In terms of production characteristics, corrugated roofing sheeting resembles metal tiles - it is also a cold-rolled galvanized steel sheet coated with polymers. The only difference is in the profile pattern - metal tiles imitate real ceramic tiles, while to make corrugated sheets, rolled steel is simply corrugated, giving the profile the appearance of a zigzag, sinusoid, etc.
Unlike metal tiles, corrugated sheeting looks simpler (and costs less), but at the same time it is more reliable , lighter and more durable than slate.
Waterproofing cold roofs - is it necessary?
The space under a cold-type roof is not heated, but the temperature inside is always different from the outside.
For this reason, condensation collects at the bottom of the profiled sheets. Therefore, the answer to the question: “When a cold roof is built, is waterproofing necessary?” unambiguous Of course it is needed. Properly installed waterproofing on the roof under the corrugated sheeting will prevent moisture from entering the under-roof space. This layer will prevent wet fumes from reaching the wooden elements of the rafter system and other parts of the roof structure. The waterproofing is laid on top of the rafters and then secured with a counter-lattice. Next, install the sheathing and corrugated sheet.
When the waterproofing layer does not prevent steam from escaping outside, then there is no need to install a vapor barrier for a cold roof. Having risen upward, water vapor gets through the film under the corrugated sheet and dries out in that place due to the movement of air currents. In this case, roofing felt, polypropylene, glassine and polyethylene are not suitable. For a cold roof, experts recommend using a non-woven vapor-permeable membrane.
Warm or cold roof
A separate unheated attic or residential attic is a question that is often encountered when building a low-rise building. Partly, this depends on whether there is a need for additional space. Therefore, the choice is often made in favor of arranging an “additional” floor. However, a cold attic also has its advantages, mainly financial ones:
- Significant reduction in costs for building materials - their cost is reduced by almost half due to the fact that during construction there is no need for heat and vapor barrier;
- There is no need to resort to the services of qualified specialists - installation of a roofing pie for a cold roof is much simpler, so you can do it yourself. Moreover, the entire cycle of work will still be shorter compared to the insulated option;
- Constant savings in the future when operating the house - the presence of a closed space under the roof will affect heating costs.
On the other hand, the construction of an attic can also be justified, at least by personal taste or aesthetic preferences.
And now the main thing is how the choice made will affect the design of the roofing pie. For a cold attic it will consist of the following layers (starting from the rafters):
- waterproofing;
- counter-lattice;
- sheathing;
- final finishing – corrugated sheeting.
But when installing a warm roof, things will be a little more complicated. You will have to arrange the following layers:
- vapor barrier;
- heat-insulating material;
- ventilation gap (counter-lattice);
- waterproofing;
- sheathing;
- corrugated sheeting
Sometimes the interior decoration is also included in the composition of the cake, but the general principles of its installation technology will not depend on whether a vapor barrier and an insulating layer are present.
A special case will be the situation when a cold roof is being erected, which will have to be insulated in the future. This is possible, but the initial (“cold”) waterproofing must be of a certain type (vapor permeable). Another option will lead to additional difficulties when laying insulation.
Important! A significant, although not critical, disadvantage of using corrugated sheeting is the need for sound insulation, otherwise it will not be possible to achieve comfort in the house, even by insulating the attic floor (with a cold roof). Therefore, the thermal insulation material must also have a high level of noise absorption.
Roofing pie of a corrugated roof
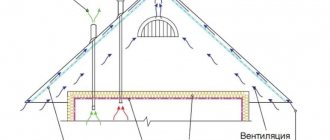
A cold roof is a roof structure that does not include thermal insulation of the slopes because the attic space is not heated. This technology is considered traditional, it is very effective, since the under-roof space serves as an air gap necessary for ventilation of the roof and rafter frame. As a rule, a cold-type roof is used in the construction of household, industrial and seasonally used structures. The roofing pie diagram in this case consists of the following elements:
- Rafter legs. Rafters for a cold-type roof made of corrugated sheets are made of wooden boards with a cross-section of 50x150 mm or metal. The maximum step between the rafter legs is 100 cm.
- Waterproofing material. On top of the rafter legs, using a construction stapler, waterproofing is fixed in overlapping strips, for which films, diffuse membranes or ordinary roofing felt are used. The waterproofing material is laid with a slight sag to prevent tears.
- Counter-lattice. The counter-lattice is made of wooden slats 2-3 cm thick, which are nailed along the rafters on top of the waterproofing. It additionally fixes the waterproofing material and provides a ventilation gap between it and the corrugated sheet.
- Lathing. The lathing is made from boards 40x100 mm or bars 40x40 mm. Lattice and solid installation schemes are used. The greater the load-bearing capacity of the profiled sheet, the less often you can take a step between elements.
- Roofing material. Sheets of corrugated sheets are laid on the sheathing, which overlap each other in the horizontal and vertical directions to create an airtight coating, and are secured with roofing screws.
Cold roof insulation technology
If your roof is cold, then the heat-insulating layer should not be on the slopes, but on the floor of the attic. This is where it stops the heat flow coming from below and prevents the cold from the roof from descending into the living space below. As a result, the temperature in the attic is kept within +1-2 degrees, the roofing material is not heated. In fact, such an attic serves as the necessary air gap between the living rooms of the house and the thin roof covering.
All roll, slab and bulk insulation materials are suitable for attic floors. Because the ceiling does not have a slope, it does not have any special requirements for the heat-insulating material used: nothing will crumble or be exposed.
Please ensure that, after insulating the roof, there remains properly organized ventilation: there should be dormer windows located opposite each other, ventilation ridges and aerators, and in the eaves there should be round-the-clock access to suck in outside air. As a result, the temperature in a non-residential attic should be as close as possible to the street temperature, and the living space below is already separated from it by proper thermal insulation of the floor.
Now let's take a closer look at insulating a cold roof.
Insulation with mineral wool
When insulating the attic floor with mineral wool, first of all pay attention to the distance between the slats or joists - it should be slightly less than the roll or mat of insulation.
Typically, thermal insulation of the internal space of the roof is complicated by the uneven surface of the attic floor, differences in its height, a large number of slats and bars, not to mention ventilation pipes and electrical wiring:
Nuances of insulation of pitched roofs covered with corrugated sheets
Private developers are paying more and more attention to profiled sheets. It's cheap, easy to install and looks good. At least better than asbestos slate. Living in your own home, there is a need to create additional living space. Agree, it would be nice if a one-story house turned into a two-story one. The attic roof provides this opportunity, but that’s not what we’re talking about now.
