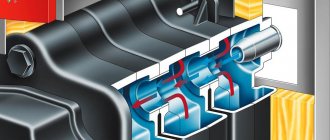
In order to provide your home with constant heat, as it turns out in practice, you need not only to know how to turn on the heating system, but also to know how it works. It is the knowledge of how it works, on what principles it works, and what can happen in unforeseen situations. It is knowledge that most often saves owners of private houses and apartments from accidents and expensive repairs. The most common situation of force majeure repairs is freezing of water in the system, and as a result, rupture of pipes, burst batteries and replacement of the boiler. But, on the other hand, if you change the water coolant to antifreeze in time, then even in the event of a long gas outage during the winter cold, nothing will happen to the pipes and batteries.
Antifreeze
Antifreeze or a mixture of ordinary water, additives and a certain component (propylene glycol or ethylene glycol) can be used as a coolant in the heating system of a private house. This substance has a lower freezing threshold, which makes it perfectly resistant to harsh cold winters. At the same time, antifreeze, unlike water, does not expand, does not harden and does not damage pipes even during an accidental shutdown of the system and strong cooling of the room. The liquid becomes gel-like and is unable to spoil radiators, which have a much higher density. In this case, when heated, the substance returns to the liquid state while maintaining its original properties.
Non-freezing coolants for heating systems from various manufacturers
In northern regions and areas with temperate climates, two types of antifreeze are used - with freezing temperature thresholds of -30 and -65 degrees. Moreover, the latter type can be easily converted into the first by simply diluting it with distilled water in a ratio of 1:2.
Before you buy, let's take an interest in the composition
Table. Types of antifreeze for heating systems.
| Main substance | Antifreeze characteristics |
| Monoethylene glycol (ethylene glycol) | This is a cheaper and more common type of antifreeze. But at the same time, this liquid is quite toxic, so you need to work with it carefully, protecting the skin, eyes and respiratory organs. Also, ethylene glycol, when in contact with zinc, easily reacts with it, so the composition of the alloy from which the entire heating system is made plays an important role here. Ethylene glycol in just one season can destroy galvanizing, if any. |
| Propylene glycol | A more expensive and safer type of antifreeze. A relative of technical propylene glycol - food grade - is used in medicine, pharmaceuticals, and the food industry, as it is completely safe for human health and the environment. That is why propylene glycol antifreeze can be used in any, including double-circuit heating boilers - if the substance gets into the water, the residents of the house will not receive any harm. Also, this type of antifreeze does in some ways the same job as lubricant, so it has a beneficial effect on possible pumping systems. Moreover, the heat transfer of this substance is significantly higher than that of monoethylene glycol antifreeze. |
Antifreeze liquid for heating systems DEFREEZE
Antifreeze for heating systems GOOD-HIM EСО -30
BauTherm 925 at -65
Flaws
But antifreeze, no matter how wonderful they are, also has its drawbacks. The main one is high sensitivity to high temperatures and overheating. In this case, antifreeze decomposes, forming acids and precipitation. The latter can form carbon deposits when they get on the heating elements. And this carbon deposits greatly affect the quality of heat transfer and cause another overheat. The acids, in turn, begin to react with the alloy elements from which the heating system pipes are made. The result is corrosion.
Pipe corrosion
Other disadvantages of antifreeze:
- high fluidity, therefore, better sealing of the heating system is necessary to avoid leaks;
- heat capacity is 15% lower than that of water;
- viscosity is twice as high as water;
- certain types of antifreeze are toxic and are used only in single-circuit heating boilers;
- the need to select a specific type of antifreeze for a specific alloy;
- ability to foam under special conditions;
- Antifreeze will have to be kept at home in case of an emergency leak in order to be able to add it to the system immediately.
The corrosion processes in this circuit are so active that they have led to the thinning of the connection and its leakage
How to choose an anti-freeze
Modern heating systems can operate according to different principles of heat transfer to heat exchange points. Traditional water, without an influx of heat from outside, begins to freeze, significantly expanding with volume. It is being replaced by special compounds - antifreeze for heating, which have a significantly lower freezing threshold.
The choice of antifreeze liquid should be based on the following criteria:
- safety for humans (Warm House ECO-30);
- harmless to the system;
- long service life;
- heat capacity.
