The efficiency of the batteries determines the speed and quality of heating. The modern equipment market offers all kinds of solutions. One of the worthy options are bimetallic heating radiators that meet the main requirements of the heating network: strength, resistance to water hammer, high heat transfer and durability.
We will tell you how to choose the right heating device, in the manufacture of which two metals were used. Our article describes in detail the varieties popular among consumers. Their technical characteristics are given and leading manufacturers are listed.
Structure of bimetallic radiators
Externally, bimetallic models resemble conventional aluminum radiators. The difference lies in the internal content. The design of composite products consists of two basic elements: an internal steel pipe and an external figure-ribbed body made of aluminum panels. Some radiators use copper instead of steel.
The coolant circulates through an internal steel or copper pipeline. Due to corrosion inertness, radiators do not rust and do not react with chemically active coolant. The external elements and the internal manifold are connected by spot welding or injection molding.
Based on their physical and operational properties, the batteries are suitable for installation in apartment buildings of any number of floors and for arranging a local heating system for cottage buildings.
The bimetallic structure determines the characteristics of the device. The steel core explains resistance to aggressive environments and endurance to pressure drops, the aluminum “shell” increases heat transfer and makes the radiator lighter
Aluminum or bimetal - learning to distinguish between radiators
Manufacturers offer various models of hybrid batteries. They come in different designs, differ in power, and in the technology of connecting to the system. Radiators are available with top and bottom connections. After installing these heating elements, it is almost impossible to visually determine the difference between bimetallic devices and aluminum batteries, especially for a non-professional. This must be done before connecting them. The main sign that you have a bimetallic radiator is the presence of an internal steel core encased in an aluminum body. This structure ensures excellent performance properties of the device. The weight can also give away a bimetallic battery: a radiator weighted with a steel core cannot be as light as an aluminum one.
Sectional bimetallic radiator Royal Thermo BiLiner 500 black 6 sections
Features of different heating convectors
You should understand the differences between different types of batteries made of two metals. Composite products are usually classified according to the following criteria: composition of the internal rod, external design and type of metal used.
Bimetallic and semi-bimetallic radiators
Users often confuse true bimetallic batteries with “half-breeds” - semi-bimetallic counterparts.
"Pure" bimetal
Aluminum is used to make the outer casing of the device. The convector core is 100% stainless steel or copper. During the production process, pipes placed in special molds are filled under pressure with aluminum - a sealed structure is formed.
The outer shell is not in contact with the coolant and acts as a heat exchanger. The main feature of bimetallic radiators is their high strength and guarantee against leaks
A high-grade bimetal withstands the pressure of centralized and autonomous heating systems.
Semi-bimetallic batteries
The internal “skeleton” of the radiator is made of two metals: vertical guides – stainless steel, horizontal pipeline – aluminum. The reverse combination is also possible.
Such an alliance of metals is not able to ensure adequate reliability of central heating communications. The coolant may contain alkali, which, when interacting with aluminum, provokes corrosion. Over time, destructive processes “transition” to the steel components of the radiator.
In addition, the integrity of the product may be at risk due to thermal expansion of metals - leaks are possible at boundary temperatures.
Externally, semi-bimetallic radiators do not differ from their full-fledged bimetallic counterparts. "Half-breed" gives lighter weight and lower cost
It is better to avoid purchasing low-quality composites, especially when it comes to centralized heating.
Sectional and monolithic models
Among the variety of bimetallic heating batteries, there are two types of designs:
- sectional:
- monolithic.
Models assembled from sections are attractive due to their variability of characteristics. They provide the opportunity to purchase a device with the exact heat transfer values required for heating rooms. Monolithic ones do not have such advantages.
Typesetting systems
Collapsible radiators, the panels of which are connected using nipples. Horizontal sections of pipes of individual sections have multi-directional threads for joining the fastening nipples and the sealing strip.
Stacked models are more popular due to their practicality - it is possible to regulate the thermal power by adding or subtracting the required number of sections. An additional advantage is maintainability.
Disadvantages of sectional radiators:
- joints are weak points of collectors where leaks are likely;
- limited operating pressure – up to 20-30 bar.
Significant disadvantages also include partial ingress of coolant onto the aluminum “jacket” during leakage.
