The appearance of air pockets in the heating system is accompanied by uneven heating of devices and alarming noise in the pipeline. The coolant moves jerkily along the circuit, increasing the likelihood of water hammer. Agree, any sensible owner would like to exclude these phenomena.
The listed negatives can be eliminated and prevented by a simple action - removing air pockets from the heating system. How to do it? How to correctly assemble the circuit, what devices should be installed so that the air is removed in a timely manner, you will learn from our proposed article.
The information presented for review is based on regulatory documentation. We have described all possible methods used against the formation of air jams. To optimize perception, the material is supplemented with photo selections, diagrams, and videos.
How to avoid air locks
The sequence of preventive measures depends on the type of heating system.
Open circuit
This type of system fills itself with hot water. All valves on radiators must be open, allowing unobstructed water access. It is necessary to monitor the pressure and prevent too strong and rapid filling. When filling the free space of the batteries, close the drain valve.
Filling closed systems
The steps to fill this type of system differ from the standards. First of all, the valves are closed. Only the one through which water is poured into the system is left open. Then a pump is connected to ensure stable pressure in the pipes. The air from the batteries is released using taps only after the entire system is filled with water.
You see, if you follow the rules and carry out preventive measures, it is quite possible to minimize the likelihood of air pockets appearing in the heating system, reducing the temperature in the apartment.
Draining through expansion tank
In households with an individual heating system, expansion tanks of closed and open type are installed. In open structures, the level of water or other heat carrier naturally drops.
It is advisable to top up the system through the lower radiator valve, but it is possible to pour coolant directly into the tank. The running system should be allowed to run for several minutes, which will allow the plug to be pushed out. Otherwise, a standard drain through the radiator is used.
Reasons for airing the system
There are several fairly common reasons that provoke the appearance of an air lock inside heating structures:
- depressurization that occurred during scheduled maintenance or repair work;
- improper flushing or pressure testing of the system followed by filling the water circuit with standard coolant;
- local violation of the integrity of pipelines and radiator batteries under negative external influences or as a result of maintenance and operating errors;
- in private households - the absence of a sufficient pipe slope and expansion tank in the installed system;
- reduced pressure level in the water supply system, filling the resulting voids with air;
- faulty condition of air intake elements;
- connection to the heating structure of a “warm floor” system with pipes of different heights;
- air suction through leaky seam joints and joint areas;
- low quality coolant, oversaturation with gases;
- replenishing the volume of thermal fluid by adding cold tap water.
One of the most common problems is the presence of errors and errors at the stage of creating design documentation or installing pipework.
Preventive measures
The most effective and accessible preventive measures aimed at preventing network airing include:
- compliance with the installation rules of all structural elements and components;
- installation of special devices that remove air manually or automatically;
- regular inspection of the tightness of joints and connection areas;
- bleeding air until the heating system is filled with water;
- monitoring the operation of water heating equipment;
- checking the characteristics of the thermal fluid for compliance with the requirements;
- monitoring of pressure gauge readings and pressure in pipelines;
- systematic visual inspection of pipelines and radiator batteries.
It is strongly recommended that during operation and maintenance periodically perform routine removal of air pockets.
Heating system without air locks
To ensure that air in an individual heating system does not accumulate in problem areas, but goes outside, it is necessary:
- correctly design and install the pipeline, correctly install radiators;
- use automatic and manual air vents.
Let's look at how to expel air from a heating system with natural circulation and top wiring
When arranging a pipeline, it is important to maintain an inclination angle at which air bubbles move freely upward, to the highest point of the circuit, without accumulating at turns and flat areas. At the highest point of such a system, an open-type expansion tank must be installed, through which air bubbles enter the atmosphere
Bleeding air from the heating system using an automatic air vent
To bleed air from a system with forced movement of coolant or a gravity system with bottom wiring, a different principle is used
. Return pipelines are installed at a slope (this simplifies draining liquid from the system), and at the top point of all individual circuits, automatic valves are installed through which air is discharged as it accumulates.
In addition to automatic air vents, the system also uses manual Mayevsky valves. Such air vents are mounted on heating radiators - on the upper pipe on the opposite side of the pipe supplying the heated coolant. To ensure that air enters the valve and does not accumulate in the upper radiator manifold, it is recommended to install the heating device at a slight angle. Air release is performed manually as needed.