But the key selection factor remains the chemical base raw material.
Traditionally, the following are used as a basis:
- propylene glycol – non-toxic, suitable for use in the food industry;
- ethylene glycol is a toxic dihydric alcohol.
Additives
An important selection criterion is the additives added to the coolant. It is customary to distinguish between organic and inorganic additives. The type of substance affects the service life and quality. The best characteristics are guaranteed by organic matter, plus it protects the system from corrosion.
Antifreeze compatibility with heating systems
It would be a good idea to evaluate how heating equipment manufacturers treat the product.
In this context the following can be said:
- a product based on propylene glycol with organic additives - demonstrates a wide range of indicators. These are safety, environmental friendliness, versatility of use, excellent physical and chemical properties. Suitable for use in food production, kindergartens, and for home heating;
- compositions based on ethylene glycol with organic additives (DIXIS) - we can talk about some restrictions in use. This is a solution for industrial facilities and systems isolated from human activity;
- propylene glycol with inorganic additives - safe for people and animals, but has a shorter service life;
- ethylene glycol with inorganic additives - shows a short service life, is toxic. But this is the most budget option. It is quite logical for a system well isolated from contact with human life.
How to calculate the required volume
Calculating the quantity is not too difficult a task. When the system is fully installed and commissioning has been carried out, you can look at the results of the control pressure test. The water drawn from the system will indicate the exact amount of liquid.
Dilution with water
Heating system manufacturers advocate for efficient and safe operation by setting their own requirements. Users, on the contrary, are inclined towards saving money. Antifreeze companies offer coolants at -30, -65 degrees . These are the most popular samples, which are guaranteed not to freeze at the time of sale. When choosing, it is recommended to look at the density.
For example, for antifreeze -25 degrees is 1.03 g/cm3, -30 degrees is 1.04 g/cm3. There is not too much deviation in the concentration of the main substance. But keep in mind that all the water may not be drained from the system; the circuit itself may be refueled. Some reserve of concentration is still necessary.
On the other hand, diluting antifreeze -30 degrees to -25 degrees will not provide significant savings . But, at the same time, you can lose some of the beneficial properties. It is much more efficient to take a product at -65 (Teply Dom 65) and dilute it; in this case, savings can result in 20%.
Life time
The longest-lasting antifreeze with organic additives. The service life reaches 10 years (10 seasons). Silicate additives provide a service life of 5 years. I advise you to check the composition after each heating season.
It is enough to drain a small amount of the substance and inspect it for the presence of impurities, transparency, and color. If there are grains or crumbs, the product must be drained, washed, and filtered. Clots and flakes indicate traces of chemical changes, which should be addressed to specialists.
The following manufacturers participate in this rating:
- COZY TECHNOLOGY – this brand hides high-quality, modern, highly efficient heat and coolants from the Russian market. This is a world-class manufacturer that produces auto chemicals and other products for the industrial and household sectors. Antifreezes for autonomous heating systems are in high demand due to their low cost, multifunctionality, and quality;
- TERMAGENT is another brand. These are high-quality products based on polypropylene glycol or monoethylene glycol, based on the best German raw materials. The company's product range includes four types of coolants;
- Teply Dom 65 is the owner of the trademark group. The holding specializes in the production of coolants for heating systems for industrial and residential premises. In its niche, the products are the standard of quality and ensure uninterrupted heating operation during harsh winters;
- DIXIS - the brand produces antifreezes based on propylene glycol and ethylene glycol using a patented additive package. All formulations and technologies of process fluids are developed by highly qualified specialists. This is one of the best solutions that is on the market today;
- Thermotrust, Aquatrust - both antifreezes are produced by Thermotrust. This Russian brand specializes in the production of instantaneous water heaters, electric boilers and a wide range of antifreezes. All produced antifreeze liquids comply with GOST requirements.
Choosing antifreeze for the heating system of a country house: basic rules
The availability of different formulations creates certain difficulties. Based on certain rules, it will be possible to select a composition that fully meets the requirements of the heating system.
