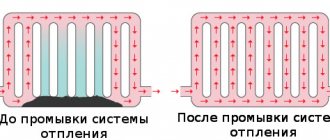
Replacing pipelines is far from a budget option for improving the functioning of the heating system. Timely flushing of the system makes it possible to get rid of contaminants inside the pipes, which cause a noticeable decrease in temperature during operation of heating equipment.
The stages of execution of work on flushing heating systems by special organizations are as follows:
- First of all, the condition of the structure is inspected. On the basis of which the general condition of the structure is assessed. The system is undergoing initial pressure testing. The working pressure cannot be higher than standard levels by 1.25 times. According to the norm, it cannot be higher than 2 atmospheres. This is necessary to ensure that no leaks occur during operation. This may lead to conflict with customer representatives. All leaks and identified deficiencies must be eliminated before starting work on flushing the heating radiators.
- Then they write an act for carrying out internal work during cleaning of the structures. Such work includes the complete dismantling of heating systems.
- Select the most effective and optimal technology for cleaning the structure. The hydropneumatic method of internal flushing of the heating battery is considered the most economical. This is done using a special pulp. In this case, a strong stream of water is formed, which flushes the heating radiators from the inside. Sometimes special equipment is used that is used to flush the battery. Some professionals use chemical cleaning agents. But this method is more aggressive and can damage the internal parts of the system.
In what cases is it compiled?
The act is required when:
- Commissioning of new equipment. The certificate will confirm that each element is in its place, the installation was carried out responsibly, and the system is working.
- The heating season is approaching. After a summer break in work, the pipes could fail. After checking their capacity, a report is drawn up.
- Already carried out repair work.
- The occurrence of contained emergency situations on the pipeline. In this way, specialists identify the amount of work required and the weak points of the existing heating network.
For the uninterrupted operation of the heating system, preventative control checks and reliable information about the quality functioning of the system upon startup are necessary.
Hydraulic test procedure
The procedure and rules for conducting hydraulic testing of the heating system are regulated by the following regulatory documents:
- SNiP 41-01-2003 “Heating, ventilation and air conditioning”;
- SNiP 3.05.01-85 “Internal sanitary systems”;
- Rules for the technical operation of thermal power plants, developed by the Ministry of Fuel and Energy of the Russian Federation, approved in 2003.
Important points in the hydropressing procedure
- Responsibility for conducting hydraulic testing lies with organizations that maintain and operate heating networks. In multi-apartment buildings - a management company, a utility service represented by specially trained and certified employees who have the necessary permits and certified equipment, or a representative of an energy supply company with appropriate authority. In administrative, social and industrial facilities - employees of the organization performing maintenance of such buildings. In private homes - a foreman, technician or engineer of an energy supply or specialized company.
- Testing of the heating system and thermal units must be carried out separately. Therefore, the circuit is disconnected from the heat source, expansion tank and main water supply line.
- The system should be filled with water having a temperature of no more than 45 0C. In this case, the test pressure must be ensured at the top point of the circuit, for which it is necessary to completely bleed air from it.
- The pressure rises in two stages: to standard operating pressure, which is recommended to be maintained for some time, but not less than 10 minutes, to inspect all elements for leaks; If there are no defects, its value is adjusted to the test value.
- The minimum pressure value during hydrotesting will depend on the standard operating indicator in each specific scheme (as a rule, it should exceed the operating value by 25-50%) and will be: - test pressure - 0.2 MPa; - when using cast iron radiators - 0.6 MPa; - when using convector or panel devices - 1.0 MPa; - for an elevator unit - 1.0 MPa.
- The tests are considered completed and the system is pressurized if:— within 5 minutes the pressure drop in the water circuits does not exceed 0.02 MPa;— after 15 minutes of testing the panel heating, the pressure decreased by no more than 0.01 MPa;— when checking strength and tightness of a polymer pipeline, the drop value within 30 minutes does not exceed 0.06 MPa;—there is no formation of “sweating” at the joints, seams, joints.
- The main document confirming the fact that a hydraulic test has been carried out in full compliance with the standards is a report, which must be correctly filled out and signed by authorized persons.
The essence and types of crimping
Nowadays heating is most often carried out by a “water circuit” system. In this case, heated water circulates through the pipes, imparting its thermal energy to the premises. Leaks are unacceptable; the pipeline must be completely sealed for normal operation. Pressure testing specifically creates a larger volume in the pipe than normal.
When this is done using air, it is called pneumatic pressing.
When using water, then hydropressing. The latter method is considered safer and therefore more popular. For this reason, an example of hydropressing is provided as a form.
When testing, it is recommended not to exceed the pressure inside the pipe more than 15 MPa. If we are talking about raising pressure with water, then there are limitations. The maximum possible pressure should not exceed the normal operating pressure by more than 30%.
