Greenhouse / Heating
Our country is huge and vast. There are many climatic conditions, so the presence of greenhouses and greenhouses in our gardens is a necessity, not a whim. If you want to get a rich harvest and not waste your energy, you need to know how to keep it warm.
- 1 Solar heating
- 2 Biological heating
- 3 Reducing heat loss
- 4 Heat accumulation using bottles and water containers
- 5 Frost protection
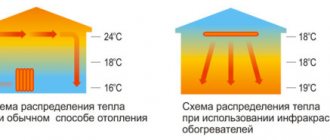
Infrared heaters
Infrared heating is ideal for greenhouses, as it is much more economical and efficient than cable heating, which until recently was considered the most reliable. The infrared heater has created worthy competition to the cable heater, heating not the air, but directly the objects inside the greenhouse.
Thanks to this type of heating, the development and growth of plants accelerates, and the crop ripens faster and pleases with its abundance.
Here are the main advantages of infrared heating:
- the entire area of the greenhouse is heated evenly;
- humidity is at the same level, the air does not dry out;
- thanks to infrared radiation, the occurrence of pathogenic fungi and bacteria in the greenhouse is inhibited;
- heat spreads from bottom to top, slowly heating the room;
- plant growth accelerates;
- dust does not circulate throughout the greenhouse;
- mobility and compactness of heaters. They do not occupy the useful space of the greenhouse, as they are installed on the ceiling covering and are easily mounted and dismantled without outside help;
- silent operation of heaters, which has a beneficial effect on both humans and plants.
Thanks to the mobility of infrared heaters, you can easily create different temperature zones in a greenhouse and grow types of vegetables with different heat needs in this room. This is achieved by raising or lowering the heaters. To grow seedlings, heaters are lowered lower to the ground so that the soil warms up faster, and when the seedlings grow, they are raised higher.
Infrared heaters are not afraid of condensation, so they can be safely used in greenhouses with high humidity.
The principle of operation of heaters is similar to natural heating by the sun - the soil is immediately heated, and then the surrounding air, which creates an atmosphere similar to the natural one. At the same time, the plants feel great, because the air does not dry out, and the heat is soft and not scalding. The temperature relay is mounted together with an infrared emitter; the minimum temperature on it does not fall below +5 degrees, which is very good for greenhouse conditions.
Infrared heaters come in different ranges of action. Older models have a flat radiation surface, while newer ones have a spherical one, which allows heat rays to dissipate in a range of 120 degrees, which improves and balances the heating of the greenhouse, and also saves half the energy. This happens because the soil itself is heated, not the air, and heat from the soil spreads throughout the greenhouse, rising upward
It is important that each heater is controlled by a thermostat, then the difference in temperature in the center and along the edges of the greenhouse will be very insignificant
To correctly calculate the intensity of an infrared heater, you need, for example, to take a greenhouse measuring 6x3 m. For such a greenhouse, two heaters 1.7 m long and with a power of 1000-1350 W will be sufficient, which will evenly heat the entire room. The main heating zone will be approximately 2.5 m in length and 3 m in width. For longer greenhouses of 8-9 m, three heaters will be needed.
Infrared heaters weigh very little, which is also one of their advantages. They are thinner and neater than their predecessors, easy to install, emit a very soft heat, favorable for plants, which gratefully respond to growing conditions with a healthy appearance, rapid growth and rich harvests, delivering to the dinner table an abundance of vitamins necessary for our body!
Thermos project – greenhouses
When building this greenhouse with your own hands, you need to go through several stages step by step.
- Perform preliminary design. That is, they draw up a drawing and design of a winter greenhouse with their own hands. They calculate how many building materials and fittings will be needed for its construction.
- Construction of a pit, which must be at least two meters deep. At the same time, its bottom and walls are leveled. Afterwards the foundation is poured. For this purpose, concrete or concrete blocks are used. This stage is considered very important, since it is the foundation that is responsible for the thermal insulation of the greenhouse. In order to pour concrete, it is necessary to install wooden formwork.
- Construction of walls from thermal blocks. The load-bearing part is reinforced concrete. An expanded polystyrene layer and thermal insulation blocks are placed inside. Fixing with each other occurs with cement mortar.
Read also: How to make a greenhouse from plastic pipes with your own hands You can find any ready-made greenhouse in gardening stores, but it does not always meet people’s wishes. By this…
Important! It is worth especially carefully choosing the location on the site where the greenhouse will be installed. The water inside the soil should be far from the surface.
Scheme for the construction of a “thermos” greenhouse:
- Foil is installed on the inner surface of the walls, which serves as a light reflector. It is best to lay it out in a couple of layers or use polystyrene foam with a reflective surface for this.
- At this stage, the required number of holes is drilled in metal profiles or wooden beams and beams. They begin to build her skeleton.
