When building a house, the most important task is its thermal insulation, the quality and durability of which determines not only comfort, but also heating costs. In suburban housing construction, ecowool is becoming an increasingly popular thermal insulation material, the pros and cons of which will be discussed in detail in this article, along with issues of installation and the feasibility of use on different structures.
Ecowool can be used to insulate almost all parts of the house Source green-agency.ru
Which is better, ecowool or mineral wool?
Ecowool or mineral wool are materials with a loose structure, consisting of many fibers. The thermal insulation effect is ensured by the presence of air between the fibers. It accumulates heat retained by the loose structure. When choosing, pay close attention to the characteristics of the material.
To make mineral wool, two types of fibers are used, obtained from glass or basalt rocks. Any of these materials belongs to the mineral category, hence the name of wool: “mineral”, “stone”, “basalt”. All these products have largely similar thermal conductivity and moisture absorption characteristics. Moreover, the technical characteristics directly depend on one parameter – density. The higher it is, the lower the thermal conductivity and moisture absorption.
Considering the demand for different types of insulation, mineral wool manufacturers offer several modifications of these materials that differ in density. The list of products, compiled in ascending order of this indicator, is as follows:
- loose rolled cotton wool;
- light slabs;
- soft slabs;
- semi-rigid slabs;
- cylinders and half-cylinders;
- hard slabs.
All mineral wool insulation, made from glass or basalt fiber, has good vapor permeability. Despite their fairly high hygroscopicity, they do not rot. Serve for at least 15 years.
Ecowool is an environmentally friendly material, as reflected in its name. It is made by shredding paper: waste paper, packaging, paper production waste. To prevent rotting of the raw material, boric acid and flame retardants are added to it: fire retardants. Mostly borax.
Mineral wool
Mineral wool is an inorganic fibrous insulation material . The mineral wool class includes: glass wool, slag wool, basalt (stone) wool. All these types have a similar composition, but differ in different fiber lengths and thicknesses, as well as other parameters.
Consider the types of mineral wool :
Glass wool
Glass wool is one of the most common and inexpensive materials, as it is made from recycled glass (glass scrap), sand, limestone, soda, and dolomite.
Is used for:
- Insulation of horizontal structures (ceilings, attics, floors).
- As roll material on pitched roofs.
- For sealing cracks.
- For outdoor work in the form of mats.
Not recommended for use in residential areas due to formaldehyde content.
Advantages:
- Good thermal insulation.
- Moisture resistant.
- Fire safety.
- Ease of transportation.
- No mold or rot.
- Affordable price.
Flaws:
- The need to use personal protective equipment during installation (glass threads can seriously injure the skin, and if they enter the respiratory tract, they cause irritation and swelling).
- Requirement for reliable glass wool insulation (to prevent glass strands from entering the room).
- Instability to direct sunlight.
- Short service life.
- Content of harmful substances.
Slag
Slag wool is a heat insulator made from blast furnace slag , which is a waste product of the metallurgical industry. Its use is now becoming rare, as it has many fatal disadvantages.
However, good technical characteristics and a budget price allow it to be used for non-residential insulation. It is not recommended for use in rooms with high humidity (baths, saunas). Not suitable for building facades.
Advantages:
- Good thermal insulation.
- Sound absorption.
- Long service life under optimal conditions.
- Ease of installation.
- Resistance to the formation of fungi.
- Low price.
Flaws:
- Instability to temperature changes.
- Low water resistance.
- Limited use.
- Low vibration resistance.
- Presence of harmful substances.
Basalt (stone) wool
Basalt (stone) wool is a material based on basalt fibers . It does not have the disadvantages inherent in glass wool and slag wool. According to hardness it is classified into:
- Soft.
- Medium hardness.
- Tough.
This provides a wide scope of its application.
Advantages:
- Good thermal insulation.
- Soundproofing.
- Resistance to mechanical stress.
- Fire resistance.
- Water resistance.
- Long service life.
- Ease of installation.
- Environmentally friendly.
Flaws:
- The cost is higher than similar materials.
