Of all the heating methods that exist today, air heating is considered the rarest. Despite the fact that 50-70 years ago these heating systems were popular and were installed en masse, today it is quite difficult to find such objects. The exceptions are fireplaces and traditional Russian stoves, which are not full-fledged air heating systems.
Of all the equipment and devices that work on the same principle, we are most familiar with heat guns, fan heaters and convectors. Heating, where the main emphasis is on solid fuel boilers, provides air heating today and is used in rare cases. Let's look at the reasons why air heating today is not as popular as other types of heating. Let's understand the principle of operation of an air heating device that runs on solid fuel.
Application of ducted air conditioners and heat pumps
Electric air heating is often supplemented with such elements as:
- multifunctional air conditioners that can both cool and dry the air and operate for heating;
- anti-dust filters;
- ultraviolet radiation filters that disinfect incoming air;
- supply and exhaust ventilation systems.
In such systems, it is electricity that is used as a heat source. Judging by numerous reviews, heating with air conditioning is easy to use and can provide comfortable living conditions. Control is carried out by one block, which sets all the necessary parameters.
If we compare this scheme with a system that includes a gas boiler for air heating, a whole network of air ducts and ventilation fans, then the first one looks more modern and thoughtful.
Due to the fact that the installation of visible heating devices (radiators and pipelines) is not required, air heating does not create obstacles to interior design. Nothing will be visible anywhere except the ventilation grilles.
Among the disadvantages of the described air heating scheme is the high cost of the equipment. Duct air conditioners, even of low power, will be quite expensive.
In addition, there are some restrictions on the operating conditions of the external unit of the air conditioner - it is not designed for temperatures below -15 ℃ - -25 ℃, otherwise the efficiency of the equipment is reduced.
An alternative solution for use in particularly cold regions could be a geothermal heat pump. Whatever the ambient temperature, below the freezing level, the soil temperature always remains at 8-12 ℃. If you deepen a heat exchanger of sufficient area into the ground, you can obtain a constant source of thermal energy and use it to heat your house.
Air heating of a private house. Points for and against"
Imagine that you are at the design stage of your own home. Considering the theme of our portal, this is not difficult to do. One of the most important issues that you have to study is the choice of heating system. Traditionally, when it comes to choosing an individual heating system, future owners of private houses think only about which energy source will be most preferable and affordable for them. As for the system itself, everything is simple: a boiler that converts energy into heat, a pipeline system filled with coolant and heating radiators or heated floors. This system is familiar and understandable to us.
At the same time, liquid heating systems are far from the only way to heat a home. Recently, the topic of air heating at home, which is certainly mentioned in the context of modern engineering systems, has been of particular interest and many questions among developers. Why modern ones? Simply because forced air heating systems are the dominant type of heating system in North America. And our marketing works in a very predictable way: if it’s American, it means it’s the most advanced, the best, and nowhere more modern. In reality, everything is somewhat simpler. In fact, air heating is no more modern than the traditional liquid systems in our country. It’s just that our traditions are different, and any of the systems can be implemented both at the simplest level and using the latest achievements of scientific and technological progress.
However, let's return to air heating. Historically, air heating systems have been known for quite a long time, and they were all implemented on the principle of transferring heat from fuel combustion directly to air masses. At one time, the fire-air system, called the “Russian system,” made a small revolution. The heating device was as follows: cold air was supplied through an air intake shaft to a stove installed on the first or basement floor, where, touching its hot surface, it was heated. Afterwards, it was supplied to heated rooms through horizontal and vertical brick distribution channels. From there, through the exhaust ducts, the air that gave off heat was released back into the atmosphere. Air circulation was natural, due to the difference in densities of hot and cold air masses. So Ivan Boyarintsev’s stove is by no means an innovation, but a kind of one of the options for implementing a fire-air heating system.
The domestic market today is represented by a large number of models of various heating furnaces made of metal, operating on the principle of natural air convection. With a fair amount of ingenuity, using such stoves you can also assemble a forced air heating system.
With a certain stretch, an ordinary electric “wind blower” that drives air currents through itself can be called local air heating. But in the context of modern times, automatic climate systems using main natural gas are of greatest interest.
System components
Air heating is a complex engineering complex consisting of many components that are tightly interconnected, while performing their specific functions.