In most cases, thermal insulation is installed during the construction of the roof itself, but if for some reason you decide to postpone this work, then it can be completed later. It is worth noting that internal thermal insulation is somewhat more difficult, because you have to work indoors and constantly raise your hands.
It is these small nuances that make this process more expensive. Of course, you can save on installation costs by doing everything yourself.
The main enemy of flat roofs, as well as pitched roofs, is condensation. It is capable of destroying rafter elements in a very short time, causing them to rot. Therefore, roofs with metal coverings must be equipped with natural ventilation, and if this is not possible, then aerators or deflectors are installed. In addition to the negative impact on wood, high humidity also affects the thermal insulation material, increasing its thermal conductivity.
Ventilated ridges are often installed on pitched roofs.
. They create an additional outlet for air, which leads to a reduction in condensation in the attic. The only distinguishing feature of a ventilated ridge from an ordinary one is that the former has perforation. It is through these holes that the humidified air leaves the room.
Roofs that are prone to condensation accumulation are best equipped with hydrophobic insulation. So you can be calm about the integrity of this material. But oddly enough, almost every person wants to save money and ends up purchasing products that are not entirely correct. Most developers use basalt slabs. They are cheap and easy to install, but have a significant drawback. If they get wet during operation, then their positive properties, such as low thermal conductivity, will come to an end.
Durable construction can be achieved by using quality materials, so if this is what you want, then consider polystyrene foam as a thermal insulation product. It has the same advantages as basalt fiber, but is not afraid of water
But why then doesn’t everyone buy this material when its quality is better? The fact is that many people listen to their acquaintances, neighbors, friends and cannot purchase products on their own. Naturally, it cannot do without its disadvantages. Expanded polystyrene is very flammable, which prevents it from being installed on most buildings; in addition, the fragility of the material makes many people change their minds.
Regardless of which thermal insulation material you choose, you will still have to lay insulating layers. One of them must protect the material from precipitation, and the other from steam that comes from residential premises. If you are wondering where it comes from, now I will explain everything to you. The human body is designed in such a way that when it overheats, sweat is released. It helps cool the body, and as this procedure is carried out, moisture from the skin dissolves into the air. In addition to sweat, air humidification is affected by such processes as: breathing, cooking and much more.
As a rule, the corrugated sheet is laid on the discharged sheathing and an underlay carpet can be placed on top of it as additional insulation. It helps to level the created plane of lumber, and the increased density perfectly resists moisture.
If you have good finances, then the lining can be laid over the entire roof, otherwise, it is placed only near the overhangs and important nodes where water will drain.
On the roofs of private houses it is not uncommon to find seals for corrugated sheets. They are a narrow strip of foam rubber, which is arranged along the eaves of the roof. Such strips have holes, thanks to which fresh air easily penetrates into the attic and removes condensation. The corrugated roofing seal is an excellent solution for isolating the roof from small rodents and birds.
Pros and cons of using corrugated sheets
The appearance of this material is very attractive. A roof covered with it looks solid and expensive. This is one of the factors that makes the material so popular among builders.
In addition to aesthetic appeal, corrugated sheeting has other advantages:
- low cost. Whatever the design of the roof - single-pitch or gable - it will be quite affordable in cost. It is worth considering that doing the work yourself will further reduce the cost of the process. It will not be possible to save on hired workers. This point should not frighten a novice master, since the process of working with corrugated sheets is not difficult;
- This material is easy not only to install, but also to transport. It does not require special conditions of transportation and storage;
- ease of use allows for high speed of construction work. Even beginners in construction can cope with fastening corrugated sheets. An important factor is the lack of special equipment for fastening. A grinder, drill or screwdriver is enough;
- the sheet weighs little, it is convenient to lift it onto the roof;
- Corrugated sheets are successfully used in regions with snowy winters. The material has proven high resistance to snow loads. With a correctly designed roofing system, a roof made of corrugated sheets does not bend or sag under the cover of snow;
- high level of waterproofing. To be completely sure that moisture will not penetrate into the house, you need to pay special attention to the processing of joints and fastenings. An additional layer of waterproofing is often used;
- proven long service life, in all weather conditions;
- It is not susceptible to rust or fading under ultraviolet rays. This means that the new roof will delight its owner with its original color for a long time;
- high level of fire safety, since the material is not flammable;
- well-fixed corrugated sheeting is not exposed to even the strongest gust of wind;
- Due to the strength of the metal, sparse lathing can be used. This item saves money on building materials;
- wide range of colors available. There is one suitable for any building.
Like all building materials, corrugated sheeting has not only advantages, but also disadvantages. Among the most significant are:
- high thermal conductivity. At any negative temperature outside, the surface of the metal will be even colder, which means that all the heat from the house will quickly go outside. For this reason, corrugated roofing is additionally insulated;
- in hot weather the material becomes very hot, which precludes the use of the attic for residential purposes. It will be hot there;
- low sound insulation. Due to their thinness, metal sheets completely transmit, and often resonate, all sounds from the outside. Drops of rain or the sound of a branch hitting the roof will be clearly audible in the attic. However, some owners of corrugated roofs claim that such a noise effect, on the contrary, has a calming effect on them;
Reasons why waterproofing is installed under a cold roof made of corrugated sheets
Precipitation
Corrugated sheeting cannot 100% eliminate the possibility of moisture getting into the under-roof space of the house. Heavy rain or snow combined with intense winds can cause moisture to seep into the roof, which in turn can lead to corrosion.
Wear of fasteners and roofing modules
The peculiarity of corrugated sheeting is that its sheets are subject to temperature deformation, as a result of which the roof can allow moisture to pass through the junction line of the roofing modules. Often water penetrates under the roof and at the points where the corrugated sheeting is attached to the rafter system, since over time the tightening of the screws weakens and the rubber sealing washers are destroyed. The ingress of water into the under-roof space is fraught with wetting of the rafter system with its subsequent rotting, and as a result - destruction of the roof frame.
Condensation Formation
With high-quality installation of a corrugated roof, when the roofing reliably protects the house from atmospheric moisture and leaks, theoretically, you can do without waterproofing.
But sources of moisture are not only precipitation from outside. This is also condensation that forms on the inner surface of the roof due to the difference in temperatures inside and outside the house.
The likelihood of condensation becoming even higher when utilities pass through the attic: heating and hot water pipes, ventilation ducts or a fireplace chimney. Liquid and gaseous media circulating through such pipelines usually have an elevated temperature and heat up the air in the under-roof space, contributing to more intense condensation.