Comparative table of two insulation materials
In order to make a choice, it is recommended to familiarize yourself with the technical characteristics of the materials. This will help you decide which is more profitable: mineral wool or ecowool.
| Characteristics | Mineral wool "TeploKnauf" (loose) | Ecowool |
| Thermal conductivity (W/m*K) | 0.038 | 0,032-0,041 |
| Moisture absorption (%) | 0.5 | According to GOST 17177.5 for 72 hours - 16% (a block with heat-insulating material is placed over a container of water and kept for 3 days, after which it is weighed) |
| Density (kg/m3) | 11 | 30-55 |
| Vapor permeability (mg/(m*h*Pa)) | 0.3 | 0.67 |
| Flammability group | NG (non-flammable) | G2 (moderately flammable) |
| Density of connection to the structure | With voids | Absolute |
| Linear shrinkage | Interslab voids form | Absent |
When the humidity level of ecowool reaches 20%, processes begin to develop in it, leading to the appearance of mold. But at the same time, the material loses its thermal insulation properties by only 2-4%. The situation with mineral wool is sadder. With 1% moisture (by weight), it loses its thermal insulation properties by 8%.
Not like fish in water
The relationship between moisture and insulating materials can be described as complex. Here we need to return to thermal conductivity again. Under normal conditions, as we have seen, this figure is approximately the same for different thermal insulators, but everything changes when moisture gets on the insulation. All materials behave differently. The most moisture-sensitive material is basalt mineral wool; when moistened by 1%, its thermal conductivity increases by 9–8%. Fiberglass also does not tolerate water well, but recently products with enhanced moisture resistance have begun to appear.
Moisture distribution inside ecowool and mineral wool fibers
What's going on with ecowool? It absorbs water, but thanks to the fibrous structure, all the moisture gets into the fibers, and the empty space with air (which is the main heat insulator) remains free, as a result, when humidified to 20%, the thermal conductivity remains unchanged.
Ultimately, the water resistance parameter is relevant only in the event of force majeure (roof leakage, waterproofing breakthrough, etc.). Subject to compliance with building codes and regulations, water should not get on the insulation, so this indicator should not become decisive when choosing a particular insulation material.
Compare by cost
The cost of glass wool, basalt or stone wool depends on several parameters:
- density;
- type of material (roll, plate);
- brand.
Thus, the average cost of glass wool “Ursa M-11”, located in a roll in two layers, with a length of 900 cm and a width of 120 cm, is 1170 rubles. The price of a package consisting of 12 slabs (50*600*800 mm) of Rockwool stone wool is 495 rubles. Pack of 5 slabs measuring 150*600*1200 mm of Rockwool wool – 930 rub. Stone wool from other manufacturers has different prices, which often depend on the promotion of the brand. Products from the most popular brands are always more expensive.
Ecowool is sold in bags or polyethylene packages of rectangular cross-section. The price for this material is indicated differently: per 1 kg or per 1 m³. The average price for 1 kg is 33 rubles, for 1 m³ – 1400 rubles. The spraying method of this insulation makes it possible to obtain different densities of the thermal insulation layer, the final cost of which is calculated taking this parameter into account.
Composition and styling
Ecowool is a material that is obtained by recycling waste paper. The product has the form of dense granules. The insulation is installed using two methods: dry or wet spraying.
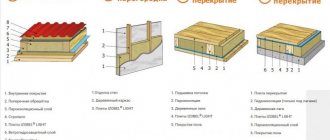
When designing vertical planes, it is recommended to use manual laying. Using ecowool, you can reliably fill cracks, gaps and other cavities in structures for a long time.
Mineral wool (basalt insulation) is not a specific product, but a separate group that includes three items. It is produced in the format of mats and rolls, which are convenient to lay on various surfaces.
- Glass wool. This finishing material is made of fiberglass, the thickness of which varies from 5 to 15 microns. The length also differs and can range from 15 to 50 millimeters. The product can be made in roll or slab form. The practical shape ensures convenient installation on both horizontal and vertical surfaces.