- Installation of polycarbonate leaves or polyethylene. For the construction of the outer side of the roof, only polycarbonate sheets are used, otherwise it may simply collapse.
- We install a convenient passage inside the winter greenhouse, which is best built in the form of a vestibule.
- Sealing from the inside. To do this, use plaster or polyurethane foam.
| Process | How many materials are needed? |
| Formwork. Install stakes, the distance between them is 30 centimeters. | Along the perimeter of the pit |
| Making a “pillow”, a mixture of sand and crushed stone | 1*1, such as a bag of sand and a bag of crushed stone |
| Making a frame from reinforcement | 4–6 rods around the perimeter |
| Foundation mortar | Crushed stone, sand, cement (3*5*1) |
| Greenhouse wall | Must exceed ground level by at least 0.5 meters. |
Biological heating of a greenhouse using biofuel
The essence of biological heating of a greenhouse is that aerobic bacteria that decompose organic materials (manure, sawdust, garbage) when exposed to air, release heat in an amount sufficient for heating.
Biofuel is any organic material that can be consumed by microorganisms, releasing thermal energy. The temperature of biofuel can reach +72°C, therefore the process of decomposition of biofuel with the release of heat is called combustion. Hot biofuel is used in greenhouses to maintain temperatures at an optimal level for plants.
Horse manure is the best biofuel for heating a greenhouse
The following are used as biofuels:
- animal manure mixed with loosening materials (straw, sawdust, peat, leaves), see Table 2
- waste from wood processing enterprises (bark, shavings, sawdust, chips), see Table 3,
- urban waste consisting of organic waste, see Table 3.
Table 2. Characteristics of manure as a biofuel for greenhouse heating
| Characteristics of biofuel | Manure | |||
| Horse | Bovine | Pork | Sheep | |
| Weight 1m3, kg | 350-450 | 400-500 | 400-500 | 550-700 |
| Acidity, pH | 8-9 | 6-7 | 7-8 | 6-7 |
| Humidity, % | 65-70 | 75-80 | 65-67 | 73-77 |
| Max. stack temperature, °C | 60-72 | 40-52 | 55-60 | 20-30 |
| Interruption period, days | 7-9 | 18-20 | 9-10 | 20-30 |
| Avg. temperature, °C | 33-38 | 12-20 | 30-35 | 14-16 |
| Burning duration, days | 70-90 | 75-100 | 90-120 | 60-70 |
Table 3. Characteristics of household waste as biofuel for heating a greenhouse
| Characteristics of biofuel | Household waste | |||
| Sawdust | Bark | Household waste | Compost from garbage | |
| Weight 1m3, kg | 150-200 | 400-500 | 700-750 | 650-750 |
| Acidity, pH | 5-6 | 5-7 | 7-9 | 7-8 |
| Humidity, % | 30-40 | 60-75 | 35-60 | up to 50 |
| Max. stack temperature, °C | 30-40 | 40-50 | 60-65 | 50-60 |
| Interruption period, days | 20-25 | 10-15 | 10-12 | 5-7 |
| Avg. temperature, °C | 15-20 | 20-25 | 36-48 | 30-35 |
| Burning duration, days | 40-60 | 100-120 | 80-100 | 120-180 |
Read more about the characteristics of biofuels in the article: Manure and straw; wonderful greenhouse! Biofuel for heating a greenhouse
If it is necessary to protect biofuel from combustion, it is placed in a stack and compacted. In a compacted state, biofuel will not burn or will burn weakly.
To heat the biofuel, it is crushed and loosely placed in a stack; hot stones or burning coal are placed inside the stack. After 3–5 days, the biofuel begins to burn and can be used to heat the greenhouse.
Biofuel heats up well in the presence of nitrogenous nutrients. Therefore, sawdust is watered with slurry or animal urine. Mixing manure with wood waste has a good effect. Active activity of microorganisms is possible with sufficient moisture content. Therefore, biofuel is humidified if necessary.
The temperature of the biofuel reaches its maximum a week after heating and then begins to decrease. The heat generation continues for 2-3 months, gradually fading.
Heating a greenhouse with biological waste helps to utilize it, rationally using the energy stored in biofuel, and also improves the air-gas environment in the greenhouse by releasing large amounts of carbon dioxide, which plants need for photosynthesis.
Spent biofuel is suitable as an organic fertilizer both in greenhouses and open ground.
Biofuel stacking. Hot biofuel is placed loosely in the greenhouse, evenly distributed over the area and slightly compacted with a pitchfork. Fertile soil is poured onto the biofuel in a layer of 15–18 cm for growing seedlings; if seedlings are grown in pots, then the soil layer is reduced to 7–8 cm. When growing vegetable plants, the thickness of the soil layer should be increased to 20 cm.
Sowing and planting of plants begins after the soil has warmed to the optimal temperature.
