High energy costs sooner or later force us to think about ways to save. Not all owners of residential and office premises realize that heat loss in winter is largely caused by ventilation. According to statistics, from 30% to 60% of the heat is lost along with the air removed from the premises. Supply and exhaust ventilation with a recuperator is a reasonable compromise between energy saving and proper room ventilation. We talk about the basic principles of operation of the equipment.
Operating principle of supply and exhaust ventilation with recovery
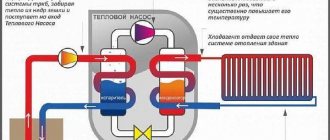
How it works? The device takes heat from the outgoing stream and transfers it to the incoming one from the street. As a result, the fresh air temperature is close to room temperature and requires almost no heating. This saves our energy costs.
Let's talk about the design of the equipment. Externally, the recuperator is a box with inlet and outlet openings. Inside there is a key component - a heat exchanger, which is responsible for transferring thermal energy. Counter air flows pass through this device, but do not mix thanks to a plate or membrane partition. The recuperator is also equipped with filters that clean both the incoming and outgoing flow. This is important for the health of people in the room and to protect the heat exchanger from dust and debris. Fans are responsible for the movement of air flow. Enclosures ensure reliable operation and proper insulation. As a rule, the equipment is equipped with automation, which allows you to regulate the power of the ventilation system in accordance with user requests. Learn more about the components of the ventilation system.
Recovery systems - characteristics in general
In general, heat recovery is divided into two types - sensible heat recovery and enthalpy heat recovery. Enthalpy heat exchangers, due to their ability to regenerate both sensible and latent heat, have the best environmental effect. Provide a large proportion of the moisture load in the ventilation system and meet the indoor air humidity requirements for modern building projects.
A typical residential building heat exchanger system typically contains:
- heat exchanger module,
- fresh air inlet,
- separate outlet for polluted air,
- recuperator.
Heat recovery in the house (classical scheme): 1 – recuperator;
2 – external air inlet; 3 – external air outlet; 4 – warm air from the bathroom; 5 – warm kitchen air; 6 – heated air to the bedroom; 7 – heated air into the hall Modern heat recovery systems make it possible to recover about 60–95% of waste energy, which seems promising. Let's look at four categories of heat recovery systems designed for residential buildings, namely:
- Rotating disk.
- Stationary plate module.
- Heat pipe.
- Circulation system.
The equipment listed in the list has its own technical and technological characteristics, which naturally affects the effectiveness of the action and the achievement of the desired result.
Types of recuperators, their features, advantages and disadvantages
There are various types of recuperators on the market. Let's talk about each of them.
Plate ones are a block cassette with a metal casing, inside of which plates (hence the name) made of galvanized steel, foil, plastic or polymerized paper are installed. The plates separate the air flows and prevent them from mixing. The efficiency of this type of recuperator depends on the material of the plates:
- metal ones are not the best choice. They freeze in cold weather and take a long time to thaw. When freezing occurs, air must periodically be released through a bypass channel, bypassing the recuperator, directly into the room;
- plastic ones do not have this problem, but are more expensive. In operation it is much more efficient. They can be used in rooms with high humidity. Both plastic and metal plates form condensation, for which a tray is provided in the design to collect it. When installing such recuperators, drainage must be provided;
- heat exchangers made of polymerized paper are highly efficient, do not form condensation and do not dry out the air. Not suitable for wet areas.
Rotary heat exchangers are cylindrical in shape and consist of an aluminum rotor enclosed in a galvanized steel housing. When rotating, the drum heats up in the exhaust duct area and cools in the supply area, returning heat to the street air. Rotary heat exchangers are more efficient than plate heat exchangers. Automation regulates the rotor speed and prevents freezing. Therefore, no defrosting is required.
Enthalpy - technically more advanced equipment. They return not only heat, but also moisture. The efficiency of the installation is estimated at 80-85% due to efficient heat exchange. The operating principle is multi-stage recovery. What does it mean? Inside the recuperator there is a membrane that works like a sponge: it absorbs heat and moisture from the exhaust air and transfers it to the supply air. There is no mixing of flows. Condensation does not form: the membrane surface absorbs a strictly defined amount of moisture.