- Slagged. For its production, blast furnace slag and formaldehyde are used. The last component is dangerous to human health. The material cannot be used on open metal substrates due to the increased acidity of the main component of the insulation. Otherwise, corrosion begins to take effect. One of the features of the material is its ability to absorb moisture, which makes it impractical to lay slag wool in damp rooms. Due to its affordable cost and efficiency, the material is in great demand. It is recommended for use in industrial and manufacturing establishments.
- Stone wool. The product is made by processing basalt rocks. Manufacturers also add hydrophobic additives. The insulation does not chip like glass wool, making it more convenient and safe to work with.
Compare by ease of use
Basalt insulation is easy to install, regardless of whether the material is rolled or slab. It is placed in the openings between frame posts (for frame house construction) or sheathing strips (for insulation of facades, including ventilation ones). During the work, the only inconvenience arises: the formation of dust consisting of tiny fibers. It settles on the skin and mucous membranes. The most unpleasant dust is from glass wool.
The thermal insulation layer of ecowool is formed in two ways: manual and automated. There are three application options:
- dry spraying;
- wet;
- using glue.
When installing thermal insulation manually, you will need to perform several steps:
- “fluff” the compressed ecowool block using a drill and mixer;
- fill the space intended for insulation with the resulting mass;
- compact ecowool.
For the mechanized application method, the following equipment is used:
- automatic blow molding installations;
- corrugated hoses.
Comparison with alternatives
Let's take two fairly popular materials: Rockwool insulation (glued basalt wool, supplied in the form of rigid mats) and the material that we are considering today. So, ecowool or basalt insulation?
Raw materials
- In the case of Rockwool, its role is played by molten basalt (rock) and a binder - phenolic-based glue.
- Ecowool, as we have already found out, consists of cellulose and derivatives of natural minerals.
In this case, the assessment is clearly in favor of a more environmentally friendly material: we have heard more than enough about the dangers of phenol. However, with external insulation, there is no threat to the health of the inhabitants of the house in both cases.
Fungus, mold
- In basalt wool, when it is moistened, mold feels at ease. Mineral fibers, albeit slowly, are destroyed by the fungus.
- Boric acid is a very effective antiseptic. The fungus does not grow in cellulose with its additive. Even though we are talking about organic material.
Thermal conductivity
It is approximately the same for both materials; the difference is in favor of cellulose insulation, but within the margin of error. However:
- Basalt wool loses its heat-insulating qualities when moistened.
- On the contrary, cellulose flakes retain them completely.
- Rockwool is laid with voids. Yes, air is an excellent heat insulator; but without the cellular structure of the insulation, heat begins to be transferred by convection currents.
- With the industrial laying method, cellulose fills all the voids. There is not the slightest gap left.
Density of abutment to structures
Even with the most careful laying of the slabs, gaps will remain.
Shrinkage
- Over time it is inevitable. Voids form between the slabs.
- When laying dry and in dry air, shrinkage is possible. When wet, the flakes form a strong structure with unchanged linear dimensions.
Vapor permeability
The ratio is approximately 1:2 in favor of cellulose insulation. A definite plus in his favor.
Breathability
It is one and a half times more than basalt wool. Wind and drafts have a much greater effect on its thermal insulation qualities.
However: when installing a wind barrier, this quality of insulation has virtually no effect on the warmth in the house.
Fire safety
In terms of this parameter, the materials are more or less on par:
- Rockwool's phenolic binder burns out at temperatures above 250 C. It is clear that nothing beneficial to health is emitted into the atmosphere.
- Cellulose is charred in the surface layer, but does not support combustion. During charring, substances of approximately the same composition are released as when burning wood.
The material is clearly not suitable as kindling for a stove.
conclusions
Insulation of frame houses is one of the important stages of construction. In fact, only one of the above materials can be used as a heat insulator, which you can purchase in our store, with all related products (OSB, Isoplat, support beams, vapor barrier membranes, bitumen shingles, etc.).
If you have any questions, our specialists will advise you and help you understand the huge selection of components, as well as offer the right type of insulation at an affordable and comfortable price for you.