Technology
The quality of thermal insulation of a house depends not only on the competent choice of insulation, but also on its correct installation. When insulating a roof made of corrugated sheets or other materials, the following order of layers is observed from bottom to top:
- covering the ceiling, for example, with plasterboard;
- lathing along the bottom of the rafters;
- vapor barrier;
- rafter legs;
- insulation between rafters;
- waterproofing and wind protection;
- counter-lattice to ensure sufficient ventilation gap (if necessary);
- sheathing under the roof made of corrugated sheets or metal tiles (moisture-resistant plywood is additionally laid under the roof made of flexible tiles);
- roof covering made of corrugated sheets or other materials.
When insulating the roof of a house, it is important to consider the following recommendations:
- mineral wool requires a mandatory ventilated layer 5 cm thick;
- The pitch of the rafters is selected depending on the width of the insulation to facilitate the installation process;
- when working with mineral wool or polyurethane foam, special clothing and personal protective equipment are required;
- vapor barrier is always located on the warm air side, and waterproofing on the cold air side;
- the height of the rafter leg should be equal to or greater than the thickness of the insulation.
Installation of the rafter system is one of the steps to properly insulate the roof
To properly insulate a house, work is carried out in the following order:
- installation of the rafter system;
- fixing waterproofing;
- installation of the top sheathing;
- insulation;
- vapor barrier;
- bottom sheathing.
Next, the installation of the roofing is completed and the interior finishing is performed. The fastening method is different for each material:
- The mineral wool is held between the rafters by friction. In this case, the width of the insulation is taken to be 2 cm larger than the pitch of the rafters.
- Polyurethane foam adheres to the surface by penetrating into the smallest irregularities and crevices. Before starting work, it is recommended to moisten the surface with water from a spray bottle to improve adhesion.
- During operation, polystyrene foam and extruded polystyrene foam are kept on the roof of the house due to the bottom sheathing, and during the installation process you can use anchors, umbrella nails, tile mastic or liquid nails.
Proper insulation of the rafter system will ensure compliance with the temperature and humidity conditions in the attic or attic, protect structures from damage and reduce the financial costs of heating the entire building.
Heated air always rises to the top, and most heat losses occur through the roof or attic floor. That is why it is important to pay increased attention to insulation during roofing work.
Source: domzastroika.ru
Basic requirements for thermal insulation materials when installing a warm roof made of corrugated sheets
Vacuum is considered an ideal insulation; the ordinary dry air around us is very close in characteristics to it. Its thermal conductivity is 0.025 W/(m°C). It is this characteristic that is most important for any insulation. The lower the thermal conductivity, the thinner the thickness of the thermal insulation layer, the higher its efficiency and the lower the cost of roof insulation. For various modern insulation materials, thermal conductivity can range from 0.029 to 0.23 W/(m°C).
Another important characteristic of thermal insulation materials is hygroscopicity, that is, the ability of the insulation layer to absorb moisture, as well as their vapor permeability. The last characteristic determines the ability of a heat-insulating material to pass moisture contained in the air without retaining it
The use of effective insulation materials allows you to create a “breathable” roof - it is this kind of roof made of corrugated sheets with insulation that will ensure the optimal level of humidity in the room.
In addition to these basic characteristics, thermal insulation materials differ from each other in compressive strength, elasticity and elasticity. These parameters are selected depending on the conditions under which the insulated roof made of corrugated sheets is used. The most widely used thermal insulation materials for roof insulation are those based on foamed polystyrene or basalt fibers.
When insulating a roof made of corrugated sheets, first of all, it is necessary to determine the thickness of the insulation layer. This calculation is quite complex, since it is necessary to take into account a large number of factors - from the temperature coefficient of the area to the humidity level. The coefficient that takes into account the necessary factors is called the heat transfer resistance coefficient for the roof and is denoted by the Latin letter R.
This coefficient has already been calculated for the administrative centers of the Russian Federation and is shown in the table below. If you need to perform calculations for another area, then you will have to use special regulatory documentation. In particular, SNiP 23-02-2003 “Thermal protection of buildings”. You can download it by right-clicking on the name of the SNiP and selecting “Save as...”.
Calculated values of the roof heat transfer resistance coefficient for cities of the Russian Federation according to SNiP 02/23/2003
| Locality | Degree-day | Heat transfer resistance for roofing, R, (m2x°C/Bt) |
| Arkhangelsk | 5700 | 5.05 |
| Astrakhan | 3400 | 3.90 |
| Anadyr | 9000 | 6.70 |
| Bryansk | 4000 | 4.20 |
| Bratsk | 6900 | 5.65 |
| Volgograd | 3900 | 4.12 |
| Vologda | 5200 | 4.80 |
| Vladimir | 4900 | 4.65 |
| Vladivostok | 4600 | 4.50 |
| Ekaterinburg | 5600 | 5.00 |
| Irkutsk | 6500 | 5.45 |
| Krasnodar | 2400 | 3.45 |
| Krasnoyarsk | 5900 | 5.15 |
| Kursk | 4200 | 4.30 |
| Magadan | 7700 | 5.05 |
| Makhachkala | 2300 | 3.35 |
| Moscow | 4600 | 4.50 |
| Murmansk | 6000 | 5.20 |
| Novosibirsk | 6200 | 5.30 |
| Omsk | 6000 | 5.20 |
| Orenburg | 5200 | 4.50 |
| Petrozavodsk | 5200 | 4.80 |
| Saint Petersburg | 4400 | 4.40 |
| Salekhard | 8300 | 6.35 |
| Syktyvkar | 5900 | 5.15 |
| Tomsk | 6300 | 5.35 |
| Tyumen | 5600 | 5.00 |
| Ulan-Ude | 6700 | 5.55 |
| Khabarovsk | 5800 | 5.10 |
| Chelyabinsk | 5500 | 4.95 |
| Chita | 7200 | 5.80 |
| Yakutsk | 10000 | 7.20 |
The table below shows an approximate calculation for the cities of Anadyr, Salekhard and Yakutsk. Due to difficult climatic conditions, clarifying calculations are necessary in these cities.
Knowing the coefficient R, it is very simple to calculate the thickness of the insulation you need - you need to multiply the coefficient of specific thermal conductivity of the insulation λB by R. The resulting value will be the thickness of this type of insulation.
