It is necessary to transmit the data of an individual meter within a certain period of time. This ensures payment is calculated according to current tariffs. But in order to avoid discrepancies and errors, you need to correctly take the electricity meter readings. In fact, there is nothing complicated here, although not everyone knows where to look and which button to press to rewrite the necessary information.
Electricity calculation method
The electric meter calculates the electricity consumed in kW/h (kilowatt per hour).
Depending on the service that provides electricity services, you need to give the recorded readings to a staff employee or personally calculate the electricity consumption on the meter for the last month, as well as the payment amount.
This is very easy to do, especially since in certain models of electricity meters the required values are highlighted in a certain color.
This is interesting! Single-phase electricity meter Mercury: model description, characteristics and tips for use
There are the following notification methods for electricity consumption:
- Report the readings in person to the office of the consumer service provider or energy supply organization.
- Use the functions of remote data transfer via the Internet, if possible.
- Dictate over the phone.
- Include the readings in the appropriate box when paying the receipt.
Power consumption calculation
All household appliances have a special nameplate or sticker indicating the main electrical parameters. Most often, the maximum power that the device consumes at peak loads is indicated. Since gadgets and devices operate at maximum only a small part of the time, you can safely reduce the average power of the device by 25%. Let the following electrical appliances be present in the apartment:
- Refrigerator – 500 W;
- TV – 200 W;
- Laptop – 400 W;
- Washing machine – 2000 W;
- Microwave oven – 900 W.
This is the maximum level of power consumption from the electrical network. Moreover, if the TV as a whole has equal consumption, then the washing machine consumes different power depending on the washing mode. Knowing approximately how long each appliance runs each day or week, you can calculate kilowatt-hours. To do this, express the power in kilowatts and multiply by the average operating time:
- Refrigerator: 8 hours a day = 0.5 × 8 = 4 kW/h;
- TV: 2 hours a day = 0.2 × 2 = 0.4 kW/h;
- Laptop: 6 hours a day = 0.4 × 6 = 2.4 kW/h;
- Washing machine: 2 hours per week = 2 × 2 = 4 kW/h;
- Microwave: 10 minutes (0.16 hours) per day = 0.9 x 0.16 = 0.144 kWh.
For monthly consumption, it is enough to multiply each value by 28. The washing machine works 2 hours per week, not per day, so we multiply the power of the “washing machine” by 4. As a result, we get the total electricity consumption for the month:
4 × 28 + 0,4 × 28 + 2,4 × 28 + 4 × 4 + 0,144 × 28 = 210,43
Thus, 210.43 kW/h of electricity is consumed per week. Knowing the cost of one kW/h, it is easy to calculate how much it will cost to pay for electricity per month. However, do not forget about gadgets such as tablets, electronic cigarettes and mobile phones. They don't indicate how much power these devices consume, but it's easy to find out.
Types of tariff systems
Until 1996, Russia had only a single-tariff system, according to which the cost of a kilowatt of resource was calculated at one rate, regardless of the time of day.
But the regime of most people is such that the main individual consumption of electricity occurs in the morning and evening hours. In the morning we get ready for work, and in the evening we use lighting, turn on the TV and other household appliances. Day and night consumption is significantly lower. Such an inconsistent rhythm negatively affects the overall operation of the power plant.
In order to avoid sharp jumps in consumption, energy supply companies have introduced multi-tariff payment systems. The point is that the tariff is differentiated by zone of the day, i.e. there is a different rate for different times of using electricity. For a two-tariff system - a day zone (from 7 to 23 hours) and a night zone (from 23 to 7 hours). For a three-tariff system - a peak zone (from 7 to 10 and from 17 to 21 hours), a semi-peak zone (from 10 to 17 and from 21 to 23 hours) and a night zone (from 23 to 7 hours).
The purpose of the system is to encourage the use of energy-intensive household appliances (dishwasher, washing machine, oven, etc.) at night. In addition to leveling the load of the power plant, such a system helps save on utility bills. In order to use a multi-tariff system, it is necessary to install a special meter that provides the ability to account for energy consumption depending on the time of day.
IMPORTANT! In order to pay for light by meter using a multi-tariff system, it turns out to be profitable, you will have to rearrange your daily routine: transfer some of your household chores to the night, which is inconvenient, for example, for a person who works during the day.
Features of determining network power
In general, the electrical network is designed so that its operation does not require special knowledge. It is enough to follow some rules, the main one of which is to prevent overload.
You may be interested in Features of resonance in an electrical circuit
Important! Failure to comply with the rules for using the electrical network can lead to failure and even fire.
It is important to note that the technical characteristics of the outlet and the household appliance differ from each other:
- In sockets, the maximum permissible alternating current is measured in Amperes: in the old housing stock of Russia it is 6 A, in Europe - 10 or 16 A;
- The power of connected devices is measured in Watts.
Information on an electrical appliance can be marked in different ways.
How to calculate the power of electricity? To calculate, you will need a formula:
P = U*I, where:
P - power,
U - voltage in Volts,
I is the current strength in Amperes.
The voltage of a working outlet is 220-230 Volts; the current can be measured with a multimeter.
To determine the current in the outlet, you should use a multimeter.
Payment methods
The formula for calculating electricity depends on whether an individual metering device (IMU) is installed in the apartment or not, and what charging system is used. In addition to individual consumption, utility bills include the cost of electricity costs for general household needs (GDN).
According to the electricity meter
The simplest and most understandable way to calculate the cost of energy consumption is based on the readings of the electric meter.
- The calculation formula for the single-rate system looks like this:
P = V * T , where
P – cost of electricity, rub.
V – volume of electricity consumed per month, kW.
T – electricity tariff established in the region, rub./kW.