- Gas air heater with a closed type heat exchanger. That is, heated air masses do not directly contact with an open flame. The fuel recovery rate of highly efficient air heaters is more than 94%. This fact is usually cited as an advantage of the air system. But this indicator does not at all exceed the efficiency indicator of the condensing gas boilers we are used to.
- A network of air ducts consisting of main channels responsible for the supply and intake of air in rooms. Channel cross-sections are calculated values, and the channels themselves are selected based on the individual characteristics of the house. The joints and connections of all channels are sealed, in addition, the channels themselves are insulated to eliminate heat loss during air transportation.
- Duct fans. They are installed on both supply and return air ducts; in the vast majority of cases, they are a structural part of the air heater.
- Diffusers or grilles. Each air duct entering the room is connected to a diffuser or grille. The grilles allow you to adjust the amount of air supplied and the direction of the air flow, providing precise adjustment for each room.
- Filtration system. Air preparation for air heating systems is a very important and popular option, since air masses continuously move throughout the living space. The design can use electrostatic, carbon, mechanical filters, as well as bactericidal treatment stations.
- Humidifier. A device that allows you to maintain a comfortable level of air humidity throughout the house automatically. The humidifier is installed on the main air duct, which collects exhaust air flows, between the filtration system and the air heater.
- Control automation. The control unit or controller is installed in the technical room and allows you to change the system operating parameters for each individual room at any time. With its help, you can set programs both by time and by indicators of the microclimate state taken by sensors. Automation makes it possible to create zoned air distribution. Each zone is equipped with an automatic damper to control the air flow supplied to it and a room thermostat to control the temperature.
Additional system elements
- Central air conditioning at home. The air heating system allows you to implement the air cooling function by installing a central air conditioner. The external air conditioner control unit is installed outdoors, and the internal one is mounted directly at the outlet of the air heater.
- Recuperator. Installation of this device into the system is optional. However, when organizing air heating in a direct-flow configuration or with partial recirculation, external air flows can be recovered to save heat. At the same time, the recuperator in air heating systems is a secondary unit connected to the CO controller.
Operating principle and various configurations.
The main distinguishing feature of air heating is the presence of a network of air ducts through which air masses are supplied to the rooms and returned back. The air is brought to the required temperature in the air heater circuit.
Next, the heated air is forced into the main supply air duct. From the main air duct, warm air masses are distributed through channels leading to the heated rooms. The specific location where the supply channel exits into each room is determined at the design stage. So, in one-story houses, warm air is directed from below, and the ducts themselves are mounted in the floor, or in the wall directly above the floor, and the return air is organized under the ceiling. In two-level cottages, the easiest way to place a network of air ducts is inside the interfloor ceiling, or along the ceiling of the first floor. In this case, warm air is supplied to the first floor from the ceiling, and to the second floor - from the floor or from the internal walls above the floor. The return flow of the first floor is collected at the floor level, where the masses are coldest, and on the second floor - at the ceiling, where excessively heated air accumulates.
Air is taken from the premises through a system of return air ducts. The air passes through the filtration system, is humidified and goes back to the air heater, where it is reheated or cooled, thus ensuring its circulation.
There are several configurations of air heating systems based on the quality of the supplied air:
- Straight-through. Only outside air is heated and supplied in them, and the same amount of air is removed from the room through the channel;
— Systems with full recirculation. They only heat and supply air taken from the room;
— Systems with partial recirculation. The most common type of modern air heating systems. They heat and supply a mixture of outside and recirculated air. In this case, the dosing of recirculated and external air is carried out based on the calculations of the ventilation system.
Thus, a correctly calculated and assembled air heating system, equipped with automation, is essentially a full-fledged climate control system that provides not only heating, but also air conditioning and air preparation (ventilation, humidification) in residential premises.
Design and installation
One of the main reasons for the low prevalence of air heating systems is the need to involve professionals in their design and installation. To be fair, it is worth noting that on our forum there is a topic that describes in detail the independent installation of air heating using natural gas. The topic provides a number of controversial, but quite logical arguments and tips for simplifying and reducing the cost of air systems. But still, the classic version requires a large number of professional calculations directly for each project, since each such system is a piece product.
In order for the air heating of the house to function without failure and be economical, it is necessary to carry out the following calculations:
Calculation of heat loss of a future home. They are carried out for each room and take into account the material of the enclosing structures, including windows and doors.
The calculation of heat loss for ventilation depends on the number of permanent residents to provide people with fresh air.
