new ceiling, without insulation, etc. fuck? Well, that is, the ceiling, a water-heated floor pipe on top, then screed and laminate - and that’s it.
Has anyone done this? Any impressions?
probably like this: “Ordinary Marketing Bullshit” (OMF) For those who didn’t go to school: IR radiation penetrates a solid body only a few microns. And it is completely absorbed by this thin layer. This means that IR radiation, reflected by the aluminum layer, will move away from it by several microns, heat the concrete, which in turn heats the aluminum. Hence the simple conclusion: with or without the film, the temperature of the concrete-thermal insulator transition will remain exactly the same. But applying an aluminum film, which costs 3 kopecks, allows suckers to sell it for 3 thousand rubles - the profitability of the “business” is 1000%.
PS: Do not confuse the operation of the reflector in air, and even more so in airless space (for example, on spacecraft, where infrared radiation is the only way to cool the device).
warm the floor under beds, cabinets, tables, . useless and meaningless.
TP is generally made for comfort, not for heating. And comfort is a constant temperature. But a constant floor temperature cannot compensate for variable external conditions.
You are making a classic mistake: you have two variables but one regulator - mathematics and logic deny such somersaults.
Therefore, 1. You do TP around the bed (this is only a couple of m2). 2. Place a standard water battery under the window, with a thermal head).
You have two regulators (TP and battery), and you can always set two comfortable parameters - so that your bare heels are comfortable, and so that it is not hot in the bedroom.
It won't work any other way.
PS: An electric TP does not consume as much as the cable power, but approximately 20 W/m2 (this is the difference between +22 in the air and +24 on the floor (my comfort)). So there will be no “ruin”.
and yet what is the task? to be heated? or for comfort?
Personally, I plan to go directly to the floor slabs so that there is a heat accumulator
be heated comfortably. > personally, I plan to use the floor slabs directly, > so that there is a heat accumulator
I planned that too, but now they say you can’t do that.
Of course you need to listen to Brutus)) but.
I think that in the “comfort” mode the stove will be heated - 23 degrees
Let's look at the system from top to bottom
item 1 room air (
23 degrees) item 2 laminate ( . ) item 3 warm floor (24 degrees - on average.) item 4 floor slab ( . ) item 5 air in the base (??
So I think yes! There is heat removal from the laminate (whether due to ventilation flows) but! the slab (item 4) is also insulated from below (item 5 is a poor heat conductor)
thus the proportions 70-30 are somewhat exaggerated
20 watts per meter - that’s per room - 20 square meters = 400 watts - that’s a lot in the mode of “maintaining” the temperature from 20 to 22.
this means that in fact it is necessary to supply less power, that is, the system is even more viable
I won’t say anything about the eerie descent of some terribly heated air somewhere
PS – by the way, I really liked the idea of insulating the ceiling of the plinth)
yes. You will insulate the ceiling, but the heat will spread to the sides - onto the walls of the basement. Moreover, concrete is perhaps the best conductor of heat (from building materials) - the heat loss zone will be approximately 1 m from the edge of the slab. How much area is the room? 20 m2? this is a 4.5x4.5 square. So, subtract 1 m along the perimeter. What remains? a square in the center 2.5x2.5 = 6 m2 - you protected this area from losses, and from the sides 14 m2 heat flows to the walls of the base.
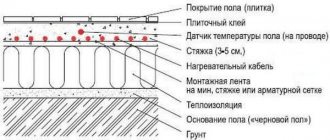
The main task performed by thermal insulation in heated floors
The home heating systems we rely on are designed to provide us with efficient heating. In houses where radiators are installed, heat enters the heated room due to the contact of the surface of the heating devices with the air mass. As a result of heat exchange, up to 60% of the heat goes to heating the internal space as a result of air convection. Water heated floors are much more effective in this regard. By heating the floor surface, heat is distributed evenly inside the room, creating comfortable living conditions.
High efficiency of an in-floor heating system can be achieved through proper installation and placement of all structural elements. Not the least important place in this regard is played by thermal insulation for your heated floor, based on the water principle of operation. An incorrectly laid insulation layer or its absence will lead to your heating system running 50% idle. The heat from the heating circuit should go up, not down, heating the concrete screed or stacked wooden structure.
Note: experts say that a warm water floor without insulation leads to significant heat loss in winter. Up to 50% of thermal energy is spent on heating the ceiling in the basement. The lack of insulation for heated floors on interfloor ceilings causes insufficiently comfortable temperatures in the heated room.
For clarity, the following example can be given:
The previously used polystyrene foam has a density of 20-22 kg/m3, however, in accordance with the technology for laying warm water floors, the density of the insulating material should be at least 35 kg/m3 for interfloor floors and 50 kg/m3 for floor equipment on the first floor. The presence of such restrictions on thermal insulation materials is caused by technological factors that are determined by the very principle of operation of heated floors.
