Insulating a PPU roof is one of the most modern and popular methods. Polyurethane foam is a synthetic substance that consists of more than 90% gas. It is included in the subtype of gas-filled plastics. Due to its cellular structure, this material is an excellent insulator and has low thermal conductivity. The material itself is obtained through a chemical reaction between isocyanate and polyol. As a result, a structure is formed, which is applied to the insulated surface. It consists of a large number of small cells completely filled with gases (either carbon dioxide or freon).
Types of polyurethane foam and its composition
As mentioned earlier, PPU (polyurethane foam) is a foamed plastic formed during a chemical reaction and having a large number of gas cells. The hardened mass of plastic accounts for only about 2%, while the remaining 98% comes from a mixture of carbon dioxide and air masses. It is thanks to this fine-cell structure that polyurethane foam has high thermal insulation properties, low weight and the ability to retain air vapor. For thermal insulation of roofs and floors, 2 types of polyurethane foam are used:
Elastic polyurethane foam
If the density of the material does not exceed 20 kg per cubic meter, then such a material is called elastic. Foam insulation is produced in the form of rolls or layers. It is very convenient to use such insulation in work. Due to the presence of a large number of cells in it, it is quite pliable, bends easily and quickly restores its original shape. The main frozen volume of elastic polyurethane foam has a density of 8 to 15 kg per cubic meter. With its help, you can carry out work both on insulating the internal ceiling and insulating the external slopes of the roof. In addition to ease of use and high insulation characteristics, polyurethane foam has another important property - sound insulation. Installing such insulation is quite simple. You just need to lay it between the wooden floor slings and secure it.
Rigid polyurethane foam
Hard polyurethane foam is a material formed from foamed plastic and also has a large number of small cells with gas. What makes it tough is the presence of up to 3% solids in the composition. Thanks to this, such a material has a structure characterized by high rigidity, low weight and resistance to various types of damage (both mechanical and chemical). Its density is approximately 2-3 times higher than the density of liquid polyurethane foam and reaches 60 kg per cubic meter. The cost of performing thermal insulation work using solid polyurethane foam directly depends on the thickness of the layer being laid.
Expert opinion
Konstantin Alexandrovich
Compared to other thermal insulation materials, the cost of roof and ceiling insulation using polyurethane foam is lower. The final cost of insulation work depends both on the size of the roof slope, its shape, and on the thickness of the applied layer. Experienced roofing repair specialists estimate that 50 to 100 mm of polyurethane foam should be sprayed. It is a layer of this thickness that will have high thermal efficiency and protect the house from the cold. The price in this case will vary from 200 to 500 rubles per square meter.
Characteristics
There is also no clarity about the characteristics of the material.
Thermal conductivity
When advertising their products, sellers indicate very low thermal conductivity values of polyurethane foam. Rarely, you can find a coefficient of 0.017 W/(m×°K), more often - 0.020-0.022 W/(m×°K). But this is from the realm of fantasy. Even in laboratory conditions, where all requirements for the quality of components and their formulation can be met, it is rarely possible to obtain a thermal conductivity index of 0.022 W/(m×°K).
Similar values are achieved only with the use of freon r141b as a foaming agent, which is prohibited for use in Europe (and therefore is not produced). The use of other foaming agents increases the value of the coefficient, and therefore in European countries a thermal insulation layer with a thermal conductivity of 0.028 W/(m×°K) is considered high quality.
In Russia, the real figures are 0.030-0.035 W/(m×°K) (the specific value depends on the experience of the performers).
However, consumers should not be upset. Even if the technology is violated, the actual thermal conductivity of the insulation deserves respect, since it is one of the best and comparable to basalt wool.
Density
The density of the insulation determines the bending strength (fragility), the weight load on the structure and the thermal insulation properties.
Two-component, closed-cell polyurethane foam, can be obtained in different densities, combined into 3 groups.
- 1 group. Low density - 28-32 kg/m3. The main scope of application is ceilings and walls from inside the room, onto which the material is applied in a thin layer. Thermal conductivity coefficient is from 0.028 to 0.032 W/(m×°K). Vapor permeability at the wood level is 0.05 mg/(m*h*Pa), which makes it possible, albeit conditionally, after detailed calculations, to use polyurethane foam for insulating the walls of wooden houses (more on the problem below).