The disadvantage of biological heating is that it is impossible to control the thermal regime if it is necessary to raise the temperature to the required level.
Heating the soil in a greenhouse with a heating cable
The use of a heating cable is a relatively new way of heating greenhouses in the spring and works on the principle of a “warm floor”. A heating cable has one or more heating elements that produce heat when electric current passes through them.
The advantages of the method of heating the ground in a greenhouse with a cable include:
- safety - they are protected from overheating even when they get exposed to leaves, soil and debris;
- Ease of Management;
- efficiency – expressed in low energy consumption;
- minimal installation costs;
- ease of installation in a greenhouse - does not require its re-equipment;
- independence from weather conditions - a self-regulating cable automatically controls the soil temperature and distributes it evenly throughout the entire planting area.
Installation of the heating cable is quite simple and even a novice gardener can do it:
- The soil is removed in a small layer and sand is poured as a base.
- Lay out a thermal insulation coating, for example, foamed polystyrene, which has a low moisture absorption coefficient. This will reduce heat loss.
- Distribute the sand in a layer of 5 cm. Water it with water and compact it thoroughly.
- Lay the heating cable, fixing it with mounting tape.
- Sand is poured on top in the same layer and watered, preventing the formation of air bubbles.
- The structure is covered with a metal mesh or perforated asbestos cement sheet. This will protect the heating cable from damage when processing the soil with garden tools.
- The top layer is filled with fertile substrate in a layer of 30–40 cm.
A greenhouse using a cable for heating the ground allows you to achieve better results in growing plants and vegetables, compared to conventional conditions, thanks to the following distinctive features:
- eliminates the risk of soil freezing;
- earlier planting of seedlings is possible;
- the harvest period is extended;
- crop growth is accelerated due to soil heating;
- in case of unfavorable weather conditions, optimal conditions for harvesting are maintained;
- self-heating cable allows you to germinate any seeds in a short time;
- temperature control creates favorable conditions for growing heat-loving crops even in Siberia and the north.
Important!
The temperature at the root level in the greenhouse should be 15 - 25 0C. To avoid overheating of the root system, the power of the heating cable should not exceed 20 W/m. When calculating the area for heating the soil in a greenhouse, it is necessary to take into account only the size of the beds. The ground under the paths does not need heating. The use of a heating cable is a convenient and practical solution to the issue of heating fertile soil in the spring.
Option 3 heating with gas
The main advantage of gas is that it is more stable in terms of supply, but the final cost of products from the greenhouse can surprise. Therefore, if heating a greenhouse with gas in winter lasts only a few weeks, then it is not necessary to pull it from a residential building and purchase expensive pipes for this. It will be enough to take a couple of cylinders for this purpose - they will last for a long time.
It is only important to remember that excess carbon dioxide can negatively affect the condition of plants, and therefore such a greenhouse must be well ventilated. And to remove combustion waste, it is necessary to use an exhaust device so that a constant flow of oxygen into the greenhouse is ensured
And so that the lack of oxygen does not lead to the cessation of the combustion process and the release of gas into the air, it is advisable to use heating devices with an automatic protective device - the sensors will immediately operate as soon as the gas supply to the burner stops.
Heating a greenhouse means increasing its efficiency
But for early or year-round use of a greenhouse, heating is needed, because there are severe frosts outside in winter, and in early spring, sub-zero air temperatures are not uncommon. And then the question arises of which heating to choose, which is personally acceptable for your household, because any of them requires a financial investment. Here you need to figure out what you have enough money for and which heating will be less expensive to maintain. In addition, it is necessary to take into account the durability and efficiency of the selected type of heating.
Heating a greenhouse is the most important part of the microclimate in the life of plants, as is watering. It is advisable to think about what it will be like before construction begins. It’s better to do it right away, as it should be, so as not to have to redo it later. Let's consider different heating methods, the pros and cons of the selected options and choose what is most convenient and least expensive.
Heating a greenhouse with water heating
When growing a large volume of commercial products, when there is economic benefit, it is advisable to use water heating in the greenhouse.
Water heating in the greenhouse allows the structure to be used all year round, supplemented with sodium lamps to compensate for the short duration of daylight hours.
The hot water boiler is selected based on the area of the greenhouse and the volume of air in the room, and then installed in the vestibule so that flue gases do not enter the greenhouse. Heating pipes are located longitudinally, along walls, under shelving, under the roof, etc.
The hot water boiler for the greenhouse is selected according to the size of the structure
Heating pipes can pass under a layer of nutrient soil, for example, in pit-type greenhouses. A layer of sand 10 cm thick is poured onto the bottom of the pit, and pipes for hot water are laid on it. They are covered with 10–15 cm of sand on top, and a 25 cm layer of nutritious soil is poured onto the sand.
What can you grow in an unheated greenhouse in winter?