Example 1. According to IPU data for August 2022, 239 kW was consumed. The apartment has a gas stove. The cost of a kilowatt in the region is 5.38 rubles. Then the cost of providing the resource is:
239 * 5.38 = 1285.82 rubles.
- The formula for calculating electricity consumption using a two-tariff meter is a little more complicated:
P = Vday * Tday + Vnight * Tnight , where
Vday , Vnight – volume of energy consumption during the day and night, respectively
Tday , Tnight – day and night rates, respectively
Example 2. According to the two-tariff electricity meter for August 2017, energy consumption was 239 kilowatts, of which from 7 to 23 o'clock - 167, from 23 to 7 o'clock - 72. The apartment has gas equipment. The electricity supply tariff differentiated by two zones of the day is 4.19 and 2.92 rubles/kW, respectively. Then the cost of the service is:
167 * 6.19 + 72 * 1.79 = 1162.61 rubles.
- You can calculate the amount for electricity using a multi-tariff meter using the formula:
P = Vpeak * Tpeak + Vhalf-peak * Thalf-peak + Vnight * Tnight
Example 3. According to a multi-tariff meter for August 2022, energy consumption in an apartment with a gas stove was 239 kilowatts, of which: peak zone - 120, half-peak - 47, night - 72. The cost of a kilowatt in the peak zone - 6.46 rubles, half-peak – 5.38, night – 1.79. The total amount is:
120 * 6.46 + 47 * 5.38 + 72 * 1.79 = 1156.94 rub.
According to the data in the examples, it turned out that the multi-tariff calculation method turned out to be the most profitable. The consumer can determine for himself which system will bring savings specifically for him. To do this, you need to find out the approximate power consumption for each zone of the day and multiply it by the current tariffs.
Payment taking into account the social norm of consumption
In 2012, Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 1650-r was approved, which proposes a project for the transition to a system for calculating utility bills taking into account the social norm of consumption. Currently, the system operates in a number of regions of the country (Rostov, Nizhny Novgorod and other regions).
The rate of electricity consumption depends on the number of residents, season, type of heating and stove, location of housing (city or village). The system has 2 tariffs: one for payment for electricity within the social norm, the other for consumption above the norm.
The calculation formula is as follows:
P = Nsp*T snp + Vssnp*Tssnp , where
Nsp - social norm of consumption
Tsnp - tariff for social norm
Vssnp – excess flow rate
Tssnp - super tariff
Example 4. Three people live in an apartment located in Rostov-on-Don. Over the course of a month, the family consumed 243 kilowatts of electricity according to the meter. The social norm is set at 196 kW. The rate is within the social norm - 3.72, above the norm - 5.19 rubles / kW. Then the amount for electricity consumption will be:
196 * 3.72 + (243 -196) * 5.19 = 973.06 rub.
The system promotes economical consumption of resources. It also applies in cases of payment by day zones.
Without electricity meter data
Depending on the reasons why there are no electricity meter readings, the calculation formula will be different.
- The meter is missing or readings have not been transmitted for more than 6 months. The cost of resource consumption will be calculated using the formula:
P = n * N * T or P = n * N * T * k , where
n – number of citizens permanently or temporarily registered in the apartment, people.
N – consumption standard established in the region
T – tariff approved in the region
k is the increasing coefficient for consumers who do not have an IPU, but have the opportunity to install it. From 2022, the coefficient is 1.6. The use of the coefficient is established by Government Decree No. 344 of April 16, 2013.
The consumption rate depends on the type of stove installed in the apartment, the number of rooms and the number of residents.
Example 5. A family of two is registered in a two-room apartment with an installed electric stove. There is no electricity meter, although there is the possibility of installing one. The consumption standard for 1 person is 117 kW. The established tariff is 4.04 rubles/kW. The cost of the resource consumed will be:
2 * 117 * 4.04 * 1.6 = 1512.58 rub.
This calculation system is beneficial when more people live in an apartment than are registered. The absence of any resource consumer is documented.
IMPORTANT! Homeowners' associations or management companies have the right to check how many citizens actually live in the apartment and take this figure into account when calculating fees according to the standard.
- The meter readings were not transmitted on time or it is faulty.
In such situations, the average energy consumption over the last six months, and in some cases over the last three, is considered.
The cost of electricity is calculated using the formula:
P = (( V1 + V2 +….+ V6 )/6)* T , where
V1….V6 - volume of electricity supply over the last six months
T – electricity tariff
Example 6. The consumer is overdue for meter readings. The apartment has an electric stove. Over the past six months, electricity consumption according to the transmitted readings was: March - 167, April - 185, May - 160, June - 179, July - 159, August - 173 kilowatts. Tariff – 4.04 rubles/kW. The amount to be paid is:
((167 + 185 + 160 + 179 + 159 + 173) / 6) * 4.04 = 686.82 rub.
Paying for electricity by meter will bring savings to the consumer. If it is possible to install an IPU, it is better to install it.
Total power and its components
Electrical power is a quantity responsible for the rate of change or transmission of electricity. The total power is denoted by the letter S and is found as the product of the effective values of current and voltage. Its unit of measurement is volt-ampere (VA; V A).
Total power can consist of two components: active (P) and reactive (Q).
Active power is measured in watts (W; W), reactive power is measured in vars (Var).
It depends on what type of load is included in the electricity consumption circuit.
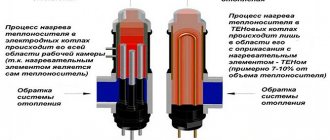
Active load
This type of load is an element that resists electric current. As a result, the current does the work of heating the load, and the electricity is converted into heat. If a resistor of any resistance is connected in series to a battery, then the current passing through the closed circuit will heat it until the battery is discharged.
Attention! An example of a thermal electric heater (TEH) can be given as an active load in AC networks. The heat generated on it is the result of the work of electricity.
