Here you will learn:
- Calculation of convector power by area
- Calculation of convector power by volume
- Energy Saving Tips
- Auxiliary heating calculation
By choosing convector heaters to heat your home, you are making an excellent choice. This equipment is highly efficient, allowing you to heat residential premises for any purpose. But before buying, you need to work with the numbers to calculate the number and power of devices. Calculating the power of a convector is not as complicated a process as it might seem at first glance. And in this review we will present you with two formulas for correct calculation.
Calculation of different types of radiators
If you are going to install sectional radiators of a standard size (with an axial distance of 50 cm in height) and have already chosen the material, model and desired size, there should not be any difficulties in calculating their number. Most reputable companies that supply good heating equipment have on their website the technical data of all modifications, including thermal power. If it is not the power that is indicated, but the coolant flow rate, then it is easy to convert to power: the coolant flow rate of 1 l/min is approximately equal to the power of 1 kW (1000 W).
The axial distance of the radiator is determined by the height between the centers of the holes for coolant supply/discharge
To make life easier for customers, many websites install a specially designed calculator program. Then the calculation of heating radiator sections comes down to entering data on your premises in the appropriate fields. And at the output you have the finished result: the number of sections of this model in pieces.
The axial distance is determined between the centers of the coolant holes
But if you’re just evaluating possible options, then it’s worth considering that radiators of the same size made of different materials have different thermal power. The method for calculating the number of sections of bimetallic radiators is no different from calculating aluminum, steel or cast iron. Only the thermal power of one section can be different.
To make it easier to calculate, there are averaged data that you can use as a guide. For one radiator section with an axial distance of 50 cm, the following power values are accepted:
- aluminum - 190W
- bimetallic - 185W
- cast iron - 145W.
If you are just figuring out which material to choose, you can use this data. For clarity, we present the simplest calculation of sections of bimetallic heating radiators, which takes into account only the area of the room.
When determining the number of heating devices made of bimetal of a standard size (center distance 50 cm), it is assumed that one section can heat 1.8 m 2 of area. Then for a room of 16 m 2 you need: 16 m 2 /1.8 m 2 = 8.88 pcs. Let's round up - we need 9 sections.
We calculate similarly for cast iron or steel bars. All you need is the following rules:
- bimetallic radiator - 1.8m2
- aluminum - 1.9-2.0 m 2
- cast iron - 1.4-1.5 m 2.
This data is for sections with an interaxial distance of 50 cm. Today, there are models on sale with very different heights: from 60cm to 20cm and even lower. Models 20cm and below are called curb. Naturally, their power differs from the specified standard, and if you plan to use a “non-standard”, you will have to make adjustments. Either look for passport data, or do the math yourself. We proceed from the fact that the heat transfer of a heating device directly depends on its area. As the height decreases, the area of the device decreases, and, therefore, the power decreases proportionally. That is, you need to find the ratio of the heights of the selected radiator with the standard, and then use this coefficient to correct the result.
Calculation of cast iron heating radiators. Can be calculated by area or volume of the room
For clarity, we will calculate aluminum radiators by area. The room is the same: 16m 2. We count the number of sections of standard size: 16m 2 /2m 2 = 8 pieces. But we want to use small sections with a height of 40 cm. We find the ratio of radiators of the selected size to standard ones: 50cm/40cm=1.25. And now we adjust the quantity: 8pcs * 1.25 = 10pcs.
Don't overdo it!
14-15 sections for one radiator is the maximum.
Installing radiators of 20 or more sections is ineffective. In this case, you should split the number of sections in half and install 2 radiators of 10 sections each. For example, place 1 radiator near the window, and the other near the entrance to the room or on the opposite wall. The same goes for steel radiators. If the room is large enough and the radiator is too large, it is better to install two smaller ones, but with the same total power.
If there are 2 or more windows in a room of the same volume, then a good solution would be to install a radiator under each window. In the case of sectional radiators, everything is quite simple.
