The emergence of new heating systems is due to the insufficient quality of the existing ones. One of these new products, the introduction of which is becoming more widespread, is the use of systems such as gas heat generators for air heating. This is a simple and, at the same time, reliable system in which the heating of the room is quite fast (especially in comparison with existing systems). At the same time, the cost of equipment, as well as its installation and further maintenance, is relatively low. Of course, such a system is not able to work without a device that is used to heat the air masses - a gas heat generator.
The room is heated by gas heat generators
Equipment selection rules
As mentioned above, gas heat guns are presented on the market in a wide variety, which makes it possible to fully satisfy consumer demand. However, when choosing these devices, a number of problems arise. It is necessary to determine the exact power of the equipment. The difference in price between heaters of different power can be very noticeable, and therefore it is necessary to accurately determine the technical characteristics. provides you with the services of competent employees who will help you with the selection and further purchase of equipment. Our specialists will calculate the power of the installation based on the conditions of your specific facility. This will allow you to save a lot on your purchase.
Buy gas air heaters in Moscow
In the city of Moscow there are many companies that operate in the field of sales of air heating systems, providing a variety of products that vary in functionality and cost. We offer consumers interested in high-quality and economical heating of their production area to purchase modern air heaters, the price of which most closely matches their operational potential.
Sonniger is an experienced company with offices in many countries in Eastern and Central Europe. We provide premises that can provide comfortable conditions for any production workshop, warehouse, industrial facility, various sports and entertainment centers, etc.
Types of heat guns
Equipment for air heating is conventionally divided into two classes:
- Mobile;
- Stationary.
But units belonging to the first type do not always have compact dimensions. Some mobile models have quite impressive dimensions. Such devices are usually equipped with special trolleys necessary for moving the equipment.
They received the name mobile only because they are designed to operate from gas cylinders and do not require connection to the central highway. They can be installed anywhere and are designed for heating industrial premises. But cavitation heat generators of heating systems require an effective ventilation system at the site, because the heated air is removed along with the exhaust gases.
Stationary devices are designed for connection to a gas pipeline. They differ in the installation method and, depending on this, the criteria are:
- hanging;
- floor
The first ones have small dimensions, which means they take up little space. They are intended for heating private households. Suspended heat generators are easy to operate and install, quickly warm up the room, and have clear instructions for use.
Floor-standing units are more bulky devices. They are used to heat large areas. Many models of such equipment can be connected to an air duct system, which allows heat to be evenly distributed throughout all rooms.
What you need to know to make the right choice
Efficient gas-air heating can only be ensured by installing equipment that matches the parameters of the room. Important characteristics in the choice are:
- Heater type;
- Power.
In addition, for reliable operation of the device, it is necessary to ensure air flow into the room. A ventilation system is most often used for this. It is capable of not only supplying oxygen to the room, but also removing exhaust gases outside.
Review of popular models
The leader among heat guns, of course, remains the products of foreign companies and in particular US manufacturers. The device under the Master BLP 73 M brand is popular among owners of private homes and industrial facilities. It can be used not only as heating equipment, but also as a construction hair dryer.
Watch a video about the Master BLP 73 model:
An American-made heat gun consumes no more than 4 kg of liquefied gas per hour, generating up to 70 kW of energy. Its power is enough to heat a room of up to 700 m² with a capacity of about 2.3 thousand cubic meters of warm air per hour. The cost of such a device is no more than $650.
But there are also domestic models on the market that meet all regulatory requirements. One of them is the Patriot GS53 heat gun. It is capable of generating up to 50 kW of thermal power at a flow rate of up to 4.5 kg of gas per hour. This is enough to heat a room of no more than 500 m². The cost of the unit does not exceed $400.
Among the models that consume main gas, the heat generator AKOG-3-SP can be noted. This is a small device whose power is enough to heat a room with an area of 30 m², while consuming 0.3 m³ of natural gas.
The thermal convector of this brand is designed for wall mounting and can heat one functional area in a country house. The cost of this device is one of the lowest and is less than $250.
Conclusion
The use of such equipment in heating systems is considered one of the most effective and economical solutions. It is easy to use, safe and therefore can be used not only at production facilities, but also in residential premises
Types of gas heat generators
Compared to diesel, solid fuel and universal heat generators, gas equipment for air heating is the most popular.
Devices are differentiated by size and weight:
- mobile - easy to transport;
- stationary - installed in one place.
Mobile models of gas heat generators are less popular, since their operation requires gas cylinders filled with liquefied mixtures of propane and butane. The most striking representative of portable heating equipment is a heat gun.
Most often, heat guns are used for a one-time increase in temperature at construction sites and in shopping malls. In everyday life it is used in extreme cases (turning off the heating in the house).
Stationary models of gas heat generators can be:
- wall-hung - hung on brackets built into the walls;
- floor - installed on the floor.
Wall-mounted models are used for heating small objects; their power usually does not exceed 35 kW. Floor-standing equipment is recommended for heating small areas. A number of floor-standing units include models that can be installed outside the building, i.e. on the street.
