.
However, polystyrene foam is often used to insulate walls outside, obtaining quite satisfactory results. The solution to the problem is to organize effective ventilation at home, removing steam from the air and relieving the problem.
Technological standards for working with expanded polystyrene
Working with insulating material such as polystyrene foam requires compliance with certain standards:
- It is impossible to carry out insulation at air temperatures above +25 degrees.
- It is impossible to carry out insulation at air humidity above 80%.
- The façade should not be exposed to direct sunlight for a long time.
- Precipitation must not be allowed to enter the façade during work.
The standards apply to every stage of work. This is the only way the insulation will be reliable, long-term and effective. High temperatures can lead to deformation of the foam and rapid drying of the adhesive solution. Precipitation will make the solution less sticky. Also, water getting into the cracks between the insulation boards will significantly reduce the effectiveness of thermal insulation.
Preparing walls for laying thermal insulation
Before installing insulation, the following steps are required:
- Sealing irregularities, gaps or cracks, depressions in the wall plane. Differences of more than 1 cm per 1 m of length must be leveled.
- The plane of the wall is covered with a contact primer (especially necessary for severe shedding).
- Installation of sheathing. This is done for subsequent installation of the casing (if planned).
The sheathing is made from wooden blocks or from drywall guides and forms a flat plane. The thickness of the planks corresponds to the thickness of the insulation (no less!) , the pitch of the planks is recommended to be about 40-50 cm from each other (in practice, a step is chosen that is a multiple of the width of the PPS sheet for greater efficiency).
Technical characteristics and fire resistance
Manufacturers of extruded polystyrene foam provide the buyer with a large list of positive characteristics and properties that distinguish the material from its relatives. But in fact, they also hide many nuances.
Let's look at environmental safety. Since EPP can serve for a long time without changing its technical parameters, it would seem that the material is absolutely safe. But it is not so. Each insulation has a certain period of time, after which the material begins to “age”.
As a result, caustic vapors and substances are released into the environment. The same substances are released when extruded polystyrene foam is heated to 80 degrees Celsius and above.
Now fire safety. Manufacturers claim that the material extinguishes immediately after the fire stops. And this has actually been confirmed in laboratory conditions, where there are no other finishing materials or elements of the main structure. But in practice everything is completely different.
There are other materials around extruded polystyrene foam that, if they do not support combustion, can heat up to high temperatures, which will cause the insulation to catch fire. In addition, it is impossible to immediately stop the access of fire.
Small pockets may remain under the casing, which will swell again and again with air currents. And the amount of smoke that is generated during the smoldering process of EPP cannot be compared even with burning rubber.
In some cases, manufacturers embellish the reality, and in others they draw conclusions solely on the basis of laboratory tests. Extruded polystyrene foam is a good insulator and has the right to exist in the modern world. But you don’t always have to rely on absolutely all characteristics.
Methods for attaching polystyrene foam to the wall
Installation of PPS can be done in the following ways:
- Tight fit between sheathing strips.
- Fastening on special dowels with wide caps - “fungi”.
- Glue installation.
CAREFULLY!
When installing tension between the lathing, there may be cases of broken pieces of material or crumbled areas . These places must be filled with polyurethane foam; gaps or holes should not be allowed.
Installation on “fungi” is done in addition to gluing; it is not recommended as an independent method of fastening.
Ready-made mixtures are used as glue , which are diluted with water and mixed immediately before installing the material. There are also synthetic types of adhesives produced in cylinders like polyurethane foam, but they are more expensive.
Installation using a dowel
Applying glue
Features of the material in comparison with other types of insulation
If a person has taken up the issue of insulating a house, then he needs to compare all the options. Therefore, we will consider several characteristics of extruded polystyrene foam in comparison with other insulation materials.
- Thermal insulation - with the same thickness, EPP takes the lead, leaving foam and mineral wool behind.
- Hygroscopicity - polystyrenes practically do not absorb moisture, but for mineral wool insulation this is a significant drawback.
- Biological inertness - neither mold nor fungi grow on extruded polystyrene foam, but rodents often use it to furnish their homes.
- Resists chemicals, but not all of them. If you do not use special glue for installation, the material may be damaged.
- Vapor permeability - here mineral wool is already in the lead, and polystyrene is left far behind.
- Fire safety - if the EPP has additional flame retardant treatment, it will not ignite, but not all manufacturers comply with the requirements in good faith. And mineral wool does not support combustion at all.
- Service life - polystyrene foam, when installed correctly, can last up to 50 years without changing characteristics. Mineral wool is not able to withstand such a long period, especially if all installation rules were not followed.
Laying polystyrene foam with your own hands
- If there is a sheathing, the PPS is cut into appropriate pieces .
- If it is not available, laying is done in whole slabs (if possible), since factory ones are smoother and more accurate than self-cut ones.
- The glue can be applied in stripes around the perimeter and in the center of the sheet, dotted or in a continuous layer.
- Installation of PPS on the wall. The slab is pressed against the wall with little effort; you can move it slightly from side to side for better adhesion of the glue to the wall material.
- After installation, the plate should be secured with a dowel . This will save time by pressing the slab against the wall while the adhesive sets.