In multi-storey buildings they resort to pneumatic pressure testing if the pipes are very old and there is a risk of flooding. But then there is a level of risk and all residents must be notified of the tests being carried out.
The work process is simple, but multi-stage. The algorithm looks like this:
- The necessary materials and equipment are being prepared.
- Draining the liquid that was previously in the heating system.
- Uploading a new one.
- Create the highest possible test pressure.
- Taking control measurements after 10 minutes.
- Flushing, adjusting the heating system to normal pressure levels inside.
- Documentation of work performed, generation of reports and acts.
But this is how the list of procedures looks only if there are no “thin spots” in the heating system and, accordingly, the tightness in it is not broken. If the pressure drops quickly and does not hold, then the system needs repair work. In such a situation, the specialist performs the necessary actions (replacing the pipe, sealing connections, cleaning, etc.), and then begins crimping from the very beginning. Only a heating system that has passed the test is allowed into the heating season.
Important nuance! Pressure testing should be carried out after cleaning and flushing the pipes. Otherwise, salt and other deposits inside them can mask possible external damage and breakthroughs.
If there are deposits of about 1 cm on the inner surface, then this reduces the overall heat transfer and efficiency by 15 percent or more of the overall indicators. To document the cleaning, a special report is also drawn up.
Chemical flushing of heating systems
In the process of chemical cleaning of elements of heating structures, the circuit is filled with reagents (an acid or alkali solution with inhibitors to prevent corrosion processes in pipelines) and their long-term circulation in the system is ensured (for more details: “Flushing a heating system in a private house - instructions and rules for flushing”).
Used compounds are disposed of, but since they are not allowed to be drained into the sewer (reagents can significantly shorten its service life), neutralization is first carried out by adding an alkaline solution to the acidic reagents and vice versa.
Chemical washing is effective in cleaning steel pipes from rust, as well as magnetic and calcium salts. As for siltation, then it is useless (about
Goals
Let's immediately separate the flies from the cutlets, so to speak.
- Testing and flushing of the yard water supply network is carried out as part of the transfer of the facility from the construction to the operating organization. , checked for leaks, cleaned of debris, foreign objects and disinfected.
Important: cold water supply is positioned as drinking water, which implies strict requirements for the composition of the water.
- If the throughput of the water supply system is significantly lower than the norm for a pipe of a given diameter, it needs mechanical cleaning or chemical washing with reagents that dissolve lime deposits and rust. The use of hydropneumatic flushing in this case, as a rule, does not bring any results.
Removing blockages
Dealing with cold water supply is very different from flushing a heating system or cleaning a sewer. The key difference is that the blockage cannot be destroyed by a stream of water or weak mechanical action: the pipes are overgrown with durable lime deposits and rust.
However: sometimes the initial cause of a blockage is sand or a piece of scale. If it is not removed immediately, after some time the blockage becomes cemented and can be destroyed with great difficulty.
Is it possible to do something with your own hands if the water pressure in a house with an old steel water supply has dropped catastrophically?
- Try plugging the faucet with your finger and simultaneously fully open the cold and hot water taps. DHW pressure is noticeably higher most of the year; the counterflow can destroy a fresh blockage, after which its fragments will be carried out by water into the sewer.
- If this does not help, repeat the operation by resetting the cold water riser. The pressure difference between the hot water supply and the empty riser will be significantly greater.
- Is the water still not flowing at normal pressure? Open the valve (with the riser down, of course). Debris deposits under the valve seat are a common problem with cast iron and, to a lesser extent, brass screw valves.
- Finally, if all else fails, try disassembling all available threaded connections and cleaning the pipe with a steel wire from the curtain rod, bending a hook the size of a pinhead at the end. On the second side of the string a handle is formed, resembling a well gate. The string is fed into the pipe with continuous rotation; after it passes the blockage, its remains are washed with water.
Tip: lime deposits dissolve well with acid solutions. It is enough to plug the pipe near the valve and fill it with the reagent for a couple of hours. As an active substance, you can use imported Cillit or, which is much better, a solution of dry oxalic acid: its price is several times lower with much greater chemical activity.
document
Download as .doc/.pdf Save this document in a convenient format. It's free.