Advantages of enthalpy recuperators:
- high efficiency;
- no condensation;
- do not freeze;
- high-quality air circulation with additional humidification.
The equipment has recently come into use. To date, little statistical data has been accumulated on the actual service life, reliability and durability of enthalpy recuperators. Manufacturers claim a lifespan of up to 10 years, but this has not been confirmed by real practical operating experience. At the moment, such devices are used mainly in ventilation installations with relatively low air flow.
The feasibility of a recuperator in ventilation
We can talk about the feasibility of installing recuperative ventilation by assessing the effectiveness of the system and comparing its advantages with disadvantages.
Part of the heat is taken from the exhaust air drawn outside and transferred to forced fresh jets directed inside the room. This allows you to reduce heat loss by up to 70% (+)
The need to use heat recovery is most relevant in buildings with forced air exhaust. As a rule, these are low-inertia buildings erected using innovative thermal insulation technologies (houses made of sandwich panels, gas silicate slabs, foam blocks).
In such buildings, the walls do not accumulate heat well, and natural air exchange is ineffective.
However, problems with air circulation are also typical for “traditional” buildings made of brick and concrete. The presence of sealed heat-sound-insulating PVC windows blocks circulation with a natural impulse - the flow of fresh air stops, and the draft in the ventilation duct overturns or tends to zero.
The solution to the problem of “Euro-windows” is the organization of forced ventilation. The system restores air exchange, but heat loss increases up to 60%. And here it is no longer possible to do without heat recovery.
The efficiency of the exchange process is expressed as a percentage and shows the amount of heat expended from the exhaust air to heat the fresh “intake”
Ventilation heat recovery efficiency indicator:
- 0% - open window - warm air is removed into the atmosphere, and cold air enters, lowering the temperature in the room;
- 100% - the supply air is heated to the “exhaust” temperature - technically impossible to implement;
- 30-90% - an acceptable parameter, recovery with an efficiency of 60% or more is considered good, an efficiency of over 80% is excellent heat transfer.
The efficiency of the system depends on the type of recuperator, room dimensions and air flow. In any case, the use of recovery ventilation, even with an efficiency of 30%, is more profitable than its absence. In addition to significant savings on energy resources, heat “regeneration” improves the overall microclimate in the room.
Disadvantages of using a heat exchanger:
- Energy dependence. The purchase of climate control equipment is justified if the electricity consumption is significantly less than its savings after installing the recuperator.
- Condensation. Due to temperature differences, moisture may condense on the walls of the heat exchanger. In winter, there is a possibility of icing, which can lead to a rapid decrease in efficiency or failure of the recuperator.
- Noisy work. Some models emit a hum during operation. If during the day this disadvantage is not particularly noticeable, then at night the noise causes discomfort. Recuperators with improved insulation operate quietly.
High initial investment is often the main argument against energy efficient ventilation.
It is advisable to invest money in a system that will pay off within 5-8 years. It should be taken into account that additional costs will have to be incurred to maintain the complex, for example, periodic replacement of fans
How advisable is it to order ventilation with recovery?
Installing supply and exhaust heat recovery is a long-term investment. The price of a ventilation unit with a recuperator is on average 50% more expensive. This equipment will definitely pay for itself over the years. The payback period and feasibility of installation also depend on climatic conditions. Useful material on the topic - what is a supply and exhaust ventilation system.
IMPORTANT! The recuperator performs well at large temperature differences. If it is -15°C outside, and the building should be +20°C, installing supply and exhaust ventilation with recovery is economically feasible.
If you live in a mild, southern climate, there is no point in overpaying for a recuperator: the temperature difference is small. This equipment is optimal for temperate and northern climates with harsh winters and long off-seasons.
Features of installation of ventilation with recovery
High-quality ventilation is the result of correctly selected design, equipment, careful, professional design and installation. In order for the recovery system to work efficiently and economically, 3 conditions must be met:
- professionally drawn up engineering project;
- reliable design of the ventilation system;
- good quality recuperator.