For a specific country house, its composition is selected
Which antifreeze is best for heating a home: making your choice
The compositions offered by manufacturers will not allow the system to freeze in winter. However, due to the large selection, it can be difficult to decide which antifreeze is best for heating your home. Before giving preference to a specific type, you should make sure that the use of such a composition is possible in principle. Antifreeze should be abandoned if:
- open system;
- natural circulation circuit;
- there are elements with a galvanized surface that will be in direct contact with the coolant;
- seals consisting of tow with oil paint are used;
- boiler equipment is not capable of maintaining temperatures within a certain range.
If you decide to give preference to an anti-freeze solution for the heating system of a private home, when choosing you should:
- Check the presence of additives and clarify their purpose. An ethylene glycol solution without modifying elements will cause corrosion of the internal surface.
- Make sure that the operating conditions of the equipment in the country house meet the required ones.
- Check the expiration date. All formulations in original packaging are able to maintain their performance characteristics for a long time.
- Make sure that the packaging material allows you to maintain its performance properties.
- Check for a quality certificate.
The composition for the heating system of a country house should be selected according to certain rules
Comparison of technical and operational parameters of heating antifreezes and water
It is worth pointing out that anti-freezing for the heating system is not the only option for solving the problem of possible freezing of the pipeline and boiler in the event of an emergency, namely a lack of electricity or a cessation of fuel supply in the form of gas.
The way out of the first situation is to use spare gasoline generators; if there is no gas, purchase a boiler with two types of fuel in advance.
That is, any user is faced with a choice - to use ordinary water with various methods of insurance against freezing or to use antifreeze. In any case, it is useful for him to have the following comparative information of these two types of coolants:
Availability. You can always get clean water by turning on the tap in your house or drawing it from a well or borehole. Antifreeze must be purchased in a retail chain, wasting time, paying for transportation costs or delivery.
Antifreeze for heating
In addition to water, special non-freezing liquids - antifreeze - are poured into heating systems. Usually these are aqueous solutions of polyhydric alcohols. Not so long ago, glycerin-based antifreeze appeared on our market. So now there are three types of non-freezing liquids for heating systems.
Types of non-freezing liquids and their properties
Antifreezes are based on two substances: ethylene glycol and propylene glycol. The first is cheaper, freezes at lower temperatures, but is very toxic. You can get poisoned not only by drinking, but even by simply getting your hands wet or inhaling fumes. The second non-freezing coolant for the heating system is based on propylene glycol. It is more expensive, but safe. Sometimes it is even used as a dietary supplement. Its disadvantage (besides the price) is that it loses fluidity at higher temperatures than propylene glycol.
Ethylene glycol coolant is very toxic
Despite their high toxicity, ethylene glycol coolants are more often purchased. This is most likely due to the price - propylene glycol is twice as expensive. But ethylene glycol antifreeze in its pure form is also chemically active, can foam, and has increased fluidity. Foam and activity are combated with additives, and increased fluidity is not corrected in any way. Paired with toxicity, it is a dangerous combination. If there is the slightest possibility somewhere, this antifreeze will leak. And since its vapors are poisonous, this will not lead to anything good. Therefore, if possible, use propylene glycol.
Table with types of coolants
Another important drawback is that ethylene glycol reacts very poorly to overheating, and overheating occurs at a fairly low temperature. Already at +70°C, a large amount of sediment is formed, which settles on the elements of the heating system. Deposits reduce heat transfer, which again leads to overheating. In this regard, such antifreezes are not used in systems with solid fuel boilers.
Propylene glycol, on the contrary, is chemically almost neutral. It reacts less than other coolants with other substances; overheating occurs at higher temperatures and does not lead to the same consequences.
Propylene glycol coolant is safe, but costs more and freezes at higher temperatures
Features of systems with antifreeze as a coolant
When designing a heating system, the coolant must initially be taken into account. This is due to the lower heat capacity of non-freezing liquids, as well as their other properties
If all the equipment was designed for water, and antifreeze is poured into it, the following problems may arise:
- There won't be enough power and the house will be cold. This is due to the lower thermal conductivity of antifreeze. This problem can be solved with little effort - increase the speed of the coolant by installing a more powerful circulation pump. But in an amicable way, an increase in the number of radiator sections is required.
- In closed systems, the volume of the expansion tank may be insufficient. This is due to the fact that when heated, antifreezes expand more than water. The solution is to install another tank. The total volume should be slightly larger than required (the volume can be taken from the table). Expansion tank volume for different types of coolant
- If regular rubber gaskets are used, if ethylene glycol or glycerin is used, they will break down and leak after a short time. Therefore, before adding antifreeze, the gaskets in all detachable connections are replaced with paronite or Teflon ones.