In order for atmospheric gas processing equipment to operate continuously, it is necessary to ensure a constant supply of air to the combustion chamber
Depending on the distribution of heated oxygen and the method of gas combustion, the equipment is divided into:
- horizontal;
- vertical.
For rooms with high ceilings, vertical devices are used, and for rooms with low ceilings, horizontal devices are used.
Design of gas heat generators
Air heating is most effective in exhibition halls, production facilities, film studios, car washes, poultry farms, workshops, large private homes, etc.
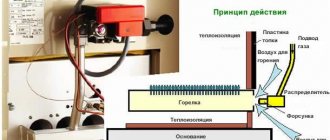
A standard gas heat generator for air heating consists of several parts that interact with each other:
- Frame. All components of the generator are hidden in it. In its lower part there is an inlet opening, and at the top there is a nozzle for already heated air.
- The combustion chamber. This is where fuel is burned, causing the coolant to heat up. It is located above the supply fan.
- Burner. The device supplies compressed oxygen to the combustion chamber. Thanks to this, the combustion process is supported.
- Fan. It distributes heated air throughout the room. It is located behind the inlet grille in the lower part of the housing.
- Metal heat exchanger. A compartment from which heated air is supplied to the outside. It is located above the combustion chamber.
- Hoods and filters. Limit the entry of flammable gases into the room.
Air is supplied to the housing via a fan. Vacuum is generated in the area of the supply grille.
An air heating device costs 3-4 times less than a “water” circuit. In addition, air options are not at risk of loss of thermal energy during transportation due to hydraulic resistance
The pressure is concentrated opposite the combustion chamber. By oxidizing liquefied or natural gas, the burner generates heat.
The energy from the combustion gas is absorbed by a metal heat exchanger. As a result, air circulation in the case becomes more difficult, its speed is lost, but the temperature rises.
Knowing the power of the heating element, you can calculate the size of the hole that will provide the necessary air flow
Without a heat exchanger, most of the energy from the combustion gas would be wasted and the burner efficiency would be lower.
Such heat exchange heats the air to 40-60°C, after which it is supplied to the room through a nozzle or socket, which is provided in the upper part of the housing.
Fuel is supplied to the combustion chamber, where during the combustion process the heat exchanger is heated, transferring thermal energy to the coolant
The environmental friendliness of the equipment, as well as its safety, make it possible to use heat generators in everyday life. Another advantage is the absence of liquid moving through pipes to convectors (batteries). The heat generated warms the air, not the water. Thanks to this, the efficiency of the device reaches 95%.
Heat generator in heating
Maintaining a certain temperature regime in industrial premises, especially in winter, is quite difficult if a heating system .
Heating a large area or installing stationary heating that receives heat from a mini-boiler room is too expensive and cumbersome. Therefore, many people, including owners of country houses with large square footage, resort to the help of heat generators.
A heat generator is a device that has a complex internal structure and produces heat, which, with the help of a fan, is distributed with air flow throughout the entire area . This unit is quite powerful, capable of heating an area to a comfortable temperature of 60-70 sq.m. in just 10-15 minutes. The only difficulty that accompanies all owners of heat generators is the cost of both the unit itself and the consumed fuel on which it operates. Otherwise, the device shows only its positive sides, allowing you to heat quickly, a lot and with high quality.
The video is about a solid fuel stove heat generator
Structure and design features
The heat generator consists of such structural parts as:
- Combustion chamber – this is where the process of fuel combustion and heating of the coolant takes place.
- Burner - supplies compressed oxygen to the combustion chamber to support the combustion process.
- Fan – ensures the distribution of heated air in a spatial room.
- Heat exchanger is a chamber from which heated air comes out.
- Filters and hoods prevent flammable gases from entering the air of a heated area.
The type and design of the burner directly depends on what kind of fuel is used (liquid, solid or gaseous). If desired, the burner can be replaced with your own hands, and the entire system is adjusted to the type of fuel that the customer desires.
The main advantage and feature of the design is the fact that the chambers and compartments of the heat generator are located in such a way that the spent fuel (more precisely, its decay products) does not mix with the air that circulates in the room.
This is very important because spent fuel is a toxic gas that can cause asphyxiation to people living in heated areas. A high level of safety, as well as environmental friendliness, allows the use of heat generators not only in industry, but also in everyday life.
Another advantage is the absence of an intermediate coolant that would require additional heating (pipes, batteries, coils, etc.). That is, the heat generated from fuel combustion is completely spent on heating the air, and is not spent on heating the coolant. This allows you to increase efficiency up to 95%, and the result is felt immediately after the heat generator starts working.
One example of an air heat generator, manufacturer Robust
Operating principle of the heating system
Fuel is supplied to the combustion chamber, where the heat exchanger heats up during the combustion process.
