A heating element is an electric liquid heater in the form of a metal tube, inside of which there is a spiral. There are many designs and varieties. Heaters are manufactured for both large and small industries.
These heaters are widely installed, for example, in electric boilers and electric boilers, and therefore are also produced by well-known manufacturers.
But in any market you can find heating elements intended for installation in heating radiators. These devices are often manufactured in Poland, Ukraine, and China. They can be equipped with built-in temperature sensors, i.e. work in semi-automatic mode, monitoring the degree of heating.
Based on such electric heaters, you can easily create a heating device with your own hands. This is what home craftsmen use, constructing the simplest heating and, as they think, “saving” a fair amount of money.
But is it really profitable to use heating elements? Where and in what situations are these electric water heaters usually used? How to install and use heating elements...
How big is the benefit from heating elements?
If you have an old battery, then why not use a heating element to turn it into a heating system for a small utility room - a chicken coop, a workshop, a garage...
There are even myths that heating with heaters is beneficial. But “dreams are shattered by harsh reality” - heating with electricity is the most expensive. Since the most expensive energy carrier is used.
It doesn’t matter whether there is a proprietary programmable electric boiler, or a barrel with a heating element lowered into it on a wire, the efficiency of such electric heaters is about 97%. And then we pay according to the meter...
Keep warm at night
But there is a loophole - a cheap nightly electricity tariff. You can find out exactly about the current tariffs and the possibility of connecting to the night power supply in the local power grid.
True, night electricity cannot be called cheap, but in combination with the “Comfort” indicator, night heating becomes very attractive to the user. What type of fuel is best for home use?
But the price of the electric heating system itself can vary significantly.
Heaters in batteries
When it is cold in apartments with central heating, they are heated additionally with electricity, as well as a gas stove or water heater.
This is where a couple of heavy cast iron batteries with heating elements are used. Compared to branded electric convectors, they have a much higher heat capacity, so you can turn them off for longer and not monitor their operation. But heating is correspondingly longer.
Craftsmen install such radiators mainly in garages, where they like to spend time. Or, for example, for heating animals in cold weather on small farms.
Heating system equipment
It happens that at the dacha, in the garage, etc. There are remains of the former heating system, for example, a couple of radiators with steel pipes. The easiest way to bring the system back to life is to insert electric heaters into it...
But heating elements can also create auxiliary heating in a home heating system. Electric heating perfectly complements a solid fuel boiler. Especially at night, with a cheap rate. And here “homemade production” is also in demand.
If you attach a pair of 2 kW heaters in a sufficiently large metal pipe, you will get a 4 kW electric boiler. The nuance is that at night it can be connected to a low-power 220 V network, since other consumers are “sleeping,” except for the refrigerator, for example.
Such a “creation”, in practice, can become the main heating during the season in an insulated house, if, of course, a buffer tank is used - a heat accumulator. How to connect a heat accumulator to the system
How much power will you need?
In a heating system for a whole house, it is better to use 2-kilowatt electric heaters.
But in individual radiators, homemade registers, heating scraps in garages... it is impossible to use heating elements that are too powerful.
The fact is that a thermal relay cannot be considered reliable protection. Bringing liquid to boiling point or overheating the device above +75 degrees is dangerous.
Therefore, the power of the heater should not be greater than the thermal power generated by the device at +70 degrees. This is approximately 75% of the radiator's rated power.
One section of both cast iron and aluminum radiators (500 mm between pipes) has a heat transfer power of 170 W at 90 degrees liquid and 20 degrees air. At +70 degrees. heating - one section - 140 W, 7 sections - 1080 W, 10 sections. — 1400 W. Thus, for a radiator of 7 sections, the power of the heating element should not be more than 1 kW. And for a radiator of 10 sections - no more than 1.4 kW.
The situation is more difficult with homemade registers - their heat transfer is unknown. All that remains is to start using the least powerful heaters.
Which radiator shades to choose
Heating elements for radiators are made on the basis of a plug (base) with a standard thread diameter of 40 mm. All that remains is to unscrew the bottom plug from the radiator and screw in the heater in its place.
What it is
Description
A tubular electric heater (TEH) is a tungsten heating coil in a ceramic insulator, placed in a sealed metal casing.
Electric heating elements for radiators have several more characteristic features.
- The heating element shell is made of stainless steel. This ensures maximum durability of the product and completely prevents contact of the energized coil with the coolant.
- The nut that ensures installation of the heater in the heating device is brass. Thread - pipe, left or right, size 1 or 1 1/4 inches (DN 25 or DN 32).
Hint: these dimensions ensure compatibility of the heating device with the threads in the sections for the radiator plugs. Cast iron radiators with heating elements are mated with 32 mm threads, aluminum sections have 25 mm threads.
The heating element turned the cast iron battery in the photo into an autonomous heating device.
- Optionally, part of the design may be a thermostat, which ensures automatic maintenance of the specified coolant temperature.
Characteristics and range
Since the rated power of devices is not regulated by any domestic or foreign standards, as an example of the model range we will present the actual product range of the Belgorod company Elektroten. This is quite enough to get acquainted with the design options and current prices.
| Kit for 1 1/4 thread (heating element for radiator with thermostat, cord and protective cap) | ||
| Power, kWt | Total length, mm | Retail price, rubles |
| 0,5 | 285 | 1706 |
| 0,8 | 285 | 1762 |
| 1 | 305 | 1819 |
| 1,2 | 305 | 1876 |
| 1,5 | 325 | 1933 |
| 2 | 355 | 2024 |
| 2,5 | 405 | 2104 |
Kit with thermostat.
| Heating element for aluminum radiator, 1 inch thread (without cord and thermostat) | ||
| Power, kWt | Total length, mm | Retail price, rubles |
| 0,5 | 250 | 1305 |
| 0,7 | 285 | 1353 |
| 1 | 305 | 1401 |
| 1,2 | 305 | 1449 |
| 1,5 | 325 | 1496 |
In addition, of the products that interest us, the company offers:
- Heating element for oil radiator (1 1/4 inch thread).
- Heater for heated towel rails (1/2 inch thread).
Please note: these heating elements can also be installed in a radiator if there is an adapter for the appropriate thread.
Installation
The instructions for installing a heating element with your own hands are extremely simple:
- The radiator or section of the heating circuit is reset.
- The lower blind radiator cap is unscrewed. As a rule, it has a left-hand thread, but when connecting a heating device on both sides, the required plug may also be right-handed.
When connecting diagonally, the heating element is installed instead of a plug with a right-hand thread (bottom right).
- The last sections are cleared of sludge.
- The thread of the heating element is wound with plumbing flax with paint or any other sealing material.
- Then the heater is screwed into the heating device using an adjustable, open-end or gas wrench. Of course, without excessive effort: brass is a relatively soft metal, and it is not difficult to strip pipe threads on it.
- The radiator is filled with water or other coolant, after which power is supplied to the heating device. The uniform heating of the radiator surface is ensured by convection of the coolant.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Video about the difference between natural and forced circulation of coolant in a heating system:
Video clearly demonstrating the differences between different heating system schemes:
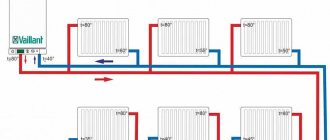
Scheme for effectively connecting heating batteries with a two-pipe system:
The heating efficiency directly depends on the choice of battery connection diagram for your home. With the right option, heat loss is minimized. This allows you to get maximum effect with the least amount of fuel used. You can install the batteries yourself
It is important to take into account the construction features so that cold radiators do not interfere with a comfortable life in a cozy home
If you are interested in the material we have proposed for consideration, have questions or a reason for discussion, we invite you to post comments.
Safety
It is believed that a radiator heating element with a built-in thermostat is an absolutely safe heating device: turning it off when the coolant reaches the set temperature will avoid dangerous overheating or boiling of water.
However, not all potential buyers of the device know that safety and operational efficiency are ensured not only by the design of the device, but also by proper installation.
- In a central heating system, when the heating element is turned on, the radiator shut-off valves must be closed . In this case, a jumper must be mounted in front of them on the supply line, which will allow the coolant to circulate through the riser when it starts. In the absence of valves, your heating element will heat the batteries throughout the riser; in the absence of a jumper, after an unsuccessful attempt to start the heating, a sad locksmith will come to you and say a lot of offensive words.
- Heating the coolant in a closed volume will turn your radiator into a full-fledged miniature boiler room and... sharply increase the pressure in it . Thermal expansion, you know. Hence the need to install on the supply line after the shut-off valve either a small expansion tank (its volume is taken equal to 10% of the radiator volume) or a safety valve. (See also the article Heating pipes: features.)
A small expansion tank will be able to accommodate excess expanded coolant.
Note: the second scenario is undesirable, since when heated the valve will periodically eject streams of hot water.
- The cross-section of the power cord must be at least 1 square millimeter per 8 amperes of current . With a heating element power of 2500 watts and a supply voltage of 220 volts, the current will be 2500/220=11.36A; the minimum cross-section of the wire core, therefore, is equal to 11.36/8 = 1.42 (rounded to the real value - 1.5 mm2).
- The maximum load per outlet should not exceed 3500 watts.
- Grounding is highly recommended.
The grounding contacts in the socket must be connected to the electrical panel housing.
- The power of the heating element without a thermostat should not exceed the rated thermal power of the radiator . For one aluminum section it is taken equal to 200 watts, for cast iron - 160 watts. Heating elements for heating radiators with a thermostat can be installed without power restrictions.
Thermostat is not working - how to check?
At the same time, do not expect any major changes when replacing a thermostat from one model to another. There is an opinion that if the warm floor does not heat up, then it is worth changing the thermostat to a more expensive one, everything will change by itself.
The air temperature in the room will immediately rise, and where it was previously cold, it will become hot. Roughly speaking, the thermostat is like the speedometer in your car.
You can draw 300-350 km/h on the speedometer, but if the engine is not capable of producing such power, then you will not see this speed. If something is to blame for the poor performance of heated floors, then first of all look at the temperature sensor.
Checking the functionality of the thermostat is very simple. Supply it with 220V power and connect the remote sensor.
Next, instead of a warm floor, connect a regular incandescent light bulb to the thermostat. You begin to unscrew the knob, changing the temperature.
At a certain moment the light should light up.
Next, hold the temperature sensor in your hand and wait. When heat comes from your body, a working thermostat will turn on and the light bulb will go out.
If the sensor is hidden deep in the screed, you can warm up the area with a hairdryer and wait for the same effect. When the lamp does not react at all, this indicates a malfunction of the device.
The fastest way to repair in this case is to transfer the work from the floor sensor to the air sensor built into the housing.
The ends of the cable on the device from the floor temperature source will have to be unscrewed, and the settings of the device itself will have to be reset.
All this will work correctly provided that the thermostat is installed directly in the heated room.
If you have an electronic thermostat with PWM control, then using the above test method, it is not recommended to heat the sensor too quickly with an extraneous heat source. What does this mean?
Firstly, the thermostat will immediately detect an abnormal increase in heat and work ahead of time. Secondly, the “smart brains” of the device will forcibly turn off the heating for the next 20 minutes.
In this case, after just 5 minutes the temperature on the device’s display will be sufficient to turn on, and startup and contact closure will not occur. As a result, you will have doubts about the correct operation of the thermostat.
Therefore, the fast heat test is ideal for mechanical devices, but be careful with electronic ones.
Efficiency mark
Everything is very simple here: 1 kilowatt of electric power of the heating element will give you exactly 1 kilowatt of thermal power, which is completely spent on heating the room. Electric radiators do not have any miraculous properties; positioning mini-boiler houses made of aluminum batteries as economical heating is nothing more than a deception of gullible people.
With a calculated thermal heating power of 100 watts/m2, the maximum power that a heating element with a thermostat for a cast iron radiator can provide—2500 watts—will allow you to heat a room of 25 m2. With an average power consumption of 1500 watts, electricity costs per day will be 1.5 kW/h * 24 h = 36 kW * h, which at current Russian electricity tariffs will cost approximately 36 * 3.8 = 166.8 rubles.
