Why do we need ceiling heights when calculating?
So, let's look at a certain “standard” option - a house with an area of 100 square meters.
In calculations based on the area of the house, we rely on the value “1 kW of boiler thermal power for every 10 square meters of area” and find that we need a 10 kW boiler to heat a house with an area of 100 m2. Now let's pay attention to the height of the ceilings in the rooms. They can be 2.20, 2.50 and, for example, 3.0 meters
In the first option, the volume of the premises will be 220 cubic meters, in the second – 250 and in the third – 300 m3.
Any heat generator that operates in your home, with the exception of IR panels and the like, heats the air inside the room. Thanks to convection, warm air mixes with cold air and ensures heat transfer throughout the entire volume. As a result, any boiler or furnace heats the air in the house. And air is measured precisely in volumetric quantities, that is, in cubic meters.
In the first case, we will need to heat 220 cubic meters of air in the interior of the house, and in the latter - 300 cubic meters. It is logical to assume that when heating 300 cubic meters of air, almost 1.5 times more heat will be required than when heating 220 cubic meters.
That is, with the same area of premises in the first case, you can use a boiler almost 1.5 times less powerful than in the latter.
Simple calculation of planned expenses
It is not difficult to find out the energy consumption for heating a house if you use generally accepted information in the calculation process:
- To heat a unit volume of heated premises, 4-8 W/h of electricity is required. A more accurate figure is obtained if you calculate the heat loss of the entire building and its specific value during the heating season. Calculations are made using a correction factor, which takes into account additional losses when the coolant passes through the walls of the house and through unheated rooms;
- the duration of the heating season is 7 months (read: “Duration of the heating season - rules and regulations”);
- to determine the average power, it is customary to use the following rule - for a room height of up to 3 meters with insulated structures, 1 kW is enough to heat 10 “squares”. For example, to heat a house with an area of 160 square meters, an electric boiler must have a power of 16 kW. If the heating device does not have sufficient power, it will not be possible to create a comfortable microclimate in the house, and if there is an excess of power, excessive energy consumption cannot be avoided;
- to find out the monthly electricity consumption for heating a house, you need to multiply the boiler power by the time it operates (in hours) in continuous mode;
- the resulting value is divided in half, since for 7 months (heating period) the heating device will not function under conditions of maximum thermal load (read: “Calculation of thermal loads for heating, calculation methods and formula”). The result obtained is the average energy consumption per month;
- the total is multiplied by 7 (months) and the electricity consumption for heating the house throughout the year is found out;
- Knowing the cost per unit of power, determine the monetary costs of heating the building.
Heating a private house, detailed video:
Calculation of different types of radiators
If you are going to install sectional radiators of a standard size (with an axial distance of 50 cm in height) and have already chosen the material, model and desired size, there should not be any difficulties in calculating their number. Most reputable companies that supply good heating equipment have on their website the technical data of all modifications, including thermal power. If it is not the power that is indicated, but the coolant flow rate, then it is easy to convert to power: the coolant flow rate of 1 l/min is approximately equal to the power of 1 kW (1000 W).
The axial distance of the radiator is determined by the height between the centers of the holes for coolant supply/discharge
To make life easier for customers, many websites install a specially designed calculator program. Then the calculation of heating radiator sections comes down to entering data on your premises in the appropriate fields. And at the output you have the finished result: the number of sections of this model in pieces.
The axial distance is determined between the centers of the coolant holes
But if you’re just evaluating possible options, then it’s worth considering that radiators of the same size made of different materials have different thermal power. The method for calculating the number of sections of bimetallic radiators is no different from calculating aluminum, steel or cast iron. Only the thermal power of one section can be different.
To make it easier to calculate, there are averaged data that you can use as a guide. For one radiator section with an axial distance of 50 cm, the following power values are accepted:
- aluminum - 190W
- bimetallic - 185W
- cast iron - 145W.
If you are just figuring out which material to choose, you can use this data. For clarity, we present the simplest calculation of sections of bimetallic heating radiators, which takes into account only the area of the room.
When determining the number of heating devices made of bimetal of a standard size (center distance 50 cm), it is assumed that one section can heat 1.8 m 2 of area. Then for a room of 16 m 2 you need: 16 m 2 /1.8 m 2 = 8.88 pcs. Let's round up - we need 9 sections.
We calculate similarly for cast iron or steel bars. All you need is the following rules:
- bimetallic radiator - 1.8m2
- aluminum - 1.9-2.0 m 2
- cast iron - 1.4-1.5 m 2.
This data is for sections with an interaxial distance of 50 cm. Today, there are models on sale with very different heights: from 60cm to 20cm and even lower. Models 20cm and below are called curb. Naturally, their power differs from the specified standard, and if you plan to use a “non-standard”, you will have to make adjustments. Either look for passport data, or do the math yourself. We proceed from the fact that the heat transfer of a heating device directly depends on its area. As the height decreases, the area of the device decreases, and, therefore, the power decreases proportionally. That is, you need to find the ratio of the heights of the selected radiator with the standard, and then use this coefficient to correct the result.
Calculation of cast iron heating radiators. Can be calculated by area or volume of the room
For clarity, we will calculate aluminum radiators by area. The room is the same: 16m 2. We count the number of sections of standard size: 16m 2 /2m 2 = 8 pieces. But we want to use small sections with a height of 40 cm. We find the ratio of radiators of the selected size to standard ones: 50cm/40cm=1.25. And now we adjust the quantity: 8pcs * 1.25 = 10pcs.
Infrared heater
The most advanced and economical heating devices are infrared heaters. A quartz emitter is more suitable for temporary heating if you do not need to heat the entire room
| Principle of operation | An infrared heater, unlike traditional heaters, heats nearby objects rather than the air. It emits thermal energy (like the sun), which is absorbed by surrounding surfaces (floors, walls, furniture, etc.) and people. Infrared heaters allow you to create zones with local heating and save energy. They heat objects and do not heat the air. Infrared heaters are designed for suspended ceilings, heating residential and non-residential premises, as well as people in open areas. They are used for heating bathrooms and shower rooms, terraces, balconies, cafes and restaurants. |
| Advantages | Energy saving, silent, local heating - when installed above a workplace, an infrared heater provides comfortable conditions for a working person without heating the entire room |
Recommendations for using heating devices:
| |
| Flaws | It only heats the area where the infrared beam is directed. If used, for example, for heating outside in the cold season, the right side of the body will warm, and the left will freeze |
| conclusions | Infrared quartz heaters are used to heat certain areas of the room. They can warm up the workplace |
Basic data
Accurate thermal calculations are quite complex, and they are done by specialists when designing a heating system. If ordering it is problematic, you can do a simple calculation yourself.
To complete it you need to have basic information:
- Initially, you need to know the dimensions of the room where the heating radiators will be installed:
- Length.
- Width.
- Height.
- Then you need to decide on the choice of batteries:
- steel plate;
- cast iron;
- bimetallic;
- aluminum.
- In the technical documentation for each radiator, the characteristics from the manufacturer indicate the thermal power of the device. This is the amount of heat in watts that can be generated by 1 modular section element in 1 hour.
For reference, one watt is equivalent to 0.86 calories of heat.
- To calculate the power of radiators, it is necessary to use the standard heat transfer values of each section, namely:
- For Soviet-made cast iron batteries - 160 W.
- Aluminum with a center height of 500 mm - 200 W.
- Non-dismountable steel panels with a length of 500 and 800 mm, respectively, 700 and 1500 W.
Calculation of heat transfer from one aluminum radiator video
In the video you will learn how to calculate the heat transfer of one section of an aluminum battery for different parameters of the incoming and outgoing coolant.
One section of the aluminum radiator has a power of 199 Watts, but this is provided that the declared temperature difference of 70 0C is observed. This means that the coolant temperature at the inlet is 110 0C, and at the outlet 70 degrees. With such a difference, the room should warm up to 20 degrees. This temperature difference is designated DT.
Some radiator manufacturers provide a heat transfer conversion table and coefficient along with their product. Its value is floating: the higher the temperature of the coolant, the greater the heat transfer rate.
As an example, this parameter can be calculated with the following data:
- The coolant temperature at the radiator inlet is 85 0C;
- The cooling of water when leaving the radiator is 63 0C;
- Heating of the room - 23 0C.
You need to add the first two values together, divide them by 2 and subtract the room temperature, this is clearly done like this:
The resulting number is equal to DT; from the proposed table it can be established that its coefficient is 0.68. Taking this into account, we can determine the heat transfer of one section:
Then, knowing the heat loss in each room, you can calculate how many radiator sections are needed for installation in a certain room. Even if, according to calculations, the result is one section, you need to install at least 3, otherwise the entire heating system will look ridiculous and will not warm the area sufficiently.
In the following article you will learn how to properly connect heating radiators: https://ksportal.ru/828-podklyuchit-radiator-otopleniya.html.
Calculation of the number of radiators is always relevant
This is especially important for those who are building a private house. Apartment owners who want to change radiators should also know how to easily calculate the number of sections on new radiator models
Radiator models: what to look for
Comfortable room temperature depends not only on how competently the heating devices of the heating system are calculated, but also on how correctly the type of batteries is selected in terms of material and design.
The most common types of radiators in apartments and houses are:
- vacuum;
- steel;
- aluminum;
- anodized aluminum
- bimetallic;
- cast iron;
- copper.
They have different operational characteristics that need to be kept in mind when solving the problem of how to calculate heating installation.
- Vacuum is the latest invention in the field of heating technology. Allows you to save the amount of coolant up to 80 percent. The housing is filled with lithium bromide liquid. Economical, compact and versatile. It is distinguished by high heat transfer, corrosion resistance, and the ability to be installed in systems that use any type of fuel as a heat source.
- Steel radiators can be of different shapes and designs. There is a fundamental difference between panel and tubular. The latest generation of panel radiators are very different from their predecessors, which in Soviet times were used to replace heavy cast-iron batteries. Consumers have the opportunity to choose devices based on the number of panels and heat exchangers, with bottom or side connections. Tubular radiators also have their own characteristics. Despite all the advantages of steel models, they have significant disadvantages - they are susceptible to corrosion, do not tolerate coolant pressure drops well, and there is a possibility of rupture of welding seams. Therefore, it is risky to install them in houses or apartments where it is impossible to control the quality and pressure of the coolant.
- Aluminum radiators are in line with steel ones in this regard. They are best used in private houses or apartments where autonomous heating is installed, coolant requirements are met, and there is no risk of water hammer. They are attracted by good performance indicators, affordable price, ease of installation and neat appearance.
- Aluminum anode radiators are almost universal in terms of the choice of coolant, since during the production process the sections are subjected to anodic oxidation. The inner surfaces of the walls are perfectly smooth. The appearance is no different from aluminum ones, but the price is much higher. Therefore, it is advisable to make purchases at retail outlets that value their reputation and can provide a certificate for the product.
- Bimetallic radiators are even more reliable. Their design is as follows: the channels through which the coolant circulates are made of stainless steel, and the outer shell is made of aluminum. In this way, all the advantages of aluminum radiators are preserved and their main drawback is completely eliminated: such batteries do not have special requirements for the quality of the coolant. In addition, they are highly durable and withstand water hammer well.
- Cast iron is still among the leaders in reliability and durability. Minus - thermal inertia, in some cases, is an advantage. For example, in heating systems that run on solid fuel. Cast iron batteries heat up slowly, but retain heat for a long time and cool down slowly.
- The thermal conductivity of copper radiators is 5 times higher than that of cast iron. They are resistant to aggressive environments, are not afraid of temperatures of 150 degrees above zero, and can withstand pressure drops of 16 atmospheres. The coolant glides over the internal surfaces without delay. It's rare that anyone doesn't like their appearance - they look great without painting. The only negative is the high price.
Online calculator
Note! Today, the Internet allows you to use a computer to calculate the power of heating radiators, taking into account all innovative construction technologies
Calculation of heating radiators
The online calculation formula is similar to the standard one, but is slightly modified to take into account adjustment factors. They are installed:
- On plastic windows that reduce heat loss.
- For external walls - the more there are, the higher the coefficient.
- To the height of the room. If it is more than 2.5 meters, then the coefficient increases.
The basic online calculation takes as a basis the average values for each type of heating battery, the center distance of which is 500 mm. For heat transfer, the following data are accepted into the standard calculation:
- For cast iron radiators - 145 W.
- For bimetallic - 185 W.
- For aluminum - 190 W.
To carry out the calculation, you need to enter all the requested data into the computer database:
- Area and height of the room.
- Number of windows and external walls.
- Type of room and selected radiator.
- Condition and material of the walls.
- Minimum temperature outside.
After filling out the fields of the online form, you only need to click the “Run calculation” option, and after a few seconds the computer will display the result. It's very simple and convenient. An online calculator can be found on the radiator manufacturer's website.