The fan uses its blades to capture air in the room and passes it through the heat exchanger. Heated air circulates throughout the room, performing several cycles. The operating principle is quite simple and has many advantages. You should not be afraid that during operation the pipe will burst and the neighbors below will end up in the water, and you will be in an unpleasant situation, which, moreover, will hit your pocket. The device is completely safe and also has automatic sensors that stop fuel combustion when there are threats of breakdown or emergency situations.
Air heated in the heat generator can be supplied to the room in two ways :
- Directly from the fan - heated air circulates and also replaces cold air, regulating and maintaining the temperature. This type of heating system is only convenient if the heated areas are not large.
- Through a system of interconnected air ducts, heated air (using artificial ventilation) circulates through the air ducts, heating several rooms at once from one generator. It is used for heating large pavilions and utility rooms with many separate rooms.
The generator itself can be installed both directly indoors and outside, on the street. The type of heat generator, which has an additional protection system from the influence of weather conditions (high humidity, frosty weather, snow cover), will depend on this indicator.
The key condition for the full functioning of a heating system using a heat generator is the correct connection of the exhaust pipe to the chimney, as well as the presence of draft from the latter. If the chimney is clogged, it is important to clear it of accumulated soot before installing the system. Otherwise, toxic substances may enter the heated room, causing poisoning.
The video shows the operation of the Totem solid fuel heat generator
Types of heat generators
A person’s heating needs determine the type of generator, of which there are a huge number today.
They are differentiated not only by the fuel used, but also by other parameters:
- By dimensions and weight:
- mobile – easy to transport;
- stationary - used only in a certain place, there are two types: hanging - can be used both indoors and outdoors;
- floor - used only indoors.
- According to the method of fuel combustion and distribution of heated air:
- horizontal – air exchange occurs in a horizontal projection, convenient when a small room is heated;
- vertical - heated air circulates from bottom to top, providing heating for rooms with high ceilings.
- By type of fuel burned:
- gas - the most common and cheapest type of fuel, allowing significant savings on heating (high heat transfer during combustion);
- diesel - they run on diesel fuel, but require annual cleaning and maintenance, as combustion products pollute the unit;
- vortex - the operating principle is based on complex physical processes that make it possible to obtain energy from water;
- universal - can work on both liquid and solid fuels, as well as on wood, vegetable oil, manure, peat and coal.
The choice of fuel directly depends on factors such as:
- intensity and speed of air heating;
- the amount of fuel consumed and heating costs in monetary terms;
- the cost of the equipment and its service life (solid fuel ones become clogged faster and also require manual removal of fuel residues).
Calculation of SVO
Q = Gc (t(hor) – t(oh))
Q (h.o.) – Heating power (amount of heat in kJ/h);
G – amount of air (kg/h);
c – specific heat capacity of air in the room (varies depending on temperature);
t (hot) – hot air temperature;
t (oh) – temperature of cooled air.
Dependence of the required power of the air heater on the volume of the heated building
Nuances t (oh) - if air is taken from a heated room at a height of more than three meters, then t (oh) is considered 3-4 degrees higher than in the working area of the room.
To increase the heating power, t(hot) should be as high as possible. But there are limitations:
If air from the heating system is supplied directly to the area where a person is located, it should not be higher than 25 degrees C;
at a distance of 2 m – 45 C;
more than 3.5 m. – 70 C.
If the installation of air heating can be done independently, then it is still better to entrust the calculations to specialists.
DIY CTG
The simplest option for implementation at home is a tubular-type cavitation generator with one or more nozzles for heating water. Therefore, let’s look at an example of manufacturing just such a device; for this you will need:
- Pump – for heating, be sure to choose a heat pump that is not afraid of constant exposure to high temperatures. It should provide a working outlet pressure of 4 - 12 atm.
- 2 pressure gauges and sleeves for their installation - placed on both sides of the nozzle to measure the pressure at the inlet and outlet of the cavitation element.
- Thermometer for measuring the amount of heating of the coolant in the system.
- Valve for removing excess air from a cavitation heat generator. Installed at the highest point of the system.
- Nozzle - must have a bore diameter of 9 to 16 mm; making it smaller is not recommended, since cavitation can already occur in the pump, which will significantly reduce its service life. The shape of the nozzle can be cylindrical, conical or oval; from a practical point of view, any one will suit you.
- Pipes and connecting elements (heating radiators in their absence) are selected in accordance with the task at hand, but the simplest option is plastic pipes for soldering.
- Automatic switching on/off of the cavitation heat generator - as a rule, it is tied to the temperature regime, set to switch off at approximately 80ºC and switch on when it drops below 60ºC. But you can choose the operating mode of the cavitation heat generator yourself.
Rice.
6: diagram of a cavitation heat generator Before connecting all the elements, it is advisable to draw a diagram of their location on paper, walls or on the floor. The locations must be placed away from flammable elements or the latter must be removed at a safe distance from the heating system.
Assemble all the elements as shown in the diagram and check for leaks without turning on the generator. Then try the cavitation heat generator in operating mode; the normal increase in liquid temperature is considered to be 3-5ºC in one minute.