A permanent greenhouse made of polycarbonate allows you to not interrupt the growing process even in the coldest time. You need to choose what can be planted in a greenhouse for the winter based on considerations of economic feasibility, personal preferences and ability to properly care for it. It is important to study the needs of the plants, recommendations for reliable operation and possible difficulties. With the right approach and investment of certain funds, it is not difficult to even organize your own business.
Advantages and disadvantages of winter planting
For the winter, seeds of frost-resistant crops are planted in open ground, capable of withstanding the harsh climate of the cold period without damage. A positive aspect of winter planting is the shift in the beginning of the growing season to an earlier time, which speeds up the possibility of harvesting by two to three weeks.
The seeds undergo stratification at a low temperature and are hardened, the seedlings are disease-resistant and strong, with powerful roots, and are less damaged by pests. The yield of such plants in a greenhouse in winter is usually much higher.
But there is always a threat of complete or partial death of seedlings if the weather is unstable with prolonged warming, which contributes to their premature development. Insufficient snow cover may not cope with the protective functions. During winter planting, you have to spend more seeds, since their germination rate is lower.
This can be avoided if you sow the necessary crops for seedlings or greens in a greenhouse in the fall. Even without heating the room, plants have a chance to receive some protection from strong temperature changes, flooding with melt water followed by freezing, and strong winds. When there is a sharp cold snap in winter, it is advisable to additionally cover the plants.
Greenhouse crops at different times of the year
In the spring and summer, polycarbonate greenhouses are used for the most capricious southern crops that are unable to ripen in the local climate, as well as for growing planting material for open ground. In winter, you can plant plants that are more adapted to the lack of light and heat, which will allow you to grow vitamin-rich fruits or greens without damage.
Examples of plant selection
What can you plant in a greenhouse for your family in winter? The main vegetables for all-season greenhouses are cucumbers, zucchini, and tomatoes. Eggplants and peppers are more demanding of external conditions and difficult to care for. Not every greenhouse is suitable for growing them. A variety of greens (onions, dill, parsley) are grown en masse in winter, even in unheated rooms.
Unheated underground greenhouse
Before winter, you can plant popular root vegetables in a greenhouse - beets, radishes or carrots, but you should choose the most cold-resistant and early-ripening varieties. It is advisable to fill the greenhouse with several types of plants with similar conditions.
Flower lovers can grow suitable varieties of roses, chrysanthemums, asters, lilies, crocuses and other flowering species. It is also worth sowing vegetable and ornamental crops as seedlings for open ground in free areas so as not to clutter the window sills in the house.
What should a winter greenhouse be like?
The greenhouse must have a strong and stable frame, be located on an elevated area or on the south side of the house (outbuilding). It is advisable to deepen the foundation by about 0.8 m and additionally insulate it from the outside. A greenhouse for winter should be well lit by the sun and have a system of protection against flooding by groundwater and melt water.
In winter, trouble-free heating systems (water, electric or air), ventilation and irrigation (better than drip - saves water consumption) are important. You also cannot do without installing additional lighting devices (preferably LED). It is advisable to use vertical adjustment of the position of the lamps.
In the most severe frosts, the air temperature in the room should not fall below +15 °C, and during most of the time it should be within +20-25 °C.
What to sow in a greenhouse for the winter
Before planting vegetables or other crops in an unheated greenhouse, you need to find out the necessary microclimate parameters to maintain a specific plant, because the temperature in such a room is low. Conditions in a heated greenhouse vary depending on its design and equipment, and the climate of the region. After all, heating devices have a limited resource, which is also affected by the cost of energy.
Soils for greenhouses and greenhouses
In greenhouses and greenhouses, root nutrition conditions differ from the nutrition conditions in open ground. Frequent and abundant watering contributes to the leaching of nutrients, and repeated fertilizing contributes to the accumulation of ballast formations in the soil. These features require the creation of special soils that can provide favorable conditions for plants.
Soils for a greenhouse must have:
- fertility,
- good air and water permeability,
- be loose
- have good moisture capacity and retain nutrients well.
For greenhouses, the best soils are those that have a neutral environment, in which the ratio between solid, liquid and gaseous phases is 1:1:1. This means that they contain a large amount of loosening materials.
The main components for creating soils are lowland peat, turf and field soils, manure humus, old (spent) greenhouse soil, sand:
- lowland peat of weak or medium degree of decomposition - 75% + turfy medium loamy soil - 25%;
- lowland peat 60% + turf soil 20% + manure 20%;
- field medium or light loamy soil 50% + manure humus 30% + lowland peat 20%;
- turfy medium loamy soil 50% + old greenhouse soil (2 years after use) soil 50%;
- chernozem soil 80% + humus 20%; lowland peat 70% + manure humus 20% + sand 10%.
Materials intended for greenhouse soils are passed through a screen and mixed well.
