A rainbow of different bottles are offered on the shelves in an auto store: dozens of markings, brands and approvals.
How to find out what exactly your car needs: antifreeze or antifreeze, red or green, Mobil or Polarnik?
If the instructions for your car indicate a clear specification: for example, Ford WSS-M97B51-A1, aka BASF Glysantin G05, aka Mazda 0000-77-507E-02, then there is no problem. Look for the treasured jar (canister) with a similar tolerance, and don’t bother with the color, the question “what’s in it, what’s in it?”, and taking a taste test: sweet or not.
Why was a branded coolant (from the car manufacturer) used as an example, or a product from a well-known chemical concern? Because the packaging contains the main characteristic for the buyer: the car manufacturer's approval for a specific car (as in the technical service instructions). This means that this antifreeze or antifreeze can be poured into the radiator, and at a minimum it will cool well, and at a maximum it will not harm your car.
What is the difference between antifreeze and antifreeze, and why do you need to adhere to the factory specifications?
Let's figure out what coolant is and what it is needed for.
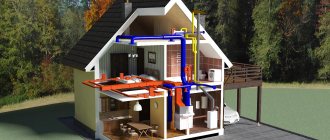
Since an internal combustion engine generates a lot of heat during operation, it must be removed to the atmosphere. For low-power applications (moped, compact car, lawn mower), it is enough to cut the radiator fins on the cylinder head and ensure good airflow. When the intensity of the load increases, the direct air flow is no longer sufficient. It is necessary to remove heat using a coolant (for example, water), which in turn is cooled by the same air, but in a separate radiator.
This is exactly how the cooling system of a modern car works. Around the cylinders there are so-called cooling jackets. The water pump circulates (constantly refreshes) the liquid through the radiator, which is intensively blown with air from the oncoming flow and the fan.
Which fluid cools the engine most effectively? This question usually transforms into: “what is better antifreeze or antifreeze?” We will answer the second part of the question later. The main secret of the cooling system is that the best coolant is ordinary water. More precisely, not just water from a river or tap, but distilled. Many people remember scenes from old Soviet films: the engine of an old GAZ-51 boiled, the driver with a bucket runs to the nearest river, and the problem is solved.
For cast iron cylinder blocks and thick-walled radiators, this is acceptable, with the exception of operation in winter. Water at sub-zero temperatures will simply freeze and “tear” the radiator, or even the cylinder head. Remember the “water drained” signs on the radiator?
On modern engines, ordinary water cannot be used. Why?
- Salts and calcium dissolved in water leave a “fur coat” on the walls of the cooling jackets. This layer disrupts heat transfer;
- Freezing of water in winter. It’s hard to imagine a car owner pouring water onto the asphalt in the office parking lot and then pouring it back in before driving home. And the design of the cooling system in modern cars is more complex; simply unscrewing the plug is not enough;
- Internal boiling (so-called cavitation). Small air bubbles gradually destroy the metal, the pump impeller is especially affected.
In addition, the coolant (which still consists of 50% distillate) contains many additives. How are they different and what are they needed for?
A little theory
If anyone has forgotten (or did not know), let us remind you: the engine’s operation is based on a series of explosions of a mixture of air and fuel. It is this that ensures the operation of the pistons and crankshaft. Naturally, the temperature during microexplosions rises to a very convincing figure of 2000°C. No material can survive such heat, so the engine must be continuously cooled.
There are 3 types of cooling:
- air. The most unreliable and ineffective. If anyone remembers, this happened on the Zaporozhets, which in the summer were constantly ventilated on the side of the road (with smoke) or drove with the hood tied with a string;
- liquid. The most common and most effective;
- combined, which combines both air and liquid cooling. A very promising and reliable development, but so far such systems are installed much less frequently than just liquid ones.
Whatever car you buy, there will certainly be either a second, or maybe a third type of cooling. This means a radiator where it needs to be filled.
{banner_content}
Chemical composition of antifreeze (antifreeze)
Water is still a solvent for the concentrate. The basis of any coolant is chemical elements.