The coefficient of thermal conductivity of the insulation can be found either on the packaging or in the accompanying certificate
I draw your attention to the fact that it is necessary to take exactly the coefficient with index B, which characterizes the use of the material in a humid environment
According to technology, the construction of a warm roof made of corrugated sheets depends on the roof structure. A warm roof made of corrugated sheets can be pitched or flat. The technology for installing insulation in the first and second cases is somewhat different.
Materials
Proper selection of materials specifically for your case can not only extend the life of the attic space, but also significantly facilitate the installation process. On the market you can find materials of different quality and price categories. But you shouldn’t buy the cheapest or the most expensive - it’s better to proceed from price-quality considerations, and also look for options to suit your case. It is important that the selected material has low thermal conductivity, can withstand environmental changes, is environmentally friendly and durable.
A membrane or film coating is ideal for creating a waterproofing layer. In the first case, not only the most complete moisture insulation is ensured, but also ventilation through special membranes. However, their price is higher, so if you decide to use a regular film coating, it is recommended to think about creating small ventilation gaps and seams.
At the moment, manufacturers provide a large selection of roof insulation materials, which have different characteristics, pros and cons. When choosing, pay attention first of all to these characteristics:
- Degree of moisture absorption. It is advisable to choose the one with the lowest indicator. However, if you are confident in the quality of your moisture-repellent layer, then you can choose one with an average rating. The higher the indicator, the lower the price and the shorter the service life.
- Thermal conductivity level. It should also be as low as possible. Porous materials have the lowest level, but they have a higher degree of moisture absorption.
- Density. It should also be lower.
Installation
Depending on the selected material, the installation technology will be different. However, expanded polystyrene boards are laid between the rafters or simply glued to the surface of the ceiling with glue, which does not cause difficulties and does not require detailed explanation. Polyurethane foam is sprayed by specialists using special sprayers and you don’t have to do anything yourself at all.
You will only have to figure out the technology for laying mineral wool. This is not difficult - the main thing is to follow the order of laying the different layers of the structure. If you count from above, from the plane of the corrugated sheet, then the order will be as follows:
- Waterproofing layer
- Insulating layer
- Vapor barrier film
- Exterior finishing (if necessary)
The rest is simple - choose the form of insulation that is most suitable. It can be a roll or slabs. The parts are cut to size with a special knife and attached either with glue or with special dowels spaced between the rafters. The insulation cannot be compressed, therefore, you need to adjust its size as accurately as possible. After laying the heat insulator, the surface is covered with a decorative coating if necessary.
The procedure for thermal insulation of the roof in the presence of an attic
Under the corrugated sheeting attached to the wooden sheathing, waterproofing material is laid in the plane of the rafters. In this case, it is necessary to maintain a gap of 5 cm, called an air cushion. As waterproofing, you can use a high-tech waterproofing membrane Tyvek Solid (Soft), dense polyethylene (depending on the financial capabilities of the developer). The membrane must be laid with the markings facing out.
Attic roof installation.
Rolls of waterproofing material are laid out at the installation site along the entire valley from top to bottom. The main waterproofing material should not sag. The rolls should be rolled out horizontally, positioned in the spaces between the joists. The waterproofing is fixed between the rafters “in space”. The material at the joints is laid with an overlap of 15 cm, and the joints should be on the rafters. The waterproofing layer should not have holes, gaps, or poor-quality joints. Otherwise, the insulation of the entire roof may suffer. For high-quality thermal insulation, all seams must be sealed.
In the event that the air cushion has not been maintained, a so-called “cold triangle” is made in the roof cavity under the ridge to ventilate the under-roof space. In this case, ventilation ducts are created with an interval of 2-3 spans, but by no means in all of them. Such a ventilation system significantly reduces the formation and accumulation of condensation in the space under the roof, which can affect its insulation.
During installation, particle boards are laid across the rafters. Insulation is placed closely under the waterproofing layer, again in the plane of the rafters. It can be glass wool or mineral wool. To insulate the attic, it is better to take the thickest insulation (10 cm). If it is laid in several layers, each of them must overlap the previous joint. A construction knife is used to cut thermal insulation material.
Thermal insulation of the roof under corrugated sheeting.
The heat-insulating layer is then sheathed with waterproofing material - vapor filler. Typically, H110 Standard and H96 Silver films are used. The vapor filler is installed from the side of the living quarters using a construction stapler, and the seams are overlapped. Its surface, like the waterproofing, must be sealed - everything must be glued with SP1 connecting tape.
The formation of the roofing pie is completed with wood cladding from the attic side. For this, you can use lining, wood, OSB boards, plywood - in general, the choice depends on the design of the interior and financial capabilities. It is recommended to make the internal lining of the attic from moisture-resistant materials with a thickness of 9-12 mm.
Each slab must have at least 2 supports.
The plates are attached with self-tapping screws 5-7 cm at intervals of 20 cm to the supports of the rafter system. The distance from the edges of the slab should be more than 10 mm. The insulation of the attic is now complete. After this, you can begin finishing and other construction and installation work, after which the attic will become suitable for living.
Roof structure
The technology for constructing a roof made of corrugated sheets is quite simple; having studied it, it is possible to perform the roofing of an individual residential or country house with your own hands. If permanent residence of people is planned in the attic or attic, then the coating must be insulated. Let's take a closer look at the technology of installing insulated and cold coverings. The lathing for corrugated sheets is made from edged boards with a cross-section of at least 22x100 mm; generally, a 32x100 mm board or a 40x40 mm beam is used. The lathing is nailed onto the counter-lattice, with a certain step depending on the grade of sheet and other indicators that were discussed earlier. It is better to make continuous lathing under the profiled sheet on overhangs, at the ridge and in the junction area. The counter-lattice is bars that are nailed along the rafters. The counter-lattice secures the wind-hydroprotective membrane, which is laid between it and the rafters, and also creates a gap, ensuring ventilation of the under-roof space. This is a very important point, since condensation inevitably accumulates on the inside of the profiled sheets, droplets of moisture accumulating on the cold metal. Ventilation should be carried out through special gaps on the ridge and eaves sections of the roof. If the coating is insulated, then the next step is effective thermal insulation, which is laid between the rafters and hemmed on the side of the premises with boards or plasterboard; a vapor barrier must be provided between the insulation and the inner lining.
Insulation of the U-shaped attic contour
If the roof is high and the area of the house is large, then the attic can be equipped without sloping walls - with a U-shaped contour, the thermal insulation of which will not come into contact with the roof.
In this case, behind the contour of the attic there will be an ordinary cold attic with its own ventilation through the eaves and ridge vents. In essence, this is a technology for insulating a frame house, but inside the attic.