Appendix 5 to Methodological recommendations for technical inspection of pipelines of heating networks of public heating systems
ACT FOR HYDRAULIC TESTING OF HEATING NETWORK PIPELINE DURING TECHNICAL INSPECTION (recommended form) ________________ "__" ____________ Object ___________________________________________________________ We, the undersigned _____________________________________________________ (name of organization (enterprise) ___________________________________________________________________ position, full name) have drawn up this act in that , that in the section from chamber N ______________ to chamber N ______________ of route ________________________________ (name of pipeline), a hydraulic test of the pipeline was carried out with test pressure _____________ MPa (kgf/sq. cm) for ________ minutes. followed by inspection at a pressure of __________ MPa (kgf/sq. cm). At the same time, it was discovered that ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ The pipeline was made according to the design ___________________________________ Drawings N __________________________________________________________ Conclusion ________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ The person who carried out the technical examination (the person responsible for the good condition and safe operation of the pipeline); representative of the State Supervision Authority; representative of a third-party organization ___________________________________ (full name, position) Representative of an organization operating heating networks ___________________________________ (full name, position)
Download as .doc/.pdfSave this document now. It will come in handy.
You found what you were looking for?
* By clicking on one of these buttons, you help form a rating of the usefulness of documents. Thank you!
Related documents
- Act: samples (Full list of documents)
- Search for the phrase “Act” throughout the site
- “Act for hydraulic testing of a heating network pipeline during a technical examination (recommended form).”doc
Documents that may also interest you:
- An act for documents, valuables and money found at the scene of an aircraft accident. Form N 5
- Act on delayed departure of aircraft
- Certificate for cleaning the pile (trench, vegetable storage). Specialized form N 14-OT
- Act on changing the quality of products. Specialized intradepartmental form N LP-7
- An act for the removal of components and parts containing precious metals from medical and other equipment products. Form N 42-MT
- Act on the exclusion of a universal container from the inventory belonging to the railway administration
- Act on geodetic, topographical and cartographic objects and works completed, accepted by the technical control department and handed over to the Fund by the enterprise
- Act on personal belongings, valuables, documents and awards of a deceased (deceased) serviceman of the civil defense forces (a serviceman or an employee of the state fire service of the Ministry of Emergency Situations of Russia, a citizen called up for military training, and a person discharged from military service (service))
- Act on personal belongings, valuables, documents and awards of a deceased (deceased) serviceman
- Act on personal belongings, valuables, documents and state (departmental) awards of a deceased (deceased) serviceman, citizen called up for military training
Personnel requirements
Important! It is allowed to independently check the heating equipment of a private home only.
All technological operations must be performed by trained personnel with established qualification tolerances, using certified equipment.
To do this, employees are required to undergo training (a special training course for six months) and certification of knowledge of the rules of operation of thermal installations and safety equipment (at least once every 3 years, and for personnel directly involved in testing, adjustment and maintenance of equipment - once every year).
After completing the training, an extract from the employee testing protocol is issued. It is provided for admission to personnel of the organization performing operation, maintenance and pressure testing of thermal installations.
Extract from the employee testing protocol.
The corresponding columns indicate:
- Full name of the employee;
- date of previous inspection;
- date of current inspection;
- Assessment of knowledge;
- employee signature;
- date of next certification;
- Full name of the members of the selection committee of 3 people (including the Rostechnadzor engineer) and their signatures.
The employee is issued a qualification certificate with stamps and marks indicating that he has been trained.
Certificate of admission to high-risk work.
The results of the training are displayed in the log of personal checks of the employee of the organization allowed to perform hydrostatic or manometric tests.
Journal of personal checks of an organization's employee.
How are hydropneumatic tests carried out?
In service organizations, all testing and flushing processes are carried out after the end of the heating season in order to have enough time before the next winter to carry out repair work. It is recommended that private owners follow the same principle. In the fall, after filling the system with water, it needs to be checked again so that no surprises arise during the cold season. The testing process is carried out in the following order:
- As soon as the heating season ends, you need to check the condition of shut-off valves, heating and elevator units, and pipeline risers in multi-story buildings.
- After this, the risers are washed to prevent seasonal contamination.
- After this, all other components and assemblies of the heating system are monitored for leaks. Identified deficiencies are eliminated, and damaged elements are replaced with new ones.
- In the basement, the thermal insulation of pipelines is monitored.
- Then test activities are carried out and the system is filled with coolant if everything is normal. The liquid can safely remain inside the system, waiting for the next season, because the pressure in it is much less than during testing.
During the preparatory work, all existing leaks must be eliminated.
The test procedure is as follows: the system is filled with coolant, after which a compressor is connected to it and it is pumped up to the test pressure level, which is prescribed in SNiP.
Manual compressor connected to the heating system
Special pumping equipment for pressurizing can be manual or electric. It has instrumentation that measures pressure. The pressure gauge has parameters and a scale that meets the necessary requirements.