The location of the main elements of the system in the design of engineering systems. Much attention is paid here to the air duct network, given their considerable dimensions and length. Air lines must be consistent not only with other utility networks, but also with the interior of the house. They must be taken into account when planning ceiling heights.
Selection of equipment based on the design parameters of the system. This includes: choosing an air heater of appropriate power, selecting an air conditioner, humidifier, filter system and, if necessary, a recuperator.
The project must include calculation of all system components, volume and cost of materials and consumables. Is it possible to make it yourself? Perhaps yes, but you will have to master many disciplines in the specialty “Heat supply and ventilation.”
Installation of the system is divided into several stages:
- Preparatory stage. During its production, the necessary technological holes are made in the floors and walls in the places where the main air ducts will pass. The number of these holes, their cross-section and exact location are determined at the design stage, and the complex of work itself is best done at the time of construction of the house, making mortgages in the necessary places.
- Installation of air ducts. Air ducts and connecting elements are made of galvanized steel and must have a cross-section corresponding to design calculations. A mandatory installation stage is insulation and soundproofing of the air ducts, as well as sealing the joints with aluminum tape. Connected and insulated lines must be securely fixed to the supporting structures of the house.
- Installation of equipment. This stage is carried out after finishing the house and includes: installation and piping of main equipment, installation of ventilation grilles and thermostats, chimney connection and commissioning.
- Setting up the control system. This is the final stage, which is performed after 100% construction readiness. When performing the setup, the air distribution system is adjusted, zoning is adjusted, and equipment operating modes are programmed to create the most comfortable microclimate.
Advantages and disadvantages of air heating systems
In order to talk about the advantages and disadvantages of air heating, you need to be, at a minimum, a user of such a system, and for quite a long time. But if we analyze various reviews, we can highlight the following advantages that do not require discussion:
- Versatility. Air heating of a private house provides not only heating or cooling, but also ventilation, air purification and humidification, essentially being a climate system for creating an optimal microclimate in the building.
— Increased reliability. The system practically does not fail and requires less frequent maintenance. Due to the absence of liquid, there is no risk of air locks or coolant leakage. Such a heating system can be completely turned off in a seasonal home, and if necessary, it can be started even in severe negative temperatures, quickly bringing the home to a comfortable temperature.
- Durability. If installed correctly, an air heating system can operate for several decades without major repairs.
Factors such as: cheaper cost, increased energy efficiency and more convenient operation, which are often attributed to air heating systems, will be considered debatable.
Obvious disadvantages of air systems include:
— The need to design the system in advance. What's bad about it? The fact is that today most of the private houses we build rarely have a full-fledged design. This is both quite expensive and often unnecessary. As a result, it is quite problematic to correctly link the air system with other utilities and the interior.
— A large cross-sectional area of air ducts requires increasing the height of the ceilings or the thickness of the walls.
— Increased noise due to constantly running fans, which we have to deal with.
In general, we can admit that with proper organization and professional execution, an air heating system, and even in the presence of main natural gas, is a fairly practical and technological solution.
Features of carrying out competent calculations
Despite the assurances of would-be experts, it is very difficult to independently calculate air heating. Only specialists can do this task.
The customer can only check the availability of all project items, which include:
- Determination of heat losses for each heated room.
- Type of heating equipment indicating the required power, which should be calculated based on actual heat loss.
- The required amount of heated air, taking into account the power of the selected heating device.
- Required cross-section of air ducts, their length, etc.
These are the main points for calculating the heating system. It would be right to order a project from specialists. As a result, the customer will receive several calculation options from which he can choose and implement the solution he likes best.
An air heating system is a complex structure consisting of many elements. To calculate it, it is better to involve professionals; to familiarize yourself with the components, it is worth studying the diagram in detail (+)
Solid fuel boiler is the main source of heat. Principle of operation
*
How do we imagine a solid fuel boiler that powers a home heating system? This is a pyrolysis type heating device familiar to many of us. Due to the combustion, first of fuel, and then of combustible wood gas, there is an intense release of heat from the interaction with which the heat exchanger is heated. More precisely, an air exchanger. Heated to a certain temperature in the heat exchanger pipes, the air circulates through a system of channels, heating the interior.
Such a heating device can be installed almost anywhere in a residential building or other premises.
Note: today models of solid fuel air heating units are produced, the design and appearance of which allows them to fit well into the interior of residential premises.