- All subsequent slabs are installed in a similar manner.
- Work is carried out in horizontal rows from the corner (or opening) of the building.
Sheet fastening
Fixation with dowels
For tightness or with uneven edges of the slabs, you can coat the joints with glue.
Where is EPS used?
This thermal insulation material has gained wide popularity not only among private developers. It is used not only for insulating buildings. Highways and heating mains are protected from heat loss and icing with this universal insulator. But still, what interests me most is how EPP sheets are used to insulate residential buildings.
Thermal insulation of walls outside
For external insulation, extruded polystyrene foam is suitable if the walls of the main structure do not allow vapor to pass through in the same way as the insulation. If the walls “breathe,” you will have to build forced ventilation or replace the windows with ones that have slot ventilation.
The insulation must be covered with finishing material, which will embellish the facade and protect the insulator from exposure to sunlight. The EPP is fixed both mechanically (dowels) and with adhesive.
Internal wall insulation
Insulation of a house from the inside is chosen extremely rarely, and even less often with the use of extruded polystyrene foam. Except for one thing. To prevent heat loss through the roof, the use of EPP is suitable. All thanks to the following characteristics:
- Low moisture absorption coefficient is very important for roofing.
- Good strength characteristics.
- Lightness of the material.
Thermal insulation of hollow walls
Here the insulation is used together with an additional wall made of facing bricks. The material is fixed using anchors. The heat insulator is put on the anchor and pressed with a washer, the other end is hidden in the facing wall.
Floor insulation
Extruded polystyrene foam is used to insulate floors both in private homes and in multi-storey buildings. The material does not absorb moisture and does not allow cold to pass through, so it does its job perfectly. Heated floors or concrete screed can be laid on EPP slabs.
Insulation of slopes and window perimeter
To insulate slopes, it is necessary to cut strips of foam plastic according to the dimensions of the slopes so that they fit tightly on the slope, resting on the ends of the slabs laid on the walls.
As an option, you can first paste over (or otherwise strengthen) the window opening with PPS strips so that the cut of the insulation strip lies flush with the plane of the wall.
Insulation of slopes
Then polystyrene slabs, cut to length, are laid on the plane.
All joints and junctions must be tightly covered with insulation ; possible cracks are filled with polyurethane foam or coated with glue.
Common mistakes
When installing extruded polystyrene foam with your own hands, frequent mistakes are made. Knowing about them, you can avoid repetition of ridiculous situations. Below are the most common:
- The surface of the walls is not completely leveled. Therefore, the slab lies unevenly; Glue is applied to the center of the slab, the corners will bend outward over time; Plaster without a reinforcing mesh will lead to cracking of the surface; Poor insulation of the seams between the slabs will lead to the formation of cold bridges; There is an opinion that the thermal insulation of a house made of aerated concrete will lead to The vapor barrier of the premises will be compromised and mold may form.
Only correct and competent installation of insulation in compliance with many conventions can benefit both the person and the entire building. This should be remembered!
Installation of reinforcing mesh and finishing with plaster
- Reinforcing mesh is used to ensure greater rigidity of the plaster and prevent it from falling off the polystyrene foam. For this, a metal or plastic mesh with a small mesh size is used.
- First of all, you need to cover the window or door slopes and corners of the house . This is done with strips of mesh, cut about 30 cm wide and bent in half lengthwise to form a stable rib. All corner areas of the house are decorated with such “corners”.
- For plastering PPS, a special composition is used - a universal mass.
- The plaster is applied with a spatula to the corners and slopes formed with a mesh. In places where there will be joints with the main mesh, free areas are left for connecting the mesh panels.
- For laying on a plane, the mesh roll is cut into pieces of 1 m.
- A layer of plaster is applied, a piece of mesh is placed on it and pressed onto the plaster with a spatula. Using ironing movements, the mesh is pressed into the layer of universal mass, so that it is completely inside.
- The next piece is laid side by side with an overlap and the procedure is repeated.
- After the mesh is completely installed, the mixture is dried for several hours (up to a day), after which the composition must be grouted.
- Then a second leveling layer is laid, which is also rubbed down after drying . Grouting is done until the surface is completely smooth.
- After this, the surface is primed for greater reliability and durability of the coating.
- Finishing is carried out - painting, applying relief or decorative plaster, etc.
Installation sequence
Installation of reinforcing mesh
Insulating the facade with extruded polystyrene foam is a completely possible procedure, but it requires ensuring that steam is removed from the room using high-quality ventilation .
Failure to comply with this condition threatens the gradual accumulation of moisture inside the wall or in the gap between the wall and the PPS, which sooner or later will cause destruction or rotting of the walls. Otherwise, polystyrene is a completely reliable and inexpensive insulation material.
The most common mistakes when finishing facades with polystyrene foam
Due to ignoring certain aspects of the work, insulation will not be beneficial. The most common mistakes are:
- A frivolous approach to the preparation process. Foam should only be applied to a flat surface;
- Lack of starting base profile. The bottom bar will help set the level, reduce the load on the bottom layer of insulation, and protect the foam from rodents.
