When designing large-scale heating systems (in particular, calculating the adjustment of the heating system of an apartment building and its full functioning), especially close attention is paid to the external and internal factors of equipment operation. Several heating schemes for central heating have been developed and are successfully used in practice, differing from each other in structure, working fluid parameters and pipe routing patterns in apartment buildings.
Single-pipe heating system diagram
Single-pipe heating system: vertical and horizontal distribution.
In a single-pipe heating system, the supply of hot coolant (supply) to the radiator and the removal of cooled coolant (return) are carried out through one pipe. All devices relative to the direction of movement of the coolant are connected to each other in series. Therefore, the temperature of the coolant at the inlet of each subsequent radiator along the riser is significantly reduced after heat is removed from the previous radiator. Accordingly, the heat transfer of radiators decreases with distance from the first device.
Such schemes are used mainly in old central heating systems of multi-storey buildings and in autonomous gravity-type systems (natural coolant circulation) in private residential buildings. The main defining disadvantage of a single-pipe system is the impossibility of independently adjusting the heat transfer of each radiator separately.
To eliminate this drawback, it is possible to use a single-pipe circuit with a bypass (a jumper between the supply and return), but in this circuit, the first radiator on the branch will always be the hottest, and the last the coldest.
Multi-storey buildings use a vertical single-pipe heating system.
In multi-storey buildings, the use of such a scheme allows saving on the length and cost of supply networks. As a rule, the heating system is made in the form of vertical risers passing through all floors of the building. The heat output of radiators is calculated during system design and cannot be adjusted using radiator valves or other control fittings. Given modern requirements for comfortable indoor conditions, this scheme for connecting water heating devices does not satisfy the requirements of residents of apartments located on different floors, but connected to the same heating system riser. Heat consumers are forced to “endure” overheating or underheating of air temperature during the transitional autumn and spring period.
Single-pipe heating in a private house.
In private houses, a single-pipe scheme is used in gravity heating networks, in which hot water circulates due to the differential densities of heated and cooled coolants. Therefore, such systems are called natural. The main advantage of this system is energy independence. When, for example, in the absence of a circulation pump in the system connected to the power supply networks and in the event of power outages, the heating system continues to function.
The main disadvantage of the gravity single-pipe connection scheme is the uneven distribution of coolant temperature across the radiators. The first radiators on the branch will be the hottest, and as you move away from the heat source, the temperature will drop. The metal consumption of gravity systems is always higher than that of forced ones due to the larger diameter of the pipelines.
Video about the installation of a single-pipe heating circuit in an apartment building:
Features of hot water supply and calculation of the volume of hot water
Calculation of the amount of hot water in the system depends on technical and operational factors:
- Estimated hot water temperature;
- Number of residents in an apartment building;
- The parameters that plumbing fixtures can withstand and the frequency of their operation in the overall water supply scheme;
- the number of plumbing fixtures that are connected to the hot water supply.
Calculation example:
- A family of four uses a 140 liter bathtub. The bathtub fills in 10 minutes, the bathroom has a shower with a water consumption of 30 liters.
- Within 10 minutes, the water heating device must heat it to the design temperature of 170 liters.
These theoretical calculations work based on average water consumption by residents.
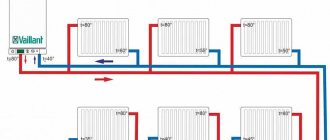
Two-pipe heating system diagram
In two-pipe schemes, the supply of hot coolant to the radiator and the removal of cooled coolant from the radiator are carried out through two different pipelines of the heating systems.
There are several options for two-pipe schemes: classic or standard, associated, fan or beam.
Two-pipe classic wiring
Classic two-pipe heating system wiring diagram.
In the classical scheme, the direction of movement of the coolant in the supply pipeline is opposite to the movement in the return pipeline. This scheme is most common in modern heating systems, both in multi-storey buildings and in private individual ones. The two-pipe circuit allows you to evenly distribute the coolant between radiators without loss of temperature and effectively regulate heat transfer in each room, including automatically through the use of thermostatic valves with installed thermal heads.