If the home owner wishes, air can be distributed through the duct naturally or under the influence of blowers, which significantly increases the speed and density of the air flow. The boiler usually has a spacious combustion chamber where the fuel burns. The firebox has a special hatch through which firewood is loaded. At the bottom of the combustion chamber there is a grate on which the fuel is placed and the combustion itself takes place. As in other solid fuel units, in the lower part of the structure there is an ash pit - a box for collecting ash and large remnants of unburned wood.
Air heating boiler design
If preference is given to the pyrolysis method of fuel combustion, then a boiler equipped with two combustion chambers is required. In one compartment, as a result of smoldering of the fuel mass, intensive release of wood gas occurs. In the second firebox, highly volatile flammable compounds, reacting with oxygen, ignite, releasing a huge amount of thermal energy. This method is characterized by economical fuel consumption. In the process of burning wood, there are practically no large residual fragments left. An air heating system with a solid fuel pyrolysis boiler is distinguished not only by fast and high-quality heating of rooms, but also by high performance characteristics.
*
Heated air accumulates in the space between the body of the heating unit and the firebox (combustion chamber). This is the heat exchanger in this case.
Due to the air flow, the walls of the combustion chamber are constantly washed with new air flows. Both primary and secondary air are used for heating. Thanks to pyrolysis in the boiler, the main work is done by the primary and secondary air. Primary air masses are the main source of heat. Air coming from outside, i.e. it is preheated to reduce heat losses, and only then enters the firebox. Secondary air is a gas-air mixture consisting of air and hot combustion products.
Note: solid fuel in most cases burns 90%. The remaining 10% is presented in the form of tiny particles that make up the smoke. The main advantage of secondary air is that it is already at a high temperature. No additional heating is required to achieve the required temperature. Due to such air exchange, a high heat capacity of the operating unit is achieved and the efficiency of heating equipment increases.
The selection of secondary air masses is carried out from the very top of the air duct. The intensity of the intake is regulated by the position of the damper. The combustion intensity of this equipment determines the volume of air supplied to the combustion chamber. More air, more intense combustion. Air supply in simple models is carried out manually, due to the natural flow of air. In expensive models, a fan is used for this purpose, which turns on and off automatically. Such fans are called blower fans. To achieve the maximum possible effect of the boiler operation, a smoke exhauster is installed on the chimney, the task of which is to improve the removal of residual combustion products from the combustion chamber.
Today, solid fuel air units of varying degrees of equipment are on sale. Most models include the following systems:
- ignition;
- combustion process control system (temperature sensors, dampers, blowers);
- mechanisms and devices that supply fuel.
Due to the interaction of all systems, the boiler allows you to regulate the heating temperature in the rooms.
Installation standards
The installation conditions for VK are simple, but for specialists, there are many nuances that need to be known so that the user is not disappointed in choosing an air-heating boiler.
Features of VK installation:
- The boiler is installed indoors during the construction of the building.
- Specialists must first complete an installation project, taking into account the actual heating and structural characteristics of the building, in accordance with which the main and auxiliary equipment will be selected.
- The system must be equipped with a backup power source.
- To increase efficiency, the boiler should be installed in a room with well-insulated walls.
- The combustion room must have a good ventilation system for ventilation.
- Air ducts make sense if you are installing them in multi-level houses with an area of more than 100 m2.
To select a VC you will need the following data:
- AC power taking into account heat losses in the building;
- the rate at which heated air enters the room;
- technical data of the air duct system;
- VK installation location.
If installing a boiler seems to be a difficult and impossible task for consumers, it is better to entrust it to a company that will perform the entire set of installation and adjustment work for the home heating system; in this case, inconsistencies can be avoided and reliable and safe operation of the equipment can be ensured for many years.
Furnace structure
Today, the most popular among consumers are the air-heating boilers of Professor Butakov, which have a wide range of applications: private residential sector, garages, greenhouses, industrial warehouses and basements.
What units does the boiler consist of? Photo source: paliwadrzewne.pl
The main structural parts of a typical hot water boiler:
- Lower drawer for collecting ash and regulating the amount of air entering the firebox.
- The door with a handle located above the ash pan may have a heat-resistant glass window.
- The combustion chamber and its volume affect the amount of loaded fuel and operating time.
- A cast iron grate is located under the chamber. The sides of the chamber are covered with convection pipes crossing at the top.
