Home / Burners for boilers
Back
Published: 06/25/2020
Reading time: 5 min
0
2806
A pellet burner is a modern energy-efficient device designed to use a special fuel for solid fuel boilers - pellets.
The main advantages of this type of boiler equipment are considered to be the high efficiency of the heating unit due to the complete combustion of pellets and the possibility of 100% automation of the combustion process using innovative diagnostic and control tools.
Modern household welding and plumbing tools allow the home craftsman to make a pellet burner with his own hands.
- 1 Design and principle of operation of a pellet burner 1.1 Gravity burners
- 2.1 Creating a drawing of a pellet burner with dimensions
Installing and setting up a pellet boiler: is it difficult?
On the one hand, pellet boilers are simple, reliable and maintainable equipment; on the other hand, these devices often use complex innovations aimed at increasing efficiency and comfort.
Therefore, it is better to hire professionals to install pellet boilers: after all, it comes down to heating. However, when trusting specialists, you need to know what to pay close attention to. First of all, it is recommended to check that the boiler is connected to the chimney correctly so that carbon monoxide does not enter the room. If you purchased a combination boiler (using not only pellets, but also coal or wood), you need to make sure that it is the pellet burner that is installed. Next, the operation of the screw mechanism and fan (including their regulators) must be checked. Of course, you should pay attention to the installation of a pressure gauge, air vent and relief valve.
“I would also advise protecting the boiler from the formation of condensation by controlling the heating of the return water,” says heating engineer Yakov Smirnov. — If the return line turns out to be cold, the equipment will not last long. In addition, it is necessary to take measures to stabilize the voltage in the network by installing an uninterruptible power supply.”
As for setting up pellet boilers that do not have automation systems, they will have to be adjusted frequently. The fact is that pellets pressed from different raw materials burn differently. Some may have a higher calorific value, which means that the fuel supply volume should be reduced by adjusting the auger. And vice versa: if the coolant in the heating system does not warm up to the required temperature, then it is worth increasing the supply of pellets. In addition, the air pressure can be adjusted by adjusting the rotation speed of the blower fan. If a flame with red tongues is visible in the firebox, then the pressure increases; if the fire in the firebox is bright white, then it decreases. Ideally you want to achieve a yellow color.
The operation of pellet boilers equipped with electronic control systems is carried out automatically. As a rule, such a device is configured once (after installation), and maintenance is carried out in accordance with the regulations.
How is such equipment connected?
The general installation scheme of heating boilers consists of the following series of stages:
- installation of distribution combs;
- installation of appropriate pumping circuits for each consumer;
- installation of safety equipment;
- installation of an expansion tank;
- installation of shut-off valves;
- connection of the boiler with the supply and return circuits;
- filling the circuits with coolant;
- testing equipment and checking its operation.
In practice, everything depends on the power of the equipment, the number of consumers, the design features of the boiler, etc. It should be noted that quite high requirements are placed on the piping of pellet boilers. Firstly, because the moisture content of the fuel must remain acceptably low, and secondly, because both the fuel and the coolant are heated to very high temperatures. Poor-quality piping can lead to the fact that the operating conditions of the equipment will be violated, and the boiler will quickly fail.
In accordance with fire safety standards, it is recommended to use non-flammable metal pipelines for piping pellet boilers. The use of polypropylene structures in practice is not only dangerous, but also unprofitable, since the temperature of the coolant at the boiler outlet often exceeds the performance indicators of polymer materials. As a result, the pipelines will have to be replaced within a couple of years.
A pellet boiler is a rather complex device. Experts strongly do not recommend that inexperienced beginners install and wire such devices. However, knowledge of the main stages of tying and some of the nuances of this process will allow you to effectively monitor the work of the invited team of installers.
The diagram shows one of the options for piping a pellet heating boiler: 1 - MK pump; 2 - mixing valve MK; 3 — pump TK1; 4 — mixing valve TK1; 5 - water recirculation in TK1; 6 — pump TK2; 7 — mixing valve TK2; 8 — water recirculation in TK2; 9 - DHW pump; 10 - DHW heat exchanger; 11 - supply of running water to the hot water supply
To piping a pellet boiler, you must:
- install the boiler;
- connect the appropriate burner (if a combined boiler model is used);
- install a pellet hopper;
- connect the auger for fuel supply;
- connect the automatic boiler control panel.
