Agree that heating a large room using a mini-boiler room is very problematic and expensive. An excellent solution would be gas heat generators for air heating. These are boilers that use gas burning in a chamber as energy to heat the coolant.
The power of the unit allows you to heat a building with an area of up to 70 sq.m. in 10-15 minutes without wiring and batteries. The equipment does not have the disadvantages inherent in traditional coolants: heat loss during transportation, inertia, difficulties in adjustment, the possibility of leaks, regular repairs.
In this article we will look at the design of gas-fired thermal energy generators. We will analyze their advantages and disadvantages, and also help you choose the best heating device. Taking into account our recommendations, you will easily find a suitable unit.
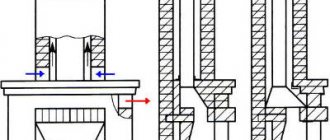
Calculation of the number of ventilation grilles
The number of ventilation grilles and the air speed in the duct are calculated:
1) We set the number of grilles and select their sizes from the catalog
2) Knowing their quantity and air flow, we calculate the amount of air for 1 grille
3) We calculate the speed of air exit from the air distributor using the formula V= q / S, where q is the amount of air per grille, and S is the area of the air distributor. It is imperative to become familiar with the standard outflow rate, and only after the calculated speed is less than the standard one can we assume that the number of gratings has been selected correctly.
Calculation of SVO
Q = Gc (t(hor) – t(oh))
Q (h.o.) – Heating power (amount of heat in kJ/h);
G – amount of air (kg/h);
c – specific heat capacity of air in the room (varies depending on temperature);
t (hot) – hot air temperature;
t (oh) – temperature of cooled air.
Dependence of the required power of the air heater on the volume of the heated building
Nuances t (oh) - if air is taken from a heated room at a height of more than three meters, then t (oh) is considered 3-4 degrees higher than in the working area of the room.
To increase the heating power, t(hot) should be as high as possible. But there are limitations:
If air from the heating system is supplied directly to the area where a person is located, it should not be higher than 25 degrees C;
at a distance of 2 m – 45 C;
more than 3.5 m. – 70 C.
If the installation of air heating can be done independently, then it is still better to entrust the calculations to specialists.
Air heaters and heat exchangers
Heating and cooling large areas using traditional radiators or fans is not always advisable. Therefore, industrial air heaters and air coolers, presented on the modern market in a fairly wide range, are especially popular when setting up air conditioning systems.
To correctly select the optimal equipment, you should understand the main types and design features of such devices.
Features of using gas air heat generators
The heat-resistant casing (usually steel) of such devices houses a fan, burner and combustion chamber.
The operation process of gas air heat generators is very simple: cold air enters the combustion chamber through a fan, where it is heated by gas and a burner. Afterwards, the already heated air enters the heat exchanger and is then distributed in the air duct system, and then enters the room in need of heating.
Modern models of gas air heat generators operate on a network of 380 and 220 volts.
Depending on the design features, such air heaters can be mobile or stationary (suspended, also called air heaters, and floor-standing - vertical or horizontal).
But stationary air heaters are in great demand because they are easy to use and highly efficient.
Air heaters with water heat exchanger
In this equipment, the source of thermal energy is superheated water (maximum - up to +180°C). Heat exchange is carried out by constant heating of the coolant on the tubular circuit of the aluminum fins, as well as washing the fins with a flow of supply air. Both centrifugal and axial fans can be used to move air together with water heaters.
Air heaters with a water heat exchanger (water heaters) are used, as a rule, for heating industrial premises: workshops, warehouses, workshops. However, provided that it is technically possible to connect to a coolant system (for example, central heating), they can also be used in private households - for example, for heating a garage and a number of utility rooms.
In addition, air heaters with a water heat exchanger can be used as part of specific technological systems: for example, complete with an axial fan for drying lumber.
In general, water air heaters as a coolant ensure the efficiency and reliability of engineering heating systems.
Types of air coolers
- Dry (superficial).