As you understand, the best coolant for a heating system is water. It has better characteristics and is several times cheaper. If the heating is in danger of defrosting, you have to fill in antifreeze, but not for automobiles, but special ones for heating. In this case, if you have enough funds, it is better to use propylene glycol. Ethylene antifreezes are a last resort. They are suitable in closed systems, in which special gaskets and automated boilers are installed that will prevent overheating.
To make it easier for customers to navigate, dyes are added to coolants. Ethylene ones are red or pink, propylene ones are green, glycerin ones are blue. After some time, the color may become less intense or disappear completely. This occurs due to thermal destruction of dyes, but does not affect the properties of the antifreeze itself.
Types of antifreeze for heating
Depending on the substance that forms the base, there are three types of antifreeze:
- ethylene glycol;
- propylene glycol;
- glycerin.
Ethylene glycol products
The main disadvantage of these substances is their high toxicity when inhaled or in contact with the skin. Because of this, they cannot be used in double-circuit networks, when the coolant can enter the hot water circuit. To reduce the risk and warn the buyer of the high level of danger, such products are colored red. This allows leaks to be detected early. Antifreezes based on ethylene glycol work at temperatures down to -65 ° C.
Ethylene glycol antifreeze is colored red to detect toxic leakage.
Propylene glycol products
This category of products does not have many of the disadvantages inherent in ethylene glycol-based analogues, the main one of which is toxicity. Propylene glycol antifreeze is a more progressive development, which has already gained popularity among owners of private houses, especially those that use an open model of the heating system, double-circuit boilers.
Propylene glycols have the best thermal properties. In addition, they take care of the internal surface of the devices. This reduces hydraulic resistance and reduces energy losses.
One of the disadvantages of propylene glycol coolants is the high price. In addition, the developers were unable to “make friends” of the substance with zinc.
Propylene glycol products are safer and green in color
Glycerin products
Experts have an ambiguous attitude towards glycerin-based products. Some believe that such antifreezes have almost no drawbacks. Others mercilessly criticize this category of coolants.
To summarize, the advantages of glycerin-based antifreeze also include:
- safety of the base substance in relation to the environment;
- lower temperature crystallization;
- lack of volumetric expansion during freezing;
- compatibility with galvanized surfaces, materials from which sealing parts are made, with some exceptions;
- does not require special cleaning or flushing of the system after draining;
- service life 7-10 years;
- explosion and fire safety;
- high level of heat transfer;
- impressive operating temperature range - from -30 to 105 °C.
Glycerin antifreeze is cheaper than propylene glycol.
The attitude towards glycerin antifreeze is ambiguous
However, glycerin antifreeze also has disadvantages:
- the density of this product is higher than the previous two;
- rapid wear of heating equipment due to the high viscosity of the product;
- low heat capacity compared to propylene glycol-based products;
- thermal instability, at 90 ° C the product decomposes, forming the poison acrolein;
- high viscosity, which is why high-power pumps are needed (another solution to the problem is dilution with alcohol);
- tendency to foam, which contributes to airing of the heating system;
- interaction with components made of non-polar rubber and plastic;
- after evaporation of water, its shelf life is lost, the product takes a solid or jelly-like form even at a temperature of 15 °C.
Critics argue that glycerin antifreeze is not a new product on the market, but also a step into the past. As an argument, they cite the fact that such products were used before the 50s of the last century. However, then chemists developed other glycol-based products with better performance properties.
Glycerin is used to produce counterfeits of high-quality antifreeze
There are no clear standards for the production of glycerin antifreeze. Manufacturers create them based on specifications that they develop independently. In addition, glycerin is a common component of counterfeit coolants that are positioned as propylene glycol. The reason is the lower cost of raw materials.
Pros and cons of aluminum radiators
The popularity of aluminum batteries is explained by the following advantages of the products:
- Light weight. The weight of one section does not exceed 2 kg.
- Cheapness. Aluminum is a common metal that is easy to process.
- Easy installation and maintenance. The coating is heat-resistant paint that is easy to clean.
- Excellent decorative characteristics.
