Advantages of bimetallic heating radiators
The popularity of this type of battery can be explained very simply. Cast iron radiators are quite reliable, but they do not look very aesthetically pleasing. In addition, they are difficult to install. Aluminum batteries look modern and attractive. However, this metal does not tolerate contact with oxygen in the coolant very well. Therefore, aluminum radiators quickly fail and begin to leak. Steel batteries last longer. However, at the same time they do not look so aesthetically pleasing.
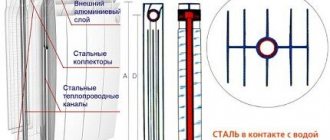
Bimetallic models combine the advantages of aluminum and steel radiators. Such batteries fit perfectly into a modern interior. The sections in them are made of aluminum. At the same time, they last a long time, since the pipes through which the coolant flows through them are made of steel.
What to consider when choosing battery sizes
Heating radiators are usually installed under windows. This arrangement allows the coolant energy to be spent as rationally as possible. Taking this into account, the sizes of heating radiators are usually chosen.
The battery is mounted in such a way that the distance from its upper edge to the ledge of the window sill is at least 10 cm. In this case, the radiator should be located at a height of approximately 8-12 cm above the floor. If these requirements are violated, effective air exchange does not occur in the area of the battery sections. Consequently, the potential of the radiator is not fully used. So, when choosing a battery, the first thing you should look at is the height. It should be approximately 20 cm less than the distance from the window sill protrusion to the floor.
More sections - warmer?
It will definitely be warmer. But not just in arithmetic sequence. That is, there were 4 sections added 8 and the heat flow into the room should be three times greater in theory. But it won’t, because your standard batteries aren’t heating well anyway. Therefore, when adding 4 * 3 here, this is a theory, but in practice, when supplying hot water from the top to heating devices in nine-story buildings, a single-pipe system is used. In this case, a three-way valve is installed on each floor. There is no doubt that the idea behind the capabilities of this valve is good. But its quality and practical implementation are poor. It works poorly for various reasons. Therefore, you need to look at what position this valve is in. My friend immediately let the entire flow through his radiators, and when he was doing repairs, he completely abandoned this pleasure and removed this three-way valve. There are also many other accompanying moments when our expectations remain just that. You need to do a good inspection of your batteries first, and then think about additionally building up sections.
Dimensions of bimetallic heating radiators: height
When manufacturing heating batteries, like any other equipment, certain standards are, of course, observed. Bimetallic radiators (depending on modification) according to the passport can have a height of 200, 350 and 500 mm. All of these options are quite popular, and you can purchase them if necessary without any problems. However, the numbers 200, 350 and 500 mm are not the actual height of the radiator, but only indicate the distance between the centers of the inlet and outlet pipes. But the battery sections themselves are usually a little longer. You can find out which height dimensions of heating radiators will be the most convenient if you add 8 cm to the center distance. Thus, a battery marked 350 will occupy approximately 430 mm under the window sill, a 500 mm model will occupy 580 mm, and a 200 – 280 mm model.
More sections - warmer?
Sergey N wrote: people on the lower floors are simply freezing
So it is, in fact, it all started with Rikota’s beloved Socialist economy. Where all people live in the same 5-story houses, they receive the same salary, wear the same clothes and receive heating from a single source. Fortunately, such a problem should not exist, the pipes should be of normal diameter and the flow should be stronger. In reality, builders lay the section lower in order to save money and the flows do not pass in the required volume. That's why the bottom ones freeze! There is nothing better than individual heating!
Sergey, what are you actually talking about?
Are you confusing me with anyone? Either point out exactly where I declared my love for the socialist economy, or I will be forced to call you a liar in front of everyone. In reality, builders set the diameters that are indicated in the project, otherwise it is impossible to deliver the completed construction project.
Radiators width
Based on this indicator, the battery should be selected as carefully as possible. The width of the radiator depends on the number of sections, which may vary. The required number of such elements for one battery is calculated using a special formula. It is believed that heating a 10 m2 room requires 1 kW of radiator power. The formula for calculating the required number of sections thus looks like this: N = S x 100/Q. In place of S you need to substitute the total area of the room in which the radiator will be installed. The Q value is the power of one section. The last indicator is easy to determine. The manufacturer usually indicates the power of one section in the technical data sheet. This indicator may vary, but most often its value is close to 180 W (for 500 mm models). 8 cm is the width that in most cases one section of a heating radiator has. The size of the battery thus directly affects its power.
How to calculate the number of radiator sections
There is a simplified way to do this quickly. To do this, we will need the standard power required to heat one square meter of room. Let's give three options.