Such a device has a two-pipe heating system in a multi-story building.
Associated scheme or “Tichelman loop”
Associated heating wiring diagram.
The associated scheme is a variation of the classical scheme with the difference that the direction of movement of the coolant in the supply and return is the same. This scheme is used in heating systems with long and remote branches. Using a passing circuit allows you to reduce the hydraulic resistance of the branch and distribute the coolant evenly across all radiators.
Fan (radial)
A fan or radial scheme is used in multi-storey construction for apartment heating with the possibility of installing a heat meter (heat meter) in each apartment and in private housing construction in systems with floor-to-floor piping. With a fan-shaped scheme in a multi-storey building, a collector is installed on each floor with exits to all apartments of a separate pipeline and an installed heat meter. This allows each apartment owner to account for and pay only for the heat they consume.
Fan or radiant heating system.
In a private house, a fan diagram is used for floor-to-floor distribution of pipelines and for radial connection of each radiator to a common collector, i.e., each radiator has a separate supply and return pipe from the collector. This connection method allows you to distribute the coolant as evenly as possible across the radiators and reduce hydraulic losses of all elements of the heating system.
Note! When distributing pipelines in a fan pattern within one floor, installation is carried out in solid (without breaks or branches) sections of pipes. When using polymer multilayer or copper pipes, all pipelines can be cast into a concrete screed, thereby reducing the likelihood of rupture or leakage at the junction of network elements.
Providing heat to apartment buildings: centralized heating system
As is known, the provision of heat to a significant portion of the housing stock is carried out centrally. And, despite the fact that in recent years more modern heat supply schemes have appeared and are being implemented, central heating remains in demand, if not among owners, then among developers of multi-apartment housing. However, it should be noted that many years of foreign and domestic experience in using this heating option have proven its effectiveness and right to exist in the future, subject to trouble-free and high-quality operation of all elements.
A distinctive feature of this scheme is the generation of heat outside the heated buildings, the delivery of which from the heat source is carried out through pipelines. In other words, centralized heating is a complex engineering system distributed over a large area, providing heat to a large number of objects at the same time.
Types of radiator connections
The main methods of connecting heating system devices are several types:
- Lateral (standard) connection;
- Diagonal connection;
- Bottom (saddle) connection.
Side connection
Lateral radiator connection.
Connection from the end of the device - supply and return are located on one side of the radiator. This is the most common and effective connection method; it allows you to remove the maximum amount of heat and use the entire heat transfer of the radiator. As a rule, the supply is at the top and the return is at the bottom. When using a special headset, it is possible to connect from bottom to bottom, this allows you to hide the pipelines as much as possible, but reduces the heat transfer of the radiator by 20 - 30%.
Diagonal connection
Diagonal radiator connection.
Connection diagonally to the radiator - the supply is on one side of the device from the top, the return is on the other side from the bottom. This type of connection is used in cases where the length of a sectional radiator exceeds 12 sections, and a panel radiator is 1200 mm. When installing long radiators with side connections, there is uneven heating of the radiator surface in the part furthest from the pipelines. To ensure that the radiator heats up evenly, a diagonal connection is used.
Bottom connection
Bottom connection from the ends of the radiator
Connection from the bottom of the device - supply and return are located at the bottom of the radiator. This connection is used for the most hidden installation of pipelines. When installing a sectional heating device and connecting it using the bottom method, the supply pipe approaches on one side of the radiator, and the return pipe on the other side of the bottom pipe. However, the heat transfer efficiency of radiators with this scheme is reduced by 15-20%.
Bottom radiator connection.
In the case when the bottom connection is used for a steel panel radiator, then all the pipes on the radiator are located at the bottom end. The design of the radiator itself is made in such a way that the supply flows through the manifold first to the upper part, and then the return flow is collected in the lower radiator manifold, thereby not reducing the heat transfer of the radiator.
Bottom connection in a single-pipe heating circuit.