Monolithic devices
One-piece modifications do not have the listed disadvantages. The cast radiator is capable of withstanding pressure surges within 100 atmospheres.
Disadvantages of monolithic batteries: there is no possibility to vary the thermal power, inflated cost - 20-30% more expensive than sectional models with similar parameters
For high-rise buildings (10 or more floors), experts recommend choosing solid radiators, since there will be significant pressure in the heating system.
Copper or steel core?
Most manufacturers offer hybrid batteries with a steel tube frame. The main reason is the affordability of the metal and good strength characteristics. The symbiosis of steel and aluminum made it possible to achieve resistance to pressure fluctuations in the heating system, increase the level of heat transfer of the convector and reduce its inertness.
In copper + aluminum radiators, the heat exchange tubes are made of copper. Heating panels - aluminum plates soldered to an internal copper frame
Advantages of copper core batteries:
- there is no likelihood of corrosion;
- a copper pipeline withstands any water hammer - the best option for use in domestic centralized heating systems;
- high efficiency of the device - the heat transfer of copper exceeds that of steel.
Copper-aluminum radiators have a service life of more than 50 years. The disadvantage of copper modifications is the high price.
Types of bimetallic batteries
In addition to bimetallic ones, the production of semi-bimetallic radiators has now been established. It is important to understand what their differences are.
Fully bimetallic
In such models, aluminum is used only for the manufacture of the outer casing of the device. The production procedure is as follows: steel cores are placed in special molds and filled under pressure with aluminum, a material with good thermal conductivity. In turn, it does not withstand aggressive environments and high coolant temperatures. But, in solid, completely bimetallic versions, aluminum simply does not come into contact with the liquid - it is used purely as a heat exchanger. This design is optimal for central and autonomous heating systems.
Some models are not equipped with a copper core, but made of stainless steel: such batteries are suitable for autonomous systems with special antifreeze as a coolant.
Semi-bimetallic
Different metals are used to make internal channels for such batteries. For example, stainless steel is used to produce vertical pipes, and aluminum is used for horizontal pipes. There are also reverse options.
This variety is not installed in central heating systems, which is explained by the quality of the coolant, which may contain a high concentration of alkali. When in contact with aluminum, corrosion processes easily form. In addition, each metal has its own rate of thermal expansion. And if the system experiences extremely high temperatures, internal components can shift, causing a leak.
Often such radiators are confused with completely bimetallic ones, since visually they are no different. If the buyer does not understand the intricacies, he, as a rule, buys the cheaper version. But, looking at the description, you can see that this is not a particularly reliable investment.
Technical and operational characteristics
All basic parameters of the radiator are indicated in the passport of the heating device.
In order not to make a mistake with your choice, you need to understand the meaning of the following characteristics:
- heat transfer;
- operating pressure and temperature;
- center distance;
- dimensions;
- capacity, section weight.
Thermal power. The parameter indicates the amount of heat transferred from the battery to the atmosphere of the room at a given coolant temperature (+70°C). The indicator is measured in W.
The average heat transfer value of a composite radiator is 140-190 W. The difference in values is explained by the dimensions of the section and the design features of devices from different manufacturers.
Based on the thermal power of one section, the required battery performance for the entire room is calculated.
Work environment indicators. The maximum coolant pressure depends on the thickness of the steel core. The choice of strength is at the discretion of the manufacturer. The parameter value ranges from 15 to 35 bar and is determined based on the operating conditions of the battery.
An important characteristic is the limiting temperature of the coolant. All high-grade bimetals can withstand +90°C. Some manufacturers claim higher thermal resistance.
The maximum temperature stated in the equipment data sheet for different trade positions: Global Style – 110°C, Tenrad – 120°C, Altermo – 130°C, Grandini – 120°C
Radiator dimensions. Dimensional characteristics include the following parameters:
- Center distance is the “distance” between the axes of horizontal collectors. The standard size is 20-80 cm. Vertically oriented models with increased interaxial distance are used if the room layout is not suitable for installing horizontal radiators.
- Geometric parameters determine the height, width, and depth of the section. The total height of the radiator often exceeds the interaxial range by 6-8 cm. The traditional width of the fins of bimetallic models is 80 mm.