Advantages and disadvantages of using heat generators
Air heat generators have the following advantages:
Heating systems that use air as a coolant are considered the most economical and safe. The equipment does not leak or freeze while operating at sub-zero temperatures
These advantages are provided by the absence of coolant liquid. Another important advantage is the absence of an intermediate heat carrier. Insignificant costs for purchasing fuel, maintaining the device and generating thermal energy. Several functions can be combined in one unit, for example, ventilation, heating and air conditioning. Since the efficiency of the device is very high, even a large room can be heated in 1-2 hours. The warm air leaving the unit can heat the entire room or its individual parts. Heating zones are not located around radiators or stoves. Additional advantages are the mobility of the device, quick and easy installation and dismantling. Supply grilles can be installed on walls, floors, ceilings or convenient open areas. The affordable price of heat generators is ensured by the fact that such equipment uses few metal elements. Heat generators are suitable for heating large premises, including production workshops. Simple coolant circulation. The system elements are reliably protected from corrosion and other damage.
The main disadvantages are related to the energy dependence of the system. In other words, the equipment will only work if there is a power supply. In regions where there are frequent power outages, these devices are not recommended. Another disadvantage is that the cost of air heating increases in proportion to the requirements placed on it.
Advantages of air gas heating at home
Among the undeniable advantages of air heating, the most correct ones would be to highlight the following:
- This heating option is characterized by high performance and efficiency due to the fact that the air is heated not in the boiler room, but directly in the living room;
- this heating method makes it possible to completely warm up the house in just 1 - 2 hours, which is a very fast time for any heating system;
- a small amount of financial resources spent on servicing the heat generator, since the installation of these devices is not difficult, and during operation they do not require increased attention from the owners due to the fact that they are fully automated. In addition, in the case of heating at a low temperature, you can also save money on the low volume of gas consumed;
- the functionality of a gas stove is very high, since in addition to the standard heating function, it is also capable of ventilating the room and playing the role of an air conditioner;
- the probability of such a system leaking is very low due to the lack of coolant as such, as well as the pipe system;
- There will be no need for central heating, which will also reduce operating costs.
Air heating using gas is an excellent heating option in terms of economy, safety, and environmental friendliness, since all harmful substances, as already mentioned, do not accumulate at the bottom of the room, but go up.
How to choose a heat generator?
When choosing heating equipment you need to take into account a lot of details
First of all, it is important to assess the area of the heated room. The larger the building, the more powerful the heat generator should be
The heat capacity of a building is calculated using the formula:
р=V·ΔT·k/860
p is the desired heat capacity;
V - heated area (the height, length and width of the room are multiplied);
ΔT is the difference in temperature in the building and outside it;
K - thermal insulation (indicators of the material with which the building is insulated).
Indicators of the most commonly used materials:
- double layer of brick - 1-1.9 W/m°C;
- single layer of brick - 2-2.9 W/m°C;
- wooden panels or corrugated sheets - 3-4 W/m°C;
- modern heat and waterproofing - 0.6-0.9 W/m°C.
The indicator for the number of kilocalories in kilowatts is 860. Generally accepted standards - for 1 kW of heat generator power, 30 cubic meters of forced air are required.
The power of the air heater must exceed the power of the burner by at least 15%. Such equipment is reliable and effective in any situation. Its use reduces energy costs
Knowing the value of heat capacity, you can select equipment that can heat the entire area of the room.
Nuances when choosing a heat generator
Before purchasing heating equipment, you must:
- arrange a chimney to release toxic gases;
- think over a system of ventilation ducts for circulating heated air;
- Using the formula, calculate the power of the device.
Having completed all these steps, you can safely go shopping.
If there are problems with ventilation in the room, it is recommended to install a powerful floor-standing generator and synchronize its operation with ventilation that takes air directly from the street
To select a high-quality gas heat generator model, you need to pay attention to the following nuances:
- type and design of the burner - relevant if a fuel change may be required;
- warranty card and technical passport - a guarantee of the purchase of original (not defective) equipment;
- high-quality components - such equipment is more expensive, but its service life is much longer.
Taking these factors into account, the selected heat generator will last for many years.
Tips for choosing reliable equipment
By following simple recommendations you can avoid purchasing low-quality goods:
- It is better to make purchases at certified points of sale. Often, at wholesale stores and on the Internet, defective products are sold under the guise of high-quality equipment. The trap is the price halved.
- If it is not possible or you did not have time to calculate the required power of the device, then the consultants in the store will do this for you. To do this, you only need to know the area of the house, the height of the ceilings and the thickness of the walls. After making calculations, specialists will offer the optimal model for your home.
- It is recommended to purchase brands that have positive reviews on the Internet. You can also find out in advance how the equipment behaves during operation and other features.
For home use, the ideal option would be models such as Airmax D 28, Titan 25 (30, 35), Fuela, TG-7.5, Dragon 12.
Requirements for installation
To connect a gas heat generator for air heating at home, you need to carry out preparatory work and purchase:
- flexible air duct, which is a galvanized tube for circulating heated air;
- tees are needed to create an air line and connect pipes;
- for taking in cold air and supplying hot air - a grille;
- to seal the line connections - aluminum tape;
- mounting fasteners;
- knife.