- Installation is not staggered;
- Not using enough dowels.
Insulating a façade with polystyrene foam boards is not a complicated process in terms of manufacturability. To carry out the work you do not need to have special skills. The main thing is a serious approach to each stage. And then the insulation will be as effective and economical as possible.
More
Working with walls inside
Interior work is the next step. Insulation of the walls of a frame house with extruded polystyrene foam is carried out when it is not possible to lay insulation on the outside. This is usually due to the peculiarities of facade decoration, when various kinds of decorative components are used that have a certain value in terms of appearance.
Internal insulation leads to a reduction in usable space, and therefore they use the same extruded polystyrene foam, which has a thickness less than in the previous case. The maximum allowed thickness is from 10 to 30 mm. First, preparations involve cleaning the surface and drying it. Prepare high-quality insulation and attach sheets of polystyrene foam to the wall with glue. Fixed to insulation and wooden sheathing.
Important Tips
Correct calculation of the thickness of thermal insulation is key. An experienced designer can provide the most correct information. He will inspect the building and after some time will issue a ready-made version of the design documentation. In the documents, he will indicate the brand of insulation that is in accordance with the text and the one that is recommended for a particular object. It is advisable that the material recommended by the specialist be available, otherwise difficulties may arise with the delivery of the product. The minimum period for delivery of expanded polystyrene to the place of work can take up to several months.
A professional builder will not advise insulating all areas of a living space with one insulation of the same thickness. Let's say that for interior and facade work, as mentioned above, polystyrene foam should have different thicknesses. This is also important for saving available space.
The disadvantage of using polystyrene foam is the release of toxic substances during combustion. But this does not mean that it should be abandoned. Most of all, this is a tip for building owners. Therefore, they need to take care of fire protection. If the area of the house allows, insulated walls can be finished with plaster and decorated with artificial stone.
Installation of extruded polystyrene foam under siding
When installing extruded polystyrene foam under the siding, it is necessary to create a vertical sheathing from antiseptic softwood bars or galvanized metal profiles. Attaching the sheathing to the facade
structures in increments of 30-40 cm, using dowels; in this case, it is necessary to control the plane of the frame using a level.
Extruded polystyrene foam is placed between the frame guides, and the insulation is secured using disc dowels. The heat-insulating layer is covered with a hydro-windproof membrane on top, which will help remove moisture from the heat-insulating layer to the outside.
It is necessary to provide a ventilation gap between the heat-insulating layer and the facing material. To do this, another sheathing is created on top of the structure, the step of the guides should be 30 cm. The height of the ventilation gap should be 1.2-1.5 cm. Siding panels are attached to the frame guides.
Details about installing a ventilated facade are here.
Floor insulation
After carrying out all the above manipulations, part of the work can be considered completed. You can move on to insulating the floor. Thanks to this manipulation, you can achieve a cozy atmosphere in your home. The process looks like this:
- Primer is carried out if the house does not have a concrete floor;
- Compact the earth mechanically. Thanks to this, it is possible to obtain a flat surface;
- After laying 1 layer of crushed stone, the floor is leveled again;
- The building material must be at least 10 cm thick;
- Next comes sand. It plays the role of bulk material, without which work is impossible. It completely fills all the voids.
Then polystyrene foam is laid, and waterproofing begins. Cover the floor surface with film and join the material with a significant overlap. To ensure that the structure is strong and takes on the load evenly, the next layer is laid out from a reinforcing mesh. The concrete screed is poured and the final coating is arranged.
Important! It is necessary to leave space between the floor and the wall throughout the entire area of the room. It must have a minimum width of 1 cm.
The optimal thickness of the screed is 50 mm. You can use the system to heat rooms - both water and electric.
Advantages
Extruded polystyrene foam has a high degree of heat retention, since the insulation has a porous structure, 90% consisting of air.
The advantages of thermal insulation material include:
- High compressive strength of the material;
- Moisture resistance, preventing biological decomposition and deformation of the insulation;
- Low vapor permeability, allowing the use of thermal insulation for external insulation;
- Resistance to external influences. The material is immune to environmental influences (precipitation, atmospheric humidity, changes in temperature conditions, exposure to ultraviolet radiation);
- Durability. If all stages of installation of a heat insulator are carried out correctly, its service life reaches 50 years;
- Biological inertia. The material does not attract insects, birds and rodents;
- Fire resistance;
- Environmentally friendly.
Description of material
Expanded polystyrene is a modern foam material of synthetic origin. There are two types of it:
- Extruded polystyrene foam;
- Styrofoam.
The latter option is more affordable for arranging thermal insulation. Extruded polystyrene foam does not lag behind in the number of advantages. Among them:
- Frost resistance;
- Moisture resistance;
- Excellent compressive strength;
- Good thermal insulation properties.
It is widely used and is suitable for any part of the building - from the foundation to the roof. This building material is vapor-tight, resistant to the growth of fungus and mold. By using this material for insulation work, it is possible to avoid additional actions to protect the structure from adverse environmental factors and excess humidity. Extruded polystyrene foam is characterized by a harmonious structure and includes cells measuring 0.2 mm.