- If the ceilings in the room are of normal height (from 2.5 to 2.7 meters), there is one wall facing outwards, and one window. Standard power is 100 watts.
- If the ceilings are the same, there are two walls outwards, and one window. Standard power is 120 watts.
- If the ceilings are the same height, there are two walls outward, and there are two windows. Standard power is 130 watts.
Now let’s multiply two values – the standard power for our option and the area of the room. If you have higher ceilings or a larger window (for example, if it has a bay window), we will additionally multiply by a correction factor of 1.1. As a result, we get the radiator power (total).
The radiator's passport indicates the thermal power for one section. The resulting total power must be divided by it. We round fractional numbers upward.
Battery thickness
The dimensions of bimetallic heating radiators, therefore, may be different. Their depth is usually 80 or 100 mm. Sometimes 90 mm options are also available for sale. In this case, the choice depends solely on the personal preferences of the home owners themselves. If the niche for the battery is deep, you can purchase a thicker radiator. If the wall is in the same plane as the edge of the window sill, you should, of course, buy an 80 mm radiator. In this case, if necessary, it will be easier to disguise it.
Dimensions of cast iron radiators
Standard Soviet batteries of this type had a height of 580 mm, a rib width of 94 mm and a thickness of 140 mm. Many owners of houses and apartments still consider such models to be the most reliable. Therefore, cast iron radiators are still in demand today. Manufacturers, of course, noticed this and began to supply the market with retro-style cast iron radiators, which have a very attractive design. If you wish, you can, of course, buy such batteries for your home. Their sizes may vary. There are low, standard and high models of this type on the market. The approximate sizes of cast iron heating radiators of different types can be seen in the table below.
When arranging a heating structure in their own apartment or house, their owners need to decide on the purchase of batteries, taking into account the size of the heating radiators.
In this case, the following basic parameters should be taken into account:
- dimensions of heating radiators;
- degree of heat transfer of one section;
- the maximum operating pressure for which these devices are designed.
Among the products on the modern market, the spread of the main parameters of batteries is quite large, since they are presented in a wide range.
More sections - warmer?
Igor_01 wrote: Sergey is a liar and what follows is a heavy slap in the face! )) Rikota, you just constantly cite different norms and rules, which in principle is not bad. But times have changed! Nowadays it is unlikely that installations such as radiators will be controlled. I haven't encountered anything like this yet
So more sections are warmer???
or colder??? or are we getting personal??? In general, it’s not proportional, but it will be warmer if we increase the number of sections. But in relation to Sergei, Rikota is simply mocking young people. But Mayakovsky also wrote that communism is the youth of the world and should be built by the young. Here Rikota is simply clarifying personal relationships, which there is no trace of... but she loves to do this business!!! Yes, God be with her. But there is no slap in the face here and there cannot be... Well, the designer Rikota is an experienced one. And she confuses the society of hardworking free masons with blinkered dogmatists who do not think creatively, but carry out all their projects according to instructions, that is, they are compiling something that is no longer new, but known to all of them in the form of norms, GOSTs and nothing more. And as far as I know, heat transfer follows a parabola. That is, 50C - let's say 100%, 60C - let's say 130%, 70C - let's say 180% or something like that.
I also support the thesis that doubling the radiator sections will not double the heat transfer. It will be significantly less. Instead of, for example, a 14-section radiator, it is much better to install two parallel 7-section radiators. This connection is not new and is practiced all the time.
The question of a parabolic change in heat transfer is generally open. A particularly specific solution to this is of interest from a practical point of view of the general formulation of the question: More sections - warmer. I would like to somehow justify a specific reduction in heat removal as the radiator sections are increased.
Rating: 328
When designing a heating system, accurate calculations are important in order to get the maximum result while spending a small amount of resources. Many home owners are interested in how to choose sizes. The decisive factor here is the heated area, although aesthetic aspects must also be taken into account.
Radiators are often installed in a special niche or under windows. Then you need to choose the size of the radiator in accordance with the allocated space. The use of decorative grilles or panels reduces the efficiency of heaters. If you can’t get rid of them, you will have to increase the radiator power by 15-20%.
Now manufacturers present radiator sections of various designs, which will help you choose an option that fits well into the interior.
Radiators can be solid or sectional. The latter are more familiar to the common man and give greater freedom of choice. You can install one long sectional or several short radiators.
To more accurately calculate sections in a radiator to select for heating, you need to take into account not only the area, but also the volume of the room in cubic meters.
The size of the radiator surface from which heat enters the room is important, as is the heating temperature of the radiator itself. There are special tables that help you get an answer based on the given parameters.
In a simpler way, you can get the following data. Typically, one radiator section is installed per 2 square meters. m of room area. Using simple calculations you can find out how to choose the size of heating radiators. True, such calculations are very approximate. In order not to suffer from inaccuracies, it is worth adding 10% to the resulting figure.
Section counting example
In addition to the parameters listed above, you need to take into account the thermal insulation characteristics of the room. They are divided into three groups: cold (housing on the top floors with thin side walls), standard (average size walls, apartments on the middle floors of the house), insulated (presence of high-quality double-glazed windows and insulated external walls).
To understand how to select the size of radiators for heating when installing a heater under a window opening, you can use the following rules. , it is hung on special fasteners under the window sill at a height of 6 cm from the floor. There should be at least 10 cm from the top of the sections to the window sill.
In order to harmoniously fit the radiator into the interior of the room, its size should be about 60-70% of the width of the window. Narrower sections of the radiator will not be able to compensate for the cold air coming from the window opening.
Variety of sizes
They differ in their power, leaving a wide choice for the home owner. The most effective are 200 mm sections. In large houses, as well as non-residential premises, for example, sports complexes, radiators with a height of more than 250 mm are installed. They are capable of handling a large volume of space and are well suited in houses where there are no special niches for installing radiators.
Tall batteries come in two types: with side (type R) and bottom (type RD) connections. Such large radiators have high heat transfer and great convection. Their sizes can reach 112 cm in height, 140 in width and up to 9 cm in depth.
In ordinary small and apartment buildings, low batteries are more often used. Their height is 30-45 cm, which is convenient for installation under a window. Low radiators have a number of advantages. They heat the air more evenly and dry it out less.
To ensure a comfortable temperature in the room, more sections will be required, which means the thermal curtain will be wider and cover a larger area. The larger and more powerful the battery, the more the air around it heats up, making it unbearable to be near the heat source. Therefore, for large areas it is more rational to divide the radiators into groups for uniform heating of the air. For the same reason, you should not overuse tall radiators in your living space.
Section calculation scheme
Heating radiator sizes
The standard height of the most popular models of heating devices with the center distance along the connections is 500 millimeters. These are the batteries that in most cases could be seen about two decades ago in city apartments.
Cast iron radiators
. A typical representative of these devices is model MS-140-500-0.9.
The specifications for it include the following overall dimensions of cast iron heating radiators:
- length of one section – 93 millimeters;
- depth – 140 millimeters;
- height – 588 millimeters.
Calculating the dimensions of a radiator from several sections is not difficult. When the battery consists of 7-10 sections, add 1 centimeter, taking into account the thickness of the paronite gaskets. If the heating battery is to be installed in a niche, it is necessary to take into account the length of the flushing tap, since cast iron radiators with side connections always require flushing. One section provides a heat flow of 160 watts at a temperature difference between the hot coolant and the air in the room of 70 degrees. The maximum working pressure is 9 atmospheres.
Aluminum radiators
. For aluminum heating devices on the market today, with the same center-to-center spacing of the connections, there is a significant variation in parameters (for more details: “Dimensions of aluminum heating radiators, section volume, preliminary calculations”).
Thermal power of 1 section
As a rule, manufacturers indicate average heat transfer rates in the technical characteristics of heaters. So for heaters made of aluminum it is 1.9-2.0 m2. To calculate how many sections are required, you need to divide the area of the room by this coefficient.
For example, for the same room with an area of 16 m2, 8 sections will be required, since 16/2 = 8.
These calculations are approximate and cannot be used without taking into account heat loss and the actual conditions for placing the battery, since you can get a cold room after installing the structure.
To get the most accurate indicators, you will have to calculate the amount of heat that is needed to heat a specific living space. To do this, you will have to take into account many correction factors. This approach is especially important when calculating aluminum heating radiators for a private home is required.
The formula needed for this is as follows:
KT = 100W/m2 x S x K1 x K2 x K3 x K4 x K5 x K6 x K7
- KT is the amount of heat that a given room requires.
- S – area.
- K1 – designation of the coefficient for a glazed window. For standard double glazing it is 1.27, for double glazing it is 1.0, and for triple glazing it is 0.85.
- K2 is the coefficient of the wall insulation level. For a non-insulated panel it = 1.27, for a brick wall with one layer of masonry = 1.0, and for two bricks = 0.85.
- K3 - this is the ratio of the area occupied by the window and the floor.When in between:
- 50% - coefficient is 1.2;
- 40% — 1.1;
- 30% — 1.0;
- 20% — 0.9;
- 10% — 0.8.
- K4 is a coefficient that takes into account the air temperature according to SNiP on the coldest days of the year:
- +35 = 1.5;
- +25 = 1.2;
- +20 = 1.1;
- +15 = 0.9;
- +10 = 0.7.