In such heat exchangers, heated air masses are cooled through contact with a heat exchanger through the pipes of which cold water or freon passes. This type of air cooler is the most common. It has only one drawback: to defrost ice on the heat exchanger, it is necessary to periodically use heat sources, for example, heating elements. - Wet (contact).
In these heat exchangers, direct heat exchange occurs between water cooled in the evaporator and air. By means of a fan, the air flow is driven through a nozzle cooled in water. The design of these heat exchangers also includes the use of nozzles that spray water. The disadvantages of contact air coolers include an increased risk of corrosion of the metal parts of the devices due to the enrichment of water with oxygen. - Combined (mixed) air coolers. In them, the water is cooled by irrigating the freon evaporator, and then cools the air mixture passing through it, created by a fan.
A large assortment of high-quality air heaters and air coolers from the famous brands Polar Bear (Sweden) and Arktos (Russia) is presented on the website https://rusholding.ru/. All products sold are provided with an official guarantee.
How to warm up a house with air?
Air is a very effective coolant, much more convenient than water. The simplest option for such heating is a conventional fan heater. This device, consisting of a fan and a heating coil, can warm up a small room in literally a matter of minutes. Of course, for a private home you will need more serious equipment.
A gas or solid fuel boiler can be used as a heat source. An electric heater is also suitable, but this option is not considered very profitable, since electricity costs increase significantly.
An interesting and environmentally friendly heating option is the use of solar panels or a solar collector. Such systems are placed on the roof. They either directly transfer thermal energy from the sun to a heat exchanger or convert it into inexpensive electrical energy. In the latter case, the fan can also be powered from the battery.
The air is heated in a heat exchanger and supplied to individual rooms through air ducts. These are rather bulky structures made of durable metal. The cross-section of the air ducts is significantly larger than the diameter of the water heating pipe.
Gas boilers and other types of heating equipment are also suitable for air heating. The efficiency of such systems reaches 90%; they are used not only in residential premises, but also in workshops and warehouses
But radiators for air heating are not needed. Warm air simply fills the rooms through special grilles. As you know, hot gas tends to rise. Cold air will be forced downwards.
From here, cold air flows move back to the heat exchanger, heat up, enter the rooms, etc.
This diagram clearly demonstrates a recirculation-type air heating device with partial intake of outside air, as well as an air conditioner, ionizer and ultraviolet purifier
Almost all air heating systems include the installation of a fan, which blows hot air and forces it to move through the heating system. The presence of such a device makes the system dependent on electrical energy.
You can also make a system in which hot air moves naturally, without any fan. However, the efficiency of such systems usually leaves much to be desired, since the rooms in this case warm up too slowly.
A convincing argument in favor of organizing an air heating system is to eliminate emergency leaks and flooding with resulting property damage. In addition, if the air ducts are damaged, the automation will stop the system.
Types of heat guns
Equipment for air heating is conventionally divided into two classes:
- Mobile;
- Stationary.
But units belonging to the first type do not always have compact dimensions. Some mobile models have quite impressive dimensions. Such devices are usually equipped with special trolleys necessary for moving the equipment.
They received the name mobile only because they are designed to operate from gas cylinders and do not require connection to the central highway. They can be installed anywhere and are designed for heating industrial premises. But cavitation heat generators of heating systems require an effective ventilation system at the site, because the heated air is removed along with the exhaust gases.
Stationary devices are designed for connection to a gas pipeline. They differ in the installation method and, depending on this, the criteria are:
- hanging;
- floor
The first ones have small dimensions, which means they take up little space. They are intended for heating private households. Suspended heat generators are easy to operate and install, quickly warm up the room, and have clear instructions for use.
Floor-standing units are more bulky devices. They are used to heat large areas. Many models of such equipment can be connected to an air duct system, which allows heat to be evenly distributed throughout all rooms.
What you need to know to make the right choice
Efficient gas-air heating can only be ensured by installing equipment that matches the parameters of the room. Important characteristics in the choice are:
- Heater type;
- Power.
In addition, for reliable operation of the device, it is necessary to ensure air flow into the room. A ventilation system is most often used for this. It is capable of not only supplying oxygen to the room, but also removing exhaust gases outside.
Review of popular models
The leader among heat guns, of course, remains the products of foreign companies and in particular US manufacturers. The device under the Master BLP 73 M brand is popular among owners of private homes and industrial facilities. It can be used not only as heating equipment, but also as a construction hair dryer.
Watch a video about the Master BLP 73 model:
An American-made heat gun consumes no more than 4 kg of liquefied gas per hour, generating up to 70 kW of energy. Its power is enough to heat a room of up to 700 m² with a capacity of about 2.3 thousand cubic meters of warm air per hour. The cost of such a device is no more than $650.
But there are also domestic models on the market that meet all regulatory requirements. One of them is the Patriot GS53 heat gun. It is capable of generating up to 50 kW of thermal power at a flow rate of up to 4.5 kg of gas per hour. This is enough to heat a room of no more than 500 m². The cost of the unit does not exceed $400.
Among the models that consume main gas, the heat generator AKOG-3-SP can be noted. This is a small device whose power is enough to heat a room with an area of 30 m², while consuming 0.3 m³ of natural gas.
The thermal convector of this brand is designed for wall mounting and can heat one functional area in a country house. The cost of this device is one of the lowest and is less than $250.
Conclusion
The use of such equipment in heating systems is considered one of the most effective and economical solutions. It is easy to use, safe and therefore can be used not only at production facilities, but also in residential premises
Pump disassembly
First of all, it is necessary to remove coupling 3 from the shaft of electric motor 2 (Fig. 10) and remove the pump 1 itself from plate 4. Then unscrew the bolts 34 (Fig. 11) and separate the right 4 and left 5 halves of the pump housing
The left half can be removed immediately; it will no longer be needed. After this, it is necessary to very carefully remove the impeller 1 from the shaft 23, unscrewing it by the blades and at the same time holding the coupling half located at the other end of the shaft 23 from turning. If you can’t unscrew it by hand, you can do it using a metal lever (crowbar). Place the lever between the blades of impeller 1 so that the edges of the lever protrude to the same length. You need to insert 2 metal rods into the coupling holes on the opposite side of the shaft and place the second lever between them, resting one of its edges on the ground.
Next, you need to carefully turn both levers counterclockwise.
There is no need to press too hard on the levers, as you can bend shaft 23. The unscrewed impeller 1 may also be needed if you want to make a more complex, but more efficient heat generator design. After this, you can unscrew the nuts 3 from the studs and disconnect the right half of the pump housing 4 from the bearing housing 2 (Fig. 11). The right half will also no longer be needed.
Let's move on to Figure 5. Here the cast-iron bearing housing is designated as position 1. The generator housing 2 is attached to it using studs 3, spring washers and nuts. Between them there is a gasket 6 made of paronite (fluoroplastic). Its thickness should be such that during assembly the emphasis falls on it, and not on the rubber lining of the rubberized surface of the housing 5. The shaft 4 is fitted with a steel ring 8, a rubber ring 9 and a pressure bushing 10. In place of the impeller there is a rotor 7. The length of the bushing 10 should be such that when the rotor is screwed onto the shaft, the sealing ring 9 is compressed and does not allow liquid to leak out during operation of the unit. The optimal length of the sleeve 10 is considered to be such that, after screwing the rotor, a gap of 0.5 mm remains between the end of the rotor 7 and the end of the sleeve 10. The size of 37 mm is indicated by an asterisk and indicates the length of the protrusion of shaft 4 beyond the body 1. The size of 22 mm indicates the length of the thread at the end of shaft 4.
Types of gas heat generators
Gas heaters for heating are divided into mobile and stationary. The latter, in turn, are divided into suspended and floor-mounted. At the same time, mobile units are less common because they use gas cylinders for their operation, which is not always convenient and possible to provide. That is why such devices are used only in extreme cases, for example, when the main heating in the room is turned off, and you urgently need to heat it when the temperature outside sharply drops. Also, such units are used as the main heating in regions with a short winter season.
The stationary type of heaters is used in various fields. Wall-mounted heat generators are hung on walls indoors and outdoors. Floor-standing devices, depending on the assembly features, can be horizontal or vertical. The former are more often used in low rooms, while the latter are suitable for installation in a private home or on the street. Floor-standing units are convenient to use for heating small rooms, installing them at the entrance and exit to the heated zone.
Construction of gas heat generators
A gas heat generator is a heater that heats the coolant (air) to the required temperature.
Its structure is as follows:
- The air fan is designed for uninterrupted supply of air masses and removal of exhaust air from the system. Exhaust air is exhausted upward.
- A gas burner burns fuel and heats the coolant.
- Complete combustion of the heat source occurs in the combustion chamber. If the fuel burns completely without any residue, then the volume of carbon dioxide that the system emits is small.
- The purpose of the heat exchanger is to ensure normal heat exchange between the room and the heat generator. In addition, the heat exchanger protects heating equipment from overheating.
- Air ducts are used to remove heated air into the room.
The operating principle of such heating equipment is as follows: a fan draws cold air into the device, it is heated during fuel combustion to the required temperature and discharged through air ducts into the room.
The operating process of a gas heater can be divided into the following stages:
- cold air from the street or room is drawn into the device by a fan and hits the heating element;
- since gas is constantly burned in the combustion chamber, thermal energy is released, which heats the air;
- after this, the fan supplies heated air to the heat exchanger;
- air ceilings are distributed through the air duct system through the use of air valves;
- Through the grilles, heated air is supplied to the room and gradually heats it up.
Calculation and selection of a gas generator
In order for the system to operate efficiently, the gas heater for air heating must be correctly selected
To do this, first of all you need to pay attention to the size of the heat exchanger. The dimensions of the heat holder should be 1/5 larger than the dimensions of the burner
To choose the right gas generator, you need to calculate its power. To do this, use the formula – Р=VхΔTхk/860, where:
- V in m3 indicates the heated area of the building;
- ΔT in °C is the difference in air temperature inside and outside the house;
- K is an indicator of the thermal insulation of a house (the number can be selected from a reference book);
- 860 - this number is a coefficient that allows you to convert kilocalories to kW.
The power of the device is selected in accordance with the obtained value. As a rule, the operating power of the equipment is indicated in its technical characteristics.
For uninterrupted operation of heating equipment for air heating, it is necessary to ensure a continuous supply of air to the device. For this purpose, the ventilation system of the structure must be properly equipped. If there are problems with ventilation, then it is better to use a hanging-type device that takes air from the street.
Popular models
The Conord gas floor-standing boiler is part of a line of budget units that are available to people with any income level.
It is not only cheap, but also quite economical to operate. And the fact that it was manufactured in the Russian Federation makes it possible to easily obtain all components in order to carry out scheduled maintenance. The cost of consumables will pleasantly surprise all clients. Multifunctional equipment is always in best demand. Therefore, gas heating double-circuit boilers under the Conord brand are most in demand on the market. They solve two problems at once: space heating and hot water supply. At the same time, the user can easily control both functions separately, since they are not interconnected. After the end of the heating season, the boiler can be turned off and only the water heater can be used, so as not to overpay for gas.
Features of industrial heating
- Firstly, most often we are talking about work on energy-intensive Objects of a fairly large area, and there is a requirement for heating systems (as well as for all other auxiliary) systems to achieve the maximum possible energy savings. It is this factor that is put at the forefront
- In addition, often in heated rooms there are non-standard conditions in terms of temperature, humidity, and dust. Therefore, the thermal equipment and materials used must be resistant to such adverse effects.
- A number of Facilities may use flammable and explosive substances, and, based on this, the installed system must meet strict explosion and fire safety requirements
- Another important difference between the systems under consideration is, as a rule, their large total power. It can reach hundreds of megawatts. Therefore, boilers used to heat homes are often not suitable for the scale considered. The use of cascades from domestic boilers is simply becoming economically infeasible
- In addition, heating of industrial buildings is often designed and installed in a single complex with climate control systems. This makes it possible to heat industrial premises with large areas and at the same time save resources and the space occupied by highways. First of all, this method is used when organizing air heating
- The next feature that industrial heating of a building has is its “unconventionality”. There are certain standard solutions on the basis of which heating of a country house is carried out. These solutions can be applied with minor nuances almost everywhere and always. Technical solutions for large-scale Objects are much more diverse. The art of engineering in this segment lies in selecting the optimal technical solution. Before the start of the design stage, the most important step will be the competent preparation of the Technical Specifications. And when heating installations for industrial facilities take place, the Technical Specifications drawn up by qualified designers and engineers will help optimize the installation process. Designers carry out various engineering calculations. Based on an individually selected engineering solution, the most effective method of heating the Object in question is determined
- Often, when it comes to production, technological equipment is located at the Facility - machines, conveyors, production lines. Also, perhaps, the people working on it. This needs to be taken into account
- As a rule, uniform distribution of heat is necessary unless the project involves the creation of zones with a special temperature regime. By the way, the presence of such zones is also a feature that must be taken into account when organizing heating of industrial buildings
- As already mentioned, the traditional method for heating housing (in particular, cottages) using a household boiler and radiators is, as a rule, ineffective under the conditions under consideration. For this reason, industrial heating systems are built according to different principles. Recently, these are most often autonomous systems of the scale of the Object, and sometimes of its individual parts. Autonomous heating is easier to control than centralized heating (through CHP) due to the ability to control and regulate the consumption of fuel resources
- There are also some peculiarities at the operational stage. In the residential sector, the level of service of the heating system is often not professional enough. If heating is installed in a building for industrial purposes, then, as a rule, you can be sure that technical service will be carried out by a qualified team (most often, this is the service of the chief power engineer or a staff department of the enterprise with similar functions). On the one hand, this somewhat eases the responsibility of the installation organization. Most likely, after the facility is put into operation, no one will deal with “little things.” On the other hand, the requirements for the composition and level of writing of executive documentation are increasing. Operations service employees, being professionals, know well what exactly it should include and how to compile it. All necessary licenses, certificates, permits, equipment passports, and work completion certificates must be provided. Only after this the system will be put into operation
Types of heat generators for air heating
A heat generator is an air heating unit that produces thermal energy by burning one of the types of fuel. Power, efficiency, installation method, operating features are largely determined by the type of fuel. For heating residential premises and social facilities, the following types of units are mainly used:
- Pyrolysis boilers. They operate on solid fuel of plant origin (wood, waste from the wood processing industry, pellets, briquettes, peat).
- Gas boilers. Natural gas is burned.
On a note! Before installing an air heating and air conditioning system that requires a long service life, it is necessary to correctly calculate fuel resources. Switching to another type of fuel requires an almost complete replacement of the system. To heat the premises, pyrolysis or gas boilers, as well as diesel and universal heat generators can be used.
For air heating of large production areas the following types of generators can also be used:
- Diesel. They run on diesel fuel. They are refueled once a day (this is an average; there are models that may not be refueled for 2-3 days).
- Universal heat generators. They also use diesel as fuel, as well as waste oil and vegetable fats that need to be recycled.
These types of fuel are cheap, which significantly reduces the economic costs of enterprises for heating production premises.
Solid fuel boilers
Solid fuel and pellet boilers are one of the most affordable ways to heat a private home without gas. They are cheaper than a heat pump and are able to completely provide the building with heat, regardless of the time of day and street temperature.
But when choosing and installing solid fuel boilers, you need to consider:
- You need to constantly monitor the combustion and add firewood 1-2 times a day. Of course, this is not so difficult, but in comparison with gas boilers it causes inconvenience. In pellet boilers this is easier, since they provide automatic supply of pellets into the firebox from the hopper.
- Wood processing is not developed in all regions and good firewood may have to be transported from afar. So make sure you have access to at least 2-3 firewood sellers.
- You need to buy firewood one year before the start of the heating season. A year is the required period for the firewood to dry out and gain energy value. Initial low humidity only for fuel briquettes.
- You become dependent on firewood instead of gas.
- At certain volumes of consumption, heating with wood is not cheaper than gas.
- Need storage space. If firewood is stored incorrectly, it will get wet and lose its energy potential. See the article on how to store firewood.
- From time to time you will have to clean the chimney and the inside of the boiler from soot.
About company
If you need to purchase first-class gas air heaters, but you have no idea where you can order them in real time, then we are ready to help you. The main direction of our activity for more than 18 years has been the sale, installation and maintenance of high-quality gas heating equipment that meets all modern standards. On this page you will find a detailed description of gas heat guns. This will help you make the right choice and purchase exactly the model that best suits your technical conditions.
Types of heat generators for air heating systems
A heat generator is a unit that transmits coolant heated to certain temperatures. The carrier heats up during the combustion of various types of energy carriers. The heat generator is an alternative to conventional heating devices for home and industrial use.
Devices differ according to the type of energy carrier:
- Universal. These are modules that run on diesel fuel, waste oil, animal or vegetable fats. The peculiarity of use is the availability of fuel in sufficient quantities, so most often the stoves are used in industrial settings. The power of the devices is slightly less than that of other devices; also, during the combustion of fuel, a lot of combustion products and slags are released - you will have to regularly clean the ash pan. To maintain continuity of operation, two combustion chambers are installed in universal units - while one is undergoing the cleaning process, the other is in operation.
- Solid fuel. The generator combines the functions of a conventional furnace and a diesel or gas unit. The device is complemented by a combustion chamber with a door and grate. Fuel - firewood, pellets, peat, coal. Efficiency up to 85%. The large size of the devices and the need to regularly clean out waste are a minus.
- A gas heat generator runs on liquefied gas, so it is considered the most popular type of equipment. Natural gas supplied through the pipeline is inexpensive, and there is no need to store fuel or allocate space for storage. A small amount of harmful emissions during combustion, high efficiency (up to 91%), and a variety of power models are advantages.
- Diesel. Kerosene or diesel fuel is used as an energy carrier. Devices differ according to the type of nozzle - drip or spray feed. With an atomizing supply, the fuel is distributed more evenly throughout the combustion chamber and the combustion process occurs faster.
- Vortex. These heat generators operate on antifreeze or water, converting electrical energy into heat.
Catalog/Model range:
All models of recuperative gas heat generators Teplorod are structurally designed according to the “indirect heating” scheme, i.e. with the removal of combustion products and can operate on both natural and liquefied gas. This design feature allows them to be used for heating any premises, including those where people or animals are constantly located, without any restrictions. Thanks to high quality manufacturing, unpretentiousness in operation, as well as good maintainability and simple maintenance, industrial air heaters have gained well-deserved popularity in the Russian market. Low operating costs, a closed combustion chamber, high air pressure and minimal energy consumption, combined with the affordable price of the equipment, make it possible to use gas air heaters in the most complex heating systems, including heating systems with an extensive air duct system. Additional financial benefits can be felt if you take into account the comparative cost of gas heaters and traditional water heating systems (taking into account the costs of installing a boiler room, laying pipes and installing heating devices). All models of gas heaters have a wheelbase, which makes them easy to load and unload, and also allows the heaters to be delivered to the installation site at the operation site without the use of forklifts or other special equipment. Mobility and the absence of installation and commissioning operations allow them to be used, including at the construction stage and the most important areas of production, and can also be easily moved from one facility to another.
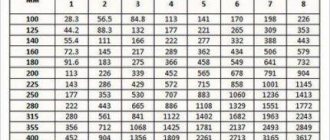
Technical characteristics of gas air heaters:
| Model | Thermal power, kW | Air flow, m3/h | Natural gas consumption, m3/h | Dimensions, LxWxH, mm | Weight, kg | Electrical power consumption, kW | Price, rub (including VAT) | Availability in stock / Delivery time |
| NP-60A | 58-66 | 3000-3500 | 5,5 | 1230x630x1030 | 110 | 0.7 | 309 984,00 | In stock |
| NP-80A | 75 | 3000-3500 | 7,5 | 1230x630x1030 | 110 | 0.7 | 332 340,00 | In stock |
| NP-100A | 100 | 8000-8500 | 10,0 | 1800x800x1350 | 280 | 1.5 | 350 496,00 | In stock |
| NP-120A | 130 | 8000-8500 | 13,0 | 1800x800x1350 | 290 | 1.5 | 375 600,00 | In stock |
| NP-150A | 160 | 8500-9500 | 16.1 | 1800x800x1350 | 310 | 2.5 | 413 880,00 | In stock |
| NP-180A | 174 | 8500-9500 | 16.9 | 1800x800x1350 | 310 | 2.5 | 455 268,00 | In stock |
| NPM-200R | 205 | 11000-14000 | 20.6 | 2600x950x1650 | 590 | 4.5 | 545 196,00 | 15-20 work. days |
| NPM-250R | 250 | 11000-14000 | 24.6 | 2600x950x1650 | 590 | 4.6 | 569 898,00 | 15-20 work. days |
| NPM-280R | 280 | 11000-14000 | 28.2 | 2600x950x1650 | 590 | 4.7 | 599 976,00 | 15-20 work. days |
NOTE:
- The delivery time for heat generators NPM-200R/250R/280R can be increased to 35 working days depending on the workload of production and the date of ordering.
- * — The indicated prices are valid from December 10, 2022. Not a public offer
| Do you want to get a great special offer on gas heaters? Just request a call back or send us your contact details and we will contact you to discuss all the details → |
Calculation and selection of equipment for heating a house with a total area of 100 sq.m.
In order to choose the right heater, you need to calculate the smallest possible power required to completely warm up the heated building.
Then gas-air equipment is selected by quantity and power.
The basic formula for calculating the heat capacity of a room is:
Р=Vх?Tхk/860
Where:
- V, m3 – total volume of the heated building (length, width and height).
- ?T, °C - the difference (in degrees) between the temperature inside the object and the temperature outside.
- k is the room insulation coefficient, which has different values and is taken from the reference book.
- 860 is a special coefficient for quickly converting power from kilocalories to kilowatts (1 kilowatt = 860 kilocalories per hour).
Example: let's calculate how much power is needed to warm up a building (house) with an area of 100 square meters. m, with a ceiling height of about 3 m, up to an average temperature of 20 °C, with a winter ambient temperature of -20 °C.
Let's take a building of ordinary construction (built from one layer of simple brick).
For such a building the value of k=2.3.
Let's calculate the power:
P = 100x3x40x2.3 / 860 = 32.09 kW.
Now, based on the calculated minimum possible power, we select the required number and type of heat generators.
There are instructions for the equipment for this.
For uninterrupted operation of heating equipment, a constant supply of fresh air is required.
In this case, ventilation performs several functions:
- pumps oxygen (for combustion)
- Helps release excess carbon dioxide
- removes by-products (hazardous to life) of combustion, such as carbon monoxide (CO)
To achieve this, it is recommended that the percentage of oxygen in the ventilated air be more than 17%.
For safety and sanitary reasons, 1 kilowatt of heater power requires 30 m3 of forced air.
To ensure air flow, you can punch a hole of 0.003 m2 per 1 kW heater with your own hands. If there is no ventilation system, then the mandatory area of open vents or windows must be at least 1 m2 for every 10 kW of power.
Insulation coefficient value:
- 3.0 – 4.0 – room made of wood or profiled sheets
- 2.0 – 2.9 – conventional design – one layer of brick
- 1.0 -1.9 – ordinary houses, double brick layer – medium insulation
- 0.6 – 09 – perfectly insulated buildings – double brick
Using a heat generator in a small workshop
Heat exchanger size
And, perhaps, the first thing that should be based on when choosing equipment for a private home is the size of the heat holder; it should be one fifth larger than the burner.
Security requirements
Also, there are special safety requirements, the meaning of which is that 0.003 m2 of ventilation opening must be allocated per 1 kW. If there is no such possibility of organization in the room, then you will have to ventilate the space with your own hands, opening windows and vents for ventilation. It should be taken into account that in this case the area affected by ventilation increases and for 10 kW you already need a little more than 10 meters square.
Examples of coefficients for calculating heating power and thermal insulation:
- 2-2.9 – ordinary brick construction, if one layer of brick is visible;
- 3-4 – houses made of wooden panels or profiled sheets;
- 1-1.9 – double insulated brick layer;
- 0.6-0.9 – houses of modern construction with new walls and windows.
Voltage waveforms
Anyone can assemble a circuit with a screwdriver. And for those who want to see the voltage and understand what real processes are taking place, they cannot do without an oscilloscope. I am publishing oscillograms at the 2T1 output of the soft starter.
The engine is turned off. Pure sine.
Isn't it a logical inconsistency - the engine is turned off, but there is voltage on it?! This is a feature of some soft starters. Unpleasant and dangerous. Yes, there is 220V voltage on the engine, even when it is stopped.
The fact is that control occurs only in two phases, and the third (L3 - T3) is connected directly to the motor. And since there is no current, all outputs of the device are affected by phase L3 voltage, which passes through the motor windings. The same nonsense happens in three-phase solid-state relays, here is my article.
Launch. Thyristors cut the phase mercilessly.
Since the load is inductive, the sine wave is not only cut into pieces, but also greatly distorted.
There is interference, and this must be taken into account - malfunctions in the operation of controllers and other low-current devices are possible. To reduce this influence, it is necessary to space and shield the circuits, install chokes at the input, etc.
The engine is almost on. About 90% of sine energy.
The photo was taken a couple of seconds before the internal contactor (bypass) turned on, which supplied full voltage to the motor.
Selecting a gas heat generator
Partly because this opportunity is quite new, partly because choosing the most optimal option, when buying a gas heater, questions arise that cannot always be answered correctly. Therefore, buying a gas heat generator can lead to disappointment due to incorrect operation of the system.
Heat exchanger size
And, perhaps, the first thing that should be based on when choosing equipment for a private home is the size of the heat holder; it should be one fifth larger than the burner.
Power calculation
For the most competent selection of a heater, you need to calculate exactly what power of the heat generator is permissible for minimal heating of rooms, for this you need to use an example formula: P = VхΔ Tхk/860, where V (m3) is the final area of the heated space, Δ T (°C ) is the difference between indoor and outdoor temperatures, k is an indicator focused on thermal insulation in the selected building, and 860 is keff, which converts kilocalories into kilowatts. Regarding mark (k), if there are difficulties with this information about the premises, you can use a specialized reference book.
In order to more clearly demonstrate exactly how the power of a heat generator device is calculated, consider an example:
- Given: area – 100 m2, height – 3m, temperature inside +20, outside temperature -20, k – 2.3 (building made of brick in one layer).
- The calculation is carried out according to the example: Р=VхΔ Tхk/860
- Result: P = 100x3x40x2.3/860 = 32.09 kW
It is with these indicators in mind that you need to select a gas heat generator for air heating at home. The power parameters of the mechanism and whether it matches the required ones should be looked at in the product characteristics.
An equally important point: for the smooth operation of the mechanism, you need to provide it with a constant flow of fresh street air. For this purpose, a room ventilation system is always used, so that as soon as cold air can be taken from there, it can support combustion. If there are problems with ventilation in the house itself, then it is better to purchase a suspended heat generator with an outlet to the street.
Air heating ventilation system
In addition, if a gas heater in an air heating system has a connection to street ventilation, this will allow the warm air to be as breathable as possible, excess hot air will not be pumped into the room, and therefore the possibility of the absence of dry air and additional mechanisms for humidifying the space will be preserved .
Security requirements
Also, there are special safety requirements, the meaning of which is that 0.003 m2 of ventilation opening must be allocated per 1 kW. If there is no such possibility of organization in the room, then you will have to ventilate the space with your own hands, opening windows and vents for ventilation. It should be taken into account that in this case the area affected by ventilation increases and for 10 kW you already need a little more than 10 meters square.
Examples of coefficients for calculating heating power and thermal insulation:
- 2-2.9 – ordinary brick construction, if one layer of brick is visible;
- 3-4 – houses made of wooden panels or profiled sheets;
- 1-1.9 – double insulated brick layer;
- 0.6-0.9 – houses of modern construction with new walls and windows.