The professional knowledge, qualifications, experience and skills of the installation company are of decisive importance. An important step is to configure the system accordingly according to the expected parameters:
- Ventilation channels are the “circulatory system” of the entire recovery system. Optimal ventilation duct routes are critical. In order for the recovery system to fulfill its task, the pipes must have correctly selected diameters to supply the required amount of air and be properly insulated.
- The correct direction of air flow in the installation is ensured by the recuperator fans. Thoughtful distribution of ventilation ducts ensures optimal and quiet air supply, which effectively ventilates all rooms.
- Equally important is the choice of a recuperator of appropriate power. To select the right heat exchanger, it is necessary to make careful calculations. Only on the basis of this parameter you need to purchase a recuperator of appropriate power. Weak equipment will not cope with maintaining a comfortable microclimate in the house and will ultimately affect the economic feasibility.
When choosing equipment, avoid the temptation to buy what is cheaper. Often, a low-cost unit means worse performance and ultimately reduces the energy efficiency of the entire system. The installation of supply and exhaust ventilation should be entrusted to a professional installation company that is engaged in design, will be able to correctly calculate the volume of air flow and install the system efficiently.
Methods for organizing recuperative ventilation
Recovery is arranged in one of the following ways: centralized and decentralized. In the first case, ventilation flows from the entire room pass through the heat exchanger, in the second - from one room.
Centralized complex – air handling unit
A centralized system is installed at the stage of construction or major modernization of the ventilation system.
A forced supply and exhaust unit (PVU) with a built-in recuperator is selected. The main selection criterion is the overall performance of the complex based on the entire volume of air in the structure (+)
A PVU with a recuperator ensures sufficient air exchange even in houses with sealed windows. At the same time, air flows are distributed evenly without creating drafts.
Complex supply and exhaust units of monoblock type are equipped with:
- fans – round-the-clock supply of clean air and emission of jets saturated with carbon dioxide;
- heaters – preheating of inflow;
- filters – retain dust and microparticles;
- recuperator - different types of installations can be used.
The functionality of some PVUs is expanded with a delay timer, power regulator, humidity level sensors, etc.
The body of monoblock models is covered with noise-absorbing material, making the operation of the PVU very quiet. Vertical, horizontal and suspended versions of ventilation units are possible
Vents (Ukraine), Dantherm (Denmark), Daikin (Japan), Dantex have proven themselves well .
Local units - an addition to the existing ventilation system
To restore the circulation of air masses in the room being used, decentralized air inlets with heat recovery are suitable.
They cut into the façade of a building or are mounted through a window. Their main task is to improve the supply ventilation in the house.
Local recuperators are equipped with a fan and a plate heat exchanger. The inlet “sleeve” is insulated with sound-absorbing material. The control unit of compact ventilation units is located on the internal wall
Features of decentralized ventilation systems with recovery:
- Efficiency – 60-96%;
- low productivity - the devices are designed to provide air exchange in rooms up to 20-35 sq.m;
- affordable cost and a wide selection of units, ranging from conventional wall valves to automated models with a multi-stage filtration system and the ability to adjust humidity;
- ease of installation - no air ducts are required for commissioning; you can install the wall damper yourself.
Popular manufacturers of local recuperators: Prana (Ukraine), O.Erre (Italy), Blizzard (Germany), Vents (Ukraine), Aerovital (Germany).
Important criteria for choosing a wall inlet: permissible wall thickness, performance, efficiency of the recuperator, diameter of the air channel and temperature of the pumped medium
Conclusion
Recuperation ventilation is an effective solution for air circulation in temperate and northern climate zones. Modern equipment allows you to efficiently process heat, replenish heating costs and save on energy bills. In this review, we tried to touch on the basic principles of operation and types of equipment. Special attention was paid to the professionalism of designers and installers.
Still have questions? — Order a free consultation. Our specialists will help you select engineering systems for an industrial and commercial facility, based on technical parameters and your needs, and will also advise on the issue of recovery in ventilation and installation of the system.