Insulating the attic ceiling:
- Boards or slats of the rough ceiling are hemmed to the top ties, which act as ceiling beams.
- A vapor barrier is installed on the side of the room. The strips are laid overlapping and all joints are glued.
- On the “attic” side of the attic, insulation is laid between the tie beams (if necessary, in two layers).
- A waterproofing membrane is spread over the insulation. It is required if it is not included in the roofing pie. If the roof has waterproofing, but the mineral wool mats are not laminated, then ordinary fiberglass can be laid on them as a wind barrier.
- On the inside, a counter-lattice is attached over the vapor barrier. It is needed to ensure that there is an air gap necessary for the functioning of a vapor barrier with an anti-condensation or reflective surface.
Insulation of attic walls:
- A waterproofing windproof membrane is attached to the outside of the posts.
- If the contour of the attic on the roof side is sheathed with plywood or OSB, counter-lattice bars are nailed to the posts on top of the waterproofing.
- Thermal insulation is laid between the racks.
- A vapor barrier is laid in a continuous layer on the inside of the racks. Tape the junction with the vapor barrier of the ceiling and floor.
- Install the sheathing for the interior lining.
If none of the options suits you, then the roof can be dismantled, and waterproofing and insulation can be carried out using standard technology.
Features of roofing pie with waterproofing
Waterproofing cold and warm roofs has its own characteristics:
- Cold roofing involves the use of materials with high strength characteristics to withstand high water pressure in case of leakage. The recommended materials in this case are roofing felt, roofing felt, and fiberglass.
- When installing a warm roof, it is better to use waterproofing material under corrugated roofing with good vapor permeability.
It is not recommended to skimp on waterproofing under corrugated sheeting, as this can significantly reduce the service life of the roofing material.
Suitable insulation materials
To make the house warm, the insulating part of the roof is simply necessary, but since the roof is covered with corrugated sheets, the task will not be easy. This is due to the special structure of the material - it is not flat, but wavy. We will have to create a structure that will not allow cold air to penetrate into the house and at the same time, reliably retain the heat inside it. There are three types of insulation that are suitable in all respects for use with wavy roofing:
- Spray polyurethane foam
- Expanded polystyrene
- Mineral wool and other fibrous insulation materials
Material characteristics
Corrugated sheeting is a modern material used for roofing, which is made from thin sheet cold-rolled steel. The production technology of this coating involves coating steel blanks with a zinc alloy and a layer of polymer or paint, which increases the corrosion resistance and impact resistance of the product. After painting, the steel sheets are placed into a machine, which uses special rollers to press a trapezoidal or rectangular profile into them. The advantages of a professional sheet are considered:
- A light weight. The weight of 1 square meter of profiled steel roofing is 8-17 kg, which is 2-3 times less than the weight of ceramic tiles or asbestos-cement slate. Light weight reduces the load on the foundation, allowing you to save on the roof rafter frame.
- Corrosion resistance. A “chronic disease” of metal roofing is rust. But zinc and polymer or paint coatings protect the steel from which the corrugated sheet is made from contact with water, thereby increasing the anti-corrosion properties of this material.
- Long service life. The service life of a roofing sheet made of corrugated sheets, depending on the quality, price and adherence to material technology, is 25-50 years, which significantly exceeds the use of roofing felt, ondulin and slate.
- Large selection of colors. The polymer and paint coating allows you to paint the corrugated sheets in any shade. The color range offered by manufacturers includes hundreds of items, including the metallic series.
Insulation materials
Scheme of thermal insulation of the roof from the inside with foam plastic
For roofing made of corrugated sheets and other materials listed above, it is best to use the following types of insulation:
- mineral wool;
- Styrofoam;
- extruded polystyrene foam;
- polyurethane foam.
For a wooden house, it is necessary to take into account the resistance of the material to fire, so it is better to use non-flammable mineral wool or extruded polystyrene foam . More information about mineral wool insulation can be found in the article “Insulating a roof from the inside with mineral wool.”
Expanded polystyrene
Despite the similarity of names, it is very different in characteristics from the previous type of insulation. Expanded polystyrene is sold in the form of slabs of different thicknesses, which can be attached to any plane using glue or special dowels with a wide head. Seams and joints between individual slabs are filled with polyurethane foam.
The disadvantages of this insulation include several points: it is flammable, capable of releasing caustic toxic fumes when melting and burning, and can also cause unpleasant olfactory sensations - a chemical smell accompanies this material almost throughout its entire service life. In addition, you will need to purchase a sufficient supply of polyurethane foam to seal the surface and fill the joints between the plates.
Let's sum it up
Films on the roof are needed to protect the insulation from moisture from the inside and outside. Without them, the thermal insulation layer will retain heat worse, and fungus and mold will begin to develop inside the roofing pie.
Which film to choose for the roof:
- For vapor barrier, polyethylene film with a thickness of more than 200 microns is best suited. The budget option is reinforced polypropylene, the optimal option is a foil vapor barrier.
- For waterproofing an attic, reinforced film is used; for a residential building, diffusion and superdiffusion membranes are used.
How to install corrugated sheeting - technology
Correct installation of corrugated sheeting on the roof is possible only if certain instructions are followed. Time-tested technology for installing roofing from corrugated sheets will allow you to build a reliable roof.
Sheet cutting
Cutting corrugated sheeting significantly increases the consumption of material and its quality characteristics, so you should buy a coating in accordance with the size of the slope. However, such an ideal situation does not always occur; therefore, it is necessary to know the rules for cutting metal sheets, as well as the tools to perform these actions.
Before installing corrugated sheeting on the roof, you need to measure it on a flat and level surface, for example, laying it on the ground.
They cut the material with a variety of tools, but a more efficient and high-quality result is obtained when using an electric drill equipped with a disk attachment. Suitable hand tools include scissors for cutting metal or a fine-toothed hacksaw.
It is not recommended to use a grinder or other devices with abrasive cutting discs for this purpose. The operation of such tools is accompanied by the release of a large amount of thermal energy, which can cause a decrease in the performance characteristics of the material.
Required tools and materials
To perform installation and preparatory work you will need (not taking into account measuring and auxiliary tools):
- electric drill - preferably with an adjustable chuck speed;
- jigsaw – useful for cutting corrugated sheets and timber. Scissors or a hacksaw are also suitable for sheets of this roofing covering.
- hammer;
- stapler for attaching waterproofing sheets;
- brushes - for applying antiseptics and fire retardants to the timber.