Similar consumers also include spirals of light bulbs, electric stoves, ovens, irons, and boilers.
Capacitive load
Such loads are devices that can accumulate energy in electric fields and create movement (oscillation) of power from source to load and back. Capacitors, cable lines (capacitance between conductors), capacitors and inductors connected in series and parallel in a circuit serve as capacitive loads. Sound power amplifiers and synchronous electric motors in overexcited mode also load the lines with a capacitive component.
Inductive load
When the consumer of electricity is certain equipment, which includes:
- transformers;
- three-phase asynchronous motors, pumps.
On the plates attached to the equipment you can see such a characteristic as cos ϕ. This is the phase shift coefficient between current and voltage in the alternating current network into which the equipment will be connected. It is also called the power factor; the closer cos ϕ to unity, the better.
Important! When a device contains inductive or capacitive components: transformers, chokes, windings, capacitors, the sinusoidal current lags in phase with the voltage by a certain angle. Ideally, the capacitance provides a phase shift of -900, and the inductance provides a phase shift of +900.
Cos ϕ values depending on the type of load
The capacitive and inductive components together form reactive power. Then the total power formula looks like:
S = √ (P2 + Q2),
Where:
- S – apparent power (VA);
- P – active part (W);
- Q – reactive part (Var).
If we display this graphically, then we can see that the vector addition of P and Q will be the total value of S - the hypotenuse of the power triangle.
Readings of electronic electricity meters
Electronic electricity meters do not have a mechanical display with “jumping” numbers, but an electronic one. It can display not only numbers showing how many kilowatts were spent, but also the date, operating time of the meter, and some other data. In most electronic light meters, these data replace each other after a few seconds. If the meter is multi-zone, readings for each zone are displayed sequentially (T1, T2, T3, T4).
To take readings from an electronic electricity meter, you can wait until the necessary information appears and write it off. The second option is to press the “enter” button. You may have to click more than once until the required information appears. It can be distinguished by the icons displayed on the screen. Usually this is T1, T2, T3, T4 or the word TOTAL.
For example, in the photo below, on the screen in the upper left corner we see the T1 icon and a little further on there are larger numbers - 72.69. If you look closely, there are units of measurement behind them - kWh. This is the consumed electricity in the first zone T1 (daily tariff).
Example of electronic meter readings
After the necessary data is displayed, they are recorded on the receipt and then calculations are carried out (described above). If the data simply needs to be transferred to the subscriber service, they can be written down on a piece of paper.
Be careful! Here, too, you only need to rewrite the whole part, not taking into account the decimal places. For example, in this case (in the photo above) it is necessary to transmit or carry out calculations only with the number 72 without a “tail”.
The Energomera looks a little different on the electronic meter
How to take readings from the Mercury 200 meter
There are single-tariff Mercury meters (in the specification they are designated as 200.00), and multi-tariff ones (with numbers after the dot other than zeros, for example Mercury 200 01, there may also be 02 or 03). They differ in the number of zones, as well as the presence/absence of a control panel.
Regardless of the model, the readings are taken the same way. You just have to press the “enter” button a different number of times or wait for more numbers to appear.
Mercury 200 electricity meters alternately show time, date, then tariffs by zone. First, the time is displayed in the usual rate - hours, minutes, seconds are shown a little higher. Then after a few seconds the date appears on the screen. It is also displayed in the standard format: day, month, year.
Time and date
After this, the display of tariffs begins. The name of the tariff appears in the upper left corner: T1, T2, T3 or T4. Their number depends on the model you have installed. They are all highlighted one by one. At this stage they can be written down (the whole part, without decimal places).
Readings of a two-tariff meter Mercury 200
After all tariffs, the checksum of all tariffs appears. Then the cycle repeats - time, date, tariffs, total value, etc.
The last one to appear is the sum of all tariff readings
The numbers on the screen change every 5-10 seconds, depending on the settings. It’s quite possible to have time to write it down. But if you didn’t have time, you can switch to tariffs manually. To do this, you must press the “enter” button at any time. In the photo it is under the red LED. Press the button (press/release) until the value you require appears. To switch to the next one, click again. It's not difficult at all.
It will be a little more difficult with the calculations, since you will have to calculate the number of kilowatts consumed for each zone. This is where all the difficulties will end. You now know how to take readings from a multi-tariff electricity meter. All other models of Mercury meters are not much different in this regard. Even their buttons look the same and are located in the same place.
Energy meters
Taking readings from the Energy Meter day-night electricity meter (two-tariff or multi-tariff) occurs in exactly the same way. The difference is that the button on these electricity meters is called “PRSM” (view). There may be two or three buttons, depending on the modification.
Electricity meter Energomera CE301
When you click on this button, numbers appear showing how many kilowatts were “increased” for each tariff zone. There are no more differences.
Saiman counters
Now in many regions they replace old induction meters with electronic ones free of charge and most often install devices from Saivan. These are very simple devices; they do not have buttons that can be used to forcefully “scroll through” the readings. You just have to wait until the required value is displayed. That is, in this case, take readings from the electricity meter - just wait until the required value (TOTAL) is displayed and write it down on the receipt (or transfer it to the appropriate service).
To make it easier to navigate, here is the order in which the data is displayed in this electric meter:
- date of;
- time;
- meter number;
- gear ratio (1600);
- TOTAL - readings of a single-tariff meter or are displayed sequentially T1, T2, TOTAL for day/night type meters (two-tariff).
It is necessary to record the TOTAL or T1 and T2 readings and also the general TOTAL readings on the receipt. Let us remind you once again that you only need to write down the whole part, without taking into account the numbers after the decimal point. You can watch the same information in video format.