Water floors are a low temperature heating system. The floor in a heated room should not heat up above 30 0 C. Exceeding these parameters will create discomfort inside the room. A negatively high floor heating temperature will affect the design features of the floor covering, and the heating devices will work with increased load. The presence of a thermal insulation layer of the required thickness will eliminate heat losses during the operation of water circuits and create optimal conditions for the spread of heat in the desired direction. A smaller thickness of thermal insulation will lead to the fact that heat will go into the underground. The large thickness of the insulating material will become a serious obstacle to heating the floor and floor covering. In this case, the operation of warm water floors will be fundamentally disrupted.
About the pros and cons of “dry” floor systems
In dry-type systems, the main components are those that look like an inverted Greek letter, ordinary metal plates. Heat pipes with a carrier inside wrap around the deepening walls on both sides. The “side wings” of a warm field without a screed help to increase the area for heat dissipation.
Each arrangement option in this case has a plus and a minus. General characteristics – light weight with efficiency. Installation is accelerated due to the absence of “wet” processes. Therefore, it is worth understanding the installation system.
Installation is accelerated due to the absence of “wet” processes.
What is the basis for choosing an insulating material?
The basis for a heated floor is the so-called “layer cake” - a stacked structure in which each layer performs its own specific functions and tasks. Insulation takes one of the leading places in this pie, so a lot depends on the quality of the insulating material, its composition and structure. Thermal insulation must meet any changes in the operating conditions of the heating communication. The safety of the insulating material is one of the main factors determining its choice.
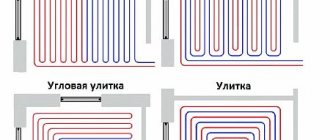
Methods for laying a water circuit
The location of the pipes requires a preliminary plan. In most cases, it is assumed that separate circuits are connected for each specific room. At the same time, the most reliable option is when they use solid pipes that have no joints.
Snake contours are the simplest and most economical to install. But they increase the likelihood of the coolant cooling down. Therefore, the method is used for rooms where it is easier to comply with the conditions.
Snake contours are the simplest and most economical to install.
Features of the practical use of various insulating materials
Expanded polystyrene
Let's start with the fact that the thermal insulation is laid at the very bottom of the layer cake, directly on the rough covering. Before laying the layer of thermal insulation, waterproofing is laid on the subfloor and only after that they begin laying the thermal insulation layer. Let's look separately at how work is done with the most common and popular materials.
Let's start with polystyrene foam. The material is available in the form of sheets or plates. This form is very convenient for installation work. The thickness of polystyrene foam may vary. The thickness of the sheets varies from 30 to 120 mm. For installation work of all categories, especially in the case of heated floors, a type of polystyrene foam is used - penoplex (extruded polystyrene foam).
Expanded polystyrene has extremely low thermal conductivity and is very convenient and practical during installation. However, this material has a significant drawback, insufficient hardness.
Important! Do not forget that penoplex is a fragile and fragile material, however, to give strength and rigidity to the entire subsequent structure of the water floor, you will need a concrete screed or a stable flooring system.
In order to get rid of this drawback when forming a pie, reinforcement for a concrete screed is used, or additional flooring is made from plywood slabs or gypsum fiber board sheets.
A simpler way out of this situation is to use a cheap analogue - ordinary polystyrene foam.
For polystyrene foam, the optimal thickness of the thermal insulation layer is at least 100 mm. When installing heated floors on ceilings, a foam thickness of 25-30% less will be sufficient.
We use mineral mats
To obtain the necessary rigidity for a layer cake, people most often pay attention to mineral mats. They are based on the well-known mineral wool, but thanks to production technology, the material has a rigid structure. With the help of mineral mats, you can easily fill the existing voids in the subfloor and fill all the cells of the layer cake with a rack layout. Despite the obvious advantages over expanded polystyrene, the material is not resistant to moisture.
Note: a damaged layer of steam and waterproofing can lead to the mats absorbing existing moisture and losing their insulating properties. The water floor can be laid on mineral mats made of basalt or fiberglass.
Other, less commonly used thermal insulation materials include cork. Cork thermal insulation has low thermal conductivity, but weakly resists moisture. Fungal growths often occur in floors with such thermal insulation. For best performance, it is necessary to use waxed cork material. In this case, the price increases, and in terms of its technological characteristics, cork is inferior to foam plastic and expanded polystyrene.
Other installation methods
The sale involves the sale of both pipes with the addition of bosses and ready-made recesses. A great way to treat smooth surfaces, or do something inside. Heating loops can also be made from different materials:
- Polystyrene, whose density is 35 kg/m3;
- Products on wood with pre-prepared cutouts, factory-made;
- Polystyrene materials with the addition of ready-made grooves.
One of the acceptable options for placing polystyrene slabs is between the joists. The grooves are also burned out with ordinary foam plastic, the density of which is sufficient.
The sale involves the sale of both pipes with the addition of bosses and finished recesses.