You should first take care of the air duct.
You can install a gas heat generator with your own hands, but it must be connected to the gas pipeline by representatives of the gas service, with which an agreement has been concluded for the supply of blue fuel and maintenance of equipment
The ideal option is to design airways - channels at the construction stage of the building.
To install heating in a finished house, you need to erect false walls and suspended ceilings. Pipes will be disguised in the resulting niches.
What does a gas heat generator for air heating consist of?
Each of these parts of the system plays a specific and important role, namely:
- the function of a gas burner is to ignite the fuel and ensure its further combustion;
- the purpose of the air fan is to continuously supply fresh air, as well as to eject exhaust air upward from the system;
- Complete combustion of the heat source occurs in the combustion chamber. Provided that the fuel burns completely, the amount of carbon dioxide released by the system is not large;
- a heat exchanger is necessary to ensure that normal heat exchange occurs between the heat generator and the room itself, that is, it prevents overheating of the heating equipment;
- Air ducts are special channels that are necessary to remove hot air to the desired areas of the room.
Varieties
The main difference between heat generator models is the type of fuel used for heating. There are also differences in the heating element . Such elements are air or water .
Diesel
Devices of this type run on diesel fuel or kerosene . Diesel heat generators are suitable for heating large industrial premises. Fuel is supplied in two ways : dropwise or using a nozzle that sprays fuel throughout the combustion zone.
In addition to diesel fuel, generators equipped with a special burner use oils and fats of vegetable origin . However, this type of fuel constantly produces waste , which over time has to be cleaned, which leads to device downtime.
Photo 1. Diagram of the diesel heat generator. The main parts, the movement of cold and warm air are indicated.
Gas
This type is designed to constantly supply hot air to the premises. Gas generators are installed vertically . The heat exchanger receives the maximum part of the heat from the combustion products, thereby reducing the volatility of the smoke. That is why heat generators of this type require the installation of a fan, which improves exhaust. The efficiency of gas units reaches 90% .
Important! When purchasing gas heat generator models, it is worth considering its ability to operate at low gas pressure.
Universal
This type of generator is similar to diesel units. , vegetable fats can be used as fuel . The power of a diesel generator is much higher compared to equipment running on oils and vegetable fats.
Vortex
Differs in complexity of design . The operating principle is based on the vortex effect, in which a gas or liquid splits into two parts and forms a vortex.
With this process, an active increase in temperature in the combustion chamber is observed.
Types of air heating systems
Among the heating systems known to science, three types can be distinguished:
- direct flow;
- recirculation (aka gravity);
- recirculation with partial intake of outside air.
Direct-flow systems are the most ancient and simplest in design. They were used back in Ancient Rome and were widespread in London before the start of the industrial and technological revolution.
This diagram shows the design of a direct-air heating system, which is characterized by low efficiency. Modern systems are more complex, but have significantly higher efficiency
With a direct-flow system, the heating device, i.e., a wood-burning stove or fireplace, was located in the lower part of the house, optimally in the basement. The heat from the air heated by the stove rose upward and was transferred to the walls and ceilings.
To improve the circulation of hot air and heating efficiency, special holes were made in the floor.
The cooled air left the room through holes in the roof, and the stove (fireplace) warmed up new air masses coming from outside, since serious thermal insulation of buildings in those days was not yet developed.
The low efficiency of direct-flow systems is obvious. It requires the combustion of a large amount of fuel, but a significant part of the heat is absorbed by the material of the walls, floors and ceilings.
At the same time, the rooms are heated unevenly: it is too hot below, and the upper rooms no longer have time to warm up. Some of the heat generally left the house through the roof along with the air.
A more modern recirculation system appeared thanks to the development of gas heating. Heating equipment of this type allows you to warm up not the entire house, but only specific air masses. They form air flows that are directed from bottom to top to specific rooms.
At the same time, hot air masses displace cold air, which escapes through grates located in the floor of the room. Cold air flows through the ducts to the heater and returns to the system in the form of a hot stream. The recycling cycle repeats over and over again.
Thermal energy consumption with a recirculation heating system is several times less than when using a direct-flow scheme. But there are also disadvantages to this option. A closed system prevents air renewal, which worsens the quality of life in the house.
In a closed recirculation air heating system, air flows constantly circulate between the rooms and the heating device, giving and taking away heat
The problem can be partially solved by using tools such as filters, ionizers, humidifiers, etc. But good devices of this type are quite expensive, and their maintenance will require additional effort, as well as automation.
The problem of restoring air flows can be solved more effectively using a recirculation heating system with partial air intake from outside.
When arranging such a scheme, they provide for the partial removal of a small amount of air to the outside and the intake of the corresponding volume of air masses from the street. As a result, the composition of the air inside the building is regularly updated.