As a constant source of heat, a heating element is an expensive pleasure.
Features of choice
Electric heaters designed for radiators may differ in several parameters. Therefore, you should approach the choice wisely
Below we will consider what you should pay attention to when choosing a heating element
Power is one of the most important parameters, since the heat transfer of the device depends on it. Therefore, first of all, you need to calculate the required power for comfortable heating of the room.
On average, 1 kW of power is required for every 10 m2. For a more accurate calculation, it is necessary to take into account the region and heat loss of the room. However, if the heaters are used as an additional heating element, then half the power is sufficient.
Note! It makes no sense to use a heater more powerful than 75 percent of the heat output of the radiator itself, since its capabilities will not be fully used
Bimetallic radiator with electric heating element
Radiator type
Heating elements for aluminum heating radiators and bimetallic batteries are structurally no different from heating elements for cast iron appliances.
However, the differences are in the following points:
- The shape of the outer part of the body.
- Plug material.
The heating element for an aluminum radiator has a plug with a diameter of one inch. The diameter of the plug for standard cast iron batteries is 1¼ inches.
Therefore, before purchasing a heater, you should pay attention to what types of batteries it is intended for. This information is usually contained in the instructions that come with the kit.
Heating element length
An important selection parameter is the length of the heating element. As you might guess, the uniform heating of the battery and the circulation of liquid depend on this. Accordingly, the length is selected depending on the number of sections of the device.
Ideally, the heating element should be 10 cm shorter than the battery. In this case, the liquid will be heated as evenly as possible.
Automation
Automation can be built-in or external. It should be noted that a radiator heating element with a built-in thermostat is cheaper than the components separately. However, outdoor electronics tend to be more functional.
The choice depends on the purpose of the heater. If it is to be used as the main heat source, external electronics can be installed to ensure maximum heating comfort. If the device is planned to be used as an additional one, a heating element for heating radiators with a thermostat in one housing is also suitable.
Inexpensive heating element with thermostat for cast iron radiator
What is a heating element for heating?
Electric heating elements are heating elements that are placed in a liquid inside a radiator. They heat a liquid: water, oil or a special agent circulating through the heating system. Passing through the pipes, the heated liquid gives off heat to the environment and returns back to the heating element. They can be installed in water heating radiators, infrared heaters, or heating boilers. They produce heating elements of various types and modifications. In all of them, the heating element is reliably protected from water getting inside and is additionally covered with a galvanizing layer. All these measures serve to prevent accidental electric shock to people.
Advantages of using heating elements for heating
Despite the fact that electricity is the most expensive type of heating, there are a number of undeniable advantages in using heating elements for heating:
- equipment for an autonomous heating system in the absence of access to gas or solid fuel;
- the possibility of heating automation when using heating elements with thermostats;
- no emissions into the atmosphere harmful to nature or humans;
- the small size of the devices allows them to be installed almost anywhere;
- a huge selection of models for any conditions of use;
- simple and inexpensive installation of equipment.
Heat dissipation
According to factory parameters, such batteries (with a height or center distance of 500 mm), when integrated into a full-fledged hydraulic heating system, are capable of dissipating slightly less than 200 W of thermal power per section (180 W aluminum, 140 W cast iron).
However, in our case, do not expect such numbers. Firstly, the heat output of 180/140W is provided only by a new battery. And for such a heater, as a rule, used options are used.
Buying a new one for such a homemade product is not economically feasible.
Secondly, such work is only possible in the 90C-supply, 70C-return mode. In this assembly we use heating elements with an optimal operating temperature of 60-65C.
When it’s cold outside down to -25C, you can turn it up to +70-75C. The maximum possible temperature is + 80C.
Therefore, you will never heat such a battery to 90C in NORMAL operation. In principle, this is not necessary, since it entails the risk of a sharp increase in pressure.
Types of heating elements
Manufacturers produce two types of heating elements. They differ in the method of manufacture and application:
- Tubular. This is the most common type of heating elements, which are used in almost all electric heating devices. They differ in tube length, diameter and configuration. Tubular heating elements are usually made of stainless steel.
- Tubular finned ones have the appearance of a tube with transverse ribs. They are used to heat air or gas in heating devices such as heat guns or convectors.
You can also assemble a block from electric heaters - a heating element. The block is used to increase the power of the device.
Other types of tubular electric heaters are not used for heating in everyday life.
Technical characteristics of homemade heaters
In most cases, home-made heat generators are a copy of those devices that are commercially produced by official companies. They may be inferior in quality to the original in terms of technical characteristics, but for a number of reasons, apartment owners still want to assemble such a unit on their own.
The fact is that when making it yourself, the equipment is several times cheaper, since improvised means are used during assembly. It will also be possible to assemble the unit of the required size and dimensions, and independently select a housing with the desired strength. This means that the master chooses all the technical characteristics himself, based on the size of the room that needs to be heated. For example, if heating elements are used to assemble the apparatus, then only two samples will be suitable for heating one room. More than 4 heating elements per room are usually not used.
A DIY battery heater may violate operating conditions
But it should immediately be noted that a self-made heater may violate the operating conditions drawn up by official manufacturers. A homemade product is not as safe as a purchased unit. The heating device will be unpredictable and may result in unpleasant consequences for others. This is due to many factors:
- Homemade heating devices often cause fires.
- There are also no legitimate manufacturer warranties.
- The technical characteristics of a homemade device are uncertain, and if assembled inappropriately, the result will be an unaesthetic design.
But if all these shortcomings do not frighten the master, and there is no desire to purchase a heating device in a store, then you can proceed to assembling the heater yourself.
Heating elements for heating with thermostat
Almost all electric water heaters - kettles, boilers, titans, radiators - are equipped with thermostats. Such heating elements are made from nickel-chrome wire. It is placed inside a stainless or carbon steel tube and filled with magnesium oxide powder. It is a good current insulator and at the same time has high thermal conductivity. When choosing a heating element with a thermostat, you need to pay attention to the following points:
- the material from which the tube is made is copper or acid-resistant stainless steel;
- Can be used in water and alkaline solutions. Such devices are marked with the letter P;
- When choosing a device, you should consider the electrical wiring capabilities. For a very powerful heating element, you will have to lay a separate cable from the panel.
You also need to study the location of the temperature sensor. It should be easy to remove if the need arises to change it.
Heating elements for heating radiators
Heating elements are installed in radiators - cast iron or aluminum batteries - to stabilize the temperature during periods when the centralized heat supply is turned off or for additional heating of the room. Such heating at night can be quite beneficial if a two-tariff electricity meter is installed in the house.
Heating elements for radiators have a thin flange and a narrow heating element. They are equipped with a special casing that protects against water ingress. A capillary thermostat helps regulate heating, and two temperature sensors protect the product from overheating. Many models of modern heating elements are equipped with convenient and necessary functions: “Turbo” - for quickly heating the room and “Anti-freeze” - to prevent defrosting of the heating system. This function is designed to maintain a temperature of at least +10 degrees for a long time.
Installing the heating element into the radiator is easy. You need to remove the plug from the bottom flange and screw the heating element into this hole. Then you should install the thermostat and connect the device to a grounded network. Installing heating elements in a water central heating system has many advantages:
- protects the system from freezing in cases of emergency shutdown;
- allows you to accurately adjust the room temperature;
- uses electricity economically due to pulsed operation;
- low price with a large selection of models.
Installation stages
Regardless of the manufacturer, heating elements are installed in heating radiators according to a single principle. To install the heating element yourself, just follow the instructions:
- The device where installation will be carried out must be de-energized.
- The supply of working fluid to the batteries is stopped, after which it is drained.
- Instead of the bottom plug, a heating element is installed, which must go into the water supply pipe.
- The fluid supply is restored, and then the radiator is checked for leaks.
- The heating element is connected to the electrical network.
Precautionary measures
When using heating elements for radiators of a heating system, you must adhere to certain safety requirements. When installing heating, it is important to check the reliability of the ventilation. Also, when performing work, it is necessary to move flammable and explosive substances to a protected, hard-to-reach place at a safe distance from the heating device. Before connecting a heating device with a heating element and a thermostat, it is worth checking once again how well the electrical wiring can cope with the load placed on it
Exceeding the permissible power is fraught with overheating of the wires, short circuits and fires.
- When connecting heating devices with heating elements, you should avoid using ordinary household carriers. The best option is to use network filters. This solution allows you to automatically de-energize the device during voltage surges in the system.
- It is absolutely unacceptable to use batteries with an electric heating element to dry things.
- When the heating element operates, the working fluid is intensively heated. Its operation for a long time leads to the burning of oxygen. Therefore, staying in such a room for a long time poses a health hazard.
Heating elements for heating boilers
The heating element can be installed in an electric or combined heating boiler. In an electric boiler, the heating element is the only source of heat; in a combined boiler, the main fuel is solid fuel - wood, coal, briquettes.
The heating element in a solid fuel boiler plays an auxiliary role, maintaining the temperature in the absence of fuel. It is very convenient to use such boilers in dachas and country houses, when there is no need to constantly maintain a comfortable temperature in the house.
The boiler can be constantly turned on in the mode of maintaining a minimum temperature, which does not allow the heating system to defrost. The boiler switches from solid fuel to electric heating automatically when a certain temperature is reached. Installing a combi boiler requires compliance with safety precautions. So, the boiler must be installed in a separate room with good ventilation. Since the boiler is heavy, it must be installed on a solid concrete base. The room must have a chimney with good draft.
Preparing the tool
Before making any electric boiler, you need to take care of a good tool - this is perhaps the weakest point. It is not difficult to assemble the units themselves, but, for example, without a welding machine it is unrealistic.
It is not possible to assemble a good home electric boiler without a welding machine.
- Welding machine - it is better to take an inverter welder (price starts from 4,700 rubles);
- Cutter - you need to be able to work with a gas cutter, so for home use, take plasma models (price from 4,300 rubles);
- Grinder - it is advisable to have 2 grinders, a large one for a 230 mm disc (price from 2800 rubles) and a small one for a 125 mm disc (price from 1800 rubles);
- Electric drill;
- Calipers;
- Hammer;
- Kern;
- Roulette.
Advantages and disadvantages of using boilers with heating elements
Heating solid fuel boilers with heating elements have a number of advantages:
- the boiler is economical when burning solid fuel;
- the transition to heating with a heating element occurs automatically and the temperature does not drop to critical values;
- the desired temperature is easy to program and does not overheat the room, thus saving money;
- the boiler has a long service life due to constant maintenance of the optimal temperature without sudden changes;
- The heating element is easy to replace if it breaks.
You also need to know the disadvantages of such boilers:
- the device cannot be installed in an ordinary apartment building in the absence of a separate chimney;
- it requires a separate room;
- for the heating element to operate, a three-phase current connection is required;
- The device requires regular maintenance.
As we can see, the disadvantages are quite relative and are not critical for installing equipment in a private home.
Buying and installing a boiler or radiator with a heating element in your home will be a convenient and beneficial help for optimally maintaining a comfortable temperature in your home.
Operating rules
A few simple rules for operation and maintenance will extend the life of the heating element and make its operation more efficient. Here they are:
- If water is used as a coolant, it must be distilled. This will protect you from scale;
- Frequent switching on and off leads to a decrease in service life, so the thermostat must be adjusted accordingly. The minimum difference in water temperature should be at least 5 degrees;
- It is mandatory to use an emergency power cut-off system. This way you can protect other household appliances in the event of a serious breakdown in the heating element;
- It is necessary to deal with voltage surges using a stabilizer or an uninterruptible power supply;
- The appearance of static electricity on the surface of the radiator indicates depressurization of the tube. The heating element must be turned off and removed, otherwise a short circuit is possible, and this means a higher level of problems or material costs.
Failed heating element