How to make an effective heating system in an apartment with your own hands
No matter how technologically advanced modern houses are, in order to maintain a comfortable temperature in the home in winter, a person must artificially compensate for the inevitable heat loss. This is why heating in the apartment is necessary. In most countries of the post-Soviet space, things are not yet very good with the energy efficiency of the housing stock, where, among other things, heavily worn-out systems are used. When making “European-quality renovations” in old buildings, owners are necessarily faced with the problem of completely replacing or modernizing the heating; apartment owners in new buildings almost always have to redo it. All heating-related activities are expensive, energy-intensive, and technically complex. Therefore, the customer who needs to replace the heating system in the apartment should understand the main points.
It is advisable to replace risers in old houses. It’s better to come to an agreement with your neighbors and do this while going through the ceiling
What to do if the batteries are cold
What could be worse than cold radiators in winter? This is not only discomfort and violation of temperature norms, but also the threat of getting sick.
It is important to know what limits the timing of a possible emergency heat shutdown. They should not collectively exceed 24 hours per month, and last no more than 16, 8 and 4 hours in a row, if the temperature is not lower than 12, 10, and 8˚C, respectively.
If the radiators remain cold during the heating season, you need to contact:
- To the heating network dispatch service. If they do not know the reasons, they are required to check for the lack of heat.
- To the management organization (or others). Perhaps they are the ones carrying out the repair work.
- To the city housing inspectorate with a complaint about violation of housing standards.
- To law enforcement agencies (Rospotrebnadzor, prosecutor's office), if the heat is not restored on time and the problem is not solved.
If the heating network does not see a problem, an independent heating expert may be required.
We recommend that you find out in more detail what to do if there are cold radiators in the apartment.
Switchgears
The elevator unit with all its piping can be thought of as a pressure circulation pump, which supplies coolant to the heating system under a certain pressure.
If the facility has several floors and consumers, then the most correct solution is to distribute the total coolant flow to each consumer.
To solve such problems, a comb is designed for the heating system, which has another name - a collector. This device can be represented as a container. The coolant flows into the container from the elevator outlet, which then flows out through several outlets, with the same pressure.
Consequently, the distribution comb of the heating system allows the shutdown, adjustment, and repair of individual consumers of the facility without stopping the operation of the heating circuit. The presence of a collector eliminates the mutual influence of the heating system branches. In this case, the pressure in the heating radiators corresponds to the pressure at the elevator outlet.
Choosing pipes
Modern design of heat supply systems is 95% based on the use of plastic, polyethylene, and corrugated stainless steel pipes. Each of them has its own disadvantages and advantages.
Metal and copper pipes also have the right to exist, but due to their tendency to corrosion, high cost, and complexity of installation, their use is declining. Preference is given to plastic products that are not inferior in characteristics. For detailed recommendations on choosing heating pipes, watch the video.
Video:
Metal-plastic, polypropylene pipes
Metal-plastic pipes are widely used when laying water supply, heating, and heated floors. They bend well, are easy to install, can withstand significant temperatures and pressure, and have a budget price.
Metal-plastic consists of heterogeneous layers with different coefficients of thermal expansion. Application experience shows that when using metal-plastic for hot water supply, the layers separate, and the pipe fails after 5-7 years. This type of installation of heating pipes in the floor is not recommended.
Polypropylene pipes
Polypropylene has no layers and easily withstands the service life guaranteed by the manufacturer. The main disadvantage is the need to strictly observe the temperature and heating time with a soldering iron during installation. Polypropylene has low thermal conductivity and cannot be used for heated floors.
Corrugated stainless steel pipe
Corrugated stainless pipe, developed using innovative technologies, is recommended for laying heat supply networks. When using such a product, it is easy to install floor heating in a new building or replace old pipelines.
Corrugated stainless steel pipe
Here are some advantages of its use:
- bends easily;
- provides simple connection of fittings, facilitates and speeds up the installation process;
- the corrugated structure compensates for fluctuations in linear dimensions and hydraulic shocks;
- durability;
- does not corrode, there is no sediment on the walls.