Recirculation systems operate on the gravitational principle: hot flows rise upward, and cold flows fall down. Unfortunately, not every building has such circulation efficiently enough. In this case, a fan is turned on in the system to force the recirculation process.
Kinds
The main task of a cavitation heat generator is the formation of gas inclusions, and the quality of heating will depend on their quantity and intensity. In modern industry, there are several types of such heat generators, differing in the principle of producing bubbles in the liquid. The most common are three types:
- Rotary heat generators - the working element rotates due to an electric drive and produces fluid turbulence;
- Tubular - change pressure due to a system of pipes through which water moves;
- Ultrasonic - the heterogeneity of the liquid in such heat generators is created due to low-frequency sound vibrations.
In addition to the above types, there is laser cavitation, but this method has not yet found industrial implementation. Now let's look at each type in more detail.
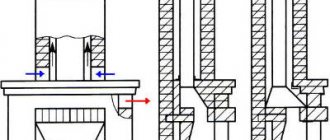
Rotary heat generator
It consists of an electric motor, the shaft of which is connected to a rotor mechanism designed to create turbulence in the liquid. A special feature of the rotor design is the sealed stator, in which heating occurs. The stator itself has a cylindrical cavity inside - a vortex chamber in which the rotor rotates. The rotor of a cavitation heat generator is a cylinder with a set of depressions on the surface; when the cylinder rotates inside the stator, these depressions create heterogeneity in the water and cause cavitation processes to occur.
Rice. 3: Rotary type generator design
The number of recesses and their geometric parameters are determined depending on the model of the vortex heat generator. For optimal heating parameters, the distance between the rotor and stator is about 1.5 mm. This design is not the only one of its kind; over the long history of modernizations and improvements, the rotor-type working element has undergone a lot of transformations.
One of the first effective models of cavitation converters was the Griggs generator, which used a disk rotor with blind holes on the surface. One of the modern analogues of disk cavitation heat generators is shown in Figure 4 below:
Rice. 4: disk heat generator
Despite the simplicity of the design, rotary-type units are quite complex to use, as they require precise calibration, reliable seals and adherence to geometric parameters during operation, which makes their operation difficult. Such cavitation heat generators are characterized by a fairly low service life - 2 - 4 years due to cavitation erosion of the housing and parts. In addition, they create a fairly large noise load during operation of the rotating element. The advantages of this model include high productivity - 25% higher than that of classic heaters.
Tubular
A static heat generator has no rotating elements. The heating process in them occurs due to the movement of water through pipes that taper in length or due to the installation of Laval nozzles. Water is supplied to the working element by a hydrodynamic pump, which creates a mechanical force of the fluid in a narrowing space, and when it passes into a wider cavity, cavitation vortices occur.
Unlike the previous model, tubular heating equipment does not make much noise and does not wear out as quickly. During installation and operation, you do not need to worry about precise balancing, and if the heating elements are destroyed, their replacement and repair will cost much less than rotary models. The disadvantages of tubular heat generators include significantly lower productivity and bulky dimensions.
Ultrasonic
This type of device has a resonator chamber tuned to a certain frequency of sound vibrations. A quartz plate is installed at its input, which produces oscillations when electrical signals are supplied. The vibration of the plate creates a wave effect inside the liquid, which reaches the walls of the resonator chamber and is reflected. During the return movement, the waves encounter direct vibrations and create hydrodynamic cavitation.
Rice. 5: Operating principle of ultrasonic heat generator
Next, the bubbles are carried away by the water flow through the narrow inlet pipes of the thermal installation. When moving into a wide area, the bubbles collapse, releasing thermal energy. Ultrasonic cavitation generators also have good performance characteristics, since they do not have rotating elements.
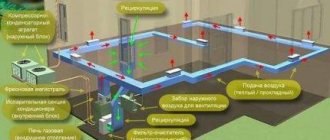
Air heating options
An air heating system (AHS) is a heating system that does not have radiators. The heat generator heats the air directly, not the liquid. SVO in a private house are conventionally divided into:
- Gravitational.
- Forced.
Gravitational principle
Warm air from the stove rises, spreads across the ceiling and cools down at the far walls. An air circulation is created without any additional devices. This is a classic system, the predecessor of water and steam heating.
Gravity hot air distribution system
Today it is also used, only the boilers that heat the air have changed. The “Russian stove” was replaced by Buleryan, Butakov’s stove and others.
The system is good in its simplicity. It does not create noise, drafts, is economical, and reliable.
The downside is that the heat is concentrated in the room where the stove is located.
Coercive principle
The air is pumped using a fan. This could be an air cannon that mixes large volumes of air in large rooms.
Another option is that warm air is supplied to adjacent rooms through an air duct system.
After which, part of the air is returned to the system for reheating, and part is discharged outside.
With the help of a recuperator installed at the outlet, warm air heats the incoming cold stream before leaving the house. Fresh air enters 15 - 20%. A recuperator is a useful thing, but not necessary. Given the low price of fuel, it can pay for itself only after 7–10 years (The approximate cost of a recuperator in Russia is 17–27 thousand rubles)
To prevent specific odors from spreading throughout the house, air outlets to the street can be installed in the kitchen and toilet.