The depth of the section is 75-100 mm. Some manufacturers, in addition to external panels, add parallel fins to the design to increase heating efficiency due to convection flows.
Overall dimensions: a – section height, b – distance between horizontal axes, c – battery depth, d – width of one section. The most popular products with a core height of 35 cm, 50 cm
Volume and mass. In bimetallic modifications, the coolant circulates through a core of round cross-section, in contrast to aluminum counterparts with a heat conductor of oval cross-section. The capacity of one bimetal section is less than the volume of an aluminum section with the same standard dimensions.
For example, in convectors with an interaxial range of 500 mm, the coolant filling is about 0.2-0.38 l, with a core height of 350 mm - 0.15-0.25 l.
The weight of a standard bimetallic battery with dimensions of 580/80/80 mm (height/width/depth, respectively) and an axial distance of 50 cm is 1.8-2 kg. Less mass is one of the signs of a semi-bimetal.
Thermal power of radiators with different center distances
The second key characteristic of bimetallic radiators is thermal power . Using this parameter, it is determined how many radiator sections are needed to effectively heat a room of a certain area. This characteristic of a bimetallic radiator directly depends on the value of the center distance :
- 500 mm - thermal power ranges from 170 to 200 W.
- 350 mm - from 120 to 140 W.
- 300 - from 100 to 145 W.
- 200 - about 100 W.
The exact value of the thermal power depends on the modification of the device; this characteristic of the bimetallic radiator is indicated in the technical data sheet for the product. It is calculated as follows: the amount of heat given off by the radiator is estimated at a working environment temperature of +70 degrees Celsius. Let us remind you that in Russia the following standard is used: to heat a room with an area of 10 square meters, a thermal power of 1 kW is required .
To determine the required number of sections, you can use the following formula: N=S*100/Q , where:
- N is the optimal number of sections.
- S is the area of the room.
- Q is the section’s passport indicator.
Comparative analysis: bimetal and competitors
Before choosing a bimetallic or other radiator, it is advisable to compare its capabilities with its closest competitors. For composite convectors these are aluminum, cast iron, steel batteries.
The assessment should be carried out according to the main criteria:
- heat transfer;
- endurance to pressure changes;
- wear resistance;
- ease of installation;
- appearance;
- durability;
- price.
Heat release. In terms of heating efficiency, aluminum units are the leaders, bimetal takes an honorable second place. Steel and cast iron radiators are noticeably inferior.
Aluminum is characterized by minimal thermal inertia - after starting the system, the air in the room warms up within 10 minutes
Resistance to water hammer. The most durable are bimetallic units, capable of withstanding up to 40 atmospheres (sectional models). The maximum operating pressure on an aluminum heating system is 6 bar, a steel one is 10-12 bar, and a cast iron one is 6-9 bar.
It is the bimetal that can withstand numerous water hammer shocks from a centralized heating system. This property is a key argument in favor of composite radiators for apartment buildings.
Chemical inertness. According to this criterion, positions were distributed as follows:
- Cast iron. The material is indifferent to adverse environments. Cast iron radiators can be used for decades, transporting an “alkaline”, “acidic” environment.
- Steel and bimetal. The steel core itself withstands the effects of aggressive components. The weak point of a steel pipeline is its interaction with oxygen, contact with which leads to the formation of rust.
- Aluminum. The metal reacts with various impurities in water.
Aluminum walls are especially susceptible to acidic environments - the pH of the coolant must be within 8. Otherwise, corrosion will actively develop.
Easy to install. In terms of installation, aluminum and bimetallic products are easier. Cast iron radiators are more difficult to install due to their impressive weight.
In terms of durability, the leaders are composite and cast iron batteries. Aluminum and steel products, subject to operational requirements, must be replaced after 10-15 years. Among the designated batteries, bimetallic ones are the most expensive
We can conclude. The purchase of a bimetallic radiator is definitely justified for assembling a heating network in a multi-storey building, where there are risks of pressure surges and contamination of the coolant. In a private house, with stable operation of the boiler and filtration of incoming water, affordable aluminum batteries can be used in the heating device.