- A chimney with a damper to regulate the speed of flue gases and the intensity of draft.
- In some VK models, an additional afterburner chamber with two nozzles for supplying oxygen is located at the top. It burns the gas that is formed during smoldering.
The long-burning air-heating boiler is equipped with all the necessary automation devices, complete with temperature sensors and electronic control units. An automated fuel supply system and an increased volume of the combustion chamber allow the boiler to operate practically without human presence.
Advantages of an air heating system
The undeniable advantages of a system using boilers of the described type include:
- Low rate of inertia of the system - heating of the premises to a comfortable temperature occurs within an hour. It is also possible to use “standby” heating - when there are no people in the premises, the temperature decreases. This makes it possible to save up to half of all energy resources;
- The combination of several functions in one system - heating, air conditioning, ventilation, air humidification and air purification;
- The fact that there is no water in the system as an intermediate coolant allows us to say that the system is not afraid of defrosting under any circumstances;
- Cost-effectiveness of the system - capital cost savings occur due to reduced costs for the system installation process. Air systems are much less metal intensive than water systems, for example. Operating costs are saved due to the rational operation of the system (low inertia and “standby” heating mode).
Purpose of the ventilation system
Whatever the purpose of the room, ventilation ducts are its integral attribute. This especially applies to residential buildings and apartments, since during human activity dust, excess moisture and unpleasant odors, as well as carbon dioxide, accumulate. All this is removed outside through ventilation, and in return fresh, oxygen-rich air enters the room. In addition, thanks to the hood, condensation does not accumulate on the walls and fungus does not grow.
Thus, ventilation systems are designed to circulate oxygen in the room. There are exhaust and supply and exhaust ventilation systems. When using a supply and exhaust ventilation system, a recuperator is installed. This means that the warm air leaving the room will transfer some of the heat to the incoming flow. As a result, heat loss will be noticeably lower.
Air heating boilers
Hot air heating using boilers combined with furnaces and duct systems is a more common option. Thus, fuel combustion is ensured not by a coolant, but by air, which is blown through a heat exchanger. Hot air travels through the house through a duct system. To reduce unnecessary heat losses, ventilation and heating systems are laid with heat-insulated sleeves, placed under the finished floor between the joists, hidden in the walls and installed above the suspended ceiling.
Air heating boilers
The cold air that is displaced from the room goes outside completely or partially. Some of this air can be used again for heating.
Note that it would seem more logical to supply warm air through the grilles, which are located as close as possible to the floor. So, due to convection, the air will evenly heat the room. But not in this case. Typically, the ventilation system supplies air heated by the boiler from above, then the cold air masses are forced out into those exhaust grilles that are located below.
Heating boilers
Much more often you can find systems in which an air-fired solid fuel boiler is connected to air ducts and operates in conjunction with a heating furnace. In this case, the thermal energy that is released during the combustion of fuel is transferred from the heat exchanger to the air passing through it. Heated air masses carry heat throughout the house through air ducts. To reduce heat loss, air hoses for heating, as well as ventilation ducts, are laid under the finished floor, in the walls, and above suspended ceilings. In this case, the pipes for air heating and ventilation are covered with a layer of thermal insulation.
Cold air masses fall down to the floor and are discharged outside partially or in full. Some air can be reintroduced into the room and used for heating.
It is noteworthy that warm air, heated in a solid fuel air heating boiler, enters the room through the upper ventilation passages. As the air cools, it sinks down and is evacuated out through the lower exhaust grilles.
Operating principle of air boilers
Heating of residential, industrial or public premises is carried out with warm air heated using an air heater. The heater is connected to a system of air ducts that are routed to each room of the building. Low-temperature (160 degrees or less) combustion gases are discharged outside.
Using an air heater allows you not only to quickly warm up a room, but also to do so throughout the entire volume of the room, that is, evenly. After cooling, the air flows back into the heat generator through return air ducts. Thus, the operating principle of the system is based on the recirculation of air masses, to which fresh street air is mixed.
To maintain the desired temperature in the rooms, a thermostat (thermostat) is used. A special additional electronic unit allows you to very finely tune any climatic air parameters. The main electronic unit (processor) is used to control the air heater. It tracks the following parameters:
- Availability and pressure of gas in the system;
- State of security elements;
- Power options.
In addition, the processor is involved in controlling the humidifier, air conditioner, electronic filter and other equipment. All of the above functions can be added modularly to the basic heating system if desired by the user.