Take readings from the Micron electricity meter
In Mikron multi-tariff electronic electricity meters, there is only one button on the case, and you need to press it to display the required readings on the screen. Only in this case, you need to wait until “checkmarks” appear on the display above the letters “T1” and “R+” (see photo). This will be the reading for the first tariff.
How to take readings from the Micron electric meter model SEB-1 src=»https://mfc365.ru/images/assets/uploads/2016/10/pokazanija-elektroschetchika-11.jpg» class=»aligncenter» width=»750″ height ="463″[/img]
Then click on the same button until the checkmarks appear above T2 and R+, if there are more zones, click further. This is how readings are taken from this day/night meter.
Where is the electricity meter located?
In apartment buildings, electricity meters are placed on staircase landings. This is done for ease of maintenance and readings by city service employees.
In this way, cunning electricians reduce cases of interference with the operation of electric meters, since the panels are locked with a key.
In the private residential sector, models with remote recording of information are used for the same purpose. They are installed on poles at the point of entry of electricity. There is also placement of devices in apartments. Usually, the supplier pays increased attention to them, since inspectors will take readings from the electric meter and check its performance once every six months.
All devices for metering electricity consumption are accepted by representatives of the supplier, with seals installed and a report drawn up. It should be remembered that if the seal is broken, the organization has the right to impose penalties. In this case, when calculating, a multiplying factor of 10 will be applied.
All electric meters belong to the “measuring instruments” group and are subject to mandatory verification in accredited testing laboratories. Its frequency is indicated in the technical data sheet for the product. The owner himself monitors the timeliness of such events.
How to take readings from three-phase meters
There are two types of three-phase electricity meters - the old type, which requires transformers, and electronic direct connection (without transformers). If an electronic one is installed, the electricity meter readings must be taken in the same way as described above. Simply write down the values, wait until the necessary information is displayed on the screen, or “scroll” the data to the required page.
Connecting an electric meter in a three-phase network via current transformers
If a large amount of power is allocated or an old-style meter is installed, a transformer is installed on each of the phases. To take readings in this case, you need to know the transformation ratio. The readings taken must be multiplied by this coefficient. The resulting figure will be the actual expense.
But in general, you need to read the contract. The calculation procedure must be prescribed there - in some organizations they write out readings, put down the transformer data or transformation ratio, and the actual calculations are made by the operator himself. So, if you have a 3-phase meter, check the form and procedure for calculations when installing and sealing the metering device and putting it into operation.
Automatic data transfer
Recently, thanks to the widely developed information network, which operates quite quickly with huge volumes of data, as well as the ability to organize separate communication channels, electronic electricity consumption meters with automatic data transmission have appeared. The only problem is the complexity of installation and configuration, but subscribers do not have to participate in the process of collecting and transmitting data.
Taking CE303 meter readings using the iRZ MC52i-485GI GSM modem (video instructions)
How to calculate electricity using a meter
To eliminate errors, it is necessary to carry out the calculation correctly.
Where to find tariff information
To independently determine the amount of electricity payment for the current period, you need to know exactly the cost of the service. Depending on the region of the Russian Federation, as well as additional parameters (type of settlement, availability of certain electrical appliances and rates at different times of the day), the tariff for the population may differ significantly.
You can find out the cost for a specific territory as follows:
- Check on the website or at the office of the utility service provider. The data must be indicated on stands in specialized payment centers.
- When tariffs increase, information is published in the official press and on the website of the regional commission that deals with this issue. The department’s website also has an online calculator that roughly calculates the fee for a specified time period.
- Look on the receipt. During the period when tariffs increase, some discrepancies are possible.
Attention! It is not recommended to use unofficial sources of information, as they may contain unverified or outdated information.
Calculation
It is not difficult to calculate the payment for consumed electricity; to do this, you need to follow a certain scheme, depending on the type of device.
Single tariff device
The simplest models of electricity meters record the consumed kilowatt-hours at one tariff. It is very easy to calculate payment for such a device. To do this, you need to record the electric meter readings to tenths and calculate the previous result from them. The resulting data is multiplied by the tariff.
Pi = ViP x Tcr
Where ViП is the volume (quantity) of electricity consumed during the billing period in a residential or non-residential premises, determined according to the readings of an individual meter.
Tkr is the tariff for electricity supply established in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
It should be taken into account that in some regions the standard for electricity consumption is 150 kW per month. If this indicator is exceeded, then everything that is above the norm is calculated at an increased rate.
For example: The difference between new and old data is 250 kW. This means that 150 kW is paid at one rate, conditionally 3 rubles, and the remaining 100 kW is paid at a higher rate, for example, 3.5 rubles.
You need to carefully count kilowatts on the meter. Sometimes people get confused in calculations and enter the decimal part of the data as a whole number, and get the wrong result.
Two-tariff IPU
Electric meter readings for the new billing period: T1 – 000898, T2 – 000576. Previous values: T1 – 000840, T2 – 000539.
The tariff for the peak zone in Moscow (in houses with gas stoves) is 6.19 rubles, for the night period - 1.92 rubles.
You need to determine consumption and payment in stages; first you need to calculate current consumption:
T1. 898–840=58 kW/h x 6.19=359.02 rub.
T2. 576–539=37 kW/h x 1.92=71.04 rub.
Total for the month: 359.02+71.04=430.06 rub.
Three-tariff electricity meter
It is necessary to take readings from three zones: T1 – 000587, T2 – 000456, T3 – 000832. Data for the past month: T1 – 000545, T2 – 000415, T3 – 000780.
Tariffs by time: peak zone – 6.46 rubles; night – 1.92 rubles; half peak – 5.38 rub.
To find out how much you need to pay per month, you need to count your expenses sequentially.
T1: 587–545=32 kW/h x 6.46=206.72 rub.
T2: 456–415 = 41 kW/h x 1.92 = 78.72 rub.