- High level of heat transfer. This is facilitated by additional ribs with thin walls. According to this indicator, aluminum radiators are almost 3 times superior to conventional cast iron batteries.
- Compact sizes.
- Fast response to temperature switching due to the low thermal “inertia” of aluminum.
Weaknesses of aluminum radiators:
- Very sensitive to the composition of the coolant (hardness, mineralization). Poor water quality often causes equipment failure. Therefore, deciding which antifreeze is best for a radiator must be taken seriously.
- Tendency to corrosion. Design, installation and repair must be carried out very carefully.
- Working pressure restrictions.
- High probability of formation of air pockets due to the chemical activity of the metal with salts dissolved in water
The choice of coolant for aluminum radiators must be done very carefully.
Features of using antifreeze
Please note the following points:
- it is necessary to purchase and connect a circulation pump that could produce sufficient pressure in the pipes;
- the boiler must have at least 20% power reserve.
.
if you use an electrode electric boiler, then it requires a special “anti-freeze”
Pay attention to the recommendations from the manufacturer; If you have a double-circuit boiler, then you will have to abandon the non-freezing liquid. There is a danger of liquid entering the DHW circuit; Low temperature solution should not be used in a system with galvanized pipes
The chemical reaction will cause the antifreeze to lose its basic properties; Filling a system with an atmospheric expansion tank with antifreeze is a bad idea. Firstly, you and your loved ones will constantly inhale harmful fumes from the antifreeze, and secondly, the volume of antifreeze will constantly decrease due to evaporation.
Advice: is it possible to pour anti-freeze into the system after water? Experts answer that it is possible, but it is important to pay attention to one aspect of the pump’s operation. It may happen that the unit, which previously operated at low or medium speeds, will simply need to be switched to its maximum power, and this will be quite enough for correct operation. If the pump power is not enough, or you see that something has gone wrong (the batteries heat up poorly), then the unit will still have to be replaced
If the pump power is not enough, or you see that something has gone wrong (the batteries do not heat well), then the unit will still have to be replaced.
Features when starting the heating system
Different compositions of solutions affect the operation of the heating system. Thus, the presence of ethylene glycol affects the initial stage of system startup. The heating process must be started at low power, then gradually increased to the required level. This method will reduce the toxic effects of this substance.
A product based on propylene glycol does not require such adjustments when starting heating equipment.
When all the requirements are met, then there is no need to be afraid of using “anti-freeze” as a coolant. It will solve a lot of problems if used skillfully.
Prices for non-freezing liquid vary, and so does the quality. The policy here should be this: when it is not possible to buy a good product, it is better to stick with water. In this case, you must ensure that the coolant is drained from the system before the onset of frost, or turn on the heating devices on time.
Choice for polypropylene pipes
Polypropylene pipes are in great demand due to a huge number of advantages, such as long-term operation, low price, resistance to corrosion, high hardness and low density. They come in two types: some contain aluminum, and others contain fiberglass. In addition, polypropylene pipes provide:
- maintaining high temperature conditions;
- long service life;
- absence of noise during coolant circulation.
What coolant is best for polypropylene pipes? Many options are suitable, which is why it is worth carefully studying the recommendations for use.
Blitz tips
- “Anti-freeze units” are ideal for heating houses that are rarely visited in winter and the system is turned off most of the time;
- Choose special equipment for using antifreeze;
- It is better to purchase radiators with a power 30–40% higher than conventional ones;
- Due to the increased viscosity of antifreeze agents, it is advisable to use pumps with enhanced hydraulics;
- If you need to prepare a solution from the concentrate, use only distilled water for this;
- Do not mix different types of antifreeze; it is better to use one. But if there is no other way out, then first mix them in a container and observe whether a precipitate forms;
- It is unacceptable to use automobile antifreeze in heating structures, since it contains components whose use is unacceptable in residential buildings;
- It is better not to use a concentrate with a freezing threshold of -65 degrees Celsius in its pure form, as this will lead to overheating of the heat exchanger and decomposition of the additives;
- But if the system uses a solution with a freezing temperature of no more than -25 degrees, and the temperature drops below (which is unlikely), then there is no need to worry. The heating installation will not be damaged at all. The antifreeze will thicken, and when the temperature rises, it will return to its original state, without loss of properties.
- To avoid leaks at the sealing joints, you can use automotive sealant.