Air circulation standards
According to SNiP 2.04.05-91, the general air circulation rate is 35% per hour, that is, complete replacement of exhaust air must occur within 3 hours. In this case, at least 30 m3/hour of air per person must enter the room. For the kitchen, this figure is increased to 60 m3/hour in the presence of electric stoves, and up to 90 m3/hour if a 4-burner stove is used.
Additionally, the room must be equipped with vents or folding transoms on the windows to ventilate the room and let in at least 180 m3/hour of fresh air. Sometimes a hood is used for these purposes.
In bathrooms and toilets, air circulation rates are 25 m3/hour for each room. In combined bathrooms, the norm doubles.
Scheme for heating a private house with air
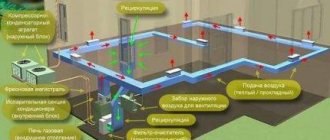
The main unit of the system is usually installed in the basement of the house in its center and includes all the main equipment:
- air heater (heat generator);
- fan;
- filter and purifier;
- humidifier;
- indoor air conditioner unit;
- various sensors.
Not all listed types of equipment are required to be installed. The minimum set will not include a fan, purifier, humidifier, air conditioner and sensors. From the main node of the system, often in the center of the house, the main, main air duct runs upward. It supplies heated air to all levels of the building.
Photo 1. Scheme of air heating of a two-story private house. The arrows indicate parts of the heating structure.
Horizontal levels of heating ducts are typically located under the floor of each floor, as well as in the ceiling of the upper level, thus covering the building from both below and above. An air collection system is installed separately inside and outside the house. Internal air is cleaned and humidified in the main unit, and external air is used for additional ventilation and renewal.
How to install
There are jobs in installing a system like this that require a professional, and some that some homeowners do themselves. The first include:
- calculation and design of the system;
- installation of gas equipment.
The second category includes the installation of some parts of the system (air ducts, sensors). This makes it possible to reduce the cost of organizing heating. It is optimal to start designing and installing such heating together with planning the house, since it is better to hide all parts in the floors and ceilings, and also immediately allocate a place for installing the main unit.
The sequence of installing air heating at home:
- system design;
- equipment purchase;
- installation of main unit equipment;
- installation of the main air duct;
- installation of other air ducts and grilles;
- installation of additional equipment (temperature, humidity sensors);
- commissioning works;
- finishing work, as a result of which the components of the heating system are closed.
Construction of gas generator furnaces
The gas generator furnace is a separate direction in the heating equipment industry. The principle of its operation is as follows: solid fuel burns with a small amount of oxygen; under the influence of low temperature values, pyrolysis gas is produced. This substance mainly consists of methane and carbon monoxide, has a high heat transfer coefficient, which helps to increase the operating efficiency of such equipment many times over. Fuel in this design burns almost completely. Heat is transferred through heat exchangers to the fluid in the system.
Gas-generating furnaces of various types are offered by many manufacturers of heating equipment. You can also make them yourself.
Self-installation
You can do air heating yourself, which will help you save money. It is best to do this during the construction stage. Installation of an air heating system consists of the following steps:
https://youtube.com/watch?v=QO2mryOkg6E
Carrying out calculations
This is one of the most difficult and lengthy stages, requiring knowledge, skills and careful work. You need to consider several important factors:
- calculate heat loss separately for each room;
- choose the type of air heater and its power depending on the heat loss indicators;
- based on the heater power indicators, calculate the amount of warm air;
- perform an aerodynamic calculation of the entire system;
- calculate the required diameter of the air channels.
Purchase of equipment
You should start by purchasing the most important part - the heat generator. It should be selected based on the size of the heated area and fuel consumption indicators.
It is better to purchase air ducts, tie-ins and throttle valves from a special enterprise that produces ventilation equipment.
Everything else, namely aluminum tape, screws, mounting tape, insulation, etc., can be found on any decent market.
Installation features
During the installation of this heating system, the main air duct is first installed. Usually it is made of galvanized steel, after which it is covered with foil insulation with a thickness of about 3-5 mm.
After this, a system of smaller air ducts is installed, which branch off from the main one. To make the system easily adjustable, a throttle valve must be installed in each supply duct.
At the end of the main air duct, it is better to leave a section 50 cm long, in which there will be no insertion of thin air ducts. This way there will be uniform pressure along the entire length of the device and equal volumes of air will enter the side branches.