A good component for soil soils are composts and leaf soil, for the preparation of which leaves that have fallen from trees are placed in a wooden box in the fall and watered with water, slurry or urine. Within 2–3 months, the leaves decompose and turn into an earthy mass; it is passed through a screen and added to the soil (up to 30% of the total volume).
Composts from waste from wood processing plants (shavings, sawdust, bark, small chips) can be added to soils as a loosening material. When composting, 44 grams of urea and 15 grams of superphosphate are added to a bucket of fresh waste, mixed thoroughly, moistened and placed in a stack or heap for 2-3 months. Ready compost can be added to peat soil (up to 30%).
The layer of soil for growing plants in a greenhouse should be 25 cm, or 0.25 m3 per 1 m2 of useful area of the greenhouse.
In film greenhouses, where plants are grown on natural soil, manure (15–20 kg/m2) or lowland peat (20–25 kg/m2) is added if the soil is light; for soils of heavy mechanical composition, add another 10–15 kg of composted wood-based materials or sand - a bucket per 1 m2.
Mineral fertilizers are also added to the greenhouse soil:
- ammonium nitrate 60–90 g/m2;
- superphosphate - 30–40 g/m2;
- potassium chloride - 10–15 g/m2.
In the fall, after applying fertilizers and loosening materials, the soil is dug up to a depth of 25 cm so that the organic fertilizers and loosening material begin to decompose, and the pests that have prepared for the winter die.
How to choose a location for a greenhouse
If possible, choose a place for the greenhouse that is windless and preferably on a hill - this will to some extent serve as an additional source of heating (in this case, solar). If there is no natural elevation, then artificial embankments are often made. The foundation is not very deep: 50-70 cm. In addition, the greenhouse is equipped with special windows for ventilation.
If the greenhouse will be exposed to the open sun all day, care must also be taken to cover it with a special mesh or blinds in order to prevent some sensitive plants from excessive light and overheating. This shelter should be easy to raise and lower when necessary.
Recommendations
When choosing an IR heater, it is important to pay attention to its power. Devices should be selected taking into account the size of the room. Usually, to heat 10 m2, a device with a power of 1000 W is required, but it is better to purchase units with a reserve
If a wall-mounted heater is selected, it is important to find out the thickness of the foil layer of the emitter. Its indicators must be at least 120 microns. Otherwise, a significant part of the energy will be spent on heating the ceiling
Usually, to heat 10 m2, a device with a power of 1000 W is required, but it is better to purchase units with a reserve
If a wall-mounted heater is selected, it is important to find out the thickness of the foil layer of the emitter. Its indicators must be at least 120 microns
Otherwise, a significant part of the energy will be spent on heating the ceiling.
Manufacturers produce heater models with various functions. You need to think in advance whether they will be used during operation, otherwise there is a high risk of overpaying for something that will not be useful in the future.
Devices may have the following options:
- regulation of temperature parameters;
- automatic shutdown of the device when it is turned over (mobile variations);
- shutdown of equipment in case of possible overheating;
- turning the unit on or off at the right time.
Before purchasing a device, you should carefully inspect its case. It can be made of steel or aluminum. The first options are more durable, the second – stylish design. There should be no traces of mechanical stress or rust on any of the housings. Corrosion can reduce the service life of the device declared by the manufacturer.
Which heater is best for a particular greenhouse?
The choice of device is based on a number of factors, for example:
- Heated area. First you need to decide what size the greenhouse or greenhouse will be. Based on this, purchase a stationary or mobile device.
- Considering all the parameters of the room, choose the power. If one of these two parameters is calculated incorrectly, you may not get the desired effect.
- Type of instalation. Not all devices may meet your needs. This refers to the type of fastening. It may be more convenient to mount the model on the ceiling, but the selected model will not have such a mount.
- Safety. Of course, this parameter is one of the most significant. It is necessary that the model has an automatic fuse against electric shock to a person, against overheating, as well as protection against moisture.
As for the type: IR, convector or soil heaters, this is a purely personal opinion. But the latter type is definitely better suited for a small greenhouse. In terms of energy consumption, IR wins. It is considered the most modern device, which in its basic indicators surpasses all others.
You can purchase the devices we are considering at any specialized store, as well as order them through an online store.
Possibilities of a heated greenhouse
A heated greenhouse has greater capabilities than a conventional structure not equipped with such a system. Using a heated room for growing herbs, berries, fruits or vegetables, the grower will be able to obtain harvests throughout the year (subject to the installation of a lighting system). In a heated greenhouse, optimal temperature and humidity levels are maintained, despite frost. Thanks to the creation of an artificial microclimate, it is possible to increase the percentage of seed germination, protect seedlings from various fungal diseases, and also harvest crops earlier than others.