14/2=7 sections under each window for a room of the same volume
Radiators are usually sold in 10 sections, it is better to take an even number, for example 8. A supply of 1 section will not be superfluous in case of severe frosts. This will not change the power much, but the heating inertia of the radiators will decrease. This can be useful if cold air often enters the room. For example, if this is an office space that clients often enter. In such cases, radiators will heat the air a little faster.
Features of operation
Heaters powered by bottled gas can differ according to numerous criteria
It is necessary to pay attention to the characteristics of the equipment, which will allow you to choose the right heater for the characteristics of a particular building and private home.
Main characteristics:
- Availability of automatic control.
- Type of convention.
- Presence or absence of a fan.
- Energy carrier used.
- Combustion chamber type.
- Installation power.
- Heat exchanger material.
Depending on the design, such heaters can be installed on the floor or mounted on the wall. Wall-mounted models are highly efficient and light weight. The power of wall-mounted liquefied gas convector heaters can reach 10 kW, which allows them to heat large rooms. Floor-standing units can be equipped with a larger heat exchanger, but their performance usually does not exceed 5 kW.
When running a propane boiler is already dangerous:
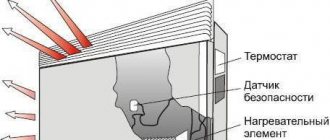
Combustion chamber type
The combustion chamber can be closed or open. In recent years, models with a closed combustion chamber have become the most popular, which ensures the highest possible efficiency and complete safety of equipment operation. Convectors with a closed combustion chamber can have a coaxial pipe instead of a classic chimney, which simultaneously takes in fresh air from the street and effectively removes combustion products outside. The only drawback of convectors with a closed burner is their high cost.
Heat exchanger material
The material from which the heat exchanger is made will directly affect the durability, efficiency and reliability of the equipment. Today on the market there are convectors with heat exchangers made of cast iron and steel. The most durable, reliable and durable devices are those made with a cast iron heat exchanger. If used properly, they will last for 50 years. The disadvantage is the high cost of models with cast iron heat exchangers.
Some convector models will last you longer than others
Convection type
Depending on their type, thermal installations can use forced and natural convention. Heaters operating with natural convection make virtually no noise, which allows them to be used in residential areas. The advantage of devices with forced convection is their improved performance and the ability to use such equipment to heat large areas. Fuel consumption in a bottled gas convector can vary significantly depending on the power of the equipment and its type of convection.
Control automation
The gas convectors we offer can be equipped with both simple automation, which includes only thermostats and control relays, and advanced logic, which ensures maximum automation of equipment operation. Depending on the automation used, the cost of heating installations will differ.
Correct power calculation
The universal formula for calculating power is 1 kW of thermal energy per 10 square meters of room area. However, such calculations will be averaged and will not always allow you to choose the right converter for a specific room. It is necessary to take into account the structural features, ceiling height, the presence or absence of windows, high-quality wall insulation, as well as the climate in the region.
When choosing a convector, you need to calculate its power
When choosing fully automated installations that have a forced convention, you can proceed from the calculation of 0.7 kW of thermal energy per 10 square meters of room area. They can be used as the main heating method only in small buildings. A propane gas convector is an ideal solution for a wooden or brick cottage.
Types of convectors by installation method
Wall-mounted appliances have more power compared to other appliances. They do not take up floor space, so they are easy to use. The disadvantages of this placement option include the fact that warm air does not fall down, but tends to the ceiling, and the floor remains cold.
Floor-standing types of appliances, although they are produced with less power, but due to their location near the floor surface, heat the room much faster. Convenient is the ability to move to different points, which cannot be done with a permanently mounted electric wall convector.
The installation of small-sized electric heating devices in floor niches significantly saves space in small rooms. In recent years, such placement has been very popular, although it requires preliminary work.
Skirting types of convectors have received positive reviews. which give a feeling of comfort to the feet. Their power is small, but to increase the flow of warm air, some users buy two or more devices, which equates to the energy consumption of a large device.