- 2nd group. Average density - 32-40 kg/m3. A classic representative of the species. The components are sold separately, in cylinders. Used to insulate all structural elements of a building. It has the lowest percentage of moisture absorption among all types of insulation.
- 3rd group. High density - 40-80 kg/m3. Achieving such density using portable equipment is theoretically possible, but practically impossible. It is used in places with high mechanical load on the heat-insulating layer, but only after special surface treatment, which experts call armoring.
Life time
Manufacturers of polyurethane foam consider their products to be durable, with a service life of 30-50 years. These figures are confirmed by the experience of using this insulation in the USA and Europe. However, in Russia, in the first years of using the new product, they were faced with the fact that the insulation from the facades of multi-storey buildings began to fall off in layers after 5-6 years of operation.
At first, the root of the evil was seen in the poor adhesion of polyurethane foam to the wall material. When the lag became widespread, they began to study the problem seriously and turned to Western experience. It turned out that the reason is in a completely different plane - the sun's rays. The material does not tolerate ultraviolet irradiation, ages, or in the language of scientists: it is subject to UV destruction. The aging rate is about 1 mm per year.
The worst enemy of polyurethane foam is the sun.
Simply painting the insulating layer with fade-resistant paint or mastic protects the material from destruction, extending its service life to 30 years when the facade is open. If the insulated facade is finished with siding or porcelain stoneware, you don’t have to worry about the safety of the insulation at all.
Adhesion
Foamed polyurethane has excellent adhesion to all types of building materials, with the exception of polyethylene film. For example, in order to tear polymerized insulation from concrete, you will have to apply a force of at least 2.5 kg/cm2, and for steel - 1.5 kg/m2. These are very large numbers. No wonder the best types of glue are polyurethane based. But such adhesion is possible only if the insulation is sprayed onto a clean and dry surface.
The insulation will not adhere to whitewash and “boiling” plaster; it will fall off along with them under minor mechanical loads due to low bending strength.
Preparatory work
Before installing thermal insulation using polyurethane foam, you should make sure that the equipment used is reliable, and also study the technical installation procedure itself. Despite the fact that the installation work is quite simple, there are certain rules. Compliance with them guarantees you high-quality thermal insulation, which will have a long service life and high insulating characteristics.
Some unprofessional craftsmen ignore the preparatory work stage. There is no way to do this. In the future, this will only lead to a deterioration in the efficiency of insulation and a significant increase in the costs of installation and thermal insulation material.
Before you begin applying polyurethane foam to the insulated surface, you must perform the following steps:
- Check the serviceability of equipment used for spraying polyurethane foam.
- Make sure you have the required amount of materials for the job.
- Carry out work to prepare the insulated surface, on which a layer of thermal insulation will be applied.
- Spray a control layer of material and check its quality.
Note! For spraying polyurethane foam, both professional equipment and special disposable installations can be used.
A variety of surfaces are suitable for applying polyurethane foam. Most often, insulation is applied to concrete, brick, wood or metal coatings. The requirements for the quality and thickness of the insulated layer are always the same, regardless of the type of coating.
Carrying out thermal calculations
Any and even simplified thermal calculations of enclosing structures should be based on the following regulatory documents:
- SNiP 02/23/2003 “Thermal protection of buildings” -
- SP 23-101-2004 “Design of thermal protection of buildings” -
- GOST R 54851–2011 “Heterogeneous building enclosing structures. Calculation of reduced heat transfer resistance" -
- STO 00044807-001-2006 “Thermal protection properties of building envelopes” -
As you can see, the calculations are complex and take time to learn and implement. Fortunately, in our time it is possible to translate these complex formulas and long tables into much more understandable calculation programs, into which you just need to enter the initial data and select the materials used and their thickness. So there are online calculators and separate software products installed on a personal computer.