Why we prefer bimetallic devices
Combining the useful characteristics and properties of different materials in one product often gives very good results. A clear example of this is bimetallic devices, which have both the reliability of steel and the high thermal conductivity of aluminum. The combination of these two metals made it possible to design batteries with high heat transfer, an impressive modern design and the ability to withstand hydraulic shocks. Initially, radiators of this type were created for use in centralized heating systems, characterized by high operating pressures and low-quality coolant. Now the scope of application of bimetallic radiators has been significantly expanded; they have begun to be successfully used in the arrangement of individual autonomous heating.
We have been using steel and aluminum radiators made in our country or abroad for a long time. Steel batteries are characterized by strength and immunity to the effects of alkalis, acids and other impurities added to the coolant composition. But the efficiency of steel radiators is not too high, since this metal, although it heats up very quickly, also cools down just as quickly. Aluminum undoubtedly has high heat dissipation, but cannot effectively resist corrosion. Bimetallic batteries use the best properties of these metals, so the heating system in which they are used is characterized by increased efficiency. This is especially important given the high price of energy.
On what principle do bimetallic batteries work? The coolant, which can be not only water, but also more aggressive liquid substances, transfers heat to the internal radiator core made of steel. It is important that contact of easily oxidized aluminum with an aggressive coolant is completely excluded. The heated steel then transfers thermal energy to the aluminum body, which directs it to heat the room.
What should you consider when choosing a radiator?
To achieve the proper thermal effect, it is necessary to calculate the total power of the battery. Bimetallic equipment is not a cheap purchase, so you should take care of its durability. The conscientious execution of the radiator is guaranteed by trusted manufacturers.
Capability assessment - thermal calculation
Having decided on the appropriate technical characteristics and dimensions of bimetallic radiators, it is necessary to calculate the required number of sections.
Basic formula: N=Ptot./Ppass., where Ptot. – required battery power for the entire room, Ppass. – thermal power of the section according to accompanying documents
The section’s heat transfer rate is taken from the radiator’s passport, and the total power must be calculated.
Calculation by area
The normalized value of thermal power per 1 sq.m of living space for the average climate zone, subject to standard ceilings (250-270 cm):
- the presence of one window and a wall with access to the street - 100 W;
- there is a window in the room, two walls adjacent to the street - 120 W;
- several windows and “external” walls – 130 W.
Example. The section power is 170 W, the total area of the heated room is 15 sq.m. Additional conditions: window – 1, external wall – 1, ceiling height – 270 cm.
N=(15*100)/170 = 8.82.
Rounding is done upward. This means that to heat the room it is necessary to use 9 sections of 170 W each.
Calculation by volume
SNiP separately regulates the amount of thermal power per 1 cubic meter of space in the amount of 41 W. Knowing the volume of the heated room, it is easy to calculate the heat transfer of the entire battery.
Example. Heating the room with the previous parameters. For the purity of the experiment, we leave the power of the section unchanged - 170 W.
N=(15*2.7*41)/170= 9.76.
It is necessary to install a radiator into 10 sections. The second calculation is considered more accurate. When calculating, attention should be paid to sources of heat loss indoors.
The calculated value must be increased by 10% if the apartment is located on the first/last floor, the room has large windows or the wall thickness does not exceed 250 mm
How to avoid fakes: radiator inspection
In addition to analyzing passport data, it would be useful to conduct a visual assessment of the product. Some manufacturers, in pursuit of customers, tend to “embellish” their products by introducing incorrect data into the documentation.
First of all, pay attention to the thickness of the core and aluminum “jacket”, overall dimensions, weight and quality of components.
Steel core. The minimum thickness of the steel tube is 3 mm. With smaller standard sizes, the declared strength of the product - resistance to water hammer and the development of corrosion processes - is significantly reduced.
The walls of thin metal provide access for the coolant to the aluminum “shell”, which, due to chemical activity, begins to quickly collapse
The result of a low-quality steel core is the formation of through holes and the creation of emergency situations in the heating network.
Radiator fins. Aluminum panels must be checked for strength - they should not bend from the efforts of the fingers of one hand. The minimum thickness of the panels is 1 mm.
It is better to choose models with profiled channels between the ribs. The formed confuser increases the speed of air flow, increasing the intensity of convective heat transfer.
To reduce the risk of injury, the outer edges of aluminum panels are rounded. There should be no streaks, uneven coloring or “gaps” on the surface.
Dimensions and weight. By individual order it is possible to produce radiators with a section width of less than 80 mm. However, store-bought models with inappropriate parameters are most likely fake.
To reduce costs, some manufacturers significantly reduce the width of the internal ribs, “masking” them behind standard-sized front panels. This measure worsens the heat transfer of a bimetallic radiator.
Battery components. It is almost impossible to check the quality of gaskets and nipples on site. Rely on the manufacturer's name and warranty period. Reliable companies guarantee up to 15-20 years of trouble-free operation.
How to calculate the number of sections
Based on plumbing standards, 100 W of power is required per 1 square meter of room. The calculation is as follows: the housing area is calculated - the length is multiplied by the width. The resulting figure is multiplied by 100 W and divided by the heat transfer of one section.
For example, let’s take a room 3 by 4 meters. It can be calculated using the above formula: K = 3 × 4 × 100 / 200 = 6. Here, the number 200 is the heat transfer rate of one section.
The calculation of sections of bimetallic heating radiators by area is more accurate. The calculations are similar, only the main data is the heating power for 1 m³. The normalized value is 41 W.
So, the room is 3 by 4 meters, the ceiling height is 2.7 meters. Volume (V) = 3 × 4 × 2.7 = 32.4 m³. Radiator power (P) = 32.4 × 41 = 1328.4 W. Number of sections (K) = 1328.4 / 20 = 6.64. The volumetric method is more accurate, as it takes into account the height of the ceilings, which will allow for optimal heating.
Rating of popular manufacturers
The review includes high-quality foreign heating systems and domestic products adapted to the changing conditions of heating networks.
In practice, the company’s products have proven themselves well:
- Global Style (Italy);
- Sira (Italy);
- Rifar (Russia);
- Tenrad (Germany).
Place #1 - Global
This is a generally recognized leader in the production of heating radiators.
The company produces three series of bimetallic batteries:
- Style – basic characteristics;
- Style Extra – compact dimensions;
- Style Plus – maximum heat transfer.
The sections are connected by paronite gaskets, ensuring the tightness of the joints. Efficient heat transfer between metals is achieved through injection molding of an aluminum “jacket”.
Additional characteristics: pressure – up to 35 atm, connection diameter – ¾ or ½ inch, coolant temperature – up to 110°C, outer shell – double painted
Place #2 - Sira
The Italian manufacturer positions its products as premium products. The devices have gained popularity among consumers due to their durability and attractive design. The manufacturer provides a 20-year guarantee for a series of full-fledged bimetallic radiators Sira Ali Metal.
Characteristics of Ali Metal products: center distance – 350/500 mm, heat transfer of models – 187/141 W (according to the center distance), pressure in the heating network – 35 atmospheres
Place #3 – Rifar
A domestic manufacturer has developed a wide range of bimetallic radiators:
- Base – models with center distances of 200/350/500 mm, warranty from Rifar – 10 years;
- Forza – reinforced external coating, resistant to scratches and mechanical damage;
- Alp – shallow depth (75 mm);
- Monolit is a one-piece radiator.
Monolit series batteries are characterized by the highest performance indicator at high coolant pressure.
Technical data: operating pressure – 10 MPa, destruction pressure – 25 MPa, maximum temperature – 135°C, warranty period – 25 years
Location #4 - Tenrad
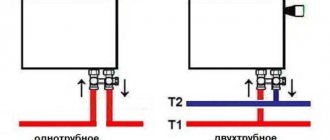
Bimetal of German quality is suitable for centralized and independent heating networks. Suitable for use in gravity, elevator and pump systems with one- and two-pipe wiring.
Distinctive features:
- the thickness of the vertical tubes is 1.8 mm, the thickness of the collector walls is 3.6 mm;
- three-row fins;
- the side panels are located at a slope, which creates a diffuser effect for convective flow.
Two-layer enamel coating made of high-quality paints and varnishes - when heated, the device does not emit harmful fumes.
Tenrad products are designed for operation in a system with a coolant pressure of up to 35 atmospheres. Bimetallic radiators are certified and comply with the European standard EN442
The following article will introduce you to the rules for calculating the power and number of radiators for a heating device, which you should read before purchasing devices.