Using a gas cutter or grinder to cut corrugated sheets is highly undesirable. In this case, the polymer coating can be damaged, making the steel sheet vulnerable to rust, and simply unaesthetic. The risk of damage can be reduced by using an angle grinder with a special attachment.
The list of basic materials for roofing should include:
- wooden beam for counter-battens and sheathing - when using corrugated sheeting, its cross-section is selected from the range 30×50, 40×50 or 50×50 mm (the latter option will be appropriate if the rafters are longer or the roof slope is small), for flat roofs the sheathing can be solid - made of moisture-resistant plywood or boards;
- galvanized nails with screw knurling;
- galvanized self-tapping screws, including those with a sealing washer;
- antiseptic and fire retardant for wood;
- mounting tape for vapor barrier;
- rolled material for laying waterproofing;
- finishing material – corrugated sheeting of the selected brand.
If you plan to insulate, you will have to take care of purchasing vapor barrier materials and insulation.
Thermal insulation of flat roofing made of corrugated sheets
In Russia, the flat roof is not particularly popular, although it is gradually gaining momentum. The structure of an exploited flat roof contains exclusively hard materials, but a non-exploited one does not matter. As a rule, creating the first type of flat roof is much more expedient, because later, you can place a recreation area on the surface, build a workshop for your business, or something else.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=tvJHSyVlp6c
Regardless of the functional purpose of a flat roof, it must include a loose layer of waterproofing. By the way, precipitation is removed from a horizontal surface quite slowly, so the overlap of the material should be at least 10 centimeters so that moisture cannot penetrate into the roofing pie.
Thermal insulation of a flat roof can be carried out using a two-layer or single-layer method. In the first case, the load on the roof will be significantly greater, therefore, such work can only be carried out after calculations. The first layer of material has a lower density and a larger width, while in the second the opposite is true. As for single-layer insulation, preference is given to any materials, the main thing is that their width is at least 150 millimeters. High-quality waterproofing must be applied over the laid slabs.
Condensation on the roof of a house - what to do, how to fix it
At first glance, small droplets of water accumulating on the roof may not cause much harm, but this is only at first glance.
If condensation collects on the outside of the roof, this is normal, especially in the morning. Well, if from the inside, then you need to think about where it comes from and how to fix it.
Let's figure out where condensation appears on the roof and what to do in this case.
Installation of warm roofing from corrugated sheets on flat roofs
The roofs of non-residential buildings and industrial buildings are usually made flat. In this case, the corrugated sheeting is usually not higher, but, on the contrary, lower than the thermal insulation. That is, it acts as an overlap.
When insulating such roofs, a waterproofing film is laid loosely over the corrugated sheets with an overlap of 100 mm. Next, the insulation boards are laid out. They can be laid in a single-layer or two-layer method.
The first method is called single-layer. Since thermal insulation boards are produced with a thickness of no more than 100 mm, they are always laid in several layers. But in a “single-layer” installation, all insulation boards have the same density.
With the two-layer method, the top layer of heat-insulating boards has a higher density, and, therefore, a higher load capacity. In this case, the top layer slabs distribute the load on the roof over the entire layer of thermal insulation. This installation method allows for usable roofs that can easily support the weight of a person.
After installing the slabs, a bitumen or PVC roofing covering is laid on top of the thermal insulation layer.
Read on topic:
Marking of corrugated roofing sheets
Don’t know which brand of corrugated sheeting is best for you to choose for your roof? Can’t figure out the decoding of the profiled sheet markings? Read the article - you will find the answers you need in it.
How to cover a hipped roof with corrugated sheeting?
There are two main differences between a hipped roof made of corrugated sheets and a classic gable roof. Features of the roof truss system made of corrugated sheets. Advantages of a 4-pitch roof compared to other options. All this is in the article.
Grounding a Metal Roof
If you want to protect your home from lightning, then read the article. From it you will learn how to properly install lightning protection, what it is like, and in which cases it is better to simply ground a metal roof.
Options for insulating a flat roof from the outside and inside
The variety of insulation options for such roofs is obvious. But they have one drawback. There is no rafter system. That is, the sinuses between the rafters. There are many options for insulating both outside and below. Choose the best insulation and hang it, for example, from a concrete floor using plastic dowels. Afterwards, the insulation is covered with a special cement mortar, painted or whitewashed.
Task number one: It is good to arrange the junction of the water removal and steam outlet. Work on the waterproofing device
Insulation of a flat roof
Mineral wool
The best would be an insulated roof made of corrugated sheets, where the heat-insulating lining will be mineral or basalt wool. This is the most popular insulation option, although installing wool will require more time and, in addition, you will need to purchase additional materials in the form of a vapor barrier and waterproofing film.
They are necessary in order to protect the fibers of the insulating material from moisture from the outside and protect it from excessively humid air coming from inside the room. The membrane will allow moisture to penetrate outside, but will not allow it to accumulate inside the insulating layer, and waterproofing will protect the heat-insulating layer from external influences such as precipitation.
How to insulate a roof from the inside
Before starting work, it is necessary to inspect the roof surface; it is very important that it is free of any obvious flaws: cracks, holes. If you skip this step, then the insulation will have a much smaller effect than it could, or will be completely useless. You will need to treat all rafters and beams with special antiseptic solutions that will destroy fungi and protect the tree from exposure to an aggressive external environment. Be sure to pay special attention to various communications: gas pipelines, electrical wiring, steam pipes.
Photo - Blowing the roof with foam
After completing all the preparatory work, you can begin to select the material for insulation. Most often, the insulation of a slate, iron or corrugated pitched (gable) roof is equipped with polystyrene foam or mineral wool. These materials perfectly withstand temperature changes, high humidity and aggressive physical impact, and are strong and durable.
In addition to them, specialists also often use:
- Foam concrete, polyurethane foam, penofol, and penoizol insulation is less commonly used;
- Fiberglass boards;
- Liquid sealants (for local action, for example, filling holes and cracks, often used to insulate loggias);
- Foam glass.
Cold roof made of corrugated sheets in utility rooms
For sheds, sheds and other utility rooms, installing a cold roof made of corrugated sheets is the best option. In this case, it is recommended to use special corrugated sheeting with an anti-condensation coating.
This profiled sheet is coated on the reverse side with a special synthetic compound, which is similar in structure to felt. Due to the large number of small air cavities, this material can retain a fairly large amount of moisture - up to 1 liter per m2. Thus, when humidity increases, the anti-condensation coating absorbs water, which then evaporates under the influence of cold roof ventilation.
