When several pumps operate simultaneously in the heating system of a private house for different consumers, it is necessary to ensure uniform distribution of the coolant. For this purpose, a special hydraulic separator is connected to the boiler equipment. Let's look at what a hydraulic arrow for heating is, what is its purpose, design, principle of operation, in what modes it can operate, how to correctly calculate its parameters and what are the features of its connection.
Modern boiler room with hydraulic switch Source san-kras.ru
What it is
For those who are faced with the need to properly distribute coolant throughout the system when there are several pumps for different consumers, a natural question arises about what a hydraulic pump is. Externally, this device is a metal vertical container in the form of a large pipe with several side pipes of smaller diameter. There are also two tubes at the base and top. The top one is designed to bleed off accumulated air, the bottom one is to remove sediment.
In addition to proper distribution of the coolant, the device ensures equalization of its heating parameters on the forward and return paths in the heating main. Such a mechanism can work optimally only if it fully complies with the characteristics of the heating system. Therefore, ideally, the hydraulic arrow should be designed and selected according to the parameters of volume, number and location of insertion of pipes in each specific case individually.
Hydraulic gun action diagram Source ytimg.com
However, in practice this requirement is rarely met. Often, universal models are installed into the system, which are widely available today - which, naturally, cannot but negatively affect the subsequent operation of the equipment.
The hydraulic arrow inside may contain a number of additional devices:
- Flow dividers.
- Filters for cleaning mechanical impurities.
- Dissolved air compartments.
In practice, not all of them are beneficial. For example, screens for cleaning solid particles quickly become clogged and first reduce the flow rate, and then completely make the system impassable.
Note! The hydraulic separator tank is made of pipes of both round and rectangular cross-section. However, round models are more effective, natural and in demand.
Device, principle of operation, purpose
A complete understanding of what a hydraulic arrow for heating is, why it is needed, what its varieties are, can be obtained by considering its detailed structure, principles of operation and purpose. Let's look at these aspects in more detail.
An example of a heating scheme for a private house with a hydraulic arrow Source project-home.ru
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in engineering systems (heating, water supply, sewerage and others) and related work
Device
Structurally, the hydraulic separator is a hollow container of round or square cross-section closed at the ends. Its dimensions depend primarily on the power of the boiler, as well as the number and capacity of the circuits. Depending on the weight, the structure is either installed on the floor using support legs, or mounted on the wall surface using a special bracket.
Working pipes, the number of which, as a rule, is at least 4, are connected to the heat pipe via threads or using flanges. The material used to make the device is very different - ordinary steel with low carbon content, stainless alloy, copper, and polypropylene. At the same time, systems operating on a solid fuel unit are equipped only with metal models.
Although the vertical position of the device is considered traditional, it is not mandatory. For example, when eliminating air pockets and filtering sediment from the coolant is not a necessary condition, a horizontal arrangement of the device is possible. In this case, the need for convection mixing of flows is eliminated.
Hydraulic separator device Source vodoteplo.ru
Principle of operation
Uniform distribution of the coolant in the presence of several consumers at the same time is ensured by a hydraulic arrow for heating - the operating principle of such a mechanism is based on dividing the total flow into independent directions for each individual circuit. If the circulation pump of boiler equipment accelerates water to 1 m/s, then in the hydraulic separator it slows down to a minimum of 0.1 m/s. In this case, several conditions are simultaneously met:
- The volume and direction of flow changes.
- Loss of thermal energy is eliminated.
- Hydraulic resistance is eliminated.
- The contours of the unit and the chain of consumers are separated - the hydraulic arrow acts as a buffer area.
- The pumping equipment for each circuit operates independently without affecting the overall hydraulic balance.
When several pumps are installed in the system, then a hydraulic separator for heating is connected, the operating principle of which is to ensure the correct operation of each circuit separately:
- Separate branches with radiators.
- Water heated floor.
- Indirectly heated boiler.
- Warm ventilation, etc.
Diagram of a hydraulic separator Source teplo.guru
As an example, we can consider a situation where several pumps are used that differ greatly in power. As a rule, all equipment is located in one room, the collector module. Turning on the most powerful pump will cause the pumping of all the coolant and deprivation of the remaining circuits. A simplified way to solve this problem is to install a hydraulic separator. Without it, all the pumps would have to be placed at a great distance from each other.
The role of the hydraulic arrow in modern heating systems
In order to find out what a hydraulic arrow is and what functions it performs, first we will get acquainted with the features of the operation of individual heating systems.