Procedure for pouring anti-freeze
If there is liquid in the system, it must be carefully drained. If the circuit has not yet been filled with antifreeze, air pressure testing is done before starting work.
When using a water pump, before adding anti-freeze, the pumping unit is assembled. A tee with a pressure gauge is installed to the drain valve, followed by a check valve. A check valve is needed so that when filling anti-freeze while the equipment is turned off, it does not flow back into the canister by gravity. Next, a fitting is installed and connected through a hose to the outlet neck of the pump. It is recommended to secure the hose with a clamp clamp, and use a high-pressure rubber reinforced hose as the hose. A hose fitting is also screwed into the inlet neck. Before filling begins, a small amount of liquid is poured into the pump cavity to create the necessary vacuum. This is done through the filler neck - the cap is unscrewed and the solution is poured.
Further all work is carried out in this order:
- The tightness is checked by pumping air;
- The performance of Mayevsky cranes is checked at all installation points;
- The injection pump is connected to the coolant drain pipe;
- Mayevsky's taps open;
- The hose is connected to the pump and lowered into the container so that the liquid completely covers the housing;
- The electric motor is connected to the network and the pipes are gradually filled;
- If leaks appear through the open air valves, the engine is turned off and the valve on the pipe is closed;
- The valves on the radiators are closed, but the valve on the heated towel rail remains open;
- The pump is turned on again and the remaining volume is pumped until all cavities are completely filled. After antifreeze appears in the tap on the heated towel rail, the tap is closed and the liquid supply stops.
After filling the entire volume, it is recommended to turn on the boiler and pump the cold coolant for 2-4 hours. Ideally, it is recommended to pump in heating mode at a temperature of 45-60 degrees. After this, the air is bled off and the missing coolant is finally pumped in. During the test run, it is recommended not to disconnect the booster pump.
Recommendations for the selection and operation of coolants - which one is better to choose
None of the coolant manufacturers will deny the fact that in case of stable operation of the heating system in winter, water is the best option as to which coolant to choose for heating. It is better if it is a special distilled liquid with modifying additives, as mentioned earlier. Those homeowners who consider purchasing store-bought water a waste of money usually prepare it themselves, softening it and equipping the system with the necessary filters.
If a decision has been made to use non-freezing coolants, it is important to have information about the conditions that exclude the likelihood of their use:
- If the house has an open type system.
- When using natural circulation in the circuits: the system simply “will not cope” with such a concentrated coolant for heating.
- The presence of pipes or other elements in contact with the coolant that have a galvanized surface is unacceptable.
- All connecting units equipped with seals made of tow or oil paint must be repacked, since glycol substances will destroy them very quickly. As a result, antifreeze will begin to leak out, creating a real threat to people in the room. You can use the old tow as a new sealing material by treating it with a special sealing paste “Unipak”
- It is prohibited to use non-freezing liquids in systems that are not equipped with devices for accurately maintaining the temperature of the coolant. The heating level, which is dangerous for glycol antifreezes, begins already at +70-75 degrees: these processes are irreversible and fraught with the most unpleasant consequences.
- Usually, after pouring antifreeze into the system, it is necessary to increase the power of the pumping equipment, install a larger expansion tank, and increase the number of battery sections. Sometimes it is necessary to change the pipes to wider ones.
- Incorrect operation of automatic air vents after adding antifreeze has been noticed: it is recommended to replace them with Mayevsky taps.
- Before adding antifreeze, the system must be thoroughly cleaned and flushed. This is done using special compounds.
- To change the level of antifreeze concentration, it is allowed to use only distilled water. In this case, it is better to refrain from even using purified and softened water.
- The correct concentration of antifreeze coolant for heating systems is of exceptional importance. It is better not to count on the winter not being very harsh by diluting antifreeze excessively. It is recommended to adhere to the threshold of -30 degrees even in traditionally warm regions. In addition to protection from abnormal frosts, this will create optimal conditions for inhibitors and surfactants, the effectiveness of which is noticeably reduced with excessive water content.
- After filling with new coolant, it is prohibited to immediately turn on the maximum system mode. It is best to increase power gradually so that the antifreeze has time to adapt to new conditions and elements of the circuit.