All this is followed by the installation of the air heater itself. It provides all mounting holes for additional equipment (filters, air conditioning, air sterilizer) and a fastening system. Assembly of the complex will take no more than an hour. However, connecting all this equipment will take time.
From all this we can conclude that air heating of a cottage is a modern and effective option that has long been used abroad and is slowly being introduced into Russian homes.
Design Features
Gas-generating stoves can be installed in residential premises.
Long-burning gas generator stoves will heat a solid fuel boiler with the same operating principle. However, the first ones are distinguished by a simple design that vaguely resembles potbelly stoves. At the same time, unlike a potbelly stove, the operation of the stove is easy to control. The basis of any gas-generating heating equipment is the pyrolysis process.
In this case, we are talking about the release of gas from the fuel with a large percentage of heat capacity. When it is burned, several times more thermal energy is released compared to conventional wood burning. As a result, with one stack of wood, relying on the pyrolysis effect, it is possible to heat a significantly larger area of the room. The release of gas from the energy carrier occurs in a special chamber at high temperatures and in conditions of insufficient oxygen. The resulting fuel was previously discharged along with combustion products outside. Now it enters the upper chamber of the equipment, where its oxidation ends, followed by the release of a large amount of heat.
Long-burning air-heating furnaces have the following schematic structure:
- body made of thick steel or cast iron;
- convection jacket;
- combustion or primary chamber;
- secondary chamber or gas afterburning chamber;
- ash pan;
- chimney;
- draft regulator;
- secondary air supply pipe.
Long-burning air-heating stoves can change their appearance and structure depending on the configuration and model. However, they all have a similar operating principle. So, first comes the laying of the energy carrier. This can be regular firewood, pellets, seed husks, straw and other solid organic products. They also read about types of fuel for long-burning stoves.
Coal and coke are not suitable for long-burning steel furnaces. As a result of their combustion, the temperature of the heating equipment rises to a critical limit. This may lead to an accident.
Next, the usual combustion reaction occurs in the primary chamber with a sufficient amount of oxygen. Then the equipment goes into long-term combustion mode, that is, the temperature in the chamber drops. Oxygen is not supplied there in full. As a result, the firewood stops burning and simply smolders. Of them
A gas generator stove can be installed anywhere, as long as there is a chimney.
gas is released. It enters the secondary chamber. Secondary, heated air is supplied there. The gas ignites, releasing a large amount of heat.
Economical long-burning stoves heat the room as follows:
- infrared radiation from a hot body;
- warm air currents that pass through the convection jacket;
- distribution of thermal air into adjacent rooms through air ducts connected to the stove.
Today you can find equipment on sale that can service the DHW circuit and allow you to cook food. In the first case, the device is additionally equipped with a heat exchanger, in the second - with a frying surface.
Advantages and disadvantages of equipment
Economical long-burning stoves have received special attention from consumers due to a number of positive characteristics:
- The efficiency of the device can reach 80-85%;
- one stack of firewood burns for 8-10 hours;
- it is possible to purchase completely energy-independent models;
- modern devices are equipped with a combustion control function;
- multifunctionality;
- durability;
- ease of use;
- affordable price;
- depending on the power, you can heat a room with an area of 40 sq. m. - 500 sq. m.
There are also disadvantages:
- You can only use fuel with a low percentage of moisture content, up to 20%;
- condensation formation;
- non-compliance with the operating rules of the equipment leads to the formation of soot accumulations on the chimney, which makes it difficult to clean;
- regular chimney cleaning;
- condensation leaking onto the floor.
If you strictly follow the rules for operating the equipment specified in the instructions, using the stoves will not create much trouble.
How much time and money do you need to spend to make solid fuel heating boilers with your own hands at home?
What components are needed to install a solid fuel boiler for water heating? The answers are here.
Air duct routing
Such air ducts are temperature resistant and provide excellent thermal insulation.
On the other hand, a ducted air conditioner can use conventional ventilation ducts made of plastic.
How to install air ducts depends on the layout of the premises and the materials used. If space under the floor allows, then between the joists; if you plan to have a suspended ceiling, then above it. Drywall walls can also hide ductwork. The main line itself uses forced air injection, and circulation from top to bottom is possible. But the ventilation grilles, through which heated air enters the rooms, are located strictly below: only in this case will the air masses in the room be mixed by convective currents.