T3: 832–780 = 53 kW/h x 5.38 = 285.14 rub.
Next you need to add up all the data:
206.72+78.72+285.14=570.58 rub.
This is the amount you need to pay for light.
It is taken into account that the final figures in the receipt may differ slightly: you need to pay attention to the “ONE” line, which reflects the general readings for the house and is included in the payment.
How is energy measured?
Translated from Greek, energy means activity, force, action. It is a scalar quantity and measures all kinds of motion and interconnections of matter. Energy is denoted by the letter E. The units of measurement for this quantity are: in the SI system - joule (J), in the GHS system - erg.
Electrical energy consumed by electrical appliances is calculated by meters. They provide numerical readings of power consumption (kW) per kWh.
The Relationship Between Strength and Energy
A connection has been established between the conservative force, which causes the potential energy of all interacting bodies, and this energy.
For your information. Conservative forces are those forces that do work to move a point. In this case, the work is determined by the extreme positions of this point: initial and final.
Conservative forces include the following forces:
- heaviness;
- elasticity;
- Coulomb forces.
If you close the trajectory of a point under the action of conservative forces, it will be equal to zero.
You can trace the connection using the following algorithm:
- When at any point in space a body is subject to the action of a conservative force, it means that it is located in a potential field.
- A change in the position of a body within a field causes a change in potential energy, in which a conservative force does work.
This work can be expressed mathematically. For example, the body moved in a random direction r, deviating from the initial position by a very small distance dr. This means that dA = F*dr*cosα = Fr, dr, where F = F* cosα is the projection of the force onto the direction r.
There is an equality: dA = – dEп, where Ep is potential energy. So, putting an equal sign between the two expressions, it turns out:
Fr *dr = – dEп, from which Fr = – dEп/dr is expressed.
The ratio dEп/dr is a quantity showing the rate of change of potential energy along a given direction; it is the derivative of Ep in the r direction.
Attention! The minus sign means a decrease in potential energy in the direction dr. The partial derivative symbol indicates that the differentiation of the potential energy Ep (x, y, z) occurs only with the argument x, with the other two unchanged.
Power and energy
Power P is the work done per unit of time. The unit of power is watt (W). To find out how many watts are 1 kW, you need to remember that “kilo” is 103. Therefore, 1 kW = 103 W, and 10 kW = 104 W.
Typically, the power of electrical receivers is measured in kilowatts. Applicable to technology, there is also a measurement of power in horsepower (hp). One such horsepower is equal to 736 watts.
Power and horsepower
The ability of a certain body or an entire system to perform work is characterized by its energy. Energy unites in its concept all events in nature. Different types of movement are characterized by different types of energy.
Advice. Mechanical energy related to the movement of a body is called kinetic, associated with the mutual position of bodies (body parts) of the system - potential.
Calories and joules
Before you figure out how to convert (convert) calories to joules and vice versa, you need to know what these two concepts mean.
The joule is a unit used to measure work, energy, or heat. In the international SI system, the joule is denoted by J (J). The work done by a force of one newton (1N) to move a point in the direction of application of the force one meter (1m) is equal to one joule (1 J).
Calorie is a quantity not separately reflected in measurement systems, used to determine the amount of heat. To heat 1 g of water by 1 C0, you need to spend energy equal to 1 calorie (cal). In this case, 1 cal = 4.1868 J.
Communication with other units
You can use an online calculator to express calories in joules and back.
The program interface allows you to enter the values of the required quantities (using abbreviations of multiple values). When you don’t have the Internet at hand, it’s easy to make a translation by making a proportion. For example, you need to find out how many kilocalories are in 100 kJ. To do this, make up the proportion:
- 1 kcal = 4.1868 kJ;
- X = 100 kJ.
Solving the proportion, we get the expression X = 100 * 1/4.1868 = 23.9 kCal. The answer is that 100 kJ contains 23.9 kcal.
How is ODN calculated?
Everyone has the right to know what they pay for
For the sample, we will introduce an indicator that will mean a part of one apartment from the total area of the building.
Example formula:
KOP = PKV / PD
- KOP – payment coefficient;
- PKV – square footage of this apartment;
- PD – area of the house.
For example, the total area of the house is 1900 m2, and part of a particular apartment is 80 m2, which means the indicator will be equal to 0.042.
What to do if there is no communal meter?
The owner of the apartment has a choice - to assign the responsibility for calculating electricity consumption according to the meter to the building management employees or to enter into an agreement to pay for the electricity supply with the company that provides energy sales.
Government Order No. 307 dated May 23, 2006 states that institutions providing energy supply are required to receive payment for services provided no more than the stated norms in the region. Electricity calculations are carried out in the same way as in houses that do not have an electricity meter:
PEL = IEL x PNL x COP
- PEL – electricity consumed per month;
- IEL – ODN index per 1 m2;
- PNZh – total area of common areas.
Let's take as an example the same house with an area of 1900 m2, in which non-residential premises are 400 m2. With an indexation of ODN equal to 1.25 kW, the indicator of electricity consumed per month is: PEL = 1.25 x 400 x 0.042, that is, 21 kW.
Calculation of readings with an installed meter
If you have entrusted the readings of electricity consumption to the company that provides electricity, then when calculating them, the difference between the total house consumption of all dwellings and energy according to the standards in premises that do not have a meter is taken.
We use our conditional apartment with an area of 80 m2 for an example calculation:
OEL =(OOD-OKV)/KOP
- OEL – parameter of electricity consumed in a certain apartment;
- OOD – total electrical energy of the entire multi-apartment building;
- OKV - the total expense of the owner or tenant of the home.
If according to the general building meter of a given house, 12,500 kW was consumed, and the amount of electricity used by all residential premises is 11,930 kW, then the OEL of our apartment will be 27 kW.