- Research shows that propylene glycol is currently considered the most reliable non-freezing coolant. Ethylene glycol is too dangerous, and glycerin is so controversial that it is used very rarely. So it’s better to overpay, but sleep peacefully at night.
Volume calculation and filling
To avoid emergency situations, liquid must be poured into the heating system strictly in a certain volume. It is calculated taking into account the following factors:
- type of heating system;
- its material;
- internal volume of the boiler;
- the area of the room that is planned to be heated.
It is recommended to carry out calculations according to the instructions for the equipment, and also take into account whether antifreeze can be used in it at all. But there are situations when the technical documentation does not contain any information on this matter, then the calculation is carried out by studying the relevant literature. And in some cases, you will need the help of a specialist who will help you carry out all the calculations and put the system into operation.
After filling, do not forget to test the equipment
You also need to know how to properly fill the coolant into the system. If there is already old media in it, then it will need to be drained. It is also necessary to check the degree of contamination; the system may need to be cleaned first, otherwise mixing two anti-freeze agents will cause an unexpected chemical reaction.
In a closed system, the filling point should be located below other heating devices. Antifreeze is poured using pumping equipment, but the pressure in the pipes must be no higher than 3 atmospheres. And if it is open, then filling must be done through the upper expansion tank.
After this, the operation of the equipment is tested. The temperature in the system increases, during which the tightness of the components and the absence of unnecessary noise during the circulation of the coolant are checked.
During the period of use of the system, antifreeze will need to be added periodically, so it is better to purchase it with some reserve.
Characteristics and properties of antifreeze
An important nuance of antifreeze is the presence of components such as inhibitors. Such elements affect the fragility of polymers, for example, in pipes such as polyethylene.
There are other nuances that may cause inconvenience in using a coolant such as anti-freeze for heating:
Compared to water, a coolant such as an anti-freeze agent in a home heating system heats up more slowly and also does not accumulate heat as effectively. In order to use antifreeze as a coolant, you will have to install a fairly powerful boiler into the system. This will entail not only the initial financial investment, but also the cost of purchasing fuel. Antifreeze liquid for heating systems has a higher viscosity compared to water
For antifreeze you will have to install a circulation pump with more power. Antifreeze has a higher ductility, so special attention should be paid to sealing various butt joints during installation.
Technical characteristics of antifreeze
Do not forget that antifreeze for the heating system must be diluted with water. The percentage of coolant directly depends on the freezing point of the antifreeze.
The amount of water added also plays an important role. Manufacturers recommend using water for dilution with a hardness value of no more than 6 units.
If non-freezing coolant for heating systems is diluted with too hard water, this can lead to the formation of sediment. Such an unpleasant factor can affect the efficiency of the heating system, and can cause a breakdown of one of the components of the heating system.
If we compare price categories, antifreeze in a home heating system will cost more than water. The financial side of the issue, as reviews show, also plays an important role in the process of organizing a heating system.
Most emergencies in heating systems in winter arise due to initially incorrectly selected coolant and the owner’s desire to save money on its purchase. As a rule, having decided to buy an antifreeze liquid for the heating system of private houses, the owners do not spend a lot of time searching for a suitable product, but purchase the first composition they come across on the market that has a suitable freezing point and a more or less affordable price.
But this approach to the issue of choice promises many troubles in the future. Of course, after the equipment stops functioning, the perplexed owner will still turn to a specialized company whose specialists are able to solve the problem. However, such requests are often belated - after all, additional funds have to be spent on restoring the functionality of the heat supply system, the size of which is not even comparable to the cost of the most expensive imported coolant.
Advantages and disadvantages
The special liquid has a number of features. It has both pros and cons. Benefits of antifreeze:
- the composition retains its characteristics and properties, even if it is constantly in the heating system;
- does not freeze at sub-zero temperatures;
- scale does not form in equipment and pipes;
- does not affect the condition of seals and gaskets: they will not dissolve, dry out or swell.
But when pouring non-freezing liquid into the heating system, there are also disadvantages:
- it has lower heat transfer properties;
- acts aggressively towards metal;
- in the event of a leak, harmful substances will be released.
In addition, antifreeze is viscous, so when choosing equipment for a heating system, you need to take its characteristics into account.
Good to know: how to choose the right antifreeze for heating.
In this video you will learn the benefits of anti-freeze: