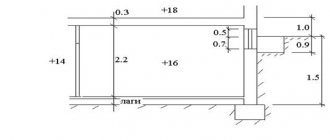
Modern houses, regardless of the material used in their construction, need to be designed and costed. It is at this stage that the characteristics are calculated for building heating systems. In those schemes where ordinary water circulates, the amount of coolant is calculated based on the thermal load of the entire building.
This indicator is necessary for accurately selecting the tank capacity intended for pressure regulation. This parameter is directly related to the design load of the heating system of a private building. Properly selected equipment used for heating a residential building will normally cope with the main task - creating a comfortable temperature regime in residential and auxiliary premises.
Table with standard indicators for residential premises Source stroypol14.ru
When performing a calculation, an exact expression is required that gives the correct result for choosing a boiler.
We calculate indicators of the amount of coolant: theory and practice
In individual residential buildings or apartment buildings the following is usually used:
- process water;
- propylene glycol;
- ethylene solution.
It is important that any coolant meets the requirements specified in regulatory documents. In Russian standard there are 5 conditions that must be met:
- optimal value of coolant movement;
- low viscosity while ensuring flow like ordinary water;
- slight expansion when the system cools;
- elimination of toxicity;
- inexpensive price.
Calculating the performance of a heating system cannot be considered simple; experience is required.
House heating system diagram Source odstroy.ru
To correctly determine indicators using calculation formulas for the further use of a reliable heat carrier, it is recommended to use the services of a specialist involved in the design of individual heating schemes or a competent plumber.
Types of radiators
The most popular among the total number of convectors are three types:
- Aluminum radiator;
- Cast iron battery;
- Bimetallic radiator.
If you know which convector is installed in your home and are able to count the number of sections, then making simple calculations will not be difficult. Next, calculate the volume of water in the heating radiator
,
table
and all necessary data are presented below. They will help to calculate as accurately as possible the amount of coolant in the entire system.
| Convector type | Average water volume liter/section |
| Aluminum | |
| Old cast iron | |
| New cast iron |
Bimetallic
Aluminum
Although in some cases the internal heating system of each battery may differ, there are generally accepted parameters that allow you to determine the amount of liquid placed in it. With a possible error of 5% you will learn that one section of an aluminum radiator can contain up to 450 ml of water
It is worth paying attention to the fact that for other coolants the volumes may be increased
Cast iron
Calculating the amount of liquid that fits in a cast iron radiator is a little more difficult. An important factor will be the novelty of the convector. New imported radiators have significantly less void space, and due to their improved structure, they heat no worse than the old ones.
The new cast iron convector holds about 1 liter of liquid, the old one will hold 700 ml more.
Bimetallic
These types of radiators are quite economical and productive. The reason why filling volumes may change lies only in the features of a particular model and pressure variation. On average, such a convector is filled with 250 ml of water.
Possible changes
Each battery manufacturer sets its own minimum/maximum permissible standards, but the volume of coolant in the internal tubes of each model may change due to pressure increase considerations. Typically, in private homes and new buildings, an expansion tank is installed on the ground floor, which allows the liquid pressure to be stabilized even when it expands when heated.
Parameters also change on outdated radiators. Often, even on non-ferrous metal tubes, growths form due to internal corrosion. The problem may be impurities in the water.
Due to such growths in the tubes, the amount of water in the system must be gradually reduced. Taking into account all the features of your convector and the general data from the table, you can easily calculate the required volume of water for the heating radiator and the entire system.
The circulation pump is selected based on two main characteristics:
G* - flow rate, expressed in m 3 / hour;
H - pressure expressed in m.
*To record coolant flow, manufacturers of pumping equipment use the letter Q. Manufacturers of shut-off valves, for example, Danfoss, use the letter G to calculate flow. In domestic practice, this letter is also used. Therefore, within the framework of the explanations of this article, we will also use the letter G. But in other articles, going directly to the analysis of the pump operation schedule, we will still use the letter Q for flow rate.
Coolant flow in the heating system: calculation formula
The volume of media used in home heating circuits is expressed in kilograms expended per second. The value is used to calculate the amount of heat generated to ensure a comfortable temperature in residential premises. Typically, modern devices - batteries - are used in heating systems of private houses.
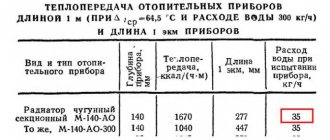
To determine the calculated indicators, equipment data is required, in particular the parameters of the heating boiler, designed to heat 1 liter of technical fluid.
An example of a heating boiler table for a private house Source kupisantehniky.ru
The expression used to calculate the coolant flow rate for a residential heating system:
G = N / Q, where:
- N is the power characteristic of the equipment, indicated in Watts.
- Q is the amount of heat, expressed in J/kg.
