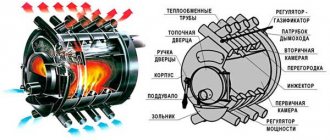
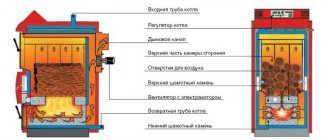
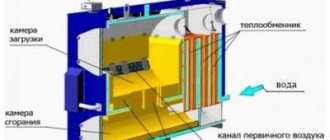
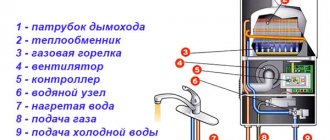
Potbelly stove in the garage: pros and cons
Car enthusiasts install a homemade potbelly stove in the garage for several reasons:
- the stove heats the room in winter;
- you can cook food or heat a kettle on a potbelly stove;
- With a design approach, a homemade heating device can become a decoration for the garage.
We advise you to read in more detail why a potbelly stove smokes and find answers to your questions.
A potbelly stove has a number of advantages compared to other heating devices:
- For kindling, you can use a variety of fuels - firewood, coals, construction waste, petroleum products, waste oil, etc.
- The main advantage of a potbelly stove is the speed of heating the room. Thanks to its high efficiency and power, the stove will heat a garage of 50-60 square meters. m. in 15-20 minutes.
- The stove distributes heat evenly regardless of where it is located.
- A potbelly stove is an economical heating device. For example, heating a garage with a potbelly stove will cost several times less than with an electric heater.
- An additional advantage of a potbelly stove in the garage is the ability to cook or warm up food. When creating a stove yourself, it is enough to attach a metal cooking surface to its upper part.
- A homemade stove will cost the car owner almost free if there is an unnecessary barrel, sheet of metal and pipe lying around in the garage.
We previously wrote an article about installing a potbelly stove for heating and recommended adding it to your bookmarks.
The potbelly stove will fit harmoniously into the interior of any garage. In addition to the heating function, the heating device has a “cooking mode”. A hob is installed at the top of the stove, where you can heat a kettle or cook food.
The disadvantages of a potbelly stove in the garage are:
- the need to install a chimney in the garage;
- periodic cleaning of the chimney;
- the need for constant fuel supply;
- inability to accumulate heat.
How it works
The part of the cylinder that was initially cut off will be used as a waste container. Do not forget that under no circumstances should you use kerosene or gasoline instead of oil - this can lead to an explosion. If desired, you can use the finished structure not only to heat the room, but also as a stove for cooking food. It is enough to weld a steel rectangle to the lid.
Fill two-thirds of the container with oil; for ignition, you can add a little kerosene or gasoline; a rag soaked in one of these liquids will do. After 3-5 minutes, all the gasoline will burn out and the exhaust will begin to work.
After finishing use, you should clean (at least partially) the cylinder itself - just tap the lid on top of the structure thoroughly so that all the carbon deposits fall off.
Stages of making a homemade potbelly stove
The construction of this heating equipment consists of several stages. You need to think about its size and determine what it will be made of. Next, a drawing of a potbelly stove for the garage is drawn up. It indicates not only the parameters of the entire structure, but also the amount of material used for its construction.
It’s quite easy to make a “potbelly stove” for the garage with your own hands. Drawings of this equipment are drawn up independently. You can also seek the help of specialists.
Then the structure is welded and refined.
About the main types of structures
Not all types of furnaces can be made at home using your own hands. Drawings, videos and technical data for certain types of structures will be a useless application, due to their complex structure. You can only make ordinary pyrolysis burners yourself, which are assembled using ready-made containers or using metal sheets.
The dimensions of the heating structure are quite compact
As for models with drip supply of liquid fuel, it is hardly worth trying to make them yourself. Such designs are characterized by economical fuel consumption, but are difficult to manufacture. In addition, they are sensitive to the quality of the fuel used.
A more complex model working in development
List of popular stove models
Great demand for installations operating with waste creates supply on the market. The Belamos company, manufactured in Germany and Russia, can boast of good quality products. You can also highlight the following options for efficient heating:
Don't miss: How to properly heat a coal stove in a house - basic rules and features of the firebox
Emelya - exhaust heater with a power consumption of 40 W, capable of heating up to 200 sq.m.;
Heat pump NT 612 – positioned as a garage unit and suitable for small spaces;
Heat 25 – suitable for air heating with hot steam;
Master wa 33 – used for heating industrial premises;
Polarus - units from Polarus have a power adjustment function from 20 to 60 kW;
Euronord at 306 – drip design with a radial-type blower;
Typhoon is a heating device for garages, car services and workshops, thermal power ranges from 4 kW to 15 kW;
Herringbone - suitable for heating small rooms;
Thermobile at 306 – manufactured from Russia, technical or diesel fuel is used for operation;
Kronburg d15 is a convenient device at an affordable price that uses machine oil;
Multeat plus - products manufactured from Novosibirsk, are distinguished by smokeless combustion of the fuel mixture.
Some Belamos models are suitable for use in a bath; they do not emit black smoke if you follow all the rules of use. Stav products from Russia performed well. Many users learn about the features of using devices from the Thermoportal forum: stoves from various manufacturers are carefully discussed by their owners, highlighting the pros and cons.
Buleryan can be distinguished separately - the device operates in a combination of firewood and oil. To remake the model, you can arrange a door at the front of the installation to add a liquid component, and also make a reservoir. The Zhuchka stove is excellent for heating a car service center, as it is small in size and has low fuel consumption.
Ready-made installations or models made by yourself are beneficial to use: they save money, have low resource consumption and are affordable. Making the unit yourself is not difficult, and this model will last a long time.
What is mining: advantages and disadvantages
Waste oil, or simply waste oil, is widely used to operate the furnace. This oil can be found in large quantities at all kinds of automotive enterprises, service stations and workshops. Industrial, transmission and motor oils are used for furnaces.
You can recycle waste, but why, when you can save good money by making a stove out of it yourself. Waste oil produces heat output that is equal to 15 kW of electric heater operation. The consumption ranges from 05 to 2 liters per hour.
Exhaust furnaces operate on the principle of direct air heating; they can be used to heat small spaces such as workshops, greenhouses, garages, and so on. Such a stove will also come in handy at a car service center, where you won’t have to spend a long time searching for the right fuel.
Exhaust furnaces have the following advantages:
- absence of burning and soot when burning oil;
- the oven is easy to use;
- high level of fire safety, since only fuel vapors burn, and not the fuel itself.
But it is worth considering the disadvantages of fuel:
- used oil contains a lot of impurities, moisture, alcohols and much more, which, when used in boilers, can clog filters and nozzles, and even cause an explosion in the heating system;
- Before using the oil in the boiler, the oil must be filtered and purified, which is impossible to do on your own;
- It is impossible to keep the waste in the cold; it must be stored either in a heated room or closed in a barrel at a depth corresponding to the freezing level of the ground.
How to build a stove from a pipe?
Do-it-yourself sauna stove from a pipe
One of the common homemade options is a bath stove made from a pipe. Let's consider how such construction is carried out.
Pipe is an excellent “semi-finished product” for constructing a furnace
Metal stoves can be made from a sheet of steel or, for example, from an old barrel. But if there is a piece of pipe of suitable diameter on the farm, then it is worth using this “blank”.
A homemade stove for a bathhouse made from a pipe can be made with a vertical or horizontal direction of a piece of rolled pipe. By using prefabricated stove pipes, the amount of welding work required when making sheet metal stoves is reduced.
Only high-quality pipes without signs of corrosion are suitable for the manufacture of furnaces.
If the pipe has been lying outside for a long time, it should be inspected first and reinforced in problem areas by welding patches.
Preparing parts
To make a good stove from a pipe, you will need a piece of rolled pipe with a diameter of 50 cm and a length of 1.5 meters. The thickness of the pipe walls must be at least 10 mm.