After this you should do:
- Installation of a safety group on the boiler supply, which includes a pressure gauge, automatic air vent and relief valve.
- Installation of a thermal valve sensor, if provided for by the design of the model;
- Installation of a chimney whose diameter and height meet the technical requirements.
- Installation of a system of devices to maintain reverse flow: two pressure gauges for supply and return, a circulation pump and a thermal head.
- If there is a high probability of sudden power outages, it is recommended to supplement the system with a suitable UPS model.
Reverse flow support allows you to control the heating level of the coolant before it enters the system. Until the return temperature reaches the required level (usually 60 degrees and above), the coolant will remain within the small circulation circle. Only when the coolant is heated to the required level will the thermal head open and cold coolant begins to flow through it, and hot coolant will begin to circulate in the main circle.
Under no circumstances should you use a pellet boiler with a low coolant temperature. A temperature of 55 degrees is the so-called “dew point”, upon reaching which a significant amount of condensation occurs. As a result, the volume of soot in the chimney, as well as on the heat exchanger, can increase significantly. The equipment will require additional maintenance efforts, and its power will noticeably decrease.
This is what the combustion chamber of a pellet heating boiler looks like after exposure to excessive amounts of condensate that appears due to errors in the installation of the recirculation system
The process of piping a combined pellet boiler is presented in detail in the video:
Many manufacturers of pellet boilers recommend supplementing the design with a special storage tank, which allows you to accumulate heat. Fuel savings can reach 20-30%. In addition, the use of a storage tank allows you to avoid overheating of the boiler and achieve the highest possible efficiency.
Correct boiler settings
When buying a pellet boiler, first of all you need to pay attention to the availability of service centers and official representative offices in the region where the boiler is installed. The pellet boiler is fully automated and requires proper configuration and maintenance. Correctly setting up the boiler will increase its service life, reduce fuel consumption and simplify cleaning the boiler. Start-up and commissioning of this kind of automated equipment must be carried out by a specialist authorized by the manufacturer. In fact, there are no restrictions on starting the boiler and putting it into operation; this procedure can be performed by the installer who installed the heating system, and of course by the user himself. But in this case, all responsibility and further maintenance falls on the person who carried out the launch.
What is important to know to set up a pellet boiler yourself? First of all, you need to understand that an automatic pellet boiler has several operating modes. The most basic and those that require more attention are three: Ignition, Work, Pause. Boiler manufacturers use different types of automation in which all kinds of additional modes can be used, such as: Combustion Stabilization Mode, Modulation Mode, Supervision Mode, etc. When we already have an idea of the modes, it is important to understand how the boiler should behave in each mode.
Ignition mode - when a certain portion of pellets is supplied to the burner using an igniter, or in manual mode it is ignited and complete combustion is stabilized. The boiler usually spends about fifteen minutes in this mode, during which time it also supplies pellets in certain portions, while the boiler automation monitors the temperature of the flue gases. In this mode, it is very important to set up a sufficient amount of pellet supply and air injection so that the temperature of the flue gases rises rapidly. After the flue gases reach 60 degrees, the chimney is considered warmed up, and the automation switches the boiler to Operating mode.
We recommend: Technology of construction of wooden panel and frame-panel houses: photos, videos, pros and cons
The operating mode is very similar to the ignition mode. The boiler spends most of its time in this mode. It is at this time that it heats the boiler heat exchanger and brings the temperature in the heating system to the set temperature. During our work, we no longer need to quickly warm up the chimney. Our task is to achieve correct and complete combustion of pellets, a stable and clean flame. Two parameters are subject to adjustment: air blowing power and the number of supplied pellets. The air power is usually regulated in a ratio from 30 to 100 percent, the number of pellets supplied to the burner is regulated in a cyclic ratio, and after a certain period of time a certain portion of pellets is supplied. It is important to understand that the portion of burned pellets corresponds to the declared power. For example, a fifty kilowatt boiler will not be able to provide heat to the room if the supplied pellets are too small, even if the flame is stable. The average heat transfer of pellets from one kilogram when burned can produce up to five kilowatts of thermal energy per hour. The quality of the fuel can greatly affect the consumption of pellets, and in some boilers, the operation of the burner.