How to find an air lock?
Ideally, the system independently copes with airing thanks to automatic valves through which air is released. If you discover that a particular heating device or part of the circuit is not working properly, you need to find the place where the air has accumulated.
Touch the radiator - if its upper part is colder than the lower part, it means that coolant is not flowing there
. To release air, open the Mayevsky valve installed on a steel, aluminum or bimetallic radiator, or the valve valve mounted on cast iron batteries.
How to determine the air lock in the battery
You can also determine the location of airing by sound - under normal conditions, the coolant moves almost silently, extraneous gurgling and sounds of overflow occur due to an obstacle in the flow
.
Metal pipes and heating appliances are tapped with light blows - in places where air accumulates, the sound is noticeably louder.
Getting rid of the airlock
If there are manual air vents on radiators, there are no problems with how to remove air from the batteries. Using a screwdriver or a standard wrench, the stem of the Mayevsky tap is slightly unscrewed, and a suitable container is placed under the drain hole (a half-liter glass jar is enough). Bleeding air from the heating system using a manual air vent is accompanied by hissing and whistling, then splashes appear, after which the coolant begins to flow in a thin stream. At this stage, the Mayevsky tap should be closed.
To remove an air lock from the heating system if it has accumulated away from the air vent (manual or automatic), proceed as follows
:
- Open the air tap or valve closest to the air bubble.
- They begin to gradually replenish the system with coolant so that the liquid, due to an increase in volume, displaces the air bubble towards the open air vent.
Automatic vent valve with corner connection
What to do in difficult cases when the plug is not removed by adding more coolant? In such a situation, in addition to increasing the amount of coolant, it is necessary to add pressure, heating the liquid to critical temperatures. You should act extremely carefully so as not to be scalded by the splashes that accompany the release of air through the automatic valve.
Causes of airiness
Air plugs form in heating systems for a number of reasons:
- As a result of replacing radiators in the apartment. It is most often produced in the summer on the eve of the new heating season. After the pressure testing is completed, the risers are filled with water, and the bleeding of air from the heating system is postponed until the fall.
- After carrying out an inspection of the shut-off valves on the risers, which are needed to drain the circuit.
- As a result of checking the shut-off valves in the elevator unit. The circuit should be reset completely.
- From coolant leaks through battery intersections, threaded connections, fistulas formed in pipes, etc. If the valves in the elevator are in good condition and closed, the pressure in the circuit gradually begins to drop. In this case, you need to slightly open the Mayevsky tap or the flusher located on the top floor. As a result, the vacuum that arises at the top of the circuit sucks in air.
Methods for removing air from water heating systems
Since heating can be with either natural or forced circulation of coolant, the air in the heating system can be removed in different ways.
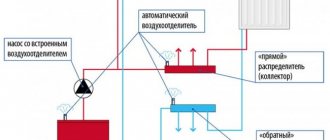
For systems with natural circulation (upper piping is considered), the air lock can be removed through the expansion tank, which should be located at the highest point relative to the entire system.
Removing air through the expansion tank. Click to enlarge.
The supply pipeline should be laid with a rise to the tank. If the wiring is bottom, air removal should be provided in the same way as in a heating system with a circulation pump.
For systems with forced circulation, an air collector should be provided - at the highest point, which will be responsible for venting air.
In this case, the supply pipeline is laid upward in the direction of movement of the coolant, and air bubbles, rising along the riser, are removed from the heating system through air valves, which must be installed at the highest point.
In any case, return pipelines should be laid with a certain slope - towards the water drainage, in order to speed up the emptying of the pipes during repair work.
In closed-type heating systems, automatic air vents are provided - they are installed at several points along the pipeline line, the air from which is discharged separately.
If the installation of the heating system and the laying of pipes at the required slope are carried out correctly, then bleeding through the “air vents” will be simple and not entail any problems.
I would like to note that removing air from the pipes is accompanied by an increase in coolant flow and an increase in pressure in them. If heating batteries become airy, poor sealing of heating pipelines or uneven temperature differences may occur.
Very often, in residential buildings equipped with an autonomous boiler with an open heating system, water can be discharged directly through the expansion tank: after emptying, it is advisable to wait at least half an hour and only then open the “vent” on the tank - all the air will come out on its own when the water temperature in the system rises .
Prevention
To avoid problems with air locks, it is necessary to install air vents at each group of heating elements. So, for example, to remove air from the boiler, an automatic valve for removing gases is mounted directly on it. All collectors are also equipped with it. Mayevsky taps are installed on the radiators at the end.
If, after bleeding the air, the radiators still do not heat up well, the coolant should be completely drained. Since it is possible that there is too much dirt in the network, and it significantly reduces the circulation of fluid in the batteries.
Reasons for the formation of air jams
To effectively heat your home, it is necessary to remove air pockets in a timely manner.
“Clogging,” or an air lock, can form in pipelines if:
- The heating system was being repaired - when carrying out repair work, the appearance of air is inevitable.
- When laying and installing pipes, the required slope and its direction were not observed.
- Pressure drops - as the water level in the pipes drops over time, the pipelines become empty and fill with air.
- A heating system with natural circulation of coolant has been installed (in private houses with small areas, heating is installed without forced circulation, i.e., a circulation pump is not installed). In this case, airing of the heating system occurs due to a possible drop in pressure in the pipes.
- Coolant leaks through poorly sealed pipeline joints. It is quite difficult to notice a leak if the flaw is small (for example, the connection is not very tight), and hot water can leak and evaporate immediately.
- The heating system does not fill correctly after a long period of inactivity (in autumn). Some home owners try to fill pipes with water quickly and “to capacity”, but this is wrong. Filling should be done slowly, while removing air from heating appliances and distribution pipes.
Air can also enter the pipes directly with the coolant - as you know, water contains some air bubbles that rise upward as the water temperature rises.
In houses where water-heated floors are also connected to a common distribution manifold, you can also observe the formation of an air lock in the heating system.
The reasons are practically the same, but eliminating this problem is quite problematic, since the pipes are located unevenly in height. The conclusion follows from this: it is necessary to constantly monitor the pressure and flow of coolant in the pipes or install air collectors (also called “air vents”).
How to get rid of an air lock
Unfortunately, the air lock is not always in an easily accessible place. If there are design or installation errors, air can accumulate in the pipes. It is very difficult to get him out of there. First we determine the location of the plug. In the area of the plug, the pipes are cold and a babbling sound can be heard. If there are no obvious signs, they check the pipes by sound - tapping on the pipes. In a place where air accumulates, the sound will be louder and louder.
Any air lock found must be removed. If we are talking about the heating system of a private house, this is done by raising the temperature and/or pressure. Let's start with pressure. Open the nearest drain valve (in the direction of flow of the coolant) and the make-up tap. Water begins to flow into the system, increasing the pressure. It forces the traffic jam to move forward. When air gets to the bleeder, it comes out. Stop feeding after all the air has escaped - the drain valve stops hissing.
This is a security group. An automatic air vent is installed at the middle outlet
Not all air locks give up so easily. For particularly stubborn ones, it is necessary to simultaneously raise the temperature and pressure. These parameters are brought to values close to maximum. You cannot exceed them - it is too dangerous. If the plug does not go away after this, you can try to open the drain valve (to drain the system) and the make-up valve at the same time. Maybe this way it will be possible to move the air lock or get rid of it altogether.
If a similar problem occurs constantly in one place, there is an error in the design or wiring. In order not to suffer every heating season, a valve is installed in the problem area to remove air. You can cut a tee into the main line and install an air vent at the free entrance. In this case, the problem will be solved simply.
What is an airy battery and how to determine it
If you notice that the batteries do not heat up at full capacity, although just yesterday the entire system worked perfectly and the house was warm, the problem is probably that you just need to bleed the air from the battery that is not quite hot. This article will tell you in detail how to bleed air from a battery.
Before bleeding air, you need to make sure that this is really the cause of the system failure.
First, check all the batteries: if they are all too cold or, on the contrary, too hot, the problem may be directly in the heater or perhaps other sediment has accumulated in the batteries. Also check to see if water is dripping from the batteries. There may be a leak in the battery, then you just need to turn off the heating system and.