Warm air should be blown as close to the floor as possible
System Design Principles
When designing air heating systems, many important factors are taken into account. First of all, this is the heat demand of each individual room, as well as the heat loss for each room. Doors, windows, vents and other objects allow precious kilojoules of heat energy to escape.
The Buleryan stove is an economical heater option that can be used to organize air heating. A long-burning wood stove can also be an excellent solution.
The most important point is the presence of high-quality insulation of the building. If the house has plastic windows, good doors, and its facade is reliably insulated, there will be less heat loss, and heating costs can be significantly reduced. If we are talking about the reconstruction of a building, we should start with the design of insulation.
After the need for thermal energy and its costs are correlated, the power of the heating equipment is calculated and its type is selected. Then the hot air flow parameters are calculated. Special aerodynamic calculations are performed to calculate the required dimensions of the air ducts.
A diffuser grille is installed at the outlet of the air duct. Its size and configuration may affect the speed of air flow
You can preliminarily calculate the power of the equipment based on the following figures: for heating every 10 sq. meters of room you will need about 0.7-0.8 kW of heat. This is provided that the house is well insulated, otherwise more powerful equipment will be needed. But it is better to entrust complete design and detailed calculations to an experienced engineer.
Incorrect calculations can have a very bad effect on the state of the finished system. An unprofessionally designed air heating system is characterized by such problems as frequent equipment breakdowns, overheating of indoor air, overheating of equipment, drafts, and increased noise levels.
Simultaneously with designing an air heating system, it makes sense to think about the placement of stationary pieces of furniture in the house. Supply and exhaust grilles should be located in places away from the constant presence of people.
They also should not be hidden under cabinets, cabinets or other objects that impede the free movement of air masses.
In a multi-storey private house, it is recommended to place exhaust grilles in such a way that on the upper floors the cooled air is taken into the system from above, and on the lower floors - from below. This will ensure a more even distribution of heat throughout all rooms. Read more about how to correctly calculate air heating in this material.
Image gallery
Photo from
Inclined airflow direction
Scheme of operation of inclined warm air supply
Horizontal direction of heat supply
Vertical supply of warm air flow
Air gas heating
An example of air heating of a private house is a system equipped with a gas boiler. Such solutions have been actively used in Canada for a long time. It has repeatedly proven its effectiveness and its advantages over classic water heating with heated floors. This heating consists of the following components:
- gas air boiler with integrated volute fan;
- a system of supply ducts distributed around the perimeter of the building with uniform spacing;
- a system of return air ducts through which cooled air is drawn back into the boiler for heating.
Simultaneously with heating, ventilation of the premises is carried out by mixing indoor air with outdoor air. This type of heating is highly efficient and economical. The main property of heated air is that it independently spreads throughout the space, uniformly increasing the temperature at all points.
Air source heat pump for home heating
The main task in an air heating system is to heat the air. An electric, gas and solid fuel boiler can cope with this work. Often it is impossible to supply gas, you don’t want to heat with wood, and electricity is very expensive, then an air source heat pump comes to the rescue for heating the house.
This is an innovative and very efficient equipment that uses natural resources to heat the air inside the building. This could be water, soil or ambient air.
There are several types of air source heat pumps, but the classic version is a standard split system. It consists of a heat pump and fan mounted outside and a heat exchanger located inside the building. The hot water boiler is either separate or integrated into the indoor unit. To heat water or warm the air inside a building, they take heat from the outside air or water. Any air heat pump has a high conversion efficiency, which differs by 5 times. For 1 kW of consumed electrical energy there is 5 kW of thermal energy.
Model range of boilers by Professor Butakov
- Gymnasium student, heating and cooking model, weight 49 kg, heat load 8 W, heating area up to 60 m2, cost up to 6800 rubles.
- Student, for private housing construction, weight 57 kg, heat load 9 kW, heating area up to 150 m2, cost up to 13,900 rubles.
- Engineer, for one-story houses and small household premises, weight 75 kg, heat load 15 kW, heating area up to 250 m2, cost up to 17,700 rubles.
- Associate Professor, for non-residential industrial premises, weight 143 kg, heat load 25 kW, allows you to heat an area of up to 500 m2, cost up to 28,000 rubles.
- Professor, for large residential and non-residential buildings, weight 57 kg, heat load 40 kW, heating area up to 1000 m2, cost up to 32,000 rubles.