By heating the greenhouse, you can obtain berries and vegetables throughout the year, collecting them several times. Thanks to a greenhouse, it is possible to create a winter garden or flower greenhouse in the cold season, increase the flowering time of crops, or grow exotic plants that are not adapted to the local climate. The above factors can significantly increase the profitability of the site and increase revenue if the greenhouse is used to grow plants for sale.
Convectors will also work
You can heat the greenhouse with electric convectors. They are installed on the walls of the structure and on the floor. Convectors heat the air well, they have timers that can be set to a certain temperature, and they will turn on and off themselves. One drawback is that they are quite energy-consuming, and electricity is now expensive.
How can I heat
In early spring, greenhouses can be heated in several ways, the choice of which will primarily depend on the purpose of the room. If you plan to heat a small building in which you grow vegetables for yourself, there is no point in purchasing expensive industrial installations. In this case, various stoves or boilers are suitable.
Stove heating in greenhouses was used 20-25 years ago, but it is still relevant today. For these purposes, gardeners and gardeners use specialized boilers or barbecues designed to maintain optimal temperatures. When using stoves, heat is generated by burning fuel. The advantages of such a system are its simplicity and low cost of maintaining the temperature, while its disadvantages are low productivity and labor-intensive operation.
Heating of large polycarbonate greenhouses can be done using water or electric heating. In the first systems, it is necessary to use boilers, pumps and pipelines through which the hot coolant will move. With water heating, heat is generated by burning gas or using electric current.
Electric heating involves the use of electrical appliances to heat the air in the greenhouse.
Heating using cables. The principle of operation of such a system is simple: the heat cable is installed under the ground (similar to the installation of a heated floor) and connected to power sources. When turned on, it will heat the soil, and from it the heat will spread throughout the room. The system is economical and efficient. Most often it is used in greenhouses for growing plants in early spring or late autumn. This heating method is ineffective for heating a room in the winter.
Year-round greenhouses can be heated using gas systems. For these purposes, summer residents and gardeners often use catalyst burners connected either to the main gas pipeline or to household cylinders. Gas heating is suitable for warming up both large and small-sized greenhouses in the winter. The best heating systems are those that use infrared (IR) heaters. They have many advantages compared to other heating options.
The principle of operation of IR devices is similar to the effect of sunlight on plants. The equipment emits heat, which is absorbed by surrounding objects and subsequently transferred to the air. Depending on the type of installation, the room can be heated from above or below. Some growers organize high-quality heating from all sides. However, this heating method is one of the most expensive.
Often, heaters are placed on the ceiling surface above the beds. The weight of one device is relatively small - its weight does not exceed 5 kg. Most modern greenhouses allow you to place any number of such units. Installation of IR equipment is not complicated, so installation can be done with your own hands without the involvement of hired craftsmen.
Choosing materials for the greenhouse
The frame of a winter greenhouse can be made of wood or metal. The first one is cheaper, but it is less durable and not as strong, despite all sorts of modern impregnations that can be used to coat it. Although metal is more expensive, it can withstand heavy loads and can last for quite a long time.
It is best to use
cellular polycarbonate for coating, since it has high thermal insulation and transmits light well. True, its transparency decreases over time, but over the course of 6-7 years it demonstrates fairly high light transmittance. In addition, polycarbonate is durable and, at the same time, lightweight.
It is very convenient to cut and install on the frame. Of course, glass is much more transparent, but its main drawback is its fragility. In addition, it is a rather heavy material. For a winter greenhouse, glass is not the best option, since in especially snowy times it may not withstand the snow cover and simply crumble under its weight. However, if there is no particular choice, then you can use a glass roof, but it must be installed at a sharp slope to avoid snow accumulation. In addition, when building a greenhouse, you can resort to different combinations, for example, making the walls glass and the roof made of film or polycarbonate.
Cable heater
This heater consists of a cable in special polypropylene insulation, braided armor made of galvanized steel wire and a special sheath. Cable diameter is 6 mm, bending radius is 35 mm.
The main advantages of a cable heater are:
- relatively easy installation;
- acceleration of plant growth;
- extension of the growing season of vegetable crops;
- increasing the number of plant species grown;
- a bountiful harvest;
- possibility of regulating soil heating.
Typically, with cable heating, the electricity consumption is 75-100 W/sq.m. Special thermostats are designed to regulate the temperature.
The optimal temperature for soil is 15-25 degrees, and for seedlings in peat pots - 30 degrees. When heating the soil with an electric cable, the heating element itself is also located in the soil or under the ground in an asphalt concrete monolith. When heating air, heating elements are suspended in a special way, and then voltage is applied to them. Heating elements can be hidden in pipes, which perfectly protect them from various damage and moisture. True, you will need a lot of such pipes.
The safest cable batteries are made in the form of an asphalt concrete sheet or asphalt expanded clay concrete slab. They have excellent accumulation properties and warm the soil much more evenly. And most importantly, they are absolutely electrically safe.