Different types of thermostats
The temperature regulator is adjusted so that if there are no residents in the house, the room is heated in a gentle mode and does not require unnecessary consumption of electrical energy. By time, you can set a mode when the switching on occurs automatically with the return of household members.
Temperature regulators can be mechanical or electronic. The first type significantly reduces the price of the device, but is not very convenient in terms of comfort. It cannot fully monitor the temperature regime; sometimes it allows, albeit minimal, additional waste of electricity.
In addition, switching is accompanied by quiet sounds, which at night can cause trouble for a sleeping person.
Heating system options
So, let's look at existing equipment that will make electric heating in the house economical and cheap.
Using the boiler
Installing an electric boiler, which will heat water in the home heating system, warming up the room, is the first, least effective option. Of course, on the Internet you can see a bunch of information that talks about economical boilers that can reduce consumption by up to 80%, but all this is nonsense. The only option to reduce costs is to install thermostats and various automation systems, which will turn on only when the temperature in the room drops, as well as at certain times of the day. All other talk about new product designs or reduced power is just a publicity stunt. If you buy a small-power boiler, it will take more time to heat the water for heating the house, so that’s what it will do.
Using IR Panels
Installing infrared heaters is a more reasonable solution and, most likely, the most profitable. The fact is that these products do not heat the air in the room, but certain objects (floor, walls, closet), from which heat is subsequently transferred. If in the previous version the hot air will rise to the ceiling and immediately cool down, then in this case the heat is directed to the floor, which is more reasonable (people do not walk on the ceiling).
This diagram shows the efficiency of an economical heating system for a private home:
You see everything for yourself, so there is nothing more to prove. It should only be noted that IR devices can work more efficiently if you add thermostats to them. One regulator is enough to control three heaters in an economical heating system for a private home. We talked about how to connect a thermostat to an infrared heater in a separate article.
Using convectors
Many manufacturers convince us that an electric convector effectively heats a room and at the same time consumes a small amount of electricity. The issue is of course controversial, because, in fact, the principle of operation of the products is similar to the option with radiators (the air rises upward). The advantage of convectors is that their installation and connection are not difficult. In addition, heating of the heating element takes about one minute, which is undoubtedly faster than in the case of water radiators.
Other advantages of electric convectors include:
- low cost (from 2 to 10 thousand rubles);
- fire safety (which is especially important when installing heating in a wooden house);
- you can gradually increase the heating system (one convector for a room is not enough, buy another one and connect it to the network without any problems);
- attractive appearance;
- trouble-free operation during power surges (also important in the private sector);
- compact sizes.
Separately, I would like to recommend that you explore a heating option such as electric heated floors. You can find out a review of this heating system by watching the video:
Application of heated floors
We analyzed reviews from customers who used this option and saw that most people were satisfied with the purchase. The main thing is to additionally install a temperature regulator in order to make economical electric heating in the house with your own hands.
Calculation of the required convector power
Professional methods are used for detailed calculation of thermal power. They are based on calculating the amount of heat loss through the enclosing structures and correspondingly compensating them with thermal heating power. The methods are implemented both manually and in software format.
To calculate the thermal power of convectors, an integrated calculation method is also used (if you do not want to contact designers). The power of convectors can be calculated by the size of the heated area and the volume of the room.
The generalized standard for heating a built-in room with one external wall, a ceiling height of up to 2.7 meters and a single glazed window is 100 W of heat per square meter of heated area.
In the case of a corner location of the room and the presence of two external walls, a correction factor of 1.1 is applied, increasing the calculated thermal power by 10%. With high-quality thermal insulation, triple window glazing, the calculated power is multiplied by a factor of 0.8.