Comparison of natural heating systems and forced heating with recuperation
An important component of the system is the air ducts. They are made from galvanized sheets, special corrugation, etc. The insulation is a self-adhesive heat insulator. They are connected to each other with clamps or special reinforced tape. Air ducts can be:
- flexible (corrugated), or rigid;
- round or square.
Round ones have a minimum of aerodynamic drag. Diameter 10 – 20 cm.
Square ones are made in the form of boxes.
If you plan to install an air conditioner, the air ducts must be well insulated to prevent condensation from accumulating.
The principle of operation of the recuperator
Air that circulates around your home over and over again requires filtration. You can install a replaceable filter, or you can install an electronic one, which does not need replacement, but only maintenance. This pleasure will cost about 20 thousand rubles.
The efficiency of forced air heating is high - about 90 - 96%. True, most modern heating boilers have an efficiency level of 85 to 95%.
The price of this air heating system for a private house is also not an advantage, since with all the additions, the system costs almost the same as conventional water heating.
If the air intake is installed at the top of the room, the air will be cleaner (it is more polluted there); if at the bottom - fuel economy (air near the floor has cooled down).
pros
- Possibility to combine ventilation and heating (good where air conditioning is needed);
- No water - no defrosting of the system and no leaks;
- Fast heating and cooling (It’s good, for example, when there is a large difference between day and night t, but this is also a disadvantage. The door was opened and the heat evaporated).
Cons of the system
Difficulties in installation. If a house was not designed for air heating, it is often difficult to reconstruct it.
Installation of a network of corrugations and filters is required.
All this needs to be decorated decoratively, or hidden in a false ceiling, which hides the height of the rooms.
Influent reservoirs can become excellent habitats for micro-life. Dust, condensation and microorganisms accumulate there, although not very quickly, but still. Once every 5-7 years, the air ducts will need to be thoroughly cleaned and treated for mites, but this is not easy, inexpensive and unpleasant.
And don’t forget that you also need to pay for the electricity that is needed to operate the fan, and if the lights are turned off, you need a backup power source.
Air duct before and after cleaning
In addition, if you make a mistake in the calculations, you may encounter the following troubles:
- Noise;
- Drafts;
- Accumulation of hair and dust in unventilated corners;
- Variation t (head – hot, legs – cold);
- Even a well-regulated flow pattern can be disrupted by simply opening the door.
Price
You don’t have to make a heat generator yourself. There are ready-made devices available for sale. Finally, I will give the cost of some popular models:
| Model | Price in rubles |
| VTG 5.5 kW | 76400 |
| NTG-11 10.1 kW | 115000 |
| EUROMIX REV 100, 100 kW | 472000 |
| Euronord H 50 for premises up to 7500 m2 | 240 000 |
That's all the information about what a heat generator is.
How to warm up a house with air?
Air is a very effective coolant, much more convenient than water. The simplest option for such heating is a conventional fan heater. This device, consisting of a fan and a heating coil, can warm up a small room in literally a matter of minutes. Of course, for a private home you will need more serious equipment.
A gas or solid fuel boiler can be used as a heat source. An electric heater is also suitable, but this option is not considered very profitable, since electricity costs increase significantly.
An interesting and environmentally friendly heating option is the use of solar panels or a solar collector. Such systems are placed on the roof. They either directly transfer thermal energy from the sun to a heat exchanger or convert it into inexpensive electrical energy. In the latter case, the fan can also be powered from the battery.
The air is heated in a heat exchanger and supplied to individual rooms through air ducts. These are rather bulky structures made of durable metal. The cross-section of the air ducts is significantly larger than the diameter of the water heating pipe.
Gas boilers and other types of heating equipment are also suitable for air heating. The efficiency of such systems reaches 90%; they are used not only in residential premises, but also in workshops and warehouses
But radiators for air heating are not needed. Warm air simply fills the rooms through special grilles. As you know, hot gas tends to rise. Cold air will be forced downwards.
From here, cold air flows move back to the heat exchanger, heat up, enter the rooms, etc.
This diagram clearly demonstrates a recirculation-type air heating device with partial intake of outside air, as well as an air conditioner, ionizer and ultraviolet purifier
Almost all air heating systems include the installation of a fan, which blows hot air and forces it to move through the heating system. The presence of such a device makes the system dependent on electrical energy.
You can also make a system in which hot air moves naturally, without any fan. However, the efficiency of such systems usually leaves much to be desired, since the rooms in this case warm up too slowly.
A convincing argument in favor of organizing an air heating system is to eliminate emergency leaks and flooding with resulting property damage. In addition, if the air ducts are damaged, the automation will stop the system.
How it works on coal, wood, coke
various types of solid fuel as fuel : coal, wood, coke. Many consumers use special waste obtained after processing plants. The most important factor for good heating of the device is the heat transfer of solid fuel, so most buyers use fuel with the highest efficiency.