Most energy efficient design
An excellent solution is a “thermos”. She is endowed with a huge number of positive qualities. The main thing is significant savings and heat conservation.
It operates 12 months a year. It is not afraid of frosts and northern winds, and is capable of supplying not only food, but also becoming a source of income. She has the following positive qualities:
- Fresh vegetables will delight you all year round.
- Works in any climate.
- Excellently transmits sunlight, distributing it evenly over the entire area.
- When high-quality insulation is used in construction, the sun's energy is converted into heat and can be retained for a fairly long period of time.
- Savings on utility bills.
- Thanks to its design, you can grow vegetables, perennials and exotic fruits, grape bushes.
Important! “Thermos” - almost everything is in the ground, but there is no shortage of lighting in it. Thanks to the huge window openings there is always a lot of light inside.
Advantages and disadvantages
Every year, an increasing number of plant growers refuse to use outdated systems for heating cold greenhouses. Today, it is rare for anyone to heat their premises using “stove stoves”, fan heaters or boilers using coal or wood fuel. All these methods are becoming a thing of the past, since they have a significant drawback. These systems heat the air, which, according to the laws of physics, tends to rise, leaving the crops being grown cool.
Infrared heaters have been able to solve this and many problems of heating a room once and for all.
Compared to other systems, they have a number of advantages.
- Optimally distributes heat around the entire perimeter. Most types of thermal devices presented on the modern market cannot boast of this effect.
- Quick heating of the room. The spread of heat is felt already in the first minute after turning on the device. The devices operate in a directional manner, making it possible to evenly heat a specific area. Due to this feature, heat-loving plants and crops for which thermal energy is not so important can be grown in one greenhouse.
- Economical consumption of electrical energy. With proper installation of equipment, it is possible to achieve energy savings of up to 40%.
- Elimination of drafts and movement of warm air currents, which not all plants like.
- Silent operation of devices.
- Elimination of “burning” of oxygen in the air. Thanks to this feature, optimal humidity is maintained indoors. This is one of the most important conditions for good growth and fruiting of plants.
- Durability of devices and their uninterrupted operation. The fact is that IR equipment does not include moving mechanisms and rubbing parts that need frequent replacement.
- Small dimensions and weight of the units, making them easy to transport and install.
Unfortunately, no heating equipment is without drawbacks. Infrared heaters also have disadvantages. These include the high cost of organizing an infrared heating system and the low fire safety of some models (mainly mobile units). In addition, there are counterfeits of equipment from well-known brands on the market, which is why the buyer runs the risk of purchasing a low-quality product.
Gas, oil and primitive types of heaters
To choose the right heater for a greenhouse, you need to immediately determine what exactly will be grown in it, what size the greenhouse is, its thermal conductivity, and in what season the heating will take place.
If the seedlings in the greenhouse are freezing, it may be enough to install a few lit candles. Another thing is a greenhouse 2.5 meters high and an area of 20 sq.m. For such a greenhouse, completely different dimensions of the heater are required. Without heating, the greenhouse can withstand temperatures down to -1 degree, and below that, additional heating is already necessary. For this purpose, you can use fan heaters equipped with a timer, in which you can specifically regulate the duration and power of operation, as well as automatic shutdown.
The advantage of fan heaters is its ability to quickly heat the air, but the disadvantage is the unevenness of the heat supplied and drying of the heated air.
The worst of all greenhouse heaters is the gas heater. It consists of a gas pipeline and a gas control system. The heat generator heats the air and transfers it to the greenhouse. The disadvantage of this heater is also that the air in the greenhouse dries out, which is detrimental to the plants.
Sometimes oil heaters are used in greenhouses, which is very irrational. They consume too much electricity, which, if used for a long time, will not be repaid by any yields. In addition, such heaters take up too much space and are not protected from condensation.
This applies to all electric heaters connected to the network. The slightest short circuit and a fire cannot be avoided. If dew falls in the greenhouse, it will settle on all surfaces, including the outlet. If a drop hits the current line, a short circuit may occur. It's good if the fuse blows. In the worst case, the socket can catch fire when the owners are not at home
Therefore, all precautions must be taken to prevent this from happening. The outlet should be outside the greenhouse, preferably inside the house, it should be sealed so that water cannot get into it
The heater should not be left on if no one will be at the dacha for a long time. For the heater, it would be a good idea to install a circuit breaker with a small power reserve, so that in the event of a short circuit it will turn off the voltage. A 500-watt heater requires a 3-amp circuit breaker that can operate with a current leak of 0.03 amperes.
Battery heater
The best option for heating a greenhouse is an autonomous heater, which has its own energy source that does not depend on external factors, such as power outages or power outages. You can build it yourself by converting it from a car battery and adding smoldering peat to it.