Thus, the calculation of the thermal power of the convector is calculated based on the area of the room - to heat a room with an area of 20 sq.m. with standard heat loss indicators, you will need a device with a power of at least 2.0 kW. With a corner location of this room, the power will be from 2.2 kW. In a well-insulated room of equal area, you can install a convector with a power of about 1.6 - 1.7 kW. These calculations are correct for rooms with a ceiling height of up to 2.7 meters.
For rooms with higher ceiling heights, the volume calculation method is used. The volume of the room is calculated (the product of the area and the height of the room), the calculated value is multiplied by a factor of 0.04. When multiplied, the heating thermal power is obtained.
Using convectors in large rooms
Using this method, a room with an area of 20 square meters and a height of 2.7 meters requires 2.16 kW of heat for heating, the same room with a ceiling height of three meters requires 2.4 kW. With large volumes of premises and significant ceiling heights, the calculated capacity by area can increase up to 30%.
Calculation of convector power by volume
You already know how to calculate the power of a convector, taking into account the area of the premises. But some experts believe that it is best to calculate by their volume. To do this, use the formula according to which per 1 cubic meter. m. volume requires 40 W of heat
. The main advantage of this formula is that it is the most accurate, since it fully takes into account the height of the ceilings.
The process of calculating the power of convectors by volume is carried out as follows:
- We take a tape measure and measure the room;
- We calculate the volume of the room by multiplying the obtained values by each other;
- Multiply the volume by 0.04 (40 W per 1 cubic meter);
- We get the recommended thermal power.
A more clear example - let's try to calculate the power of convectors for a room 3 m long, 2.5 m wide and 2.7 m high. Its volume is 20.25 cubic meters. m, therefore, the power of the convector heaters used should be 0.81 kW (feel free to buy a 1 kW model). If we make similar calculations for the area, the recommended figure will be 0.75 kW.
As in the case of calculating the power of convectors by area, it is necessary to take into account in the calculations possible heat losses that may be present in any room.
Our houses lose a lot of thermal energy. In order not to overpay for electricity, just get rid of heat loss.
By making calculations based on area or volume, and not taking heat losses into account at all, you risk getting an insufficiently efficient heating system - the rooms will be cool. The worst thing is if severe frosts hit in winter, which are not very typical for this area - if the calculations were made incorrectly, the convectors will not cope
Next, we will tell you how to reduce heat loss. The banal lining of the household with an additional layer of brick and thermal insulation will help reduce them by 10-15%. Yes, the costs may be high, but you must remember that when using electric convectors, the costs of light can be gigantic - this is associated with large heat losses (in fact, you are heating the air “outside”).
You also need to work on the windows:
- Single-glazed windows require a 10% increase in power;
- Double windows do not lead to any heat loss (already a plus);
- Triple windows can save up to 10%.
In theory, three-pane windows can lead to significant savings, but there are other factors to consider.
During the insulation process, it is necessary to work in the attic. The whole point is that having an unheated attic entails losses. Therefore, you need to lay a layer of effective thermal insulation on it - it is not very expensive, but you can save up to 10% of thermal energy. By the way, the figure is 10%, based on the area of the house of 100 square meters. m, this is approximately 24 kW of heat per day - equivalent to monetary costs of 100 rubles / day or 3000 rubles / month (approximately).
Basic data
Accurate thermal calculations are quite complex, and they are done by specialists when designing a heating system. If ordering it is problematic, you can do a simple calculation yourself.
To complete it you need to have basic information:
- Initially, you need to know the dimensions of the room where the heating radiators will be installed:
- Length.
- Width.
- Height.
- Then you need to decide on the choice of batteries:
- steel plate;
- cast iron;
- bimetallic;
- aluminum.
- In the technical documentation for each radiator, the characteristics from the manufacturer indicate the thermal power of the device. This is the amount of heat in watts that can be generated by 1 modular section element in 1 hour.
For reference, one watt is equivalent to 0.86 calories of heat.
- To calculate the power of radiators, it is necessary to use the standard heat transfer values of each section, namely:
- For Soviet-made cast iron batteries - 160 W.