Review of popular brands and their prices
Buying bimetallic heating batteries is not a problem now, since their price in Moscow starts from 2,550 rubles (for a model with 8 sections).
Brief information about the most popular manufacturers:
- Italy . It produces Royal Thermo radiators, which are characterized not only by an attractive and non-standard design, but also by technical features. High-alloy steel is used for their manufacture. In the Thermo Beeliner model, the collector is made of stainless steel, which makes it almost eternal. From 570 rubles for one section;
- Germany . Oasis products are popular: they are sold inexpensively and have good characteristics. The product can easily withstand operating pressure up to 30 atmospheres;
- Ukraine . San Teh Rai company that produces Elegance batteries. Italian and Swiss equipment is used for production, and the models themselves are optimal for domestic heating systems. The cost of one section is 320 rubles, and the stated operating pressure is 30 atmospheres. Another Ukrainian brand is Altermo. Their radiators are designed for loads up to 18 bar, but are offered in different colors;
- Russia . Bilux company, whose production is located in China. These are technically high-quality products, with a 10-year warranty and a heat output of 182 W per section. Another Russian manufacturer is the Rifar company. Their products have a distinctive feature: they can withstand pressures of up to 100 atmospheres. Recently, products manufactured under the Lammin brand, priced from 1,650 rubles, have become popular;
- South Korea . Pioneer company, whose radiators have the following characteristics: coolant temperature no more than +130 ° C, pressure - up to 20 atmospheres. For the most part, these are classic models, available in the usual white color. From 1,820 rubles for 4 sections.
When choosing a manufacturer, first of all you need to take into account the technical characteristics. Not all models are suitable for domestic heating systems. Read our article about which stove is best to install in a bathhouse.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The video review clearly demonstrates the design features of composite radiators and the basic requirements that a high-quality device must meet:
Full bimetallic radiators combine the positive characteristics of both materials. The batteries are distinguished by high thermal power, resistance to water hammer and excellent decorative properties. Their purchase is a justified investment provided that you purchase a certified product.
Tell us about how you chose a bimetallic heating device for your own apartment or country house. Share what argument was decisive in your choice? Please leave comments in the block below, ask questions, post thematic photographs.
Blitz tips
- When choosing a bimetallic heating device, you should not completely trust sales consultants who praise this or that model. You should slowly check the heating device yourself for compliance with the parameters set out in this article. If you have doubts about the country in which the heating device was manufactured, you need to read the documentation for the product.
- Installing a bimetallic radiator is a very responsible undertaking that is best left to professionals.
- There is no point in purchasing the most expensive model. The fact that a heating device is more expensive than all other models does not prevent you from purchasing low-quality products for a lot of money.
Which ones are better
Manifolds made of steel completely eliminate contact of the coolant with aluminum. This is the moment that interferes with the normal operation of aluminum batteries in our high-rise buildings. The second point is pressure drops that can occur during system startup and in emergency situations. In general, in normal conditions this indicator in any network is within 6-9 atm. But they try to install heating devices with multiple reserves: water hammer can be very strong. According to these parameters, batteries made from full bimetal are better:
- their operating pressure is approximately 5 atm higher than that of partial (on average 30-40 atm depending on the manufacturer),
- 100% exclusion of contact with coolant.
What is the disadvantage of such radiators? They are expensive. The manufacturing technology is complex: first you need to weld the structure, ensuring the tightness and reliability of the connection, then fuse aluminum onto the frame, giving it a certain shape. It is also necessary to ensure a reliable connection between two different metals, which is not easy. All this affects the price.
Not a single manufacturer wrote: this model only has a vertical steel tube. You have to look into the manifold to understand what it is made of
Another negative point: the lower thermal power of the section. The difference is approximately 10% compared to partial bimetal, and 15-20% with a similar aluminum section.
Partial bimetal has lower strength characteristics. Its horizontal collectors are made of aluminum, that is, they are destroyed by the coolant. But the practice of using aluminum radiators has shown that in most cases it is vertical collectors that are destroyed. So aluminum in horizontal ones does not greatly affect the durability of heating devices. However, the main task and idea - to exclude the contract between aluminum and coolant - have not been completed. In any case, they are more demanding on the quality of the coolant (pH should be in the region of 6-9, and preferably 7-8) and have lower burst pressure (and operating pressure too).