The car battery has 55Ah, and the entire greenhouse requires at least 500 watts. Therefore, experienced gardeners came up with the idea of using a battery in pulse mode, which operates as follows: using a clock mechanism, the burning is turned on, the spiral burns out and the contact breaks, after which the tinder in the peat is ignited. After some time, the next spiral is connected. This mode saves battery power, which will last for a whole week or even more.
Samopal
The simplest and most primitive way to heat a greenhouse is “homemade”. It works as follows: garbage is burned in the stove, in which two bricks and a bucket of water are heated. In the evening, in the greenhouse, a bucket of water is placed on a wooden stand, and hot bricks are placed on a sheet of iron.
Some gardeners use candles, which are placed in the middle of the greenhouse along the path and set on fire. This is an ineffective heating method, but it looks very nice.
How can you heat a polycarbonate greenhouse in early spring?
There are many ways to heat a greenhouse in the spring. They differ in degree of complexity, efficiency and cost and are divided into basic and auxiliary. The main heating methods include:
- Solar. Does not require additional costs and is based on the greenhouse effect. This method is effective only during periods of solar activity. Polycarbonate is able to retain light, thus increasing the temperature inside the greenhouse. But in case of frost, the soil and plant roots will be unprotected.
- Biological. It consists of heating the soil by adding biofuel. Most often, gardeners use bird and animal manure mixed with peat, straw, sawdust or bark. You can use a solution made from slaked lime, straw and superphosphate. This method is quite labor-intensive and does not allow timely control of soil temperature.
- Technical. Involves the use of various electric heating devices and devices - electric heaters, heat guns, radiators. When operating a greenhouse only in spring, there is no need to install expensive and complex heating devices.
These and other methods allow you to heat the greenhouse in the spring with your own hands. They have both their positive sides and disadvantages, which must be taken into account in order to make the right decision in choosing a specific type of heating for a polycarbonate greenhouse.
Types of infrared heaters
Infrared heaters of the following types:
- light;
- long wave.
In IR light heaters, the surface heats up to 600 degrees. This equipment is suitable for very large greenhouses. Long-wave devices heat up much less and are better suited for small greenhouses.
Infrared devices can operate from:
- electricity;
- gas;
- liquid fuel.
Infrared heaters for greenhouses are able to heat a greenhouse with an area of 18 square meters. m. When operating on gas, only two cylinders of liquefied gas are consumed during the winter.
The shape of such heating devices is different. They are produced in the form:
- lamps;
- film (tape) panels.
Option #1 – solar batteries
It is possible to heat the greenhouse using solar heat accumulators. First, they dig a 15 cm hole in the greenhouse and cover the ground with a layer of thermal insulation, possibly polystyrene. A layer of plastic film is placed on top for waterproofing.
Then coarse wet sand is placed on top and the whole thing is covered with excavated soil. This simple device allows, using the accumulated energy of the sun, to maintain a satisfactory temperature in the greenhouse even at a temperature of -10°C.
Greenhouse boron heating
Bore heating of the greenhouse is carried out by hot flue gases coming from the brick oven through the hog on the way to the chimney. Essentially, the hog is the beginning of the chimney, located almost horizontally along the greenhouse.
When hot gases pass through the chimney, heat is accumulated by the walls of the hog and then, when cooled slowly, heats the greenhouse.
The stove is installed in the end part of the greenhouse so that the combustion door opens into the vestibule, and the stove itself is located in the greenhouse. A hog runs along the greenhouse from the stove, placed on brick trenches so that there are air passages in the lower part of it and there is no contact between the hog and the ground. From the stove to the chimney, make a slight rise in the hog (at least 1:100) to prevent smoking.
In lean-to greenhouses, hogs are placed along the south wall under the shelving. In gable greenhouses, two hogs (respectively, two ovens) are laid under the racks running along the side walls. The riser must be of sufficient height to provide good traction.
Heating a greenhouse with a heating cable is an original and economical solution. It is used in Alaska.
The stoves are heated in the evening, and in severe cold weather - in the morning, in order to maintain the thermal regime at a sufficient level.
Rating of greenhouse heating options
In conclusion, we will make a comparative analysis of the considered options for heating greenhouses.
The easiest way to organize heating is with gas boilers and stoves running on solid fuel. Gas installations are easy to automate and create a comfortable microclimate for plants without auxiliary heat sources.
Buleryan stoves are not very convenient to use (the need for periodic manual loading of firewood). Their main advantages are low fuel cost and high heat transfer.
In second place you can put infrared emitters, cable heating systems and solar collectors. They are relatively inexpensive, easy to install and operate automatically. However, in terms of the cost of energy spent on generating a unit of heat, they are significantly inferior to gas and wood.
Heat guns occupy the third step in our rating. They are easy to maintain, can operate automatically, but are not economical. Heat pumps are located in the same niche. Despite the minimal cost of energy, the price of these installations is high and pays off for a very long time (8-12 years).