The workpiece should be cut into two parts, measuring 0.6 and 0.9 meters, respectively. A longer piece is needed to build a firebox and heater, and the remaining piece will be used to make a tank.
Making a furnace
An example of using a pipe stove in a bathhouse
- First of all, you should take care of the blower. A hole 5 cm high and 20 cm wide is cut at the bottom of a long section of pipe. A thick round steel plate is welded above the hole.
- Next, a niche for the firebox is formed and a door is made for it. The door is hung on hinges or hooks.
- A piece of pipe is welded above the firebox, which will be used as a heater. The height of the segment is 30-35 cm.
To fill the heater, you should use rounded cobblestones; in extreme cases, you can pour electrical insulators made of ceramics.
A steel coupling is installed in the upper part of the future furnace, which will be required to fix the water heating boiler.
Making a water heating tank
Assortment of pipe bath stoves
When building a sauna stove with your own hands, a water heating tank is also formed from a pipe.
- For its manufacture, a piece of pipe 0.6 m high is used.
- A steel circle – the bottom – is welded to the end part of the pipe section.
Advice! The thickness of the metal for making the bottom of the water tank is at least 8 mm
A hole is cut in the bottom of the tank to accommodate the chimney. It should be moved towards the rear wall of the tank. The chimney is fixed to the bottom of the tank by welding
It is important that the seam is of high quality to prevent water leaks into the firebox. The upper part of the tank is closed with a metal lid with holes made for the passage of the chimney and for filling with water. The chimney is welded tightly to the lid, and a neck with a lid is installed in the hole for filling water.
Example of calculating furnace dimensions
As mentioned above, fuel consumption is about 1...2 liters per hour. At the same time, the radiated heat is about 11 kW/hour per liter. Thus, the furnace can produce 11...22 kW per hour. To calculate the required volume of the firebox taking into account the burning time, we accept:
- volume of the room (garage) – 7x4x2.5=70 cubic meters, area 28 sq.m.;
- We believe that for every square meter of a garage-type room, at least 500 W are required (basic 100 W, we enter coefficients for all external walls, non-insulated roof and foundation, large entrance opening, metal structure);
- Accordingly, an area of 28 squares requires 14 kW of energy per hour.
By slightly increasing the minimum power of the stove (increasing the draft), we will obtain the required temperature in the room. But fuel consumption will increase to approximately 1.5...1.6 liters per hour. Therefore, for a burning time of at least 6 hours, the volume of the firebox should be 10 liters. This corresponds to 0.001 cubic meters, that is, the container should have a size, for example, 10x10x10 cm. In reality, the volume of the firebox exceeds the required volume of fuel by 1.5...2 times, that is, the dimensions should be 20x10x10 cm or more, this is suitable for a mini stove. Usually they take it with a substantial reserve, that is, 50x30x15 cm. This allows you not to add fuel every time you ignite.
Important: with large firebox sizes, it becomes necessary to extinguish the fire in the furnace during exhaust before the fuel burns out completely. The extinguishing process is shown in the video
The length of the pipe is 40 cm, respectively, its diameter is 10 cm. The area of the lateral surface of the cylinder is equal to its height multiplied by the circumference of the base (diameter multiplied by the number π), in our case 40x3.14x10 = 1256 cm2. Accordingly, the area of all holes is one tenth of the total - 125.6 cm2. Considering that the area of one hole with a diameter of 10 mm is equal to πx0.52=3.14x0.25=0.78 sq.cm, such a pipe will require 125.6/0.78=160 holes.
Note! The accepted value is the area of the holes 10% of the total area of the side surface of the pipe - conditionally! The number of holes during manufacturing is taken, among other things, from the strength of the product and is usually noticeably less!
Considering that the unfolded cylinder is a 31x40 cm rectangle, and the holes should be placed in a checkerboard pattern, we will have to make 12 vertical rows of 13 or 14 holes each. Marking vertical rows is simple - divide the upper or lower circumference of the base of the pipe into 12 parts in any geometric way and draw vertical drilling lines.