- Aluminum with a center height of 500 mm - 200 W.
- Non-dismountable steel panels with a length of 500 and 800 mm, respectively, 700 and 1500 W.
Climate zones are also important
Climatic zones also have their own coefficients:
- central Russia has a coefficient of 1.00, so it is not used;
- northern and eastern regions: 1.6;
- southern stripes: 0.7-0.9 (minimum and average annual temperatures in the region are taken into account).
This coefficient must be multiplied by the total thermal power, and the resulting result divided by the heat transfer of one part.
conclusions
Thus, calculating heating by area does not present any particular difficulties. It’s enough to sit a little, figure it out and calmly calculate. With its help, every owner of an apartment or house can easily determine the size of the radiator that should be installed in the room, kitchen, bathroom or any other place.
If you doubt your abilities and knowledge, entrust the installation of the system to professionals. It’s better to pay professionals once than to do it wrong, dismantle it and start work again. Or do nothing at all.
Choosing an installation location
Or rather, the question is not this: which convector is suitable for fulfilling your wishes. If you want to bring the appearance of the room closer to the standard one, you can hang rectangular wall convectors under the windows. Models that can be installed under the ceiling attract a little more attention, but they are inaccessible to children and pets - they will not be able to get burned or “adjust” in their own way. The installation method is the same here - on brackets fixed to the wall. Only the shape of the brackets differs.
You can choose any location for installing the electric convector. It is only advisable that it is not covered by furniture
If you want your heating appliances not to be visible, you will have to choose between baseboard and in-floor models. There is a big difference in installation: skirting boards are simply installed and connected to the network, but for in-floor ones you will have to make special recesses in the floor - their top panel should be on the same level as the finished floor. In general, you cannot install them without major repairs.
These are floor-mounted convectors. They are also electric
Calculations of electricity consumption by household appliances
Before finding out how much electricity a heater consumes, let’s consider the consumption of other household appliances. All devices that require electrical energy to operate consume this energy in accordance with their power. However, not all such devices operate in the same way and, accordingly, electricity consumption is not the same. Appliances such as an electric kettle, TV, and various types of lighting fixtures begin to consume the maximum amount of energy when turned on. This amount of energy is indicated in the technical characteristics of each device and is called power.
Let's say a kettle with a power of 2000 W was turned on to heat water and worked for 10 minutes. Then we divide 2000 W by 60 minutes (1 hour) and it turns out 33.33 W - this is how much the kettle consumes in one minute of operation. In our case, the kettle worked for 10 minutes. Then we multiply 33.33 W by 10 minutes and get the power that the kettle consumed during its operation, i.e. 333.3 W and it is for this consumed power that you will have to pay.
The operation of a refrigerator, electric stove and electric convector works somewhat differently.
Methods for determining the electricity consumption of household appliances and tools
The average electricity consumption in citizens' apartments per month is the sum of the total electricity consumption of all electrical appliances used by its residents. Knowing the electricity consumption for each of them will give an understanding of how rationally they are used. Changing the operating mode can provide significant energy savings.
The total amount of electricity consumed per month in an apartment or house is recorded by the meter. There are several ways to obtain data for individual devices.
A practical way to calculate electricity consumption based on the power of an electrical appliance
The average daily electricity consumption of any home appliance is calculated using the formula; just remember the basic characteristics of electrical appliances. These are three parameters - current, power and voltage. Current is expressed in amperes (A), power in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW), and voltage in volts (V). From the school physics course, we remember how electricity is measured - it is a kilowatt-hour, it means the amount of electricity consumed per hour. All home appliances are equipped with labels on the cable or on the device itself, which indicate the input voltage and current consumption (for example, 220 V 1 A). The same data must be present in the product passport. Based on current and voltage, the power consumption of the device is calculated - P=U×I, where
- P – power (W)
- U – voltage (V)
- I – current (A).
We substitute the numerical values and get 220 V × 1 A = 220 W.