Simple option
The simplest version of a heating system equipped with a circulation pump will look something like this.
Of course, this diagram is significantly simplified, since many network elements in it (for example, the security group) are simply not shown in order to “make the picture easier to understand.” So, in the diagram you can see, first of all, a heating boiler, thanks to which the working fluid is heated. Also visible is a circulation pump, through which the liquid moves through the supply (red) pipeline and the so-called “return”. Typically, such a pump can be installed both in the pipeline and directly in the boiler (the latter option is more typical for wall-mounted devices).
If the pump is correctly selected in terms of pressure and performance, then it alone will be quite sufficient for a single-circuit system, therefore, there is no need to use other auxiliary devices.
More complex option
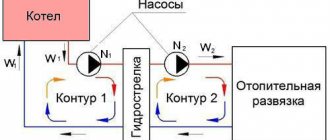
If the area of the house is large enough, then the diagram presented above will clearly not be enough for it. In such cases, several heating circuits are used at once, so the diagram will look slightly different.
Here we see that through the pump, the working fluid enters the manifold, and from there it is transferred to several heating circuits. The latter include the following elements.
- A high temperature circuit (or several), in which there are collectors or ordinary batteries.
- DHW systems equipped with an indirect heating boiler. The requirements for the movement of working fluid are special here, since the temperature of water heating in most cases is regulated by changing the flow rate of the fluid passing through the boiler.
- Warm floor. Yes, the temperature of the working fluid for them should be an order of magnitude lower, which is why special thermostatic devices are used. Moreover, the contours of the heated floor have a length significantly exceeding the standard wiring.
It is quite obvious that one circulation pump cannot cope with this kind of load. Of course, today high-performance models with increased power are sold, capable of creating quite high pressure, but it is worth thinking about the heating device itself - its capabilities, alas, are not limitless. The fact is that the boiler elements are initially designed for certain pressure and performance indicators. And these indicators should not be exceeded, as this can lead to breakdown of the expensive heating installation.
In addition, the circulation pump itself, operating at the limit of its capabilities in order to supply all circuits of the network with liquid, will not be able to last long. What can we say about the loud noise and electrical energy consumption. But let’s return to the topic of our article – to the hydraulic arrow for heating.
Operating modes
To understand why a hydraulic arrow is needed in a heating system from a technical point of view, it is necessary to consider the main options for its application in practice. The following three schemes are distinguished:
- Equilibrium operation of the system. The hydroseparator operates in neutral mode without affecting the system. In this case, the pumping equipment of the heating unit pumps the same amount of coolant as is required for the heating system. At the same time, the indicators of heating, pressure, flow and generated heat correspond to theoretical calculations - both on the supply and return lines. However, in reality such conditions never arise, since after a short time all the characteristics of the system undergo changes.
3 operating modes of the hydraulic gun Source stroychik.ru
- The heating circuit consumes more coolant than the heat exchanger. This is the most common situation that arises in practice when the hydraulic separator works for its intended purpose. Vertical redistribution flows arise in it - from the return the coolant is mixed into the supply. There is a threat of heat stroke, since the lack of a thermal agent activates sensors, which in turn send a command to increase the operation of the heat generator. In this case, the consumer will still not receive the required amount of heat.
Video description
Video about what a hydraulic gun is and how it works:
- The flow of the heat exchange circuit is stronger than that of the heating circuit. This is the most optimal and correct option for operating a heating system with a well-designed and installed hydraulic valve. The flow required by the consumer is less than the flow supplied by the boiler. In this mode, a portion of the hot coolant is returned to the unit, so it will operate at a normal or even slightly reduced volume.
Important! The presence of a hydraulic arrow is mandatory in the heating system when several boilers are connected simultaneously in a cascade. In addition, it is needed for a unit equipped with a cast iron heat exchanger. Since the large difference between the heating of the outgoing and cooling of the incoming coolant flow leads to gradual cracking of the material.
Advantages
If we briefly summarize all the advantages that the installation of a simple dismountable device provides, we get:
- pressure balance in the system;
- temperature distribution in different circuits;
- protection against water hammer;
- the ability to disable a separate system without losing the functionality of the others;
- increasing boiler efficiency, saving resources and energy;
- air vent;
- protection of pipes, fittings and boiler from damage by impurities in the coolant.
Video description
Video about the hydraulic separator and its purpose:
The calculation is carried out in the following several ways:
- Maximum coolant flow rate.
Calculated by the formula:
D = 3*d*√Mp/Vd
D is the diameter of the hydraulic needle, d is the diameter of the nozzle, MP is the maximum flow for the boiler, Vd is the maximum speed (0.2 m/s).
For example:
7*3*√8/02 = 21*√40 = 21*6.32 = 132.8 cm – 133 cm – diameter of the hydraulic needle.
The diameter of the pipe is 7 cm, the boiler flow rate is 8 cubic meters per hour.
- Highest boiler power.
The calculation is carried out using a similar formula:
D = 3*d*√Mk/(Vd * Traz)
However, some replacement parameters appear in it:
Mk – maximum boiler power, for example 60 kW,
Traz – the difference in heating of the coolant in the supply and return flows, for example 15 degrees.
For example:
21*√60/(02 * 15) = 21*4.4 = 94 cm.
- The length of the body of the hydraulic needle itself. The length of the device depends on the diameter and location of the pipes. Below is a diagram for calculating the characteristics. In the first version it will be equal to 12 diameters, in the second - 13.
Scheme for calculating the length of the hydraulic arrow according to the location of the pipes Source stroychik.ru
Advice! When calculating the parameters of a hydraulic arrow, it is important to determine the maximum possible coolant speed. If the flow moves quickly enough, a characteristic noise will arise in the system, significantly reducing the comfort in the house. Therefore, in order to avoid this negative effect, this parameter is limited to a value not exceeding 0.2 m/s.
Where can I buy?
Hydraulic distributors are produced here from high-carbon steel with a thickness of 3 mm.
Simple devices with 4 pipes cost from 3.1 thousand rubles. (up to 50 kW). A similar device up to 100 kW will cost almost 4 thousand rubles.
There are models combined with a collector. Such a kit for three circuits will cost 6.8 thousand rubles. Five-circuit – 9.3 thousand rubles. Among the products there is also powerful boiler equipment. For example, a DN100 switch, designed to operate up to 500 kW, will cost 25 thousand rubles.
You can contact the organization by phone +7 913-953-16-80.
Many other manufacturers also produce hydraulic distribution equipment (only the prices are much higher):
- Italian company Immergas;
- Ariston;
- Meibes and others.
Connection features
Knowing what a hydraulic valve is in a heating system allows you to correctly select it according to its parameters and correctly connect it. Installation of the device is carried out according to the general rules of plumbing installation. The device must first of all be correctly selected according to the main parameters - throughput, number of pipes, dimensions.
It is also necessary to remember what a hydraulic arrow is - the operating principle of this device is based on forced circulation. The system must have at least two pumps. One of them ensures the operation of the heat exchange circuit of the boiler, the other – the consumer system. If this condition is not met, the device will not only be useless, but even harmful and will act as an obstacle to the movement of the coolant.
Hydraulic separator without filter
The design of the arrow, which excludes the presence of the functions of an air separator and a sediment filter, also deviates somewhat from the accepted standard. Meanwhile, with such a design it is possible to obtain two flows with different speeds (dynamically independent circuits).
A non-standard design solution for the manufacture of hydraulic arrows. It differs from the classics in that there are no filtration or air removal functions. In addition, the distribution of heat flows has a perpendicular transport pattern, which achieves speed decoupling
For example, there is the heat flow of the boiler circuit and the heat flow of the heating device (radiator) circuit. With a non-standard design, where the direction of flow is perpendicular, the flow rate of the secondary circuit with heating devices increases significantly.
On the contrary, movement along the contour of the boiler is slower. True, this is a purely theoretical view. It is practically necessary to test under specific conditions.
Briefly about the main thing
A hydraulic separator for heating is a metal closed container with pipes mounted in front of the boiler. Designed for optimal distribution of coolant between consumers, as well as regulation of the heating level between forward and reverse flows in heating systems with forced circulation and at least 2 pumps. The need to install the device arises when the following consumers are simultaneously present:
- Separate radiator lines.
- Water heated floor system.
- Boiler operating on a heating boiler.
- Warm water ventilation.
The device is also needed to smooth out the effects of temperature changes on the cast iron heat exchanger. In this case, the hydraulic arrow can operate in three modes - in equilibrium, with insufficient power of the heating circuit and its superiority over the consumer. The last option is the most optimal. Before installation, the device must be calculated in terms of throughput, diameter and length, depending on the diameter and location of the connected pipes.