The distance between the rows will be 3.3 cm. Marking the vertical rows is a little more difficult, since in every second row it is necessary to shift the upper (or lower) marking point by half the distance between the holes. Considering that we need to make holes not on the edge of the pipe, we add 1 to the planned number of holes and calculate the step: for 13 holes it will be 40/(13+1)=2.85 cm, for 14 – 40/(14+1) =2.6 cm.
Important: when drilling, the axis of the drill must be directed towards the axis of the pipe!
Furnace for processing from steel sheets
Materials and tools
The designs of waste oil furnaces made from steel sheets are very popular among craftsmen among the people. This stove has compact dimensions (70/50/35 cm without chimney), weighs 27 kg, heating can be connected to it, it can be used in cold weather, and the upper part of the stove can be used for cooking. To make such a stove we will need:
- steel sheet 4 mm thick
- steel sheet 6 mm thick
- Bulgarian
- file
- welding machine and electrodes
- a pipe with an internal diameter of 10 cm, a length of at least 4 m and a wall thickness of 4-5 mm for the chimney
- steel corners 20 cm high 4 pieces as legs for the stove
- drawing
- level and tape measure
- hammer
- burner tubes made of steel, copper or painted sheet metal
Stages of manufacturing a furnace from steel sheets
First, we print out a drawing of the future furnace with the details drawn on it.
Next we make the details according to the drawing. Parts for the tank are made of 4 mm thick steel sheet, and for the bottom of the firebox and the tank lid from 6 mm thick sheet. The sheets are laid out on a flat surface, markings are made on them and parts are cut out using a grinder. All welds are checked for leaks and cleaned with a file. A strip 115 mm wide is cut out of a sheet 4 mm thick, and on a sheet bending machine we fold the strip into a ring with a diameter of 34–34.5 cm. We electric weld the strip. We have a pipe for an oil container. From the same steel sheet we cut out a circle with a diameter of 34.5 cm. This will be the lid of the oil container. We weld the lid to the pipe for the oil container. We also weld corners to the lid on 4 sides. The oil container is ready! From a steel sheet 6 mm thick, cut out a strip 6 cm wide and roll it into a ring to get a diameter of 35.2 cm. From the same sheet, cut a circle with a diameter of 35.2 cm into 6 mm. Make a hole with a diameter of 10 cm exactly in the middle of the circle. The chimney pipe will be inserted into it. To the right of the hole we retreat 4 cm and make another hole of 5-6 cm into which the oil will flow. We weld a ring with a diameter of 35.2 cm to a circle with a diameter of 35.2 cm. The tank for filling the oil is ready! We make the lower part of the tank. From a steel sheet 6 mm thick, cut out a circle with a diameter of 35.2 cm. Step back a few centimeters from the edge of the circle and cut a hole with a diameter of 10 cm. From the center of the hole to the center of the circle itself should be approximately 11 cm. This will be the hole for the pipe into which the chimney is inserted pipe. From a pipe with a diameter of 10 cm, cut a part 13 cm high. This will be the pipe. From a sheet 6 mm thick, cut out a rectangle 7 cm wide and 33 cm long. This will be the partition. It must be placed in a circle with a diameter of 35.2 cm closer to the hole with a diameter of 10 cm and welded. Insert a 13 cm high exhaust pipe into the 10 cm hole. Prepare the pipe for the burner. On it from below, at a distance of 36 cm, we make evenly 48 holes of 9 mm, 6 circles of 8 holes 6 cm apart. We insert a pipe with holes into the lid of the oil container, made of a sheet 4 mm thick. Using a level, make sure that the pipe is inserted evenly. If there are any deviations, they are eliminated using a file and a grinder. The parts should fit tightly into each other, but not be welded. We insert an exhaust pipe 16 cm high into the hole in the tank for filling oil. Connect the lower and upper parts of the tank
ATTENTION! We don't weld! The parts must fit into each other. To strengthen it, we make an O-ring with a diameter of 35.4 cm and put it on top of the tank structure
We check the accuracy of fit of the parts with a level. We electric weld the oil filling tank to a pipe with 48 holes. On the other side of the pipe with holes, we weld a structure fastened with an O-ring. Before welding, we carefully check the accuracy of installation of parts with a level! We equip the oil filling hole with a round plate, which can be easily moved and moved according to the principle of a door peephole. Now we install a chimney from a 4 m long pipe. If indoors it can be located at an angle, then outdoors it is strictly vertical so that the wind does not blow. ATTENTION! Under no circumstances should the chimney be installed horizontally! If the inclined pipes are long, they can be strengthened with special bends made of steel rods.