Next, knowing the power of the device, we calculate its energy consumption per unit of time. For example, a regular liter electric kettle has a power of 1600 W. On average, he works 30 minutes a day, that is, ½ hour. We multiply the power by the operating time and get:
1600 W × 1/2 hour = 800 W/h, or 0.8 kW/h.
To calculate costs in monetary terms, we multiply the resulting figure by the tariff, for example, 4 rubles per kWh:
0.8 kW/h×4 rub.=3.2 rub. Calculation of the average monthly fee - 3.2 rubles * 30 days = 90.6 rubles.
In this way, calculations are made for each electrical appliance in the house.
Counting electricity consumption using a wattmeter
The calculations will give you an approximate result. It is much more reliable to use a household wattmeter, or energy meter - a device that measures the exact amount of energy consumed by any household device.
Digital wattmeter
Its functions:
- measuring power consumption at a given moment and over a certain period of time;
- current and voltage measurement;
- calculation of the cost of consumed electricity according to the tariffs you have set.
The wattmeter is plugged into a socket and the device you are going to test is connected to it. The display shows power consumption parameters.
Current clamps allow you to measure the current and determine the power consumed by a household appliance without disconnecting it from the network. Any device (regardless of manufacturer and modification) consists of a magnetic circuit with a movable disconnect bracket, a display, a voltage range switch and a button for recording readings.
Measurement procedure:
- Set the desired measuring range.
- Open the magnetic circuit by pressing the bracket, place it behind the wire of the device under test and close it. The magnetic core must be located perpendicular to the power wire.
- Take readings from the screen.
If a multi-core cable is placed in the magnetic core, the display will show zero. This happens because the magnetic fields of two conductors carrying the same current cancel each other out. To obtain the required values, measurements are carried out on only one wire. It is convenient to measure energy consumption through an extension cord-adapter, where the cable is divided into separate cores.
Determining energy consumption using an electric meter
A meter is another simple way to determine the power of a household appliance.
How to count light using a meter:
- Turn off everything in the apartment that runs on electricity.
- Record your readings.
- Plug in the desired device for 1 hour.
- Disable it and subtract the previous readings from the received numbers.
The resulting number will be an indicator of the electricity consumption of the individual device.
Heating convector power table
This section of the article provides a table for selecting the power of convectors depending on the area of the heated room and volume.
| Heated area, sq.m., room height – up to 2.7 meters | Convector thermal power, kW | Thermal power of the convector (ceiling height -2.8 m) | Thermal power of the convector (ceiling height -2.9 m) | Thermal power of the convector (ceiling height -3.0 m) |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 6 |
| 10 | 1,0 | 1,12 | 1,16 | 1,2 |
| 15 | 1,5 | 1,68 | 1,74 | 1,8 |
| 20 | 2,0 | 2,24 | 2,32 | 2,4 |
| 25 | 2,5 | 2,8 | 2,9 | 3 |
| 30 | 3,0 | 3,36 | 3,48 | 3,6 |
From the table below you can select a convector according to the heated area. Heights are given in 4 options - standard (up to 2.7 meters), 2.8, 2.9 and 3.0 meters. For angular configurations of premises, an increasing factor of 1.1 must be applied to the selected value; for construction with high-quality thermal insulation, a decreasing factor of 0.8 must be applied. If the ceiling height is more than three meters, the calculation is carried out using the above method (by volume using a coefficient of 0.04).
After calculating the thermal power, heating convectors are selected - quantity, geometric dimensions and installation method. When selecting devices in rooms of large area and volume, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics and power value of each individual convector. It is necessary to be guided by the principle of increased power of the convector installed in the blockage zone of maximum heat losses. That is, a device installed along a full-profile glass display case should have a higher thermal performance value than a convector placed near a small window or an external wall.
Formula for calculating the thermal load taking into account the temperature difference
To more accurately determine the required thermal power of a heater or convector, we recommend using the following formula.
V (room volume) x T (temperature difference) x φ (heat loss coefficient) = kcal/h
Where:
- V is the volume of the room mentioned above: width * length * height.
- T (temperature difference) – depending on the climate zone, the temperature outside can be -5 C or -30 C. Therefore, a parameter was introduced into the formula to express the difference between the average winter temperature outside and the desired temperature indoors. Example: the average winter value outside is -15C, and in the room 25C is required - it turns out T = 40C.
- φ – coefficient of heat loss of premises depending on the design and insulation. 3-4 – lack of thermal insulation. Simple wooden or metal buildings without insulation.
- 2-2.9 – low thermal insulation. Single brick masonry, simplified building design, single windows.
- 1-1.9 – average thermal insulation. Buildings with two bricks, standard buildings, ordinary roofing, a small number of windows.
- 0.6-0.9 - high thermal insulation. Few windows, double glazing, brick walls, double insulation, insulated roof and thick subfloor.
To obtain the power value of a convector or heater in kilowatts, you need to divide the resulting number by 860.
How to calculate and choose an electric convector
We calculate the required power of the convector
- Calculation of convector power by room area. Provided that the room is well insulated and has a ceiling height of no more than 2.7 m, 1 kW of thermal energy will be sufficient for every 10 m² of heated area. For a 6 m² bathroom, one 1 kW heater should be enough. A 20 m² bedroom has a convector with a capacity of 2 kW.
- Number of windows. The operating principle of the devices is associated with the use of convection, this in a certain way makes adjustments to the choice of heaters. The total thermal energy required to heat the room should be divided by the number of window openings. So, for a room of 20 m² and having two windows, you will need to install 2 heaters of 1 kW each.
- Presence of heat loss. The technical characteristics of electric convectors given in the operating instructions for the device, in particular the coefficient of heated area, are taken taking into account the absence of significant heat loss in the room. If you have an uninsulated basement or house walls, you should choose a heater with a sufficient power reserve.
Choosing an electric convector based on functionality
What do manufacturers offer?
- Mechanical thermostat. Almost every device is equipped with a mechanical or electronic thermostat. The mechanics do not withstand loads well and cannot accurately regulate the temperature. Leaving an electric convector unattended is strongly discouraged. If overheated, the mechanical control unit may fail, resulting in a fire hazard.
- Electronic thermostat – maintains the set temperature with a minimum error of no more than 1/10 degree. Comes complete with timer and temperature sensor. Using an electronic thermostat reduces energy consumption. Wall-mounted energy-saving electric heating convectors with an electronic thermostat are recommended to be used as the main source of heating. The control unit has several degrees of protection to ensure safe operation.
- A programmable thermostat is a control unit installed in premium heaters. Typically, such modifications are equipped with remote control and can even be connected to a GSM alert system. Programming of operating modes is provided. 2-4 ready-made programs are installed, and it is also possible to set an individual heating mode. The heater is turned on by the control panel.
- Additional functions. Climate control equipment from well-known manufacturers often has built-in modules that affect the quality of operation. Models with an air humidifier are popular. Premium heaters automatically monitor and maintain the required humidity in the room.
Does an electric convector dry the air?
When using a fan, a slight decrease in moisture is observed. This is especially noticeable if the heaters are operated in constant mode. Compared to heat guns, a convector does not dry the air at all.
As an additional measure to maintain a healthy microclimate, it makes sense to install an air humidifier complete with an ionizer, or purchase a modification of the heater with a built-in device of this type. The control system itself will automatically monitor the humidity level and maintain it at the proper level.
Which is better, an electric convector or a fan heater?
Unlike fan heaters, convectors operate in a safer mode. Thanks to this, you can even hang electric convectors on a wooden wall. The surface temperature of the housing rarely exceeds 60°C.
Of course, you should follow the rules for installing electric convectors in a wooden house:
- The electrical wire is laid on top of wooden surfaces in a special fire-resistant corrugation.