Thanks to the use of corrugated sheets with anti-condensation coating, the design of a cold roof becomes much simpler and cheaper, since neither waterproofing nor counter-lattice is needed. In addition, such material is indispensable for gazebos, verandas, canopies and other open structures, since they generally do not use waterproofing, and condensation appears no worse than in a cold attic.
Why is insulation necessary?
Measures to protect against cold are necessary both during the construction of a wooden and stone building. Most often, in private low-rise construction, pitched roofs are chosen. The supporting structures of such a roof are in most cases made of wood, but it is possible to use metal trusses.
Schematic diagram of roof insulation
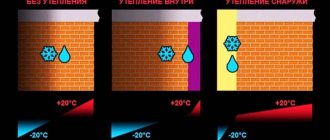
When choosing a wooden material, insulation is especially important, since it not only ensures a comfortable stay, but also protects structures from condensation . Damage caused to structures by moisture can be as follows:
- the appearance of mold and mildew on the surface of the wooden frame;
- the appearance of corrosion when using metal;
- increasing humidity in the house.
Factors that affect the roof
Any structure that is used as housing must meet certain standards and requirements. Only if they are followed will life in the house be comfortable and peaceful. Every detail is important - the correct laying of the foundation, the construction of walls, the laying of communications and the construction of the roof. The choice of roofing depends on the weight that will put pressure on the supporting structures of the house, the time and cost of installation work. In addition, an equally important step in arranging the roof is its insulation from the inside. It will not only protect the premises from the effects of external cold air masses, but will also act as a good sound insulator.
The roof must withstand freezing temperatures and a layer of snow
In different climatic zones, roofing elements are affected by many factors. The following natural phenomena correspond to our latitudes:
- rain;
- hail;
- excessive ultraviolet radiation from the Sun;
- snow;
- strong gusts of wind;
- icing, etc.
A typical private house is a structure that usually includes a main floor (one or two) and an attic. If the latter is used for housing, it is built in the form of an attic. It has been proven that with an uninsulated roof, in the cold season, up to 15-20% of the heat from the room is lost through the ceiling. This entails the need to increase heating and, as a result, increased energy bills.
Heat is lost through an uninsulated roof
The peculiarity of the space under the roof is not only in its geometric component, but also in the method of distribution of thermal energy. In summer it is hotter here than in other rooms, and in winter, on the contrary, it is colder. To create a comfortable microclimate inside and maintain optimal temperature, experts recommend creating a multi-layer “pie” from various materials. It usually includes a waterproofing layer, vapor barrier and insulation.
Schematic representation of the roofing “pie”
How to make insulation with polyurethane foam
This is high-tech in the technology of insulating any structures of private houses. To create consistency, equipment has been created and sold that can be used to insulate both vertical and horizontal structures.
The blowing or pouring method is used. It is more productive to use a spraying method in which the following occurs:
- filling all gaps of any size;
- expanding in volume, creates a solid, durable coating.
Polyurethane foam is obtained by mixing polyol and polysacyanate, which are in a liquid state. Mixing occurs without access to oxygen during spraying. Apply the consistency to the structural elements with a pistol. As the material cools down, it increases in volume several times.
Important! Polyurethane foam is a universal insulation material. Used for insulation of walls, ceilings, floors, roofs
Polyurethane foam
This option will be the most expensive, but at the same time it can become a universal solution for any buildings and premises. Its most important advantage will be a very thin layer of applied mass, which reliably retains heat and does not let cold air into the house. However, spray polyurethane foam creates a completely vapor-tight surface and the room will need high-quality ventilation.
The advantages of this method of insulation include the fact that by removing dirt, no other surface preparation is required. The foam, in the form of which the insulation will be sprayed, adheres perfectly to any surface. After spraying, it hardens and forms a solid mass that perfectly retains heat.
Why does condensation form on the roof of a house?
Condensation on the roof itself is not so bad; it is much worse when it begins to drip in large quantities onto the insulation, reducing its thermal insulation properties, or form wet spots on the ceiling and walls.
Condensation is formed due to the temperature difference between the roofing material and the surrounding air. In other words, when the roofing material is cold and the air surrounding it is warm, water droplets form on it.
In the case of a roof, condensation can form due to the following factors:
- The roof or ceiling of the upper floor is not insulated enough.
- Poor-quality vapor barrier of the ceiling of the last floor, or its absence.
- Insufficient ventilation of the attic space.
- Insufficient ventilation between the vapor barrier film and the roofing material itself.
- Poor quality materials or gross violations during roof construction.
Now let's look at how each factor affects the formation of condensation on the roof and what needs to be done to fix it.
Insufficient insulation of the roof of the house
This is a very common phenomenon, especially in old houses, when the roof or ceiling of the top floor is insulated either with a layer of insulation that is too thin or of poor quality.
During the cold season, such a roof will transmit heat into the unheated attic space, thereby heating it. The roofing material, especially if it is metal, will remain cold and condensation will form on it.
Slab insulation for garages
Thermal insulation materials in the form of slabs are more affordable, however, to secure softer types, the construction of an additional structure in the form of sheathing will be required.
When using such insulation, it is necessary to carefully treat the joints of the blocks to prevent freezing.
Basalt slabs
Compared to other insulation materials, this environmentally friendly material is one of the leaders in heat-insulating, sound-absorbing properties, vapor permeability, and non-flammable. A significant disadvantage is the high cost of basalt slabs.
Glass wool slabs
An inexpensive, non-flammable heat insulator, the structure of which is formed by prickly, needle-like fibers. To work with the material, you will definitely need protective equipment to protect your skin from direct contact with it, as well as glasses.
Due to their ability to absorb moisture, glass wool boards can lose their thermal insulation properties over time, shrinking due to the fragility acquired by the fibers. The service life is 10-15 years.
Extruded polystyrene foam
The material has a high density, does not absorb moisture, and due to its unnatural origin is unattractive to rodents.
For fixation on insulated surfaces, it is sufficient to use an appropriate adhesive composition, although this material is slightly heavier than polystyrene foam.
Those who insulate their garage with polystyrene foam in the most budget price category are more at risk, since this material does not meet fire safety standards, unlike extruded polystyrene foam.
Material selection
The most suitable materials for attic insulation are:
- mineral wool;
- Styrofoam;
- polyurethane foam;
- ecowool.
Mineral wool
Mineral wool and fibrous materials have excellent thermal insulation characteristics. They do an excellent job of removing water vapor from the roof. A special membrane film is responsible for the direction of condensate drainage from the inside to the outside.