We build a boiler from a 50 liter cylinder - any craftsman can do it!
We prepare all the necessary parts and begin assembling the stove for testing. Before starting the main work, you should completely empty the cylinder of condensate and gas residues in it. Advice. It is easy to check the quality of the work performed. Coat the valve outlet (the hole at the end) with concentrated dishwashing liquid or regular soap. Open the faucet. If there is no condensate or gas left in the cylinder, foam bubbles will not appear at the outlet. This means you did everything right.
First of all, the valve is dismantled
We remove the valve from the cylinder. If you have a gas container with a non-removable tap, you will have to tinker. Use an electric drill to drill a hole in the bottom. And then unscrew the valve. Note! Experts advise performing this operation very carefully. Even if you are sure that all the flammable composition has left the cylinder, there is still some possibility of the container exploding. Do not press down on the power tool with excessive force. Even better, water the drill with ordinary water while making a hole in the bottom. Then the risk of explosion will be zero. After dismantling the valve, fill the cylinder with water to the top and wait a couple of minutes until it all comes out.
Now we cut out two windows on the gas cylinder. The height of the first (lower) is 20 cm, the second (upper) is 40. The width of the openings is a third of the cross-section of the cylinder used. There should be a jumper between the cut windows. Its height is 5–7 cm. We have a full-fledged compartment for burning fuel. By the way, you can even put coal and firewood in it if you wish.
The next step is to make a device that will separate the heat exchanger from the oil combustion chamber. We will make the separator from a steel sheet 4 mm thick. We cut out a circle from it with a diameter corresponding to the cross-section of a 50-liter gas container. That's not all. In the central part of the completed workpiece, we again cut out a circle (necessary for installing the burner). Its diameter is 10 cm.
The burner itself is made from a pipe with a height of 20 and a cross-section of 10 mm. The finished product will need to be perforated - drill several 1.5–2 cm holes. All burrs must be removed from the latter. If cleaning is not done, soot will constantly settle on the holes during operation of the stove. This will cause a narrowing of their cross-section, which over time will lead to a significant decrease in the efficiency of the home-made heating unit.
We put a membrane on the burner made according to all the rules. Weld the last one strictly in the center. Then install the entire workpiece into the cylinder and securely connect it by welding around the perimeter. Advice. The pipe can be welded to the bottom of the chamber divider. Then it will be possible to load special pellets and briquettes, as well as sawdust and other solid fuels into the stove.
Bottom of the firebox chamber and burner
I cut out the bottom from steel. I decided to make the burner 20 cm long - that would be enough.
This will be the burner
I made many holes around the circumference so that air could easily get to the fuel. Once all the holes were done, I sanded down the inside of the burner. You should definitely do this too, because... soot will begin to actively accumulate on the protrusions and other defects.
First, I welded the burner into the bottom of the upper chamber, and then installed them in their proper place. You can safely lay wood on such a stove shelf. Relevant for cases when it is not possible to replenish mining reserves.
First I welded the burner into the bottom of the upper chamber
Types of furnaces for mining
It has already been said above that the simplest potbelly stove is not very convenient or effective. Therefore, various modification options have appeared, which we will consider below.
Exhaust stove from an old gas cylinder
Here you will also need 4 mm sheet metal (about 50 sq. cm), but another basic element is more important - a waste gas cylinder with a capacity of 50 liters, better than the old Soviet model, propane. Oxygen is heavier and more massive, making it difficult to work with. In addition, you need:
- steel pipe with a diameter of 100 m, a length of 2000 mm;
- valve with ½ inch thread;
- steel corner with shelf 50 mm, meter or a little more;
- clamps;
- loops;
- a piece of fuel supply hose;
- car brake disc. We select the diameter so that it fits freely into the cylinder;
- another cylinder (freon) to create a fuel tank.