How to calculate boiler power two methods
To ensure a comfortable temperature throughout the winter, the heating boiler must produce the amount of thermal energy that is necessary to replenish all heat losses of the building/room. Plus, it is also necessary to have a small power reserve in case of abnormal cold weather or expansion of the area. We’ll talk about how to calculate the required power in this article.
To determine the performance of heating equipment, you must first determine the heat loss of the building/room. This calculation is called thermotechnical. This is one of the most complex calculations in the industry as there are many components to consider.
To determine the boiler power, it is necessary to take into account all heat losses
Of course, the amount of heat loss is influenced by the materials used in the construction of the house. Therefore, the building materials from which the foundation, walls, floor, ceiling, ceilings, attic, roofing, window and door openings are made are taken into account
The type of system wiring and the presence of heated floors are taken into account. In some cases, they even consider the presence of household appliances that generate heat during operation.
But such precision is not always required. There are methods that allow you to quickly estimate the required performance of a heating boiler without plunging into the jungle of heating engineering.
Example of thermal calculation
As an example of a thermal calculation, we have an ordinary 1-story house with four living rooms, a kitchen, a bathroom, a “winter garden” and utility rooms.
The foundation is made of a monolithic reinforced concrete slab (20 cm), the external walls are concrete (25 cm) with plaster, the roof is made of wooden beams, the roof is metal tiles and mineral wool (10 cm)
Let us designate the initial parameters of the house necessary for the calculations.
Building dimensions:
- floor height – 3 m;
- small window on the front and rear of the building 1470*1420 mm;
- large facade window 2080*1420 mm;
- entrance doors 2000*900 mm;
- rear doors (exit to the terrace) 2000*1400 (700 + 700) mm.
The total width of the building is 9.5 m2, length 16 m2. Only living rooms (4 units), a bathroom and a kitchen will be heated.
To accurately calculate heat loss on the walls, you need to subtract the area of all windows and doors from the area of the external walls - this is a completely different type of material with its own thermal resistance
We start by calculating the areas of homogeneous materials:
- floor area – 152 m2;
- roof area – 180 m2, taking into account the attic height of 1.3 m and the purlin width – 4 m;
- window area – 3*1.47*1.42+2.08*1.42=9.22 m2;
- door area – 2*0.9+2*2*1.4=7.4 m2.
The area of the external walls will be 51*3-9.22-7.4=136.38 m2.
Let's move on to calculating heat loss for each material:
- Qfloor=S*∆T*k/d=152*20*0.2/1.7=357.65 W;
- Qroof=180*40*0.1/0.05=14400 W;
- Qwindow=9.22*40*0.36/0.5=265.54 W;
- Qdoors=7.4*40*0.15/0.75=59.2 W;
And also Qwall is equivalent to 136.38*40*0.25/0.3=4546. The sum of all heat losses will be 19628.4 W.
As a result, we calculate the boiler power: Rboiler = Qloss * Room heating * K / 100 = 19628.4 * (10.4 + 10.4 + 13.5 + 27.9 + 14.1 + 7.4) * 1.25/100 = 19628.4 * 83.7 * 1.25/100 = 20536.2 = 21 kW.
We will calculate the number of radiator sections for one of the rooms. For all others, the calculations are similar. For example, a corner room (on the left, lower corner of the diagram) has an area of 10.4 m2.
This means N=(100*k1*k2*k3*k4*k5*k6*k7)/C=(100*10.4*1.0*1.0*0.9*1.3*1.2*1.0*1.05)/180=8.5176=9.
This room requires 9 sections of heating radiator with a heat output of 180 W.
Let's move on to calculating the amount of coolant in the system - W=13.5*P=13.5*21=283.5 l. This means that the coolant speed will be: V=(0.86*P*μ)/∆T=(0.86*21000*0.9)/20=812.7 l.
As a result, a complete turnover of the entire volume of coolant in the system will be equivalent to 2.87 times per hour.
- Calculation of the heating system of a private house: rules and calculation examples
- Thermal engineering calculation of a building: specifics and formulas for performing calculations + practical examples
Calculations depending on the volume of the room
More accurate data can be obtained by calculating the sections of heating radiators taking into account the ceiling height, i.e., by the volume of the room. The principle here is approximately the same as in the previous case. First, the total heat demand is calculated, then the number of radiator sections is calculated.