In work, it is better to use mineral wool in the form of slabs, since, unlike rolled wool, it holds its shape perfectly and does not slide down an inclined plane. For a living space, you will need material 10 cm thick; for outbuildings, a three-centimeter insulation is sufficient.
When insulating the roof from the inside of the attic, mineral wool is cut into pieces of the required size with a margin of 2 - 3 cm. Before installing the insulation between the rafters, it is slightly compressed. After installation, it will straighten out and completely fill the required space.
If one of the sides of the material has a foil layer, then the mineral wool must be laid with a shiny surface inside the attic. If necessary, mineral wool can be replaced with glass wool.
Styrofoam
For a simple way to insulate the roof of a house with your own hands and save money, foam plastic is suitable. The material slabs are lightweight, so you don’t have to worry about excessive load on the roof structure. Among the disadvantages of polystyrene foam, one can note its poor vapor conductivity and attractiveness to rodents, which can cause significant damage to the thermal insulation of the attic.
Polyurethane foam
Foam material is sprayed onto the surface to be treated of any configuration and complexity. This process is carried out by using a special portable installation, which, under pressure, supplies the substance to a plane with any degree of inclination.
Its main advantage is that this method of insulating the attic or attic of a house allows you to create a dense monolithic layer without seams or gaps.
In addition, there is no need for an additional vapor barrier device to protect the decorative finish from condensation. The price of polyurethane foam is higher than that of alternative insulating materials.
Ecowool
The material is produced in compressed form and requires loosening before installation. In most cases, blow molding equipment is used to fluff and apply ecowool.
How to calculate the required insulation thickness
The choice of insulation thickness directly depends on the climatic conditions of the region of residence and the thermal insulation properties of the material. First you need to find the heat transfer value for the roof (R) - it is constant and is calculated separately for each region. For Moscow, this parameter is 4.67 m²×°C/W.
Next, you need to find out the coefficient of thermal conductivity of the insulation (λB). As a rule, it is indicated on the packaging and measured in W/(m×°C). To determine the thickness of the thermal insulation layer, the values of R and λB are multiplied.
Procedure for insulating walls from the inside
Preparing the base
The load-bearing wall must be cleaned before starting work. Afterwards, all possible cracks and through holes should be sealed. When insulating from the side of the room, it is recommended to treat the base with antifungal agents. For a house made of wood, the “Nortex”-Lux composition is well suited. There is an antiseptic with the same name intended for treating other types of concrete and stone walls.
Hanging the wall
Before installing the frame, it is necessary to determine possible irregularities on the load-bearing wall. Inside the room, this can be done using a long rule 2.5-3 meters long, into which bubble levels are integrated. If the wall is too long, then differences can be easily found by pulling control cords. The cord is pulled along the base being examined near the floor, near the ceiling and diagonally. When identifying localized “bulging” zones, the frame indentation must be taken from them. In some cases, if the base defect is small, it is easier to knock it down than to extend the false wall too far into the room.
Bracket installation
When insulating from the room side, the frames are assembled from galvanized “ceiling” profiles. In a wooden house, these can be dry edged bars with a cross section of 50x50 mm, which have been thoroughly antiseptic. In both cases, perforated “direct hang” brackets are used. To install the brackets on the wall, you must first mark their location. Since the profiles will be spaced at intervals of 400 or 600 mm (a multiple of the width of the plasterboard slabs), the rows of fasteners will be located along the axes at precisely these distances. In each vertical row, the distance between the U-shaped brackets should be about 600-750 mm. Direct hangers are fixed to the wall using “quick installation” dowels measuring 6x40 mm (for concrete), 6x60 or 6x80 for brick. The “pawns” are attached to the wooden wall with stainless self-tapping screws with a large flat head of 45 mm in length. There are two hardware for each bracket; they must pass through the side eyes. Important! It is recommended to install direct hangers on the wall through a thermal insulating gasket, then it will be possible to interrupt heat transfer through the metal and minimize cold bridges.
Laying insulation
Very often, thermal insulation is installed after the entire frame has been assembled. That is, mineral wool, polystyrene foam or EPS expands between the racks, but there is no insulation behind the profiles. In this case, it is better to lose the extra 3-5 centimeters, but reliably insulate the wall with a continuous layer. To do this, the insulation boards are “pinned” onto brackets and attached to the wall. Obviously, some kind of fixation of the insulating material will be required. For this, it is best to use the adhesive method. Among the different types of adhesives, the most preferable is polyurethane glue in cylinders, but you can also use water-mixed dry mixtures intended for the method of bonded thermal insulation. Important! When installing insulation on the wall, we recommend pressing it as much as possible to eliminate the gap through which moist air could circulate. For the same reason, it is better to apply glue to the beacons using a notched trowel-comb. If you use glue from a balloon, then it is advisable to make a continuous strip of it in the form of a closed contour around the perimeter of the slabs. It is better to foam the gaps between the slabs of foam plastic or EPS. It makes sense to use foam to seal the gaps near the passage of the brackets, as well as the gaps where the insulation joins the floor, ceiling and other structures.
Installation of vapor barrier
As you remember, our important task is to prevent moisture (in any of its manifestations) from penetrating to the dew point. Therefore, it is necessary to hang a vapor barrier construction canvas on top of the insulation; it can be either ordinary reinforced polyethylene, or more technologically advanced membranes or foil-coated polyethylene foam. The canvases can be pre-fixed using double-sided tape. It doesn’t matter how the stripes will be positioned (vertically or horizontally), but they must be hung with an overlap of at least 100 mm relative to each other. Important! The vapor barrier must extend to adjacent structures so that the insulating layer is reliably protected, including at the ends. The joints of the strips and the places where the vapor barrier adjoins other structures must be taped with waterproof construction tape.
Installation of frame profiles
Now you can install profiles on top of the thermal insulation layer. In any case, we need a combination of CD and UD. First, the UD guide profiles are fixed in place along the perimeter of the wall using dowels. Then the outermost wall profiles are positioned in the brackets and fixed strictly vertically with LN 9 mm self-tapping screws. When the outermost CD profiles are aligned, several control cords are pulled into alignment with their front surfaces. These will be lighthouse cords along which the remaining subsystem profiles are positioned one by one. If the height of the ceilings is greater than the height of the cladding panels, then you will need to assemble jumpers to ensure reliable joining of the plasterboard sheets on the short side. The jumpers are made from CD profile scraps, and they are secured in place with “single-level” brackets (these are the so-called “crabs” and the like).