Sequence of work:
- we drain the remaining gas from the cylinder, drill a hole in the bottom and rinse the cylinder with water;
- We cut out two openings in the side wall - a large lower one and a smaller upper one. The fuel chamber will be located in the lower one, and the afterburning chamber in the upper one. By the way, if the dimensions of the lower opening allow, in addition to mining, it will be possible to use firewood as fuel;
- We make the bottom of the afterburning chamber from a steel sheet;
- We make a burner from a pipe - a place where volatile gases mix with air and ignite. Holes are drilled in the burner (according to the principle described above), the inside of the pipe is GRINDED, this is necessary for greater efficiency of the product;
- the finished burner is welded into the bottom of the afterburner chamber;
- We make a waste tray from a brake disc and a piece of steel sheet. We weld the lid in its upper part;
- It is better to use a coupling to connect the burner and the pan cover - this makes servicing the stove easier;
- We provide a fuel supply. To do this, a hole is made in the wall of the cylinder into which a pipe with a threaded edge is welded;
- A valve is placed at the outer end of the pipe and a hose is connected to it. The hose, in turn, is connected to the fuel cylinder;
- the chimney pipe is welded into the upper part of the cylinder, then “taken away” in a smooth upward transition until leaving the room.
In fact, this completes the work with the furnace itself, but it is better to additionally build a heat exchanger - this will increase efficiency.
One of the heat exchanger options - plates welded onto the body - is shown in the photo below.
The finished oven with the doors open (the hinges were needed specifically for them; the pieces of the cylinder cut out in step 2 are attached to the hinges).
Pressurized furnace in operation
This design is also assembled on the basis of a 50-liter cylinder.
The air supply here comes from a fan (for example, from the stove of a VAZ 2108 car), which allows you to increase the draft in the afterburner and at the same time actually make the entire surface of the cylinder a heat exchanger.
The operation process and ignition are shown in the video.
Exhaust furnace with water circuit
Manufacturing a furnace with a water circuit can be almost the same as in the simplest version. The main difference is the organization of heat extraction into the water coolant. In the photo below, this possibility is realized by winding a pipe around the furnace body. In this case, cold water is naturally supplied from below, and heated water comes out from above.
A more “advanced” option is a stove with a “water jacket”. In fact, the body is enclosed in a second, hollow one, inside of which water circulates. The heated liquid is supplied to heating radiators.
True, the phrase “does not smoke” from the manufacturer is a bit of an exaggeration - this is only possible with regular cleaning of the chimney and the use of sufficiently high-quality, filtered fuel.
In the drawing, the device looks something like this.
Drip furnace
This type of stove is safer than those designs into which fuel is poured at once. In addition, in the case of gradual feeding, the burning duration can be freely adjusted.
A mandatory element of the system is a separate fuel tank, the waste from which is supplied in small portions - almost drops - using a special device.
The photo below shows a design where there is a separate tank with an oil line located above the fuel chamber. The base of the furnace is a gas cylinder; a valve is used to regulate the flow rate of the waste. The design of the furnace is discussed in more detail above.
Another type of product is with a retractable fuel compartment and a double afterburner.
It is realized in metal.
Please note: due to supercharging and the absence of fuel loss during filling, the exhaust consumption is reduced by 20...30%
Types of used oil units
Similar to gas and diesel guns, mining devices can be of two main types: direct and indirect.
For models of the first type (direct heating), a round gas burner is located inside the cylinder body, which is blown from all sides by an air flow flowing from the fan. The heated air mass, together with combustion products, is released through a pipe located on the opposite side of the gun.
A direct-heating gun has greater heat output, but during its operation harmful substances enter the room. Models with indirect action do not have this drawback.
Since gaseous waste contains substances harmful to the health of people and animals, it is recommended to use cannons only in well-ventilated spaces. Direct heating devices can be used to maintain a comfortable temperature in unoccupied areas: buildings, garages, workshops.