Now about the positives. These batteries are priced between fully bimetallic and aluminum. They have higher heat transfer. Some models can catch up with aluminum. For example, Rifar Base 500 allows you to shoot more than 200 W from one section (at a temperature delta of 70oC).
Read about radiators here.
This is the only fully bimetallic radiator from the Russian
So, which bimetallic radiators are better? I will express my own point of view: if we install bimetal, then complete it. It may be expensive, but it is reliable. And the manufacturer must be chosen wisely. It is quite possible to find high-quality full bimetal, which will be only slightly more expensive in price than partial. But I emphasize once again - this is a personal opinion.
In general, you need to approach it from the point of view of operating conditions. You will need to know the following parameters of your heating network:
- Maximum temperature;
- working and maximum pressure;
- hydrogen index of the coolant (the same pH).
Having this data in hand, you can already decide exactly what is better: a bimetallic radiator with a partially steel manifold, or do you need a frame entirely made of steel.
When asking about network parameters, do not ask for an official answer. You will be given “protocol” values, which, to put it mildly, do not always correspond to reality. It is better to find out this from plumbers who know the real picture, and not the official one.
Disadvantages and/or advantages?
It is recommended to equip bimetallic radiators with thermostats for quick heating.
Bimetallic radiators are usually blamed on the small cross-section of pipes,
because of which they can quickly become clogged with solid suspensions present in the water. However, you can cope with this problem (and also prevent premature failure of the unit) using a simple mechanical cleaning filter installed at the inlet. But if the radiator is equipped with a thermostat, then due to the same small diameter of the channels, temperature adjustment will occur in a matter of minutes.
Perhaps, the really “weak link” of combined instruments, paradoxically, is the very “duality” of their design. Due to the different thermal expansion of their constituent metals and the friction that arises between them, over time, radiators begin to make squeaks.
However, for high-quality products this should not lead to a decrease in strength and deterioration in heat transfer.
As for the high cost of bimetallic radiators compared to their aluminum, steel and cast iron “competitors,” the reliability, durability and efficiency of these devices will undoubtedly justify the costs incurred.
The smooth surfaces of bimetallic radiators and the absence of hard-to-reach cavities and “pockets” in their design make cleaning the devices convenient and easy
Reviews
Oksana Bought in August 2022 for the kitchen an 8.5 m instead of the Soviet 4-rib battery, took 6 sections. Mirado (Ukraine) is still ok, the main thing is it’s warmer than it was with cast iron.
Vladimir Tikhonov Decided to replace cast iron radiators with high-quality bimetallic radiators. The choice of GLOBAL was a conscious decision (it was recommended by friends). At first I doubted how such a neat design could be better than our cast iron batteries, but the manager clearly explained their advantages to me.
Firstly, they are made of aluminum alloy and their core is made of steel, so they are durable. Secondly, they are not exposed to low-quality coolant. After their successful installation, I was convinced that I had made the right choice.
Anastasia Ivanchenko Of all the offers on the market of bimetallic radiators, I chose the Ukrainian company MIRADO. And I was not mistaken. The heat output of MIRADO is 202 W, and this is exactly what I needed. They promise a 10 year guarantee.
White, neat and so much warmth - I didn’t even expect it. Compared to my old radiators, the new ones are an order of magnitude higher in functionality and look more aesthetically pleasing. The apartment became warm and cozy.
Anton
I bought bimetallic radiators, the price is reasonable, the quality of the product is good. The only thing that didn’t really suit me was delivery of goods from 9.00-18.00. But the company accepted my situation, and the director of the company made the delivery to me in the morning at 7.00 (when it was convenient for me!!), on the way to work.
Alexey Grigorievich
I have an old 16-story house, the local plumber said that it is better to replace the old ones with bimetallic radiators, since pressure surges often occur in the house. I contacted the store and they recommended Italy Global Style or the cheaper option Tianrun. I bought an Italian because I didn’t want to worry about the heating system either. Installed, everything is fine.