The pressure gauge has parameters and a scale that meets the necessary requirements
For example, a pressure gauge with accuracy class 1.5 is used to monitor pressure. The diameter of its body must be no less than 160 mm, the division value should not be more than 0.1 kgf/cm2, which is 0.1 atmosphere or 0.01 mPa. The maximum measured value shall not be less than 4/3 of the pressure used during testing. It is worth noting that the pressure gauge, like any other measuring device, must be checked and sealed by the state metrological service.
The test pressure values, in accordance with the norms and regulations, on main pipes should be 16 kgf/cm2 (1.6 MPa)
This pressure is maintained for 5 minutes, after which it is reduced to working pressure and all components and parts of the system are inspected, paying special attention to the condition of the shut-off valves. The test is considered successful if no leaks, breakthroughs, or fogging of oil seals and flanges were detected.
At the initial start-up, intra-house wiring is tested at a pressure one and a half to two times higher than the working one, and on the old system the pressure is increased by 25 - 50%. The test pressure values also depend on the devices installed in the system. The indicators can be presented in table form:
Pressure indicators depending on installed equipment
When testing, the coolant temperature should be no more than 40 - 45 degrees. The room temperature should not be negative. Before starting work, air pockets and air from the system are completely removed.
Manual pressurization of the pressure system
Indicators at which the test is considered successful
Test pressure testing confirms the suitability of the system for operation subject to the following indicators:
- If the system is water or steam, then the pressure drop in a 5-minute time interval does not exceed 0.2 kgf/cm2 (0.02 mPa).
- When using panel heat exchangers, the pressure should not drop by more than 0.1 kgf/cm2 (0.01 mPa) within 15 minutes.
- When pressure testing a hot water supply system, this indicator should be less than 0.5 kgf/cm2 (0.05 mPa) in 10 minutes.
- Any leaks, fogging, or wetting must be completely excluded.
A decrease in the above indicators indicates a malfunction that should be identified and eliminated. To identify it, you need to check absolutely all devices and components of the system. It is especially worth looking inside ceilings, walls and other difficult areas.
After identifying faults and eliminating them, crimping is carried out in full again. Only when positive results are achieved, working pressure is created in the system and a pressure test report for the heating system begins to be drawn up.
Hydropneumatic tests
Flushing and pressure testing of the heating network are processes that are performed after the end of the heating season. Hydropneumatic tests are organized to confirm the readiness of the system for launch during the heating season. The easiest way to carry out the procedure is in the fall after the main line has been idle in the summer.
The preparation and testing proceeds step by step as follows:
- at the end of the heating season, check the condition of components, shut-off valves, pipelines and heating devices;
- preventive network flushing;
- elimination of leaks, depressurization of joints, replacement of worn-out equipment;
- visual assessment of the quality of insulation in open sections of the pipeline;
- carrying out hydropneumatic tests.
After checking, fill the system with coolant and leave until startup. If all checks are passed, the network is ready for operation; it will wait until the start of the heating season without loss of quality indicators. The tests are carried out under pressure higher than the working pressure, so the tightness due to the presence of coolant while waiting for the launch will not be compromised.
Hydropneumatic tests are carried out as follows:
- The technician will fill the network with coolant. Then connect a manual or electric pump. It will raise the pressure level to a certain standard - the limit values are prescribed in SNiP. Injection is performed using equipment with built-in instrumentation.
- After test measurements, the pressure decreases. If there are no defects, the system is considered suitable for continuous use.
Pressure control is carried out by pressure gauges with an accuracy class of 1.5, a division value of up to 0.1 kgf/cm2, and a body diameter of 160 mm. Untested pressure gauges without the seal of the state metrological organization are not allowed for use.
Indicators of pressure values during testing:
| Types of networks, types of equipment | Test pressure |
| Water heaters for heating networks, hot water supply, elevator units, air heaters | Limit of 1.25 of the working pressure, but not lower than 10 kgf/cm2 |
| Heating networks in multi-storey buildings with cast iron radiators or registers | Limit of 1.25 of the operating pressure, no more than 6 kgf/cm2 |
| Heating systems with radiators made of steel, bimetal, aluminum panel/convector type | Not lower than 10 kgf/cm2 |
| DHW system circuits | Based on the operating pressure plus 5 kgf/cm2, but not higher than 10 kgf/cm2 |
Conditions for confirming network readiness:
- in water/steam networks, during 5 minutes of testing, the pressure dropped by no more than 0.0.2 MPa;
- in a network with panel devices, the load indicator did not decrease by more than 0.01 mPa during 15 minutes of testing;
- in the DHW network, the permissible decrease is up to 0.05 mPa within 10 minutes of testing;
- there are no leaks, violations of the tightness of seams or joints.
If defects are detected, the technician repairs the leaks and then conducts tests again. The process is repeated until the requirements are met, then the pressure can be reduced to working pressure and a test report can be drawn up.