If the situation does not change as a result of the actions taken, the nut may be corroded and needs to be replaced. There are times when the radiators on the upper floors remain cold, while on the floor below the radiators are very well heated. In such cases, it is advisable to call a master who specializes in this field.
And if, as a result of a detailed examination of the heating system, you have not found any other problems, except that some battery is partially or completely cold, then you just need to understand how to bleed the air from the battery.
What can an airy heating system lead to?
But first, let's figure out what the consequences may be from such a seemingly harmless airiness of one battery.
As it turned out, the fact that the radiator does not heat the room is not the biggest problem. The main problem is that air in the batteries leads to rusting from the inside, and as a result, a decrease in the service life of the heating radiator.
The next nuance is that if you have an autonomous heating system, then the boiler is forced to “drive” air through the system, not liquid. And this leads to premature damage to the bearings on the shaft and, as a result, the pump fails in advance.
How to properly bleed air from a battery?
Useful diagram for work
In order to release air from the heating battery, use a special key that can be used to open the “air valve”.
Most often, in such cases, a special radiator wrench is used, which can be purchased at a hardware store. Modern batteries allow you to use a screwdriver for such purposes.
Now that you have a key or a screwdriver, as well as a container for draining water, at hand, inspect the battery and on any side of it, find a small valve, which is popularly called the Mayevsky tap.
Today you can install several such valves, or you can get by with just one, in the upper part of the radiator. When you have found the valve you need, unscrew it to the side until you hear air hissing.
Place a container under the tap and wait until all the excess air comes out and water begins to drip. Wait until the water stops bubbling and runs in a thin stream. Now all the air in the batteries has been drained, and the tap can be screwed back to its original position.
In addition to the above-mentioned Mayevsky tap, an automated air bleeder or a regular valve can be installed on the heating radiator, which is simply screwed into one of the upper radiator plugs. The automated bleeder will spontaneously perform all actions to bleed excess air from the battery.
Reasons for the formation of air jams
Getting rid of air in the system
Why does air appear inside a sealed heating system? This may happen due to:
- Failure to comply with the standard for the direction of slope and places of kinks in main pipelines during installation work.
- Incorrect filling of the entire system with water.
- Loose connections of various components and elements that facilitate the absorption of air from the external environment.
- Incorrect operation of air vents or their absence.
- Carrying out repair work to replace risers, locking mechanisms, heating devices, as a result of which air enters the heating system
- Using fresh water to refill the system. Cold water contains a fairly large amount of dissolved oxygen. As the temperature increases, its concentration in water decreases significantly. Air from the coolant is released into small bubbles, which rise and are collected by an air plug at the uppermost points of the heating system and radiators.
Where does the air in the system come from?
Practice shows that it is impossible to ideally isolate a water heating network from the external environment. Air penetrates the coolant in various ways and gradually accumulates in certain places - the upper corners of the batteries, turns of highways and highest points. By the way, the latter should be equipped with automatic bleed valves shown in the photo (air vents).
Types of automatic air vents
Air enters the heating system in the following ways:
- Along with water. It's no secret that most homeowners replenish the lack of coolant directly from the water supply. And from there comes water saturated with dissolved oxygen.
- As a result of chemical reactions. Again, water that is not properly demineralized reacts with the metal and aluminum alloy of the radiators, releasing oxygen.
- The pipeline network of a private house was initially designed or installed with errors - there are no slopes and loops are made that face upward and are not equipped with automatic valves. It is difficult to remove air accumulations from such places even at the stage of filling with coolant.
- A small amount of oxygen penetrates the walls of plastic pipes, despite the special layer (oxygen barrier).
- As a result of repairs with dismantling of pipeline fittings and partial or complete drainage of water.
- When microcracks appear in the rubber membrane of the expansion tank.
When cracks occur in the membrane, gas mixes with water
Note. Water taken from wells and shallow wells is prone to chemical reactions, since it is saturated with active salts of magnesium and calcium.
Also, a situation often arises when, after a long period of inactivity during the off-season, the pressure in a closed heating system decreases due to air ingress. Draining it is quite simple: you just need to add a couple of liters of water. A similar effect occurs in open-type systems if you stop the boiler and circulation pump, wait a couple of days and start the heating again. As the liquid cools, it contracts, allowing air to enter the lines.