- Regular mineral salt lowers the freezing point. However, it is a corrosion catalyst, so it is practically not used in engines;
- Ethylene glycol, or dihydric alcohol. Excellent resistance to freezing, but promotes corrosion. Moreover, it is when diluted with water that aggressive qualities appear: aluminum parts become covered with shells, and eventually the radiator leaks. In the worst case, the aluminum cylinder head corrodes. In addition, ethylene glycol is far from the cheapest product;
- Glycerol. It resists freezing well and is quite cheap to produce, but there is a serious problem: water-glycerin solutions are viscous, so circulation of liquid through the radiator honeycomb is impossible. The mixture is diluted with methanol, a monohydric poisonous alcohol, but this component is unstable: at 90 ℃ it boils away and can ignite if it gets into the engine compartment. In addition, it is aggressive towards aluminum. Water-glycerin antifreezes (antifreezes) are common among Russian manufacturers. The cost is extremely low; the packaging, as a rule, does not contain car manufacturer specifications;
- Inhibitors. These are mineral or organic additives that protect metal from corrosion. They make up from 3% to 10% of the mass of the coolant, and essentially determine its compatibility with types of engines. The same specifications of the automaker.
Types of coolants for aluminum radiators
Installation of aluminum radiators.
The most common coolant for a heating system is water, but it sometimes leads to numerous difficulties. This is not only corrosion, but also the formation of scale, the need for more frequent cleaning of the system. In addition, water freezes already at temperatures close to zero degrees, pipes and individual circuit elements can simply burst due to thermal expansion. Therefore, it is important not only to choose the right batteries, but also to use a non-freezing coolant. Among the advantages, it is necessary to note complete safety for humans. If the system leaks, there will be no harm to health, while antifreeze is poisonous.
Organic or inorganic, what's the difference?
Mineral inhibitors simply coat the metal walls of the system with a thin layer of protective film. It may be uneven, and corrosion still appears, although it is spotty.
This “chemistry” works effectively; the aggressive effects of antifreeze are practically reduced to nothing. However, the film conducts heat poorly; as a result, it is not removed by the liquid from the heating zone. Over time, heat transfer becomes worse and the engine overheats, and this is fraught with increased wear of parts, earlier oil changes, and increased fuel consumption.
The chemical composition of such inhibitors: nitrates, borates, silicates, phosphates, amino acids.
Organic inhibitors are based on salts of carboxylic acids. Carboxylates do not “stick” to the metal, so there are no obstacles to heat transfer. The molecules of these substances block only pinpoint corrosion. They act as if targeted, leaving most of the area free from film.
Inhibitors are based on carbonates – organic acids that are neutral to metals. The cost is significantly higher than that of mineral water.
Hybrid additives contain carboxylates (usually more of them) and mineral additives. By using the right combination, coolant manufacturers compensate for the disadvantages of different types of additives without reducing the positive effect.
And finally, the answer to the main question: what is the difference between antifreeze or antifreeze? In fact, the name does not convey information about the composition or compatibility with different types of engine. The argument that antifreeze is poured into carburetor engines, and the injector runs exclusively on antifreeze, is groundless.
Additional functions
In addition to reducing the temperature of operating mechanisms, the cooler must meet some other requirements and perform parallel tasks.
- Protect the metal components of the engine from rusting. And this is important, because when metals interact with liquid compounds, corrosion is a very possible thing;
- Lubricate the pump bearing
. Otherwise, due to constant friction, it will gradually wear out and cease to perform its functions; - Increase the limit after which the liquid boils. It is very important in the summer heat, when engine temperatures are complemented by natural ones.
If you delve into this list, it will become clear why you cannot pour water into the radiator.
Two conditions for normal operation will be violated at once: metal parts will rust, and an unlubricated pump will fail. In a hopeless situation, just to get to the “place”, you can fill the radiator with water for a short time, but using it constantly means ruining the car.
History of coolant names:
As we noted earlier, initially ordinary water from a nearby pond was used to cool the engines. Then more technologically advanced internal combustion engines appeared, and accordingly the need for high-quality coolant arose. Foreign manufacturers have combined all coolant options under the definition of “antifreeze”. That is, not freezing.
At the same time, the Soviet government instructed scientists to develop a similar drug for domestic cars (so as not to buy expensive liquid abroad). One of the chemical research institutes quickly developed (or simply copied) the technology. Foreign and domestic liquids were absolutely identical in properties and composition. The domestic development of the “Organic Synthesis Technology” department was called the abbreviation of this division; "TOS". The suffix used in the names of alcohols (ethanOL, methanOL) was added, resulting in TOSOL. This name has become as common a name as “copier”. Despite the fact that the composition of domestic antifreeze and foreign coolants changed from year to year, the common names stuck.