Important: you need to constantly regulate the electricity calculations at the one-way distribution point, and also send readings to the service company every month so that there are no incorrect calculations and overpayments.
If the ODN calculation has not been sent for a certain apartment for a long period of time, then the average amount of consumption for one month is taken into account.
The balance of used and unpaid electricity is divided among residents in proportion to the electricity consumption in each apartment.
If you have an old-style electricity meter (disk type), you can calculate the energy consumption of all electrical appliances currently running using a spinning disk.
To do this, you need to calculate the number of full revolutions of the disk (the beginning of each subsequent circle is indicated by a black mark) in 1 minute.
Let's assume this figure is 25. We multiply the resulting value by 60 (the number of seconds in a minute), thereby obtaining 1500. One kW of energy is equal to 1200 revolutions. Therefore, the energy consumption of all electrical appliances currently operating in your apartment will be: 1200 / 1500 = 0.8 kW.
From joule to kilowatt
Since 1 kW is one thousand watts, the relationship between these two system quantities is considered initially based on one watt.
Joule concept
How is power measured?
When applied to an electrical circuit, 1 J is equal to the work that electric field forces do in 1 second (s) to maintain a current of 1 ampere (A) at a voltage of 1 volt (V). In other words, 1 kJ = 1 kWh.
Converting joules to kilowatt hours
To convert a known number of joules into kilowatt-hours, this is done by direct and reverse conversion of mechanical and electrical energy. This is necessary when performing calculations of the performance of electrical machines: engines and generators.
Important! For calculations, the well-known relation 1 MJ = 0.277(7) kW⋅h is used, from which it follows that 1 kW⋅h = 3.6 MJ. Mega is 1*106.
For example, you need to convert 15 MJ to kWh . To do this, multiply 15 by 0.277:
15*0.277 = 4.15 kWh.
If it is necessary to determine how many joules are 15 kW h , calculate as follows:
15*3.6 = 54 MJ = 54000 kJ = 54*106 J.
The fairness of such calculations is based on the fact that the implementation of the transition to another measurement system was carried out taking into account time. One hour in minutes is equal to 60 minutes. A minute, in turn, consists of 60 seconds, and there are 3600 of them in one hour. One kilowatt contains 1000 watts. Multiplying the number of watts by the number of seconds gives the size of one joule - 3.6 million (MJ). Recording energy consumption in kilowatts for billing calculations has made it easier to evaluate meter readings.
Changing the dimension of power units
You can often come across questions related to the dimension of P units . The most common questions are:
- what is a kilowatt?
- how many kWh in kW;
- how much is 1kW equal to watt;
- 1 kW is how much watt or quat is it;
- how many watts are in 1 kW;
- what is the number of kilowatts per kilowatt hour?
Despite all the variations of letter abbreviations, everything is simple. A kilo is a thousand, so 1 kW is equal to 1000 watts (W). This is also true for volts - 1 kilovolt (kV) is equal to 1000 volts. One thousand kilowatts is equal to 1 megawatt (MW). The multiplicity of units helps to clearly determine the ranks of power values P.
Using these data, it is convenient to plan your family budget. By multiplying the power consumed by the device by the amount of time it is in use, you can estimate its daily consumption. Multiplying the daily load by the number of calendar days in a month allows you to accurately estimate the energy consumption of the entire home.
How to pay ODN if the house does not have a common house meter
If the house does not have a common house meter or its calibration interval has come to an end and the readings are considered invalid, then the electricity consumption is calculated based on the established regional standard. Also, the energy supply organization, at its discretion, can add an increasing factor of 1.5 to it. This applies to situations where it is technically possible to install a common meter in a house, but the residents (or the management company) are not willing to do so.
The utility bill includes the following:
- Number of people registered on a permanent or temporary basis;
- Apartment area;
- Current standard for electricity consumption in the region.
How is power consumption measured?
The amount of current spent is measured in Watts (W) or Volt-Amperes (VA). Measurement in Volt-Amps is often found among foreign manufacturers, and in Watts - among Russian ones.
Important! Often they indicate not Watts (W) or Volt-Amps (VA), but kiloWatts (kW) and kiloVolt-Amperes (kVA) - a thousand Watts and a thousand Volt-Amps.
Many people believe that W and VA are equal quantities, but this is not so. Active power is measured in Watts (the amount of energy consumed, denoted by the letter “P”), in Volt-Amps - total power (the sum of active and passive powers, denoted by “S”). That is, these quantities are not equal; it is impossible to equate Watts to Volt-Amperes.
The required values can be indicated directly on the equipment
To translate you need to use the formula:
P = S*power factor.
If the coefficient is unknown, it is taken as 0.8 (0.8-0.95 is a good value, 0.65-0.8 is satisfactory).
You can also use online calculators when calculating. If using the formula does not work, you can approximately equate: 1 kVA = 0.7 kW.
How to calculate electricity if there is no meter
If a meter is not installed in the house or its calibration interval has expired, then it is impossible to transmit the readings. In such situations, accruals are made according to the standards, that is, according to the indicator established in the region. Here it is worth considering that the energy supply company has the right to apply an increasing factor of 1.5 if residents have the technical ability to install a meter, but they do not do this for some reason.
The following indicators are taken into account:
- Number of permanently and temporarily registered persons.
- Living space area.
- The current standard in the region.
All data is multiplied and, if necessary, increased by a factor of 1.5. The result is the amount to be paid.
Electricity consumption rates without a meter directly depend on the following points:
- Number of rooms.
- Number of residents, including those temporarily registered.
- The region where the object is located.
- Type of stove installed (gas or electric).
Reference! Currently, a program has been implemented aimed at attracting consumer interest in installing electricity meters. Therefore, it is expected that tariffs will increase by up to 20% for those facilities where there are no meters, while the increase in rates for electricity using meters is from 5 to 10%.