Is insulation needed for underfloor heating (specific case)
Dear specialists! Having shoveled through a bunch of threads about heated floors, I still haven’t resolved one question for myself. Whether to put insulation under the screed or not. The diagram of the house is shown in the figure below.
The house is one-story, made of expanded clay concrete, with a pile foundation, more than twenty years old. It doesn't move or move anywhere. All floors are covered with reinforced concrete slabs. In a year, additional external insulation is planned. The underground is made with the possibility of storing vegetables and other natural gifts there. To do this, a square concrete container is dug in the middle. Between the walls of this container and the perimeter of the house there is simply earth. From the ground to the ceilings is about 90 cm, and the height of the container itself is about a meter or more. This winter, the house was heated purely “to support the pants” with three electric heating elements of 1.5 kilowatts each, the windows in some places were without glass, the outside was clogged with film, but even at -38 outside the house remained at +12. But there was a specific disadvantage in the underground. The walls of the basement were covered with a cap of frost, the water in the concrete container froze even in slight frosts. Most likely this was due to poorly closed vents and sagging earth under the walls.
So I have questions. The first is whether there will be enough heating for the house with purely warm floors (although I think it will be enough). And is it necessary to separate the heated floor screed from the reinforced concrete slab? On the one hand, I like the idea of a stove as a heat accumulator and low-temperature emitter (heat it once and then just maintain it), but won’t it be too warm in the underground later? I'd like to hear your opinions.
When is it better to use a deck structure?
Polystyrene or wood are equally used for decking structures. In the first case, the use of special mats is assumed, in the second, strips and ready-made modules are used. It is easy to mount steel and aluminum plates on top of any type of structure. The grooves are filled with heating pipes.
Compliance with such conditions is associated with the possibility of using warm, dry floor coverings:
- Restrictions on the height of premises. An example is when there are low ceilings or the design solution itself does not involve adjustments to the floor level;
- Weakness of overlap. The lower weight of dry screeds makes a difference;
- A specific object does not allow the installation of a conventional concrete screed.
The disadvantages include the need for waterproofing due to fear of moisture.
It is easy to mount steel and aluminum plates on top of any type of structure.
Additional constructs
For better heat dissipation in heated floors without screed, special panels are used. This is a profile element made of aluminum alloy. It has a straight recess for the tube. These structures are located in straight areas of the contour and work as an effective reflector, distributing heat over a larger area.
The use of dissipative panels improves the performance of underfloor heating without screed. This is especially noticeable if the surface is covered with a finishing layer with high thermal conductivity, for example, ceramic tiles. Be careful when working with diffuser panels.
They perform well (do not move, do not creak) on a solid base surface. When installing heating circuits without screed on ready-made structures made of wood-containing materials or on a slatted structure created from boards, the dissipating panels can be fixed with self-tapping screws.
Installation of extruded polypropylene boards
After the floor is leveled with the self-leveling mixture, you can proceed directly to laying the system itself. To do this, you first need to spread polyethylene on the floor, this is done for complete waterproofing. Polyethylene must be at least 100 microns thick.
When joining on the floor, polyethylene must be laid with an overlap of 10-12 cm and with a margin of 8-10 cm on each side of the wall. Next, extruded polypropylene plates are laid on the floor, the thickness of which in this case should not be less than 30 mm. Polypropylene boards are primarily a very good thermal insulation material, with almost zero capillarity, very low water absorption and high compressive strength.
In addition to these characteristics, polypropylene is durable (does not rot) and chemically resistant. The slabs have standard dimensions of 1250x600 mm and locks at the ends for better joining.
When laying slabs, each subsequent row must be shifted from the previous one by 30-40 cm, so that the end seams are ultimately in a zigzag position. When installing polypropylene, liquid polystyrene foam nails are applied to the sheet lock using a sealant gun, the quantity and method of application of which is carried out according to the instructions. Polypropylene is easy to cut with a knife, so if you need a smaller sheet, it can be cut without much difficulty.
Lightweight decking system design
During installation, you can equally use waterproofing and vapor barrier. Each technique has negative and positive sides.
But the general design remains approximately the same in all cases:
- Base for laying insulation;
- Thermal insulation material;
- Heat distribution type plates;
- Pipelines through which water circulates;
- Supporting covering in the form of a finished floor.
During installation, you can equally use waterproofing and vapor barrier.
Common mistakes
Usually they are associated with a violation of the general repair order or the fact that one material is confused with another. Therefore, it is important to take additional notes to avoid confusion. The job is not that difficult if you follow the directions. An electric floor quickly produces results and pays for itself.
Warm floors can be a means of serious savings if you approach the installation process correctly.
Warm floors can be a means of serious savings if you approach the installation process correctly. It is necessary to study in advance the compatibility between different bases and coatings in order to select the material that will be most effective. Then the result will please you for many years, and you can forget about minor repairs.