As for the centralized heat supply systems of apartment buildings, air penetrates into them exclusively along with the coolant or when the network is filled at the beginning of the season. How to deal with this - read below.
Example from practice. It was necessary to remove air pockets from the open heating system every day due to a completely clogged mud trap. A working pump created a vacuum in front of itself and thus drew oxygen into the pipelines through the slightest leaks.
The thermal image shows the area of the heating device where an air bubble usually lingers.
Installation of air vents
At all upper points of the system, be it pipeline bends or radiators, you need to install air vents - the main weapon in the fight against traffic jams. The air vent can be automatic (valve) or manual (Maevsky valve). The automatic valve will do everything itself, unnoticed by the owner.
In order for the automatic air release valve to work properly, you need to ensure that the coolant is clean at all times.
Internal structure of an automatic air vent
In manual mode, if signs of airiness occur (decrease in temperature in the area, gurgling, drop in pressure), you need to immediately take care of bleeding the air.
When replacing a radiator, they buy an installation kit, which contains everything necessary for installation, including the Mayevsky tap. But air vents are also sold separately. They are placed in the upper fitting of the radiator, on the opposite side from the supply inlet.
Installing air release valves
To remove air from heating, air vents are installed on radiators - manual and automatic air valves. They are called differently: bleeder, air vent, bleeder or air valve, air vent, etc. The essence does not change from this.
Mayevsky air valve
This is a small device for manually bleeding air from heating radiators. It is installed in the upper free radiator manifold. There are different diameters for different collector sections.
Manual air vent - Mayevsky tap
It is a metal disk with a conical through hole. This hole is closed with a cone-shaped screw. By unscrewing the screw a few turns, we allow the air to escape from the radiator.
Device for removing air from radiators
To facilitate air outlet, an additional hole was made perpendicular to the main channel. The air actually comes out through it. When deflating using a Mayevsky tap, point this hole upward. After this you can unscrew the screw. Unscrew it a few turns, but do not unscrew it too much. After the hissing stops, return the screw to its original position and move on to the next radiator.
When starting the system, it may be necessary to bypass all the air collectors several times until air stops escaping altogether. After this, the radiators should heat up evenly.
Automatic air release valve
These small devices are installed both on radiators and at other points in the system. They differ in that they allow you to bleed air in the heating system automatically. To understand the principle of operation, consider the structure of one of the automatic air valves.
The operating principle of the automatic release is as follows:
- In normal condition, the coolant fills the chamber by 70 percent. The float is at the top, pressing the rod.
- When air enters the chamber, the coolant is forced out of the housing and the float lowers.
- He presses the protrusion-flag on the nozzle, squeezing it out.
- The depressed jet opens a small gap, which is enough to allow the air that has accumulated in the upper part of the chamber to escape.
- As water comes out, the air vent body fills with water.
- The float rises, releasing the rod. It returns to its place due to the spring.
Various designs of automatic air valves operate on this principle. They can be straight or angular. They are placed at the highest points of the system and are present in the security group. They can be installed in identified problem areas - where the pipeline has an incorrect slope, which is why air accumulates there.
Instead of Mayevsky's manual taps, you can install an automatic drain for radiators. It is only slightly larger in size, but works automatically.
Automatic air release valve
Cleaning from salts
The main problem with automatic valves for venting air from the heating system is that the air outlet hole is often overgrown with salt crystals. In this case, either the air does not come out or the valve begins to “cry”. In any case, you need to remove it and clean it.
Automatic air vent disassembled
So that this can be done without stopping the heating, automatic air valves are installed in pairs with non-return valves. The check valve is installed first, followed by the air valve. If necessary, the automatic air collector for the heating system is simply unscrewed, disassembled (unscrew the lid), cleaned and reassembled. After this, the device is again ready to bleed air from the heating system.
Top supply in an apartment building - how to release air
Buildings with a top spill have the following characteristics:
- The supply bottling is located on the technical floor, and the return bottling is in the basement;
- each riser is a jumper between them, disconnection is possible both from below and from above;
- the feeding bottling is done with a slight slope;
- at the very top there is an expansion device with a discharge outlet, while the discharge is often discharged through all floors to the elevator unit in the basement or at most close to it.
The function of the air vents is assigned to the vent on the expansion device. Thanks to the discharge to the basement, the start of heat supply in the fall is simplified.
Filling the system with water
- To begin with, we open all the taps (on both sides of the pump, on all radiators, on the water floor collectors, on the expander), and close the Mayevsky taps.
- The system must be filled from the bottom up. The inlet hole is made in the very bottom part (the coolant is drained and filled through it).
- The main valve opens at the top (at the highest point of the system) to release air and slowly fill. There is no need to rush, just so that the air has time to escape. The liquid supply remains open until water flows from the valve.
- The system accumulates the pressure recommended for it as working pressure. Then, one by one, the air is bleed from each radiator in the house (it’s time to close the tap when the water starts to trickle).
- There is a screw in the central part of the circulation pump that can be loosened using a screwdriver. The air is bled from the pump, then screwed on.
- After the air is released, the pressure in the system will drop and the water supply will need to be turned on again to make up for the losses.
- After this, a test run of the boiler is made at a low temperature (about 40 ° C), with the pump turned on. During this start-up, it is recommended to go around and inspect all elements of the system - are there any leaks, is air escaping somewhere, are all radiators heating up evenly. Then, you may need to add water again and then start the boiler in operating mode.
Filling the system with water
If suddenly one of the taps remains closed, and the system is already filled and the pressure is high, you need to open the valve very slowly and carefully. Otherwise, you will get a decent water hammer.
Bleeding the pump
If the heating circuit has a built-in circulation pump, then an air lock, as a rule, disrupts its functioning. When installing pumping equipment above the comb, or using only a standard unit (heating boiler), you need to loosen the screw located in the central part of the cover. As a result, all the accumulated air will come out. After bleeding the air, the circulation pump must be turned on for 5-10 minutes to pump the pipeline network.
Methods for removing air lock from the cooling system
How to remove an air lock from the cooling system of a VAZ classic
There are three main methods by which you can eliminate an air lock. Let's list them in order. The first method is great for VAZ cars. Its algorithm will be as follows:
Remove from the engine all protective and other elements that may prevent you from reaching the expansion tank with coolant. Disconnect one of the pipes that are responsible for heating the throttle assembly (it doesn’t matter whether it’s direct or reverse). Remove the expansion tank cap and cover the neck with a loose cloth. Blow inside the tank. This will create a slight excess pressure, which will be enough for excess air to escape through the pipe. As soon as antifreeze comes out of the hole for the pipe, immediately put the pipe on it and preferably secure it with a clamp.
Otherwise, air will get back into it. Close the expansion tank cap and reassemble all previously removed engine protection elements.
The second method is carried out in accordance with the following algorithm:
- Start the engine and let it run for 10...15 minutes, then turn it off.
- Remove the necessary elements in order to get to the expansion tank with coolant.
- Without removing the lid from it, disconnect one of the pipes on the tank. If the system has been aired, then air will begin to escape from it.
- As soon as the antifreeze flows out, immediately replace the pipe and secure it.
When doing this, be careful, since the temperature of the antifreeze can be high and reach +80...90°C.
The third method of how to remove an air lock from the system must be done as follows:
It is necessary to place the car on a hill so that its front part is higher
It is important that the radiator cap is higher than the rest of the cooling system. At the same time, put the car on the handbrake, or better yet, put chocks under the wheels. Let the engine run for 10...15 minutes. Unscrew the caps from the expansion tank and radiator. Periodically press the accelerator pedal and add coolant to the radiator
This will cause air to escape from the system. You will notice it by the bubbles. Continue the procedure until all the air is released. In this case, you can turn on the stove to maximum mode. As soon as the thermostat opens the valve completely and very hot air enters the cabin, it means that the air has been removed from the system. At the same time, you need to check for bubbles coming out of the coolant.
As for the last method, on machines with an automatically turned on cooling system fan, you don’t even have to over-gas, but calmly let the engine warm up and wait until the fan turns on. At the same time, the movement of the coolant will increase, and under the influence of circulation, air will leave the system
In this case, it is important to add coolant to the system in order to prevent airing again.