The designs of heat guns of the second type (indirect heating) are equipped with a built-in system that allows the separation of flue gases released when oil burns. At the same time, the heat from them is transferred to the air blown by the fan, which accumulates in a heat exchanger provided for this purpose, which avoids direct contact between the gas and air masses.
The latter, after heating, leave the heat exchange chamber through a special opening equipped in the housing, while combustion products leave the gun through the side pipe, which is connected to the chimney pipe.
Indirect heating models are environmentally friendly; when used, no harmful gases enter the room, and there are no odors, making such devices suitable for heating rooms in the presence of people.
All heat guns in testing can also be divided into the following categories:
- Stationary - high-power devices that are installed in one place and connected to the chimney.
- Mobile – compact devices that can be moved around the room. As a rule, they have direct heating and low power, since devices with large-scale heat transfer emit a lot of combustion products.
Devices operating on waste oils vary in size, shape, design, and the presence of additional functions.
Factory furnaces, their characteristics and features
A waste oil stove is good because it can operate on the lowest quality and cheapest fuel. In this regard, lucky are those who work as a car repairman in their own garage - by doing routine engine oil changes, you can extract waste in almost unlimited quantities. The oil furnace itself is distinguished by its low cost, because it can be assembled from the remains of old iron.
Used oil is a very cheap type of fuel, and for auto repair shops it is completely free.
An oil stove burns fuel in the safest possible way. If you set fire to used oil poured into any container, it will fume and smoke, giving rise to hellish aromas and filling heated rooms with acrid and far from safe smoke. And very little heat will be generated from such combustion. A waste oil furnace, having a well-thought-out design, burns fuel so that it does not form soot.
Depending on the design of the stove and its size, it can heat an area of up to 500 square meters. m. and even more. Oil consumption is scanty - it ranges from 0.5 to 5 l/hour, depending on the power of the unit. The combustion temperature reaches 400-500 degrees. The average chimney height is from 4 to 5 meters. Stoves can operate on both clean and contaminated fuel. The resulting heat can be used for a variety of purposes:
- For direct heating of premises due to the generated heat;
- For cooking (only some models are suitable);
- For use as part of water heating systems.
Thus, the exhaust furnace is a fairly universal heater with a simple design, high efficiency and low cost.
The photo shows the factory furnace Teplamos NT-612, running on waste oil.
Teplamos NT-612 is a closed type oven. It contains a chimney and a pipe for air supply. Combustion of fuel occurs in the inner chamber. In order for the stove to reach operating mode, it must be heated with a small amount of diesel fuel poured into a special bowl. After the fuel burns, we get a stove ready for refueling and further work - we open the waste supply and set it on fire.
The design of this unit has a built-in tank that can hold up to 8 liters of fuel.
A mini-furnace of the “potbelly stove” type is as simple as a matchbox. It is made of sheet iron and is characterized by versatility - it heats non-residential premises and allows you to cook food (small pots, pans and kettles are placed on the surface of the afterburning chamber). The power of such units varies widely. The equipment operates on the basis of pyrolysis.
Zhar MS-25 can operate on both waste oil and diesel fuel.
Let's consider a more solid stove - this is the heat generator Zhar MS-25. The unit can operate on both waste oil and diesel fuel. For its operation, electricity is required to power the built-in fan. The thermal power of the device is 25-50 kW, which allows it to heat an area of up to 500 square meters. m.
Such units consist of a rectangular or cylindrical body. Inside there is a combustion chamber, in the lower part of which there is a container intended for waste oil and holes that provide air flow.
After heating, the fuel evaporates, and then the vapors combine with the air in the chamber. The resulting mixture as a result of convection is directed upward through the firebox, where, when burned, it releases a significant amount of heat.
If desired, a water or air heat exchanger is built into the upper part of the drip furnace during processing, as a result of which it becomes possible to heat the room more evenly and better or to arrange a circuit for supplying hot water.