The value obtained during the calculation is multiplied by a factor (3.6 x 1000) to convert to kg/hour.
Formulas for calculating the volume of liquid in heating
The total volume of liquid will consist of the amount of coolant in the boiler, pipelines and batteries. The volume of the expansion tank is not taken into account here, because water will flow into this device only in critical cases when temperature and pressure increase.
To calculate the amount of liquid in a pipe, the following formula is used: V=S*L, where
S is the internal cross-sectional area of the pipe;
L – pipeline length.
Information regarding the cross-sectional area of the pipe taken from the tables may differ from the actual dimensions (material used, features of the production of plumbing products). That is why the diameter is measured with a caliper, after which the cross-sectional area is calculated. It is better to entrust such calculations to specialists, since heating systems are quite extensive and branched structures.
Calculation of heat consumption taking into account periodic addition of liquid to the system
In real practice, a situation often arises when it is necessary to refill heating pipes with a new coolant. This mainly happens after completion of repair work or modernization of piping units. For this purpose, the volume of water consumption in the heating system is calculated.
Formula for calculating coolant Source probaltur.ru
Usually, they use the indicators specified in the technical documentation and simply add up the values. You can calculate this parameter using a simple calculator using the diameter and length of the pipes. The values are multiplied with each other and added to the heating battery data. Basically, the volume of sections of a standard radiator is 0.45 l for the following types:
- aluminum;
- steel;
- made from alloy.
For a cast iron battery this figure is different - 1.45 liters.
There is another formula that allows you to calculate the approximate value of the volume of fluid (total) in the piping system:
- V = N x VkW, where:
- N is the boiler power, Watt.
- VkW is the amount required for the system to transmit 1 kilowatt of heat, expressed in dm3.
Expansion tank calculation
Basic Rules:
- The volume of the expansion tank must be at least 10% of the volume of the heating system. This volume will be sufficient to expand the coolant when heated within 45...80 °C.
- For large extended systems with high coolant temperatures, the volume reserve should be at least 80% of the volume of the heating system. This is relevant for boilers with a maximum coolant temperature above 80...90 °C, and steam heating systems from furnaces.
- The volume of the expansion tank with a safety valve can be 3-5% of the volume of the heating system. But at the same time, it is important to control its operation: when the valve operates, it is necessary to replenish the system with water.
- When calculating, it is necessary to take into account the pressure in the system. In most cases, for one and two-story cottages it is 1.5...2 atmospheres. The weight of the finished tanks is calculated for these indicators with a margin. When designing a large-volume heating system with increased pressure characteristics in communications (for high-rise buildings), it is necessary to take this parameter into account.
- It is imperative to take into account the type of coolant when choosing. The lighter the fluid in the system, the larger the expansion tank it requires.
Comparison : Which boiler to choose for heating your home? Advantages and disadvantages.
How is the lowest water flow rate calculated?
It is calculated in exactly the same way as the coolant consumption used to heat a residential building in one hour. The minimum consumption is calculated in the interval between seasons when the heating system was turned off, since this value depends on the hot water supply.
There are 2 expressions used in calculations. In those cases where the heating system does not provide for forced circulation of hot water supply or it is turned off for the period of preventive measures.
The parameter is calculated with previously known values of coolant consumption (average):
Gmin = $ x Qgr / [(Tp - Tob3) x C], where:
- Qгср is the amount of heat transferred by the devices per hour of operation during the season when the heating is turned off (average), J;
- $ is the coefficient of fluctuation of fluid consumption in winter and summer. Data corresponding to 1.0 and 0.8 (winter, summer) are accepted;
- Tp – temperature value of the coolant during the heating season;
- Tob3 – the same, but in the return pipe connected in parallel;
- C – heat capacity of the liquid, taken taking into account the coefficient 10-3, J/°C;
- temperature parameters that are inserted into the calculation formula with specific values: 70 and 300C.
Antifreeze parameters and types of coolants
The basis for the production of antifreeze is ethylene glycol or propylene glycol. In their pure form, these substances are very aggressive media, but additional additives make antifreeze suitable for use in heating systems. The degree of anti-corrosion, service life and, accordingly, the final cost depend on the additives introduced.
The main task of additives is protection against corrosion. Having low thermal conductivity, the rust layer becomes a heat insulator. Its particles contribute to clogging of channels, disable circulation pumps, and lead to leaks and damage in the heating system.
Moreover, the narrowing of the internal diameter of the pipeline entails hydrodynamic resistance, due to which the speed of the coolant decreases and energy consumption increases.
Antifreeze has a wide temperature range (from -70°C to +110°C), but by changing the proportions of water and concentrate, you can obtain a liquid with a different freezing point. This allows you to use intermittent heating mode and turn on room heating only when necessary. As a rule, antifreeze is offered in two types: with a freezing point of no more than -30°C and no more than -65°C.
In industrial refrigeration and air conditioning systems, as well as in technical systems with no special environmental requirements, ethylene glycol-based antifreeze with anti-corrosion additives is used. This is due to the toxicity of the solutions. Their use requires closed expansion tanks; use in double-circuit boilers is not allowed.
A solution based on propylene glycol received other possibilities for use. This is an environmentally friendly and safe composition that is used in the food, perfume industry and residential buildings. Wherever it is necessary to prevent toxic substances from entering the soil and groundwater.
The next type is triethylene glycol, which is used at high temperatures (up to 180°C), but its parameters have not led to widespread use.
Selecting a circulation pump
Today, not a single heating system is installed without a circulation pump. Two characteristics by which the device is selected:
- Q is the coolant flow parameter for one hour, calculated in m3.
- H is a pressure indicator expressed in meters.
The coolant, which is heated to the temperature required for heating the premises, circulates through the system and releases part of the heat into the walls facing the street. This indicator is the heat loss of the heating system of the house. The pump helps in this situation by moving the coolant through the pipes and radiators in the required mode.
Circulation pump VIEIR TsN25-4 180 mm Source zonacomf.ru
How to correctly determine the type of heating boiler and calculate its power
In the heating system, the boiler plays the role of a heat generator
When choosing between boilers - gas, electric, liquid or solid fuel, pay attention to the efficiency of its heat transfer, ease of operation, and take into account what type of fuel predominates in the place of residence
The efficient operation of the system and a comfortable room temperature directly depend on the power of the boiler. If the power is low, the room will be cold, and if the power is too high, fuel will be wasted. Therefore, it is necessary to choose a boiler with optimal power, which can be calculated quite accurately.
When calculating it, you must take into account:
- area of the heated room (S);
- specific boiler power per ten cubic meters of room. It is set with adjustments taking into account the climatic conditions of the region of residence (W spec.).
There are established specific power values (Wsp.) for certain climatic zones, which are for:
- Southern regions - from 0.7 to 0.9 kW;
- Central regions - from 1.2 to 1.5 kW;
- Northern regions - from 1.5 to 2.0 kW.
Boiler power (Wbot) is calculated using the formula:
W cat. = S*W beat. / 10
Therefore, it is customary to choose the boiler power at the rate of 1 kW per 10 kW. m of heated room.
Not only the power, but also the type of water heating will depend on the area of the house. A heating design with natural water movement will not be able to effectively heat a house with an area of more than 100 square meters. m (due to low inertia). For a room with a large area, you will need a heating system with circular pumps, which will push and accelerate the flow of coolant through the pipes.
Since the pumps operate in non-stop mode, they are subject to certain requirements - noiselessness, low energy consumption, durability and reliability. On modern models of gas boilers, the pumps are already built directly into the housing.
Volume of water in the boiler
For wall-mounted gas boilers 3-6 liters.
For floor-standing gas boilers and parapet gas boilers, depending on the power and, accordingly, the size of the boiler, the value ranges from 10-30 liters. More accurately, you can look at the characteristics of the device itself.
In this simple way, adding up all the values. we can determine the volume of the system.
Section volume and coolant flow
Today, not all autonomous heating systems are filled with water. This is due to two factors.
Section size
- A situation arises when the owners need to leave the house without heating for a long time, since due to a long absence there is no need to heat the premises.
- Water tends to freeze even at zero temperatures. When water freezes, it expands and turns into ice, that is, it changes from one physical state to another. During this process, the intermolecular bonds of water are released and changed, resulting in a huge force that breaks radiators and pipes made of any metal.
To prevent such situations from occurring, instead of water, another coolant is used to fill the heating system, which does not have the problem of freezing. These can be household antifreezes such as:
- ethylene glycol;
- saline solution;
- glycerin composition;
- food alcohol;
- petroleum oil.
Thanks to special additives that are introduced into these components, coolant compositions retain their state of aggregation in liquid form even at subzero temperatures.
Coolant calculation
Determining the volume of coolant flow required for an autonomous heating system requires accurate calculation. For a simple way to find out how much antifreeze is needed to fill the heating system, there are various calculation tables.
Water volume in one section
For basic calculations, you can use the information presented in thematic reference books:
- A standard aluminum battery section contains 0.45 liters of coolant.
- A linear meter of a 15 mm pipe contains 0.177 liters, and a pipe with a diameter of 32 mm contains 0.8 liters of coolant.
Information about the characteristics of the charging pump and expansion tank can be taken from the passport data of this equipment.
The total volume of the heating system will be equal to the total volume of all heating devices:
- radiators;
- pipelines;
- boiler heat exchanger;
- expansion tank.
The refined formula for the main calculation is adjusted taking into account the expansion coefficient of the coolant. For water it is 4%, for ethylene glycol ─ 4.4%.