What is power consumption?
Power consumption is a numerical measure of the amount of electrical energy required for the operation of an electrical appliance or converted by it during operation. For static devices (stove, iron, TV, lighting), current energy turns into heat during operation). During conversion (electric motors), the energy of electric current is converted into mechanical energy.
The basic unit of electrical power is Watt, its numerical value
P = U × I,
where U is voltage, Volts, I is current, amperes.
Sometimes this parameter is indicated in V×A (V×A for imported equipment), which is more correct for alternating current. The difference between Watts and VA for household networks is small and can be ignored.
Electrical power consumption is important when planning wiring (the cross-section of the wires depends on it, as well as the choice of ratings and the number of circuit breakers). During operation, it determines the costs of maintaining the home.
Federal Tariff Service
In 2004, a federal executive body was created - the Federal Tariff Service (FTS of Russia).
The task of this service is to regulate prices for services and goods, as well as control their use.
On the official website of the Federal Tariff Service of Russia, you can correctly calculate online, based on meter readings, fees for electricity and other utilities, as well as view tariffs for all types of household services for each region.
Please note: it should be borne in mind that this resource is for informational purposes only, and the calculation result cannot be used as a payment document.
Energy-saving lamps
Belarusians are still not particularly active in purchasing energy-saving lamps. “People buy incomparably more incandescent lamps,” Anatoly Zelev, head of the purchasing department of this company, looks at the sales statistics of Oma LLC, which has 7 construction buildings in Belarus. “We attribute this to the fact that our tariffs are still low, and energy-saving lamps are expensive - the payback period is long. For a person to immediately shell out 300 thousand to buy ten light bulbs is expensive. But we must take into account that later there will be significant savings on electricity.” Although, recently, the specialist notes, energy-saving lamps are being purchased more actively. People began to show interest three years ago, and it is growing. Anatoly Zelev himself replaced all the lamps in the apartment with energy-saving ones two years ago. “This allowed me to reduce electrical energy consumption by 1.5 times.” From September 1, 2012, the production and sale of incandescent lamps is completely prohibited in the European Union. Very soon they will completely disappear from the lives of Europeans. Since last year, restrictions on the circulation of incandescent lamps have been introduced in Russia - it is forbidden to produce, import and sell incandescent lamps with a power of 100 W or more, and also to buy any incandescent lamps for government needs.
We have no plans to introduce such bans, says Zhanna Zenkevich: “How can we prohibit our pensioner from buying a cheap light bulb instead of an expensive one?” Yes, in the store today a cheap energy-saving one costs about 30 thousand rubles, and a regular incandescent one costs 3,800 rubles.
Saving Tips
There are two ways to reduce your electricity bill, both of which involve reducing consumption:
- You can independently regulate consumption by turning off the most “gluttonous” devices. To calculate how much they consume, you can check their data sheets or turn off all devices and turn on only the ones you need. The value will be immediately reflected on the electricity meter.
- You can also switch to “night” mode, shifting the main load on the network to the dark. This will reduce costs, but may not be very beneficial for people who sleep at night, but it will help in some situations. For example, if you postpone making jam or drying mushrooms in the oven overnight, you can reduce your bills a little.
Another option would be to use appliances with minimal consumption, especially large appliances and lamps.
To pay for electricity, you only need to know a few data: the amount of electricity consumed and the tariff. You can find out both on your own if you have a meter and the Internet.
Sources
- https://potrebiteli.guru/zhkh/kak-schitat-platu-za-elektroenergiyu-po-schyotchiku.html
- https://ozhkh.ru/kommunalnye-uslugi/raschet-stoimosti-elektroenergii
- https://kak-sdelano.ru/elektrica/kak-pravilno-snimat-i-schitat-pokazaniya-schetchika-elektroenergii
- https://4schetchika.ru/elektroenergiya/kak-pravilno-snimat-i-schitat-pokazaniya/
- https://oschetchike.ru/elektroenergii/kak-poschitat-elektroenergiyu-po-schetchikku
- https://mosenergosbyt24.ru/oplata/raschet-stoimosti-elektroenergii
- https://teplo.guru/elektrichestvo/kak-poschitat-po-schetchiku.html
Anti-magnetic seals on the electric meter: what are they for?
Electricity theft is not new. Some may say that huge companies will not become poor from a small electricity leak, but the problem is different. The money that the energy sales organization missed will be paid by bona fide tenants of the entire building.
The most common method today, as before, is to slow down the torque using a magnet (applies to induction devices). The anti-magnetic seal is designed to prevent such cases.
It is a sticker with a special capsule, which is destroyed under the influence of a magnetic field, changing color. The very first Energonadzor controller will notice this. As a result, there is a minimum fine that will cover all savings. It will also not be possible to peel it off - in this case the inscription “OPENED” will appear.
Under the influence of a magnetic field, the capsule collapses and changes color. Helpful information! It is very difficult to purchase such stickers. But even if this succeeds, it will be of little use. Each of them has an individual number, which is entered by the controller in the inspection log. Changing it is the reason for drawing up a report on violation of the anti-magnetic seal.
Similar antimagnetic seals are glued to both water and gas meters. To date, this method of combating theft has proven itself well.
What are the penalties for breaking the seal?
The fine for such an act, if the owner’s guilt is proven, is calculated for each apartment separately. Calculations are made as follows. The cost of 600 kW is multiplied by the number of sockets in the apartment. It is clear that the amount will be huge. But this is only subject to an examination of the electric meter and proof of the owner’s intervention in the device circuit for the purpose of stealing electricity. If guilt is not proven, the consumer will pay for the last month at the average expense for the previous three.