The simplest compositions based on glycerin or ethylene glycol with mineral additives are usually called antifreeze. Although abroad there is antifreeze with the same components. Both names can be found on the packaging; there is no fundamental difference.
Making a choice
Let's say right away that the choice of coolant should be made even before the heating system is installed in the house. This is because the equipment needed for water is significantly different from that needed for antifreeze.
Deciding, in general, is quite simple. If you live in a fairly warm region where there are no sub-zero temperatures, then use water. We talked above about which one should be used as a coolant.
If your place of residence periodically experiences frosts or prolonged cold weather, then you should definitely choose antifreeze.
It is important to know which product you need to purchase specifically for your heating system. We will talk about all the features of different types of anti-freeze below.
How to determine whether the coolant is suitable for your car or not?
Serious manufacturers certify their technical fluids at car factories. On the same principle as motor oils, so you can always check compliance with catalogues. For example, compatibility table for BASF antifreezes:
This is where the catch lies. There are no universal specifications “for all Fords” or for any diesel VW. Each car is designed for a certain type of antifreeze, and mixing them is strictly not recommended. When silicate and carboxylate additives come into contact, dense clots are formed. They clog the radiator honeycombs, interfering with water circulation.
Some alloys inside the engine or radiator can actively corrode precisely under the influence of a certain mineral additive, so look for the only correct answer in the instructions for your car.
Specifications G11, G12, G12+, etc. for Volkswagen cannot be used in the selection of antifreeze for KIA. Some car owners simply buy fluid of the same color as in the expansion tank. Color has nothing to do with the composition of the coolant. This dye is a marking.
Instructions for use
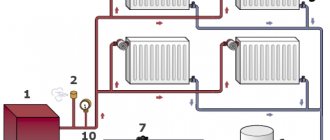
If your system previously ran on water, switching to antifreeze will not be easy. Theoretically, radiators with a boiler can be emptied and filled with cold-resistant coolant, but in practice the following will happen:
- due to lower heat capacity, the output of batteries and the efficiency of heating rooms will decrease;
- due to viscosity, the load on the pump will increase, coolant flow will drop, and less heat will reach the radiators;
- antifreeze expands more than water, so the capacity of the old tank will not be enough, the pressure in the network will rise;
- To improve the situation, you will have to increase the temperature on the boiler, which will lead to excessive fuel consumption and increased pressure.
Addition. After filling the liquid, the old connections sealed with flax and paint are guaranteed to flow.
Leaking joints must be repacked, sealing the threads with dry flax or thread with sealant
. In order for heating to function normally using a chemical coolant, you need to calculate in advance or remake the existing system according to the new requirements:
- Select the capacity of the expansion tank at the rate of 15% of the total volume of liquid (water was 10%);
- The pump performance is assumed to be 10% more, and the generated pressure is assumed to be 50% more. Let us explain with an example: if previously there was a unit with a working pressure of 0.4 Bar (4 meters of water column), then use a 0.6 Bar pump for antifreeze.
- In order to operate the boiler in optimal mode and not raise the temperature of the coolant, it is advisable to add 1-3 (depending on power) sections to each battery.
- Pack all joints with dry flax or use high-quality pastes - sealants such as LOCTITE, ABRO or Hermesil.
- When purchasing shut-off and control valves, consult with the seller about the resistance of rubber seals to glycol mixtures.
- Pressure test the system again by filling the pipes and heating equipment with water.
- When starting the boiler unit at negative temperatures, set the minimum power. Cold antifreeze needs to be warmed up slowly.
Advice. The total amount of coolant is easy to calculate - the cross-sectional area of the pipe is multiplied by its length, the capacity of the boiler and radiators is indicated in the product data sheets. Find out how to properly place and connect the expansion tank in our separate publication.
Before pumping in frost-resistant liquid, fill in water and test the pipelines with a pressure exceeding the operating pressure by 25%. The
concentrated coolant must be diluted with water, ideally with distillate. Do not rely on an excessive reserve of frost resistance - the more water you add, the better the heating will work. Recommendations for preparing coolant:
- For heating elements, electric and gas double-circuit heat generators, prepare the mixture at minus 20 degrees. A more concentrated solution may foam upon contact with the heater, and carbon deposits will form on the surface of the heating element.
- In other cases, mix the components at freezing point according to the table below. Proportions are indicated per 100 liters of coolant.
- If there is no distillate, first conduct an experiment - dilute the concentrate in a jar with plain water. If you see a precipitate of white flakes - a product of the decomposition of inhibitors and additives, this water should not be used.
- A similar check is done before mixing antifreeze from two different manufacturers. It is unacceptable to dilute ethylene glycol with propylene composition.
- Prepare the coolant immediately before pouring.
The ratio of concentrate and water is given per 100 liters.
To find out the amount of ingredients for a volume of 150 liters, multiply the given figures by a factor of 1.5. The maximum service life of any non-freezing substance in pipes and heating radiators is 5 years. At the end of the specified period, the liquid is drained, the system is flushed twice and filled with fresh antifreeze.
Technical certificate
It is also important to take into account that the technical description for such equipment usually indicates only those parts and elements that are not affected by such a liquid. Naturally, it is also important to remember that often the technical documentation for a heating boiler and similar equipment contains a list of coolants used. Also, in most cases, the passport for heating equipment indicates “water can be used as a coolant.” But still, the majority of buyers either do not look at the technical documentation data at all (which they later regret very much), or look there only after the purchase.
StepUp SP9020
Price: 153 rub.
An American product that, judging by the description, is capable of neutralizing a hole along the antifreeze route in just a couple of minutes. The composition is suitable for both passenger cars and trucks. Radiators and heaters compatible with it can have any design, even flat-tubular.
SP9020 sealant hardens exclusively in the area of the hole, and this occurs due to the vigorous evaporation of individual components of the composition. Thus, the drug automatically blocks leaks where antifreeze passes.
Advantages:
- compatibility with all known antifreezes;
- the product does not harm the coolant;
- After adding the drug, replacing antifreeze is not required.
K-Seal
Declared manufacturer: USA
Approximate price: 430 rub.
The thick brown emulsion is declared to be “long-lasting” and does not require subsequent replacement of parts. Contains copper powder that forms durable plugs. It works quite effectively, but healing of large holes is slow. But there are very few deposits.
+ Low level of residual contamination.
— The most expensive drug in our sample.
2nd place. Liqui Moly Cooling System Sealant
"BBF Super"
Declared manufacturer: Russia
Approximate price: 55 rub.
The white emulsion works classically - it consistently and relatively quickly closes the holes from smaller to larger. There are very few residual deposits. After opening, neat fungi of polymer plugs are visible in the place of the holes. And at the same time - the cheapest composition among those tested!
+ The best price/quality combination. Lowest sediment level.
- Not detected.
Final table (click to open full size):
Cottage heating system using ethylene glycol
The cottage heating system in the form of ethylene glycol is used quite often in the north and in the middle zone. However, such filling (using ethylene glycol) is dangerous for metal pipes and can destroy them.
It is important to remember that this chemical liquid can react noticeably to increases in temperature in the pipeline. And if at some point the temperature of ethylene glycol rises to a dangerous value and reaches its highest point, its decomposition will occur. As a result, a lot of acids and strong particles are formed, which can damage the entire heating system.
Important: any acids flowing in the pipes, if there is a noticeable increase in temperature, can damage it, causing premature release of the pipes and rapid corrosion. In addition, such acids can significantly reduce the operating time of carbon cells, which will ultimately damage the batteries and create a leak.
- Naturally, many readers will say that after you have filled in the antifreeze, all you need to do is monitor the operation of the system from time to time and adjust it, trying to prevent excessive temperature rises in the pipes. But are you able to carry out this control constantly? Most likely you won't succeed. This is why companies that produce heating systems warn their customers against adding antifreeze. Because, having taken into account the sufficient list of positive qualities of this coolant, some do not take into account many of its disadvantages - and then are forced to pay for their arrogance.
- Another negative quality of antifreeze, which almost no one knows about, is its ultra-high fluidity, which can lead to leaks in the home heating system. Such leaks can occur when the pipes in the house are not working or the pipes are cold. In this case, the possibility of expansion of the steel structures of the system increases - which allows antifreeze to leak out in some places.
GUNK Radiator Sealer Super
Declared manufacturer: USA
Approximate price: 160 rub.
The thick brown emulsion works effectively and relatively quickly; holes of different diameters closed almost simultaneously. But there were a lot of deposits left after it. On old and dirty radiators this can be dangerous.
+ Works quickly and efficiently.
— Relatively high level of residual deposits.