- Thermal insulation with foil coating is placed under the heater installed on the wall.
- Floor-mounted electric heating convectors for a wooden cottage are installed in such a way that the distance to the nearest wall is at least 0.5 m. There is no need to place non-combustible material under the heater.
Type
Oil radiator
One of the most popular household heaters. They have a power of 1.0 to 2.5 kW and are used in apartments, offices, and country houses.
| Principle of operation | Inside a sealed metal case filled with mineral oil, there is an electric coil. When heated, it transfers its heat to the oil, which in turn transfers to the metal body, and then to the air. Its outer surface consists of several sections (fins) - the greater their number, the greater the heat transfer, with equal powers. The heater maintains the set temperature in the room and automatically turns off in case of overheating. As soon as the temperature starts to drop, it turns on. |
| Advantages | Low heating temperature of the housing (about 60 o C), due to which oxygen is not “burned”, fireproof, silent thanks to the thermostat and timer, some models do not require switching off, high mobility (the presence of wheels makes it easy to move them from room to room) |
| Flaws | It takes a relatively long time to warm up the room (however, it retains heat longer), the temperature of the radiator surface does not allow you to freely touch it (which is extremely dangerous if there are children in the room), relatively large dimensions |
| conclusions | Oil radiators are ideal for heating apartments. Quietness, efficiency and safety are very important here. One heater is enough to heat a living room or bedroom. Oil radiators are equipped with wheels and can be easily moved from room to room. For the summer, you can simply take the oil radiator out to the shed or put it in the pantry. |
Traditional methods of skin lightening
Only with comprehensive lightening of the face and body will the effect look organic. Milk baths are suitable for this.
. All fermented milk products contain acids and compounds that reduce the number of melanocytes - cells that produce melanin. These cosmetic procedures do not require huge investments. For one session, 1.5 liters of fresh milk and about 30 grams of honey are enough.
Milk bath
How to make a milk bath at home:
- Milk (exclusively homemade) is heated to a pleasant warmth, but not boiled - otherwise there will be no effect;
- The specified amount of honey is dissolved in hot liquid. Buckwheat is considered the most useful for the procedure - it is rich in active substances and has an increased amount of vitamin compounds. At worst, you can take acacia, but in no case synthetic;
- The prepared concentrate is poured into a bathtub filled with water at 39 degrees (it feels warm, but not hot). Afterwards you can lie down in the liquid and enjoy for 30 minutes;
- When time has passed, it is additionally recommended to wipe yourself with cucumber lotion. You can repeat sessions daily or at least 12 times a week.
It is important to remember that before you make your skin pale at home, check the components of the masks for allergenicity. Apply the product to an inconspicuous area of the body and wait 20 minutes
If during this time there is no redness or itching at the site of use, you can safely apply it to your face.
Even dark skin can be made quite pale if you wipe it with a slice of lemon
.
Some girls use orange zest tincture for the same purpose, but it has a strong drying effect. After wiping, you need to wait about half an hour and rinse off any remaining product with cool water. Repeat every day (best in the morning). Lemon for pale skin
If you are allergic to citrus fruits, an analogue of this method is rubbing with a slice of aromatic melon
. With its help, the skin is saturated with essential acids, mineral compounds and vitamins (in particular, PP, which protects against UV rays and brightens it). You need to use melons in the same way as lemon.
To get beautiful and matte white skin, girls used to use a decoction of chamomile and linden
. Take a glass of dried flowers for half a liter of water. To preserve beneficial properties, the plants are not boiled, but infused in hot water for 2 hours. The resulting liquid should be washed off the body and face every evening after a shower.
An unusual combination of castor oil and hydrogen peroxide gives a bright pallor to the entire body. These products are combined in equal proportions and applied using a sponge. You don’t have to rinse it off – the main thing is to distribute the solution evenly. Conveniently, this method is suitable for lightening the delicate skin under the eyes, in the bikini area and armpits.