According to SNIP recommendations, 41 W of thermal power is required to heat each cubic meter of living space in a panel house. By multiplying the area of the room by the height of the ceiling, we get the total volume, which we multiply by this standard value. Apartments with modern double-glazed windows and external insulation will require less heat, only 34 W per cubic meter.
For example, let’s calculate the required amount of heat for a room with an area of 20 sq.m. with a ceiling height of 3 meters. The volume of the room will be 60 cubic meters (20 sq.m. X 3 m.). The calculated thermal power in this case will be equal to 2460 W (60 cubic meters x 41 W).
How to calculate the number of heating radiators? To do this, you need to divide the obtained data by the heat transfer of one section indicated by the manufacturer. If we take, as in the previous example, 170 W, then for the room you will need: 2460 W / 170 W = 14.47, i.e. 15 radiator sections.
Manufacturers tend to indicate overestimated heat transfer rates for their products, assuming that the coolant temperature in the system will be maximum. In real conditions, this requirement is rarely met, so you should focus on the minimum heat transfer rates of one section, which are reflected in the product data sheet. This will make the calculations more realistic and accurate.
Room volume
This calculation approach also involves taking into account the height of the ceilings, because
The entire volume of air in the home is subject to heating. The calculation method used is very similar - first the volume is determined, after which the following standards are used:
- For panel houses, heating 1 m3 of air requires 41 W.
- A brick house requires 34 W/m3.
For clarity, you can calculate the heating radiators of the same room of 15 m2 to compare the results. Let’s take the height of the home to be 2.7 m: in the end the volume will be 15x2.7 = 40.5.
Calculation for different buildings:
- Panel house. To determine the heat required for heating, 40.5 m3x41 W = 1660.5 W. To calculate the required number of sections 1660.5:170 = 9.76 (10 pcs.).
- Brick house. The total volume of heat is 40.5 m3x34 W = 1377 W. Radiator count – 1377:170 = 8.1 (8 pcs.).
It turns out that significantly fewer sections will be required to heat a brick house. When the calculation of radiator sections per area was carried out, the result was averaged - 9 pieces.
Fan heater
The simplest and most affordable heating device. Used to quickly warm up small rooms. Fan heaters have a power of 2.0-2.5 kW. Compared to an oil radiator and convector they have small dimensions. Fan heaters can be located on the floor, on a table, or there are models with wall mounting
| Principle of operation | In the fan heater, the air is heated by a hot electric coil and is supplied by a fan to the heating zone. The temperature of the open electric coil is about 80°C, and the air at the outlet of the fan heater is always up to 20°C. To improve the uniformity of heating of the room, the fan rotates in the housing. The material of the fan heater body is usually plastic |
| Advantages | The air is heated very quickly and distributed throughout the room. Turns off if dropped. Protected from overheating. Thanks to the thermostat, the set temperature is regulated and does not require shutdown. Compact and aesthetic |
| Flaws | Noise produced when operating at high speeds. Air pollution due to the combustion of oxygen and dust particles. Collected dust, burning on a hot spiral, can be a source of unpleasant odor in the room |
| conclusions | Fan heaters provide the highest rate of room heating, but create increased noise at high speeds, and models with an open spiral have another drawback: they burn oxygen and pollute the air with combustion products |
Specifics and other features
It is also possible that the premises for which the calculation is being made may have other specific features; not all of them are similar or exactly the same. These could be indicators such as:
- the coolant temperature is less than 70 degrees – the number of parts must be increased accordingly;
- absence of a door in the opening between two rooms. Then you need to calculate the total area of both rooms in order to calculate the number of radiators for optimal heating;
- Double-glazed windows installed on windows prevent heat loss, therefore, fewer battery sections can be installed.
When replacing old cast iron batteries. which ensured normal temperature in the room, for new aluminum or bimetallic ones, the calculation is very simple. Multiply the heat output of one cast iron section (average 150 W). Divide the result by the amount of heat of one new part.
Climate zones are also important
It’s no secret that different climatic zones have different needs for heating, so when designing a project it is necessary to take these indicators into account.
Climatic zones also have their own coefficients:
- central Russia has a coefficient of 1.00, so it is not used;
- northern and eastern regions: 1.6;
- southern stripes: 0.7-0.9 (minimum and average annual temperatures in the region are taken into account).
This coefficient must be multiplied by the total thermal power, and the resulting result divided by the heat transfer of one part.
Thus, calculating heating by area does not present any particular difficulties. It’s enough to sit a little, figure it out and calmly calculate. With its help, every owner of an apartment or house can easily determine the size of the radiator that should be installed in the room, kitchen, bathroom or any other place.