One of the most comprehensive online thermal calculators is. When making calculations, he operates with data and conditions from all four of the above regulatory documents. At the same time, it allows you to use both the existing database of materials with their properties, and supplement it with your own materials. In addition to determining the required thickness of the thermal insulation layer, it allows you to assess whether excess moisture will accumulate in the structure during operation, as well as estimate heat losses.
A program for thermal engineering calculations is often used as a free software product for PCs. The program carries out calculations based on all necessary regulatory documents. The program management interface is very simple. The program makes it possible to carry out calculations in two modes - calculating the required thickness of the heat insulator and checking the designed “pie” of the structure.
A software product for specialists, which is designed to calculate temperature fields and thermal resistance of buildings and structures, requires special attention. In addition to the functions included in the above programs, “Temper-3D” allows you to conduct a three-dimensional thermal analysis for each individual node or section and display a graphical 3D picture of the temperature distribution, as well as draw up documentation with calculation results and conclusions, and calculate the power of heating devices.
Further in the article, we will consider simplified calculations that will allow you to make a preliminary assessment of the required thickness of polyurethane foam, and also give examples of calculations using polyurethane foam.
What are the restrictions when using polyurethane foam?
Polyurethane foam has the following characteristic property: it adheres extremely poorly to polyethylene surfaces such as films or membranes. It is not recommended to install this material on such surfaces. Over time, the degree of its adhesion to the polyethylene surface will greatly decrease.
Practical tips:
- Polyethylene films and membranes can be used to cover insulated surfaces. This will keep them intact and protect them from destruction, and the low degree of adhesion will not allow the polyethylene and insulation to stick together.
- The optimal temperature in the cylinder before spraying is from 18 to 20 degrees.
- The insulated surface should be warmer than 5 degrees (to clarify other parameters, read the instructions).
- The consumption of polyurethane foam with a layer thickness of 5 cm is approximately 2.3 kg per 1 sq. meter
What alternatives do PPU have?
In addition to polyurethane foam, the following are used:
- mineral wool;
- Styrofoam;
- glass wool;
- cellulose insulation (ecowool);
- isover;
- expanded clay
The most commonly used from this list are ecowool, mineral wool and isover. Other insulation materials are rarely used due to their low thermal insulation properties or high price.
Such a feature of insulation as susceptibility to moisture absorption is unacceptable. Glass wool, for example, has this feature. In addition, some materials are subject to shrinkage and caking, which causes the insulation layer to decrease and performance to deteriorate.
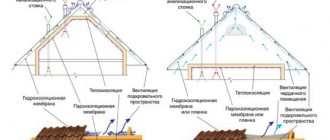
Note! From the list of alternatives, the most preferable is the basalt variety of mineral wool, which has thermal insulation efficiency. When using such material, we must not forget that it is necessary to additionally install vapor and waterproofing, creating a so-called roofing “pie”. This is done so that the insulation does not lose its properties over time.
When choosing a material, study its strengths and weaknesses. Reliable vapor and waterproofing allows the use of almost any insulation.
Let's sum it up
Polyurethane foam is one of the most effective and high-quality insulation materials. By using this material to insulate the roof of a residential building, you will not only protect yourself for many years from the cold in winter and heat in summer, but also from extraneous noise from the street. PPU has a long service life and does not lose its insulating characteristics over time. Compared to alternative options, polyurethane foam benefits in terms of quality and efficiency of thermal insulation functions.
Thermal insulation of PPU roofing: your benefits, our efforts
For construction organizations - thermal insulation of PPU roofs and waterproofing of roofs of newly constructed or reconstructed facilities according to your or our turnkey project. You are getting:
- reduction of construction time;
- The guarantee covers the period of liability of the developer (performer of the work).
Owners of industrial buildings - insulation of the roof of an industrial building. You are getting:
- thermal insulation of roofs in any condition, the ability to postpone the replacement of the existing roof covering;
- carrying out work without disrupting the operation of the enterprise.
Management companies, housing and communal services organizations and municipalities - insulation of roofs of apartment buildings, public and administrative buildings. You are getting:
- guaranteed compliance with the requirements of Federal Law N 261-FZ “On energy saving and increasing energy efficiency...”;
- “minimal presence effect” during work - no disturbance for residents, employees of organizations, customers, etc.