PE-X pipes
PE-X – products made from cross-linked polyethylene. Cross-linking is the process of imparting strength to the connection of polyethylene molecules, obtaining a round-shaped product. The pipes are marked (GOST 52134-2003 for Russian manufacturers) indicating the stitching method:
- PE-Xa,
- PE-Xb,
- PE-Xc.
PE-Xa molecules are cross-linked by peroxides. This is an expensive, time-consuming process. PE-Xb – steam crosslinking. The process is simple, so these are the cheapest products in the PE line. PE-Xc - cross-linking with radioactive isotopes.
Polyethylene allows oxygen to pass through well, which allows bacteria to grow inside the heating elements. To prevent oxygen from passing to the coolant, the product is made multilayer. A layer of EVOH is inserted inside.
Innovative developments have led to the creation of polyethylene that is more resistant to high temperatures - PE-RT. In modern construction, heating pipes in an apartment are laid across the floor using PE-RT.
Important! It is recommended to choose a pipe marked PE-RT/EVOH/PE-RT; it is five-layer and does not allow oxygen molecules to pass through to the coolant.
| Name. | Diameter, mm. | thickness , mm. | Price, rub./meter |
| PE-Xb | 16.0 | 2 | 59 |
| PE-X/EVOH | 16.0 | 2 | 28 |
| Elsen PE-Xa | 25 | 3,5 | 208.6 |
| PexPenta PE-Xc | 16 | 2 | 50 |
| Stainless steel corrugated pipe S9 304 | 15 | 95 | |
| Casing, HDPE corrugated for polyethylene 16 mm | 25 | 12 |
Wiring types
According to clause 6.3.3 of SP 60.13330, pipelines made of polymer materials are allowed in apartment heating systems when the coolant parameters should not exceed: temperature - +90 0C, pressure - 1.0 MPa.
Important! The method of laying pipelines should ensure easy replacement during repairs.
According to the paragraph, it is recommended to install heating under the floor made of polymers hidden in a corrugated pipe. Open installation is allowed behind baseboards and screens where mechanical damage and direct exposure to ultraviolet radiation are excluded.
It is recommended to use the following types of wiring:
- double-tube beam;
- two-pipe perimeter;
- mixed.
Radial
Two-pipe radial wiring involves connecting a separately located device to the apartment's distribution cabinet. Filling of the floor is carried out only after installing the corrugation, installing fastenings to the floor, installing a compensation loop, and testing it to the permissible pressure.
According to building codes, heating under the floor in an apartment is laid without joints. Products of the PE-X line are produced by enterprises in coils; it is recommended to calculate the required footage in advance.
system for distributing pipes along the floor from the comb
The best option is radial wiring, in which each device is connected to the distribution manifold individually. There are no intermediate connections on the path from the collector to the device, which ensures high reliability. In addition, changing the flow rate through one of the devices has virtually no effect on the operation of the others.
Perimeter, mixed
When radial wiring in the middle of the floor is undesirable for any reason, two-pipe perimeter wiring is used. It is laid along the baseboards under the floor or openly, but surrounded by screens.
When installing the plinth, take into account the location of the perimeter wiring so as not to damage the heat pipe. When several individual radiators are located along the wall farthest from the distribution cabinet, radial wiring is used to the nearest device, then perimeter wiring between the remaining devices.
Laying a heating pipe under the floor in an apartment is invisible, does not affect the appearance of the room, and does not require opening when repairing or replacing the pipeline.
Installing a heating meter
Many are not satisfied with paying for heat at an average tariff based on consumption standards. In this regard, some people prefer to install a heat meter and pay only for the heat received.
The design features of heating systems, in particular, the widespread vertical distribution, do not allow apartment-by-apartment accounting of consumed heat, be it an open or a closed heating system of a high-rise building.
The only way out is door-to-door accounting. In this case, the procedure will be as follows:
- The management organization develops technical specifications for the installation.
- Housing departments or residents purchase a heat meter on their own.
- Based on the documents for the meter, a project for its installation is developed and agreed upon with the heat supply organization.
- The metering device is installed, the heat supply representative seals the meter and draws up the corresponding report.
Find out how a common house heat meter is installed in an apartment building.