Drip supply occurs through a metal tube, which is connected to an oil evaporator. Its second end is brought out and connected to the tank with a flexible hose. In the upper compartment of the drip-type furnace during exhaust there is a smoke pipe, which is connected to the chimney.
Ignition and operation
Lighting up a cold furnace at work is not an easy task. Oil vapors only burn when heated. Therefore, you have to ignite it with the help of other flammable liquids - gasoline, alcohol. They are poured in a thin layer on top of the oil in the pan and set on fire.
When burning, they heat the upper layer of waste, the oil begins to evaporate, and the furnace starts in operating mode. After this, open the valve on the oil supply hose and adjust its flow into the furnace. To stop the furnace, simply close the valve. The fuel supply will stop and as soon as the oil in the pan burns out, the stove will go out.
Cleaning the stove from soot and soot is done using metal brushes or small gravel, throwing it into the chimney. Passing along the walls of the chimney, the gravel knocks off the soot, and it falls inside the combustion chamber. Open the door and sweep away the soot with a brush. Then they take out the pan, clean out sediment and fallen soot, gravel and other contaminants from it.
With proper operation and compliance with fire safety, a gas cylinder stove can serve for many years. It is not recommended to install it in a residential area due to the unpleasant odor that accompanies the combustion of waste, but you can install it in a boiler room and connect the water circuit. In this case, a drip-type stove can be used to heat a private house.
Furnace technology
A drawing of a furnace operating on waste oil is shown in the figure.
Drawing of a waste oil furnace
- Making the lower chamber. The primary combustion chamber in such a furnace is combined with a fuel tank. It is a round tank with a lid; the lid has holes for filling oil and for a pipe, which is the second chamber of the furnace. According to the dimensions indicated in the figure, cut out the parts of the lower tank, clean the edges with a grinder and weld them. It is more convenient to make the walls from pipe trim. Weld a bottom made of sheet metal and legs from a corner to the walls of the tank. Cut out a cover with holes: a 100 mm hole in the center and 60 mm closer to one of the edges. The lid can be removable - this will make it easier to clean the tank and transport the stove.
- In a piece of pipe with a diameter of 100 mm and a length of about 360 mm, holes are drilled for air supply. Their diameter should be approximately 1/10 of the pipe diameter; in this case, the figure shows a size of 9 mm. The holes should be spaced evenly around the circumference and height of the pipe.
- The pipe is welded to the lid of the lower tank, maintaining perpendicularity. There is also an air damper on the lid; it can be held on by a rivet or bolted connection. The diameter of the hole for the damper is 60 mm. Through the same hole, oil is poured in and the stove is ignited.
- The upper tank is made in the same way as the lower one. It is also convenient to make the walls of the tank from a 355 mm pipe. In the plate that acts as the bottom, a 100 mm hole is made, offset to one of the edges of the bottom. From the bottom, a small piece of pipe with a diameter of 110 mm is welded to the hole - it is used to put it on the perforated combustion chamber of gases.
- The lid of the upper tank is exposed to the highest temperatures, so it is better to make it from 6 mm metal. A hole is made in the top cover for the chimney; it is located on the side opposite the hole in the bottom of the chamber. Between them, a cutter is welded to the top cover - a partition made of thick metal. The cutter should be located closer to the smoke hole.
- A chimney pipe is welded to the top of the lid, which is later connected to the chimney. To impart rigidity to the structure, a spacer from an angle or pipe with a diameter of 20-32 mm is welded between the lower and upper chambers. The stove itself can be painted with high-temperature metal paint.
Security measures
Working with fuel is always accompanied by increased danger, so we advise you to adhere to basic safety rules.
As for the placement of the stove, it should be located far from objects that are easily flammable. Make sure that it is not standing in a draft.
The fuel must not contain water. We advise you to buy well-refined oil, otherwise the effectiveness will be much lower, and, plus, you will create a lot of problems for yourself. Unrefined oil can clog your oven quite quickly without producing the proper amount of heat.
Periodically check operating equipment, because all things tend to break. In this case, this may cause a fire or other emergency.