If you doubt your abilities and knowledge, entrust the installation of the system to professionals. It’s better to pay professionals once than to do it wrong, dismantle it and start work again. Or do nothing at all.
Calculation of the number of radiators in a private house
If for apartments it is possible to take the average parameters of heat consumption, since they are designed for standard room dimensions, then in private construction this is incorrect. After all, many owners build their houses with a ceiling height exceeding 2.8 meters, in addition, almost all private premises are corner, so more power will be required to heat them.
In this case, calculations based on taking into account the area of the room are not suitable: you need to apply the formula taking into account the volume of the room and make adjustments using coefficients for reducing or increasing heat transfer.
The coefficient values are as follows:
- 0,2
– the resulting final power number is multiplied by this indicator if multi-chamber plastic double-glazed windows are installed in the house. - 1,15
– if the boiler installed in the house is operating at its capacity limit. In this case, every 10 degrees of heated coolant reduces the power of the radiators by 15%. - 1,8
– the magnification factor that needs to be applied if the room is corner and has more than one window.
To calculate the power of radiators in a private house, the following formula is used:
- V
– volume of the room; - 41
– average power required to heat 1 m2 of a private house.
Calculation example
If there is a room of 20 m2 (4 × 5 m - the length of the walls) with a ceiling height of 3 meters, then its volume can be easily calculated:
The resulting value is multiplied by the power accepted by the standards:
60×41=2460 W – this is how much heat is required to heat the area in question.
Calculation of the number of radiators comes down to the following (taking into account that one radiator section emits on average 160 W, and their exact data depends on the material from which the batteries are made):
Let's assume that a total of 16 sections are needed, that is, you need to purchase 4 radiators of 4 sections for each wall or 2 of 8 sections. At the same time, one should not forget about the adjustment coefficients.
Accounting for thermal insulation
Thermal insulation plays a significant role in calculating the required power. For example, a 2 m layer of mineral wool will significantly reduce heat loss, λ = 0.06 (for the above parameters):
Q= 0.06*30*40/0.2 = 360 (W) = 0.36 (kW).
When calculating floor heat loss, it is taken into account that the soil has an initial temperature of about 5 degrees Celsius.
If the room is insulated, then an average of 3 to 5 kW will be needed to compensate for heat loss. You can make your own calculation using the example given; data on specific materials can be easily found in reference books.
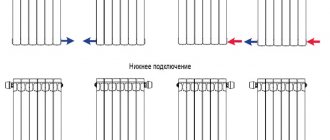
Dependence of radiator power on connection and location
In addition to all the parameters described above, the heat transfer of the radiator varies depending on the type of connection. A diagonal connection with a supply from above is considered optimal; in this case, there is no loss of thermal power. The largest losses are observed with lateral connections - 22%. All others are average in efficiency. Approximate percentage losses are shown in the figure.
Heat loss on radiators depending on connection
The actual power of the radiator also decreases in the presence of obstructing elements. For example, if a window sill hangs from above, the heat transfer drops by 7-8%; if it does not completely block the radiator, then the loss is 3-5%. When installing a mesh screen that does not reach the floor, the losses are approximately the same as in the case of an overhanging window sill: 7-8%. But if the screen completely covers the entire heating device, its heat transfer is reduced by 20-25%.
The amount of heat depends on the installation
The amount of heat depends on the installation location
Adjusting results
In order to obtain a more accurate calculation, you need to take into account as many factors as possible that reduce or increase heat loss. This is what the walls are made of and how well they are insulated, how large the windows are and what kind of glazing they have, how many walls in the room face the street, etc. To do this, there are coefficients by which you need to multiply the found values of heat loss in the room.
The number of radiators depends on the amount of heat loss
Windows account for 15% to 35% of heat loss. The specific figure depends on the size of the window and how well it is insulated. Therefore, there are two corresponding coefficients:
- ratio of window area to floor area: 10% - 0.8
- 20% — 0,9
- 30% — 1,0
- 40% — 1,1
- 50% — 1,2
- three-chamber double-glazed window or argon in a two-chamber double-glazed window - 0.85
Walls and roof
To account for losses, the material of the walls, the degree of thermal insulation, and the number of walls facing the street are important. Here are the coefficients for these factors.
- brick walls two bricks thick are considered the norm - 1.0
- insufficient (absent) - 1.27
- good - 0.8
Presence of external walls:
- interior space - no losses, coefficient 1.0
- one - 1.1
- two - 1.2
- three - 1.3
The amount of heat loss is influenced by whether the room is located on top or not. If there is a habitable heated room on top (the second floor of a house, another apartment, etc.), the reduction factor is 0.7, if there is a heated attic - 0.9. It is generally accepted that an unheated attic does not affect the temperature in any way (coefficient 1.0).
It is necessary to take into account the characteristics of the premises and climate in order to correctly calculate the number of radiator sections
If the calculation was carried out by area, and the ceiling height is non-standard (a height of 2.7 m is taken as the standard), then a proportional increase/decrease using a coefficient is used. It is considered easy. To do this, divide the actual ceiling height in the room by the standard 2.7 m. You get the required coefficient.
Let's do the math for example: let the ceiling height be 3.0m. We get: 3.0m/2.7m=1.1. This means that the number of radiator sections that was calculated by area for a given room must be multiplied by 1.1.
All these norms and coefficients were determined for apartments. To take into account the heat loss of a house through the roof and basement/foundation, you need to increase the result by 50%, that is, the coefficient for a private house is 1.5.
Climatic factors
Adjustments can be made depending on average winter temperatures:
Having made all the required adjustments, you will receive a more accurate number of radiators required to heat the room, taking into account the parameters of the premises. But these are not all the criteria that influence the power of thermal radiation. There are also technical subtleties, which we will discuss below.
How is the area of a house calculated?
But the technical inventory authorities use the Instructions on the accounting of the housing stock of the Russian Federation to determine the area of premises. And therefore, the BTI documents for determining the area of an apartment or individual residential building contain general information, where the accounting includes a balcony, loggia, terrace, etc. Such premises are included in the total area, but with a reduction factor: 0.5 – loggias; 0.3 – terraces and balconies; 1.0 – also terraces and cold storage rooms.
In accordance with the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, the concept of total area includes the sum of the areas of all rooms and parts of a given premises, including the areas of rooms (premises) for additional or auxiliary purposes (use), which are intended for household and other needs of citizens. Such premises are considered to be: kitchens, corridors, bathrooms, etc.
Boiler power for apartments
When calculating heating equipment for apartments, you can use SNiP standards. The use of these standards is also called calculating boiler power by volume. SNiP sets the required amount of heat to heat one cubic meter of air in typical buildings:
- heating 1 m 3 in a panel house requires 41 W;
- in a brick house there is 34W per m3.
Knowing the area of the apartment and the height of the ceilings, you will find the volume, then, multiplying by the norm, you will find out the power of the boiler.
Calculation of boiler power does not depend on the type of fuel used
For example, let’s calculate the required boiler power for premises in a brick house with an area of 74 m2 with ceilings of 2.7 m.
- We calculate the volume: 74m2 *2.7m=199.8m3
- We calculate according to the norm how much heat will be needed: 199.8*34W=6793W. We round and convert to kilowatts, we get 7 kW. This will be the required power that the thermal unit must produce.
It’s easy to calculate the power for the same room, but in a panel house: 199.8*41W=8191W
In principle, in heating engineering they always round up, but you can take into account the glazing of your windows. If the windows have energy-saving double-glazed windows, you can round down
We believe that the double-glazed windows are good and get 8 kW.
The choice of boiler power depends on the type of building - brick buildings require less heat to heat than panel ones
Next, you need, just as in the calculation for a house, to take into account the region and the need to prepare hot water. Corrections for abnormal cold weather are also relevant. But in apartments, the location of the rooms and the number of floors play a big role
Walls facing the street need to be taken into account:
- One external wall - 1.1
- Two - 1.2
- Three - 1.3
After you take into account all the coefficients, you will get a fairly accurate value that you can rely on when choosing heating equipment. If you want to get an accurate thermal calculation, you need to order it from a specialized organization.
There is another method: to determine real losses using a thermal imager - a modern device that will also show the places through which heat leaks are more intense. At the same time, you can eliminate these problems and improve thermal insulation. And the third option is to use a calculator program that will calculate everything for you. You just need to select and/or enter the required data. At the output you will receive the calculated power of the boiler. True, there is a certain amount of risk here: it is not clear how correct the algorithms are at the basis of such a program. So you still have to at least roughly calculate it to compare the results.