Manufacturers of pellet boilers provide standard operating settings. Each power has its own number of pellets per hour and its own air blowing power. Our task as a user or boiler setup specialist is to adjust these parameters so that pellet combustion is complete and consumption is minimal without loss of boiler performance.
This begs the question, where to start setting up a pellet boiler?
We recommend that you first start by adjusting the air and blowing power of the fan. The blowing power may vary for each boiler; it is usually influenced by a number of factors, such as chimney draft, pellet quality and even burner type. The amount of air pumped into the burner should be the minimum necessary for complete combustion of the fuel. This can be determined by the color of the flame.
The correct flame has a yellowish tint, the flames rise upward, the combustion is even, high and stably kept at the same height. It is in such a flame that maximum efficiency is achieved.
Is the flame reddish with noticeable smoke? There is not enough oxygen for combustion; this can be affected by both an incorrectly installed chimney and too little air blowing power. Try adding blowing power and observe the result.
If we observe an aggressive flame, and pellet coals jump up and fall into the ash pan as unburnt pellets, there is too much air blowing, we recommend reducing the air to the minimum required for combustion.
After the flame has been normalized and it meets all the parameters of proper combustion, it has a yellowish tint. Let's move on to adjusting the auger feed. As mentioned above, the auger operates cyclically, feeding certain portions into the burner. Before setting up the auger feed, you need to understand what type of burner your boiler has. A torch burner requires the minimum required number of pellets when burning, so that the pellets do not clog the air supply holes. In such burners, pellets are usually fed in small portions. If we are dealing with a retort burner in the form of a bowl with bottom fuel supply. Here the fuel supply occurs somewhat differently; the pellets supplied from below constantly raise the combustion. Our main task is to adjust the optimal supply of pellets to the burner so that the fuel during combustion is always at the same level. Combustion should occur in the upper part of the burner, and the pellets should not spill over the edge of the burner or sink below the level.
After we managed to select the ratio of pellet supply and air inflation, we should observe the temperature of the water in the system, whether it tends to the set one, and at what speed. Is the boiler gaining temperature very slowly or is the temperature stuck in one place? This means that the boiler is not operating at rated power; it is necessary to add fuel supply and adjust combustion.
The final mode is Pause or Stop mode. The pellet boiler goes into this mode when the set task, namely the set temperature, has been achieved. In this mode, the boiler completely turns off the operation of the auger and fan, and waits for the water temperature in the system to drop by several degrees, after which it starts working again, before checking the combustion.
We recommend: Izoplat: properties, characteristics, advantages and disadvantages, installation features
The question is very often asked: Is it necessary to reconfigure the boiler when changing fuel? If these are fundamentally different fuels then - Yes.
For example: We made a tincture using wood pellets, and a little later we decided to switch to husk pellets. Husk pellets burn a little faster than wood pellets and the feed ratio of the auger to the fan needs to be changed.
If the fuel is simply from different batches or from a different manufacturer, then only a slight adjustment of one of the parameters will be necessary. Pellets may differ in density, humidity, calorie content, as well as ash content and the likelihood of caking and cake formation.
Pellet boilers have gained popularity in the line of solid fuel boilers due to their autonomous operation and convenient operation. Such boilers can work from 2 to 10 days on one loading of the bunker and with cleaning the boiler every 4-5 days, while a long-burning boiler with automation will not last even 24 hours and needs regular cleaning before each loading of firewood. However, pellet boilers require proper tuning and it is better to entrust commissioning work to a specialized organization. A properly configured boiler will easily develop the specified power, and the savings on pellets will pleasantly surprise you.
Common mistakes
If you neglect the installation rules, problems will arise even when you first start the device. The most common installation errors are:
- Soot appears too quickly, the boiler does not produce heat well, although all the settings on the panel are set correctly. Reason: during installation, the installation of a system for monitoring the level of heating of the return water was ignored. This is a serious mistake that can soon lead to failure of the heating system.