As you can see, the methods of how to get rid of an air lock in the engine cooling system are quite simple. They are all based on the fact that air is lighter than liquid. Therefore, it is necessary to create conditions under which the air lock will be forced out of the system under pressure. However, it is best not to bring the system to that state and take preventive measures in a timely manner. We will talk about them further.
Why do batteries heat poorly?
Cold batteries
During the heating season, many radiators do not heat very much, so the room is cold and uncomfortable. There may be several reasons for this phenomenon.
The first is that air has simply accumulated in the battery. This is indicated by a characteristic sound similar to gurgling. The radiator becomes partially cold due to insufficient coolant circulation. In such a situation, it is very easy to blow out the battery. If an aluminum radiator is installed, which has a thermostat, it is enough to open it completely and bleed the air. If there is no thermostat, open the Mayevsky tap or plug.
When opened through the hole, air will escape with a strong hiss. It must be drained until it all comes out and water flows out. A uniform stream will indicate that the air lock has been eliminated and the radiator can be operated in normal mode. On cast iron radiators, special taps are used to bleed air.
The second reason for poor coolant circulation is not air, but a dense plug of scale and large particles that circulate through the heating system along with hot water.
Experts point out that even a millimeter thickness of scale deposits reduces the heat transfer of the battery by 15%. Therefore, it is advisable to bleed the system before the start of each season and do it correctly
How to understand that the reason for the ineffective operation of heating devices in an apartment is accumulated scale? You need to pay attention to the following signs:
- The walls are covered with scale if the riser is hotter than the radiator.
- Feel the radiators in all rooms in the apartment. The different intensity of their heating is a reason for “treatment”.
- Uneven heating of sections of one battery.
What methods exist to eliminate such problems?
How to drain water from different types of batteries
The de-airing technique largely depends not on the type or material of the battery, but on the air venting devices installed on it. These can be conventional control valves, Mayevsky valves or automatic air vents.
How to drain water from cast iron batteries
Old cast iron models have simple shut-off and control valves. In this case, you just need to turn the knob or valve and drain the water. If there is a cap installed on the radiator, unscrew it with an adjustable wrench. The main problem is the imperfection of old communications. It is not always possible to remove airiness even on the top floor. Often you have to go down into the basement or up into the attic to the expansion tank to open the valve.
Modern cast iron models are equipped with air vents. For lovers of antiquity, there are even retro-style modifications of Mayevsky cranes. They differ from the standard options only in design. There are no structural differences between them.
To remove the plug, take a container and bring it to the drainage device. Turn the valve with a wrench or screwdriver. Water with bubbles will flow out. To be sure to get rid of the problem, you will have to bleed about 30 liters.
Cast iron batteries produced these days are best equipped with automatic air venting devices that do not require outside intervention. In this case, you won’t have to release anything - the gas-air mixture will come out automatically.
How to drain water from steel and bimetallic batteries
These modern models are equipped with Mayevsky valves. There is a screw on the device that needs to be loosened slightly with a screwdriver or wrench. Air will begin to escape through the side hole. Then you need to drain the water through it. In a multi-storey building - approximately 30 liters, and in a private building - less, until the air bubbles disappear.
It is advisable to install an automatic air vent on steel and bimetallic models. They immediately release the gases. Otherwise, the hydrogen and oxygen contained in the radiator space will react with metal surfaces. Rust will appear, leaks will begin and everything will have to be repaired.
How to drain water from aluminum radiators
Automatic or manual air vents are always installed on aluminum radiators. Otherwise, aluminum, which easily comes into contact with hydrogen and oxygen, will quickly lose strength.
In this case, it is quite easy to eliminate airing. If you have a Mayevsky manual valve, take a container and place it under the radiator. Turn the screw in the middle with a wrench or screwdriver, releasing the air. Then drain the water and tighten everything up.
In order for an aluminum radiator to last a long time, it is highly advisable to install an automatic air vent on it. However, with very hard water, the automation may become clogged, malfunction and not release accumulated gases. Therefore, you will have to periodically check for traffic jams.
To do this, put your ear to the radiator and listen. If you hear noise, hum, or other strange sounds, it means that there is an air blockage inside that needs to be removed.