- K5 indicates adjustment if there are external walls.For example:
- when she is alone, the indicator is 1.1;
- two external walls – 1.2;
- 3 walls – 1.3;
- all four walls – 1.4.
- K6 takes into account the presence of a room above the room for which calculations are made.In the presence of:
- unheated attic - coefficient 1.0;
- heated attic – 0.9;
- living room – 0.8.
- K7 is a coefficient that indicates the height of the ceiling in the room:
- 2.5 m = 1.0;
- 3.0 m = 1.05;
- 3.5 m = 1.1;
- 4.0 m = 1.15;
- 4.5 m = 1.2.
If you apply this formula, you can foresee and take into account almost all the nuances that may affect the heating of the living space. Having made a calculation using it, you can be sure that the result obtained indicates the optimal number of aluminum radiator sections for a particular room.
Whatever principle of calculation is undertaken, it is important to do it as a whole, since correctly selected batteries allow you not only to enjoy warmth, but also significantly save on energy costs. The latter is especially important in the context of constantly rising tariffs.
Low batteries
Radiators with a small center distance have the following advantages:
- they can be placed under a low window sill;
- they have maximum heat transfer per unit area.
Cast iron radiators
.
The dimensions of the MS-140M-300-0.9 heating radiator sections are:
- length 93 millimeters;
- depth – 140 millimeters;
- height – 388 millimeters.
Due to their smaller dimensions, the heat transfer of cast iron heating radiators is reduced - it is equal to 106 watts from one section at an operating pressure of 9 kgf/cm². Among foreign analogues, there are cast iron products with an interaxal distance along the connections equal to 200 and 350 millimeters; the power of a section of a cast iron radiator of this type is much higher.
Aluminum radiators
. For low batteries made of aluminum, both domestic and imported, the spread of the center distances is quite large. You can find radiator sizes of 150, 300 and even 450 millimeters. Since the possible section length starts from 40 millimeters, the device looks compact and unusual. Low aluminum heating radiators have height dimensions starting from 200 millimeters. The depth of many models compensates for the lack of the other two parameters and is 180 millimeters.
As for thermal power, it varies from a minimum of 50 watts per section to a maximum of 160 watts. The determining factor is the fin area of one section. At the same time, the change in dimensions does not significantly affect the operating pressure - low aluminum devices are designed for 16 atmospheres, and when testing - 24 atmospheres.
Bimetallic radiators
. All the sizes of heating radiators that they have are also typical for aluminum heating devices. Thermal power is within the same limits. On sale you can find aluminum low radiators with heat output of 80 and 140 watts per section. The working pressure is 25-35 atmospheres.
Bimetallic low radiators, such as in the photo, have two nuances:
- among heating devices there are batteries not with solid steel cores, but with steel tubes placed between aluminum collectors. Their operating pressure, indicated by manufacturers, is usually 12 or 16 atmospheres;
- they often do not have vertically located channels and, in the case of a lateral connection, can be heated by the collectors due to the thermal conductivity of aluminum. The circulation of the coolant is ensured by the last section, since it is flow-through.
Advantages and disadvantages
By purchasing an installation made of bimetal, your heating system will be provided with many positive aspects:
- First of all, it has a long service life. Thanks to the high quality of the design, which combines two good materials, such radiators can operate effectively for 30-50 years.
- Durability and reliability. These qualities are ensured thanks to the steel core, which is able to withstand high operating pressure and hydraulic shocks.
- Bimetallic heating radiators are suitable for any heating system, even with low-quality coolant.
- High heat transfer is another important positive quality. Due to the fact that the outer casing is made of aluminum, heat is distributed throughout the room very quickly. Standard models, in which the distance between the axes is 500 mm, have a heat transfer of up to 190 W, which is significantly more than in radiators made of only one metal.
- Thanks to the built-in thermostat, you can control and regulate the heating temperature.
- Externally, bimetal batteries are very attractive. Various color and design solutions allow everyone to choose a radiator to suit their taste.
As you can see, bimetallic radiators have a large number of advantages, which determine wide demand for such products. However, there are also some disadvantages that cannot be ignored when choosing:
- Different coefficients of expansion of steel and aluminum. In this regard, after long-term operation, noise and squeaks may occur in the heating circuit, and the strength of the structure will be lower.
- During the installation of radiators in a central heating system, heat-conducting pipes can quickly become clogged. This is due to the fact that they have a small diameter. Given this feature, it is better to be careful and install a coarse filter.
- High price of bimetallic radiators.
You can find out what material radiators are made from in this article.