Cost of sealing an electricity meter
When installing or replacing an electric meter, sealing is provided free of charge. If the company talks about paying for the initial filling, you can safely go to court. If the seal is broken, the organization has the right to demand payment. The cost of resealing is set by the energy sales company. There is no fixed rate here.
Sources
- https://ZKHinfo.ru/kommunalnye-uslugi/schetchiki-elektroenergii
- https://homius.ru/kak-snyat-pokazaniya-schetchika-elektroenergii.html
- https://electrobox.su/schetchiki/kak-schitat-pokazaniya-elektroschetchika.html
- https://stroyday.com/kak-snyat-pokazaniya-schetchika-elektroenergii/
- https://seti.guru/kak-snyat-pokazaniya-schetchika-elektroenergii
- https://internet-zdrav.ru/peredat-pokazaniya-schetchikov/bels-balashixa.html
- https://mosenergosbyt.info/kak-peredat-pokazaniya-schetchikov/
Did the article help you?
Learning to count
When a person counts his own money, he quickly learns how to count correctly. How to calculate how much light was used? There are no big difficulties in this. First, you need to take readings for the past month. The display shows the total consumption, but the payment receipt has three columns - initial readings, final readings and consumption.
The mathematics is simple, you need to subtract the initial readings from the final readings and get the sum of the numbers that determine the monthly consumption. All readings are expressed in units of power consumption per hour - kW/hour. A payment tariff is set for each kW of electricity. To determine the cost, you need to multiply the resulting difference by the cost of 1 kW. The result will be the required amount.
All payment data is entered into the receipt and paid. Payment must be made regularly - once a month, because late payment is subject to penalties.
Procedure
To take readings from a multi-tariff meter, you need to:
- First of all, determine the number of tariffs on the installed meter. There may be two or three. On the first days of the month, it is necessary to write off the readings recorded on the accounting device. On the three-tariff version, these data are indicated: T1, T2, T3. On the two-tariff electric meter, this information is indicated: T1 and T2, respectively. There is no need to write down the entire indicator; you can write down the numbers that come before the decimal point and the one after it. For example, if the display shows 564.233, then you need to enter 564.2.
- To remove the indicators, you must press the “Enter” button. The display will alternately highlight the required combinations T1, T2, T3 or T1 and T2 with a two-tariff view. The button is pressed once, and the device will automatically display the data with a break of 30 seconds.
- After this, it is necessary to determine payment tariffs for energy consumed. If a gas stove is installed in the house and the accounting is kept by a two-tariff device, then the T1 readings (daytime) are paid at a cost of 3.80 rubles, and the T2 data (nighttime) are calculated at 0.95 rubles. If the house has a gas stove and the accounting is kept by a three-tariff device, then the first two costs remain the same, and T3 data is calculated at 3.20 rubles.
If an electric stove is installed in the house, the tariffs change slightly. Indicators T1 with a two-tariff and three-tariff system are calculated as 2.66 rubles, T2 - 0.67 rubles. And half-peak hour (T3) is calculated at the rate of 2.24 rubles. - Next, fill out the receipt. When multi-tariff accounting is maintained, different payment codes are used. With a three-tariff meter, these indicators are as follows: T1 - 13, T2 - 2, T3 - 15. When a two-tariff meter is installed, the following codes are used: T1 - 1. T2 - 2. From the last readings, you need to subtract the previous indicators of the device and multiply them by the corresponding tariff value.
- Next, the results for three or two obtained indicators are summarized. If the home owner has any benefits, their amount is deducted from the payment amount received. The receipt can be paid at any savings bank or post office.
- If you lose your last payment receipt, all the necessary numbers can be found on the meter. To do this, press the “Enter” button and hold it for 2 seconds. The device alternately displays all previous indicators at the time of the last payment. The multi-tariff meter retains all information about the indicators throughout the entire period of use. This greatly simplifies the comparison of the device readings with the figures of the latest payments.
Please note: local authorities have the right to establish temporary standards for existing tariffs, but they are obliged to notify all users of multi-tariff electricity metering devices in advance about the changes.
The benefit in this situation is very noticeable. These devices are a real opportunity to save your own money.
You may find this article about checking electricity meters useful.
Read the article about installing an electric meter in a private home here.
Watch the video, which shows in detail how to take day-night electricity meter readings:
Replacing the device
For a number of reasons, the meter needs to be changed - for example, when switching to differentiated metering (a multi-tariff device is installed). Another reason for replacement is that the existing accounting device is morally outdated (accuracy class 2.5). Electricity meters are also periodically removed for verification.
In cases of replacement, follow the following procedure:
- contact energy sales with a request for a visit from an inspector. His main task is to make sure that the seal on the meter being removed is not broken. The unauthorized breaking of the seal by the owner without a representative of the energy sales company gives reason to suspect him of fraud. For such actions, administrative liability is provided in the form of a fine;
- Having arrived at the place, the inspector checks the integrity of the seal, records the readings on the device display and fills out a certificate of removal of the device;
- the meter is dismantled and a new one is installed in its place. In this case, the controller activates the installation of a new meter, records the readings on it and seals the device.
If the meter is not replaced, but only removed for verification, the controller will transfer the subscriber to pay according to the average indicator.
Household expenses
It is difficult for ordinary residents to calculate their own general house expenses for water, electricity, and heat, but it is possible. Because only the management company and the person in charge of the house have access to UDPU (common house metering devices).
Readings are taken once a month. Residents of the house also have the right to be present during this process. You need to know the current and previous readings of the common house meter and tariffs. All this is divided by the number of square meters in the house. Only the most meticulous, caring (or suspicious) residents consider these expenses personally. By the way, such people often manage to grab utility workers by the hand and convict them of incorrect charges.
The majority are content with the figures they receive on their receipts, where general household expenses have already been calculated.