This is what a thermal image image looks like
We hope you now have an idea of how to calculate the boiler power. And don’t be confused by the fact that this is a gas boiler. and not solid fuel, or vice versa.
Based on the inspection results, heat leaks can be eliminated
You may be interested in articles on how to calculate the power of radiators and the choice of pipe diameters for a heating system. In order to have a general idea of the mistakes that often occur when planning a heating system, watch the video.
Installation of floor-standing and wall-mounted boilers
Design of a three-phase electric boiler.
It is advisable to install electric boilers in rooms with an area of up to 500 m2. You can install the heating system and connect the boiler to it yourself. In the wall version they are secured with anchor bolts, and in the floor version they are usually installed on a special stand. If you do not have experience installing and connecting circuit breakers against short circuits and leakage currents, then it is better to contact a specialist electrician. In this matter, liberties are unacceptable.
The cross-section of the cable cores must comply with the requirements specified in the accompanying documentation; it depends on the power. There may be problems with protective grounding. Keep in mind that grounding is not just a pin driven into the ground, but a device on which life depends. All metal parts of the heating system must be connected to the ground loop.
And most importantly. The resistance of the grounding loop must meet the standards for the corresponding soil. The maximum value of grounding resistance depends on the physical properties of the soil and must be indicated in the issued permits. The lower the ground resistance, the better. The maximum value should not exceed 10 ohms. To reduce the resistance of the grounding circuit, copper plates must be used, and the grounding site must be impregnated with a saline solution. The grounding resistance value must be checked before the start of the heating season.
How to calculate the number of radiator sections
There are several methods for calculating the number of radiators, but their essence is the same: find out the maximum heat loss of the room, and then calculate the number of heating devices required to compensate for them.
There are different calculation methods. The simplest ones give approximate results. However, they can be used if the premises are standard, or coefficients can be applied that allow one to take into account the existing “non-standard” conditions of each specific room (corner room, access to a balcony, wall-to-wall window, etc.). There is a more complex calculation using formulas. But essentially these are the same coefficients, only collected in one formula.
There is another method. It determines the actual losses. A special device - a thermal imager - determines real heat loss. And based on this data, they calculate how many radiators are needed to compensate for them. Another good thing about this method is that the thermal imager image shows exactly where the heat is lost most actively. This could be a defect in work or building materials, a crack, etc. So at the same time we can improve the situation.
The calculation of radiators depends on the heat loss of the room and the rated thermal power of the sections
How is the area of a house calculated?
But the technical inventory authorities use the Instructions on the accounting of the housing stock of the Russian Federation to determine the area of premises. And therefore, the BTI documents for determining the area of an apartment or individual residential building contain general information, where the accounting includes a balcony, loggia, terrace, etc. Such premises are included in the total area, but with a reduction factor: 0.5 – loggias; 0.3 – terraces and balconies; 1.0 – also terraces and cold storage rooms.
In accordance with the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, the concept of total area includes the sum of the areas of all rooms and parts of a given premises, including the areas of rooms (premises) for additional or auxiliary purposes (use), which are intended for household and other needs of citizens. Such premises are considered to be: kitchens, corridors, bathrooms, etc.
Oil radiator
One of the most popular household heaters. They have a power of 1.0 to 2.5 kW and are used in apartments, offices, and country houses.
| Principle of operation | Inside a sealed metal case filled with mineral oil, there is an electric coil. When heated, it transfers its heat to the oil, which in turn transfers to the metal body, and then to the air. Its outer surface consists of several sections (fins) - the greater their number, the greater the heat transfer, with equal powers. The heater maintains the set temperature in the room and automatically turns off in case of overheating. As soon as the temperature starts to drop, it turns on. |
| Advantages | Low heating temperature of the housing (about 60 o C), due to which oxygen is not “burned”, fireproof, silent thanks to the thermostat and timer, some models do not require switching off, high mobility (the presence of wheels makes it easy to move them from room to room) |
| Flaws | It takes a relatively long time to warm up the room (however, it retains heat longer), the temperature of the radiator surface does not allow you to freely touch it (which is extremely dangerous if there are children in the room), relatively large dimensions |
| conclusions | Oil radiators are ideal for heating apartments. Quietness, efficiency and safety are very important here. One heater is enough to heat a living room or bedroom. Oil radiators are equipped with wheels and can be easily moved from room to room. For the summer, you can simply take the oil radiator out to the shed or put it in the pantry. |