Most solid fuel generators are capable of delivering an efficiency of 90% . The devices generate heat for 5-8 hours , and one addition of solid fuel is enough.
The most common boilers are those made of cast iron or steel . Cast iron heat generators are more popular, since this metal is capable of generating heat for a long time.
However, this material is quite fragile, since cast iron is subject to overheating , and as a result, cracks form on the boilers.
Steel boilers are less susceptible to temperature changes, but have a number of other disadvantages.
When working with these heat generators, it is necessary to constantly load fuel into the combustion chamber. Solid fuel equipment requires special and constant attention from humans, but at the same time, their convenience lies in the availability of solid fuel.
Types of gas heat generators
Gas heaters for heating are divided into mobile and stationary. The latter, in turn, are divided into suspended and floor-mounted. At the same time, mobile units are less common because they use gas cylinders for their operation, which is not always convenient and possible to provide. That is why such devices are used only in extreme cases, for example, when the main heating in the room is turned off, and you urgently need to heat it when the temperature outside sharply drops. Also, such units are used as the main heating in regions with a short winter season.
The stationary type of heaters is used in various fields. Wall-mounted heat generators are hung on walls indoors and outdoors. Floor-standing devices, depending on the assembly features, can be horizontal or vertical. The former are more often used in low rooms, while the latter are suitable for installation in a private home or on the street. Floor-standing units are convenient to use for heating small rooms, installing them at the entrance and exit to the heated zone.
Construction of gas heat generators
A gas heat generator is a heater that heats the coolant (air) to the required temperature.
Its structure is as follows:
- The air fan is designed for uninterrupted supply of air masses and removal of exhaust air from the system. Exhaust air is exhausted upward.
- A gas burner burns fuel and heats the coolant.
- Complete combustion of the heat source occurs in the combustion chamber. If the fuel burns completely without any residue, then the volume of carbon dioxide that the system emits is small.
- The purpose of the heat exchanger is to ensure normal heat exchange between the room and the heat generator. In addition, the heat exchanger protects heating equipment from overheating.
- Air ducts are used to remove heated air into the room.
The operating principle of such heating equipment is as follows: a fan draws cold air into the device, it is heated during fuel combustion to the required temperature and discharged through air ducts into the room.
The operating process of a gas heater can be divided into the following stages:
- cold air from the street or room is drawn into the device by a fan and hits the heating element;
- since gas is constantly burned in the combustion chamber, thermal energy is released, which heats the air;
- after this, the fan supplies heated air to the heat exchanger;
- air ceilings are distributed through the air duct system through the use of air valves;
- Through the grilles, heated air is supplied to the room and gradually heats it up.
Calculation and selection of a gas generator
In order for the system to operate efficiently, the gas heater for air heating must be correctly selected
To do this, first of all you need to pay attention to the size of the heat exchanger. The dimensions of the heat holder should be 1/5 larger than the dimensions of the burner
To choose the right gas generator, you need to calculate its power. To do this, use the formula – Р=VхΔTхk/860, where:
- V in m3 indicates the heated area of the building;
- ΔT in °C is the difference in air temperature inside and outside the house;
- K is an indicator of the thermal insulation of a house (the number can be selected from a reference book);
- 860 - this number is a coefficient that allows you to convert kilocalories to kW.
The power of the device is selected in accordance with the obtained value. As a rule, the operating power of the equipment is indicated in its technical characteristics.
For uninterrupted operation of heating equipment for air heating, it is necessary to ensure a continuous supply of air to the device.
For this purpose, the ventilation system of the structure must be properly equipped. If there are problems with ventilation, then it is better to use a hanging-type device that takes air from the street. Date: September 25, 2022
How does the heating system work?
The fan blades capture air and direct it to the heat exchanger. The air flow heated by it circulates throughout the building, performing several cycles.
The main advantage of the gas heat generator design is that the arrangement of the chambers and compartments prevents the mixing of spent fuel decay products with the air from the room
While operating the equipment, there is no need to worry that a pipe will burst and you will flood your neighbors, as often happens with water heating systems. However, the heat-generating device itself contains sensors that, in emergency situations (threat of breakdown), stop the fuel supply.
Heated air is supplied to the room in several ways:
- Ductless. Warm air flows freely into the space being processed. During circulation, it replaces the cold one, which allows you to maintain the temperature regime. The use of this type of heating is advisable in small rooms.
- Duct. Through a system of interconnected air ducts, heated air moves through the air ducts, making it possible to heat several rooms at the same time. Used for heating large buildings with separate rooms.
The movement of the air mass is stimulated by a fan or gravity. The heat generator can be installed indoors and outdoors.
Using air as a coolant makes the system as profitable as possible. The air mass does not cause corrosion and is also not capable of damaging any elements of the system
In order for the heating system to function correctly, the chimney must be correctly connected to the gas thermal energy generator.
If the smoke duct is installed incorrectly, it will become more likely to become clogged with soot build-up. A narrowed and clogged chimney will poorly remove toxic substances.