- Too much condensation occurs. The reason may be that the room temperature is below +10 degrees. This creates sudden temperature changes when the device is turned on and off. If condensation forms under the boiler, it means that it was placed on the wrong foundation (the situation will be corrected by thermal insulation of the floor).
- A leak of pyrolysis gases occurs. Reason: during installation, sealing of the boiler, fuel bunker, and chimney was not ensured.
- The boiler smokes, and unburnt pellets remain in the ash pan. Reason: incorrect settings are set, the system needs to be re-configured.
- The burner goes out regularly. Reason: there is no supply ventilation hole in the room, the device does not have enough oxygen.
basic settings
A pellet solid fuel boiler is considered very convenient to use, but unlike other solid fuel models it requires proper configuration. A correctly configured ratio of parameters directly affects indicators such as the power and efficiency of the boiler.
A very common question: is it necessary to reconfigure the boiler when changing a batch of pellets? Yes, your solid fuel boiler using different pellets will work differently. The ratio of components from which pellets are made is different for each manufacturer and therefore the combustion process will also be different.
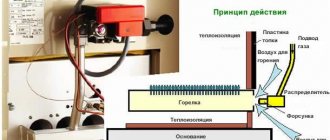
The principle of a pellet solid fuel boiler is quite simple: a worm mechanism (auger) feeds small granules of compressed wood, coal, biomass, etc. (pellets) into the burner, and air is also forced into it to ensure the required flame power.
Two parameters are subject to adjustment: pellet supply speed and air blowing power. The air supply is adjusted by simply selecting the rotation speed of the blower fan, usually either on a scale from 1 to 10 or in % from 1% to 100% (depending on the model of the solid fuel boiler). The pellet feeding speed is adjusted by increasing or decreasing the period between activations of the worm mechanism. The rotation speed of the screw is always the same.
The amount of air pumped into the burner should be the minimum necessary for complete combustion of the fuel. This can be determined by the color of the flame. A red flame with noticeable smoke is a sign of lack of air. A white flame means the fan is blowing too much air.
The correct flame is yellow. An additional sign of proper air supply is that the flame not only rises upward, but also diverges slightly to the sides.
When adjusting the air supply, do it in the minimum permissible increments. The more accurately you set the minimum required point, the more boiler power and less pellet consumption you will achieve.
First of all, the air supply is adjusted, and then the pellet feeding speed.
The feed rate of pellets into the burner should be optimal. If too few pellets are supplied, then it will be difficult to accelerate the solid fuel boiler to rated power - there will simply be nothing to burn, and if there are too many pellets, then excess fuel will fall out of the burner.
The APG-25 Teplodar pellet burner is started by pressing the button located on the side of the hopper once. The device is put into standby mode. To go to the main equipment settings, you must simultaneously press the “Left” and “Right” arrows. Secondary parameters of APG-25 are set during heating or maintaining temperature.
We recommend: How to connect a well pump - installation and electrical diagram, installation in a well
The user needs to set two main parameters:
- Feeding time in “Heating” mode
. The default is 9 seconds with a cycle time of 20 seconds. This is a system setting for a 20 kW boiler heating a room of 180-200 square meters. m. If such power is not needed, the indicator is reduced to 5-6 seconds. The feeding time in the “Maintenance” mode is determined automatically. - Fan power
. The user manual indicates which blade rotation power is selected depending on the pellet feeding time. The parameter is set manually. If the fuel supply is short, the fan operates in moderate mode.
The fan power also affects the speed at which ash is blown out of the fryer. For poor quality pellets, it is necessary to set the parameter slightly higher than the table value, in particular, when working in the “Maintenance” mode.
Why are thermal relief valves necessary in principle?
It would seem that such a valve is not really needed. After all, other devices also provide security. In particular, a safety valve that is triggered (broken) when the pressure is exceeded. It is often called that - disruptive or disruptive.
On most heating systems you can see so-called “safety groups”. They consist of a pressure gauge indicating the pressure in the circuit, an automatic air vent and a safety blow-off valve (on the left in the illustration).
We will not focus on this device now - such valves have already been reviewed on our portal earlier. Well, so why “fence the garden” - there is already protection, right? If something goes wrong, for example, an increase in temperature in the circuit causes an increase in excess pressure, the valve will operate and the emergency will be prevented
Is it true?
Well, so why “fence the garden” - there is already protection, right? If something goes wrong, for example, an increase in temperature in the circuit causes an increase in excess pressure, the valve will operate and the emergency will be prevented. Is it true?
Alas, this is not always 100% true. From excess pressure, yes, such protection should help. But with temperature, the question is more complicated.
Allowing the coolant to reach the boiling point (conventionally 100 ℃) in household boiler equipment is unacceptable! Therefore, the border of 95, maximum 100 ℃ should become “impassable”. Too high a temperature can lead to deformation of the boiler heat exchanger, rupture of the pipes of the laid circuit or connections between them. to massive vapor formation and the appearance of gas locks, to other not only unpleasant, but also extremely dangerous consequences.
Do not forget that in closed volumes, with increased pressure in the system, the boiling point shifts significantly higher. That is, if the temperature is uncontrolled, an extremely dangerous situation can arise. The water has already been superheated above the limit of 100 ℃, but there is still no boiling. However, as soon as the pressure drops (a leak has appeared or a relief tap or valve has opened somewhere), the entire superheated mass of water boils at once. Explosions happen such that they simply blow down walls.
These are the consequences of a boiler explosion!
For some reason, popular rumor attributes “increased explosiveness” to gas boilers. Apparently, due to occasional reports of explosions due to gas leaks. Meanwhile, this is not so. Indeed, gas leaks are dangerous in themselves. But the greatest danger is posed by solid fuel boilers, no matter how strange it may seem.
Meanwhile, this is explained quite simply. The combustion temperature of solid fuel is much higher than that of gas, and so is the energy potential. But monitoring and managing the combustion process is no example more difficult. “Tightening the wick” on gas or liquid fuel equipment is a matter of a few seconds. We are not talking about electric ones - the control there is even simpler and more sensitive. But the operation of a boiler using wood or coal is always characterized by significant thermal inertia, that is, even changes made to the fuel combustion mode do not work immediately. It is not for nothing that many solid fuel boilers are equipped with special cooling circuits - this is a necessary measure in order to prevent overheating above critical temperatures.
Yes, the pressure safety valve should take over the protection duty here. But, firstly, the operating accuracy of such spring devices is low; ±30% of the nominal value is considered the norm. For some systems, such “punctuality” is not enough. And secondly, and this is the main thing, if the heating system is equipped with an open type expansion tank, then the pressure valve becomes completely useless. It will not in any way protect the system from possible overheating and reaching the boiling point.
In open-type heating systems, the pressure safety valve becomes a useless “decoration”.
Therefore, a protection system is needed that would trigger when the upper temperature threshold is reached.
Such a “line of defense” is also necessary in other circumstances. For example, a solid fuel boiler operates in a system with forced circulation of coolant. If, due to power supply problems, the pump suddenly stops and circulation stops, an extremely dangerous situation can arise. This means that the “temperature” protection system must be completely energy-independent, capable of helping out in any case.
These types of devices include thermal relief valves.
Additional settings
When the main parameters are set, you can move on to the auxiliary ones.
The first option is that you can adjust the ignition time of the pellets. By default it is 5 minutes. This is exactly how long the special halogen lamp is turned on, which is responsible for igniting solid fuel.
High quality pellets ignite faster - in 3-4 minutes, and in this case the ignition time can be reduced. In the case of inexpensive fuel, it is recommended to increase the parameter to 6-7 minutes.
Also, installing a pellet burner in a solid fuel boiler necessarily involves setting such indicators as:
- burn-out time (characterizes the maximum fan power after stopping the fuel supply);
- coolant temperature “return” (once it is reached, the burner changes the “Heating” mode to “Maintenance” - it is set to approximately 60 ° C);
- supply coolant temperature (critical value within 90-95° - at this temperature the supply of pellets stops, and an “Overheating” warning signal appears on the control panel display);
- auger control (two modes - “On” and “Off” - when activated, pellets are smoothly fed into the combustion chamber).
If the burner operation must be stopped, under no circumstances should the plug be pulled out. Such a sudden disconnection from the power supply will provoke a pressure surge inside the system, which will lead to the fan stopping, which, in turn, will provoke the release of soot and ash onto the internal elements of the boiler and extinguishing the pellets. Next time the fuel will ignite noticeably worse.
APG-25 will pause operation if you press the red “Stop” button on the control panel twice. Pressing once will enter the system into pellet burning mode.
Correct setting of a pellet boiler is the key to its smooth operation.
How to calculate the required volume of a heat accumulator
A tank that is too large or too small for storing heat in the form of a heated coolant is an ineffective solution, therefore the required volume of the tank is subject to mathematical calculation, the exact results of which are difficult to obtain due to the approximate initial data - heat losses in the room, the properties of the insulation of the walls and the foundation of the house, heat-insulating qualities of building materials of walls, ceilings and partitions, the same parameters of window and door openings. But it is still possible to roughly calculate the heat accumulator, and this technique is designed specifically for ignorance of the exact heat losses of the building, especially if it is just to be built.
The choice of size and volume of the tank for the heat accumulator can be made based on the following parameters:
- Total area of heated premises;
- Thermal power of heating equipment.
These two parameters determine the volume of TA.
Let's say you need to calculate the volume of a heat accumulator for a heating system based on the heated area of the room. The formula for calculation is simple: the area in square meters is multiplied by four (Sx 4). For example, a house with a total heated area of 50 m2 will require a 200 liter tank. With such a volume of TA, as practice shows, the boiler can be loaded with solid fuel only once a day. This is very good savings and very good efficiency.
Knowledgeable owners will say that you can simply install a pyrolysis boiler, which will work the same way. But the operation of such a boiler is a little more complicated and less efficient, since:
- First, the fuel ignites and burns;
- Then the air supply is limited;
- The last thing to activate is the smoldering of the fuel (pyrolysis).
When the fuel ignites, the temperature of the coolant increases sharply, and the pyrolysis process maintains it at a given level, and during pyrolysis a lot of thermal energy simply disappears into the chimney pipe, heating almost nothing. Another disadvantage is that during heating peaks, the coolant can boil and splash out of the expansion tank, and when using PVC pipes for heating distribution, they quickly fail due to high temperatures.
We make it ourselves
Having decided to do everything yourself, you should first develop a project. Guided by the drawings, you should purchase everything you need, as well as prepare the tools.
What will you need?
It is better to purchase the most complex elements already assembled. Thus, a factory-assembled pellet burner is always preferable to one assembled by yourself. The same applies to sensors and programmers, a fan, an electric motor for the auger, a grate, two oven doors, if you do not plan to manufacture them yourself. You will also need:
- steel sheet 3mm and 6mm thick;
- steel square and round pipes (wall thickness 4 mm);
- asbestos sheet and in the form of a sealing cord;
- fireclay brick for the combustion chamber;
- round bar (20 mm);
- electrodes.
To carry out the work, you need to prepare a grinder, a welding machine, a ruler, and a drill.
Pellet supply unit
We are preparing a bunker for pellets. We connect it to the auger shaft. The latter can be in the form of a pipe. If a fuel dispenser is provided, install it at the entrance to the auger shaft and connect it to the electric motor.
Heat exchanger
Square pipes are used as front pipes, round pipes are used as connecting pipes. In the front ones, round holes are cut for supply and removal of coolant.
The spatial arrangement of the connecting pipes at the time of welding is carefully controlled. After completing the welding work, check the tightness of the seams by filling the heat exchanger with water.
Case manufacturing and assembly
The body is made from sheet steel 6 mm thick. We provide two doors for subsequent maintenance of the equipment, located in the front and rear parts. We lay fireclay bricks inside the chamber.
We place the heat exchanger inside the housing, providing a small gap between the outer surface of the first and the inner surface of the second. Install the fan at the top of the case.
In many regions, the problem of heating private houses still remains relevant. Of course, the modern market offers a huge range of equipment that uses a wide variety of materials as fuel, be it gas, firewood, electricity or oil, etc. However, access to gas mains and stable power grids is not available everywhere, so solid fuel heating remains the most preferable in many regions.
One of the best options for a solid fuel heating unit is a pellet boiler, which you can